当前位置:网站首页>Bucket of P (segment tree + linear basis)
Bucket of P (segment tree + linear basis)
2022-06-26 13:58:00 【__ LazyCat__】
Line segment tree + Linear base
link :P4839 P Brother's bucket - Luogu | New ecology of computer science education (luogu.com.cn)
The question : Insert data at a single point in the interval , Find the exclusive or sum of the largest subset of the interval .
Answer key : Consider the combination of linear bases , Let's take another linear base log Take out the numbers and merge them into the first linear basis , Because numbers that can be synthesized from another linear basis , After merging this linear basis into the first linear basis , The first linear basis can also be combined into a second linear basis , Then we can synthesize those numbers through the second linear basis . Then the union of these linear bases can be maintained by using the line segment tree . Since the linear basis merging complexity is l o g ∗ l o g log*log log∗log, Line tree single point modification , The interval query complexity is q l o g n qlogn qlogn, Then the overall complexity is q ∗ l o g n ∗ l o g 2 p q*logn*log^2p q∗logn∗log2p,q For the number of operations ,n Is the length of the sequence ,p Value range .
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#pragma GCC optimize("unroll-loops")
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=5e4+5;
int n,m,op,u,v,w;
struct node{
int l,r,p[32];
node():l(0),r(0){
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));}
}t[maxn<<2];
void insert(node&t,int x)
{
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)
{
if(x>>i&1)
{
if(!t.p[i]){
t.p[i]=x; break;}
x^=t.p[i];
}
}
return;
}
void pushup(int k)
{
memcpy(t[k].p,t[k<<1].p,sizeof(t[k].p));
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)
{
insert(t[k],t[k<<1|1].p[i]);
}
return;
}
void build(int k,int l,int r)
{
t[k].l=l,t[k].r=r;
if(l==r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build(k<<1,l,mid);
build(k<<1|1,mid+1,r);
return;
}
void update(int k,int pos,int w)
{
int x=t[k].l,y=t[k].r;
if(x==y){
insert(t[k],w); return;}
int mid=x+y>>1;
if(pos<=mid)update(k<<1,pos,w);
else update(k<<1|1,pos,w);
pushup(k); return;
}
node query(int k,int l,int r)
{
int x=t[k].l,y=t[k].r;
if(l<=x&&y<=r)return t[k];
int mid=x+y>>1,flag=0; node res;
if(l<=mid)res=query(k<<1,l,r),flag=1;
if(mid<r)
{
if(!flag)res=query(k<<1|1,l,r);
else
{
node q=query(k<<1|1,l,r); res.r=q.r;
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)insert(res,q.p[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m,build(1,1,m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>op>>u>>v;
if(op==1)update(1,u,v);
else
{
node q=query(1,u,v); int ans=0;
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)ans=max(ans,ans^q.p[i]);
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
You can find , This kind of merger is really right , Complexity is also correct . But consider , When we update, we merge from the bottom to the top , Each time, the number will be added to the original linear basis , No fewer numbers . So there is no need to merge , You only need to insert the traversed points when updating .
//#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
//#pragma GCC optimize("unroll-loops")
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=5e4+5;
int n,m,op,u,v,w;
struct node{
int l,r,p[32];
node():l(0),r(0){
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));}
}t[maxn<<2];
void insert(node&t,int x)
{
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)
{
if(x>>i&1)
{
if(!t.p[i]){
t.p[i]=x; break;}
x^=t.p[i];
}
}
return;
}
void build(int k,int l,int r)
{
t[k].l=l,t[k].r=r;
if(l==r)return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build(k<<1,l,mid);
build(k<<1|1,mid+1,r);
return;
}
void update(int k,int pos,int w)
{
int x=t[k].l,y=t[k].r; insert(t[k],w);
if(x==y)return;
int mid=x+y>>1;
if(pos<=mid)update(k<<1,pos,w);
else update(k<<1|1,pos,w);
return;
}
void query(node&q,int k,int l,int r)
{
int x=t[k].l,y=t[k].r;
if(l<=x&&y<=r)
{
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)insert(q,t[k].p[i]);
return;
}
int mid=x+y>>1;
if(l<=mid)query(q,k<<1,l,r);
if(mid<r)query(q,k<<1|1,l,r);
return;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m,build(1,1,m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>op>>u>>v;
if(op==1)update(1,u,v);
else
{
node q; query(q,1,u,v); int ans=0;
for(int i=31;i>=0;i--)ans=max(ans,ans^q.p[i]);
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
Query operation small optimization : It is found that it takes too much time to re create the structure every time each point is queried . Then create one initially and insert it slowly .
边栏推荐
- There are many contents in the widget, so it is a good scheme to support scrolling
- 【MySQL从入门到精通】【高级篇】(二)MySQL目录结构与表在文件系统中的表示
- Common operation and Principle Exploration of stream
- 程序员必备,一款让你提高工作效率N倍的神器uTools
- Bug STL string
- shell脚本详细介绍(四)
- Go language - pipeline channel
- KITTI Tracking dataset whose format is letf_ top_ right_ bottom to JDE normalied xc_ yc_ w_ h
- d的is表达式
- ES基于Snapshot(快照)的数据备份和还原
猜你喜欢
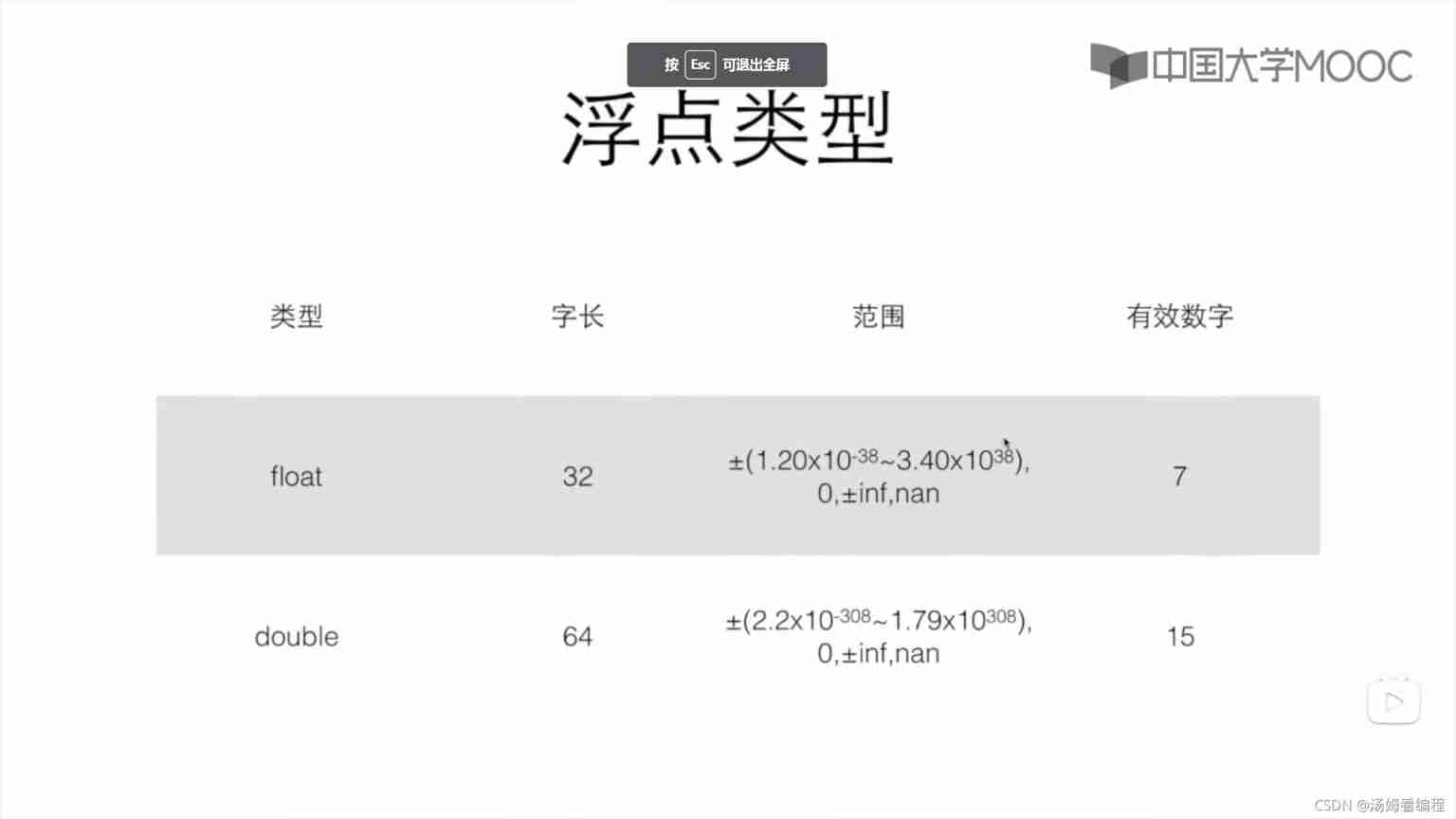
Range of types

Here document interaction free and expect automatic interaction

12 SQL optimization schemes summarized by old drivers (very practical)

Mongodb series window environment deployment configuration

Nexys A7开发板资源使用技巧

2021-10-18 character array

What is the use of index aliases in ES

Cloudcompare - Poisson reconstruction

MediaPipe手势(Hands)

Some conclusions about Nan
随机推荐
虫子 类和对象 中
D check type is pointer
Formal parameters vs actual parameters
GC is not used in D
Mediapipe gestures (hands)
Half search, character array definition, character array uses D11
Applicable and inapplicable scenarios of mongodb series
虫子 内存管理 下 内存注意点
KITTI Tracking dataset whose format is letf_ top_ right_ bottom to JDE normalied xc_ yc_ w_ h
Free machine learning dataset website (6300+ dataset)
HW蓝队溯源流程详细整理
2021-10-09
A collection of common tools for making we media videos
Guruiwat rushed to the Hong Kong stock exchange for listing: set "multiple firsts" and obtained an investment of 900million yuan from IDG capital
李航老师新作《机器学习方法》上市了!附购买链接
Aesthetic experience (episode 238) Luo Guozheng
Input text to automatically generate images. It's fun!
Es common grammar I
CVPR 2022文档图像分析与识别相关论文26篇汇集简介
Range of types