当前位置:网站首页>MySQL_ Create and manage tables
MySQL_ Create and manage tables
2022-06-22 12:44:00 【YHSevenWater】
There are several steps to learn about creating and managing tables :
• Create database
• Create table
• Describe the various data types
• Modify table
• Delete , Empty table and rename
(1) Create database
● Create a database to store teacher information
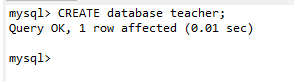
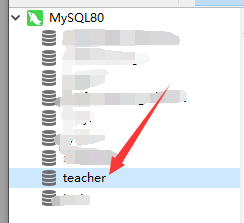
open Navicat Medium MySQL, Right click to open the command line interface , Enter the following sql sentence . The figure below shows that the creation was successful , Finally, right-click to refresh the database , Can show teacher.
CREATE database teacher;
● Related other commands
View all current databases , The following figure shows nine records .
show databases;

“ Use ” A database , Make it the current database , This should be combined with the corresponding DML Statement together .
use `teacher`;
| Naming rules |
|---|
| The database name cannot exceed 30 Characters , Variable names are limited to 29 individual |
| Must contain only A–Z, a–z, 0–9, _ common 63 Characters |
| You cannot leave spaces between the characters of an object name |
| Must not have the same name as other user-defined objects |
| You must ensure that your field has no and reserved words 、 Database systems or common methods conflict |
| Keep field names and types consistent , When naming fields and specifying data types for them, be sure to ensure consistency . If the data type is an integer in a table , Then don't turn into character in another table |
(2) Create table
CREATE TABLE sentence
• Must have :
– CREATE TABLE jurisdiction
– Storage space
• Must specify :
– Table name
– Name , data type , Size
• grammar
CREATE TABLE demo
(id INT(2),
name VARCHAR(14));

• confirm
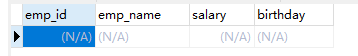
DESCRIBE demo;

new table :
CREATE TABLE emp (
#int type , Self increasing
emp_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
# Save at most 20 Chinese and English characters
emp_name CHAR (20),
# The total number of digits shall not exceed 15 position
salary DOUBLE,
# The date type
birthday DATE,
# Primary key
PRIMARY KEY (emp_id)
) ;

(3) Describe the various data types
| type | explain |
|---|---|
| INT | Use 4 Bytes hold integer data |
| CHAR(size) | Fixed length character data . If not specified , The default is 1 Characters , Maximum length 255 |
| VARCHAR(size) | Variable length character data , Save according to the actual length of the string , Length... Must be specified |
| FLOAT(M,D) | Single precision , M= Integer bit + Decimal places , D= Decimal places . D<=M<=255,0<=D<=30, Default M+D<=6 |
| DOUBLE(M,D) | Double precision . D<=M<=255,0<=D<=30, Default M+D<=15 |
| DATE | Date data , Format ’YYYY-MM-DD’ |
| BLOB | Long text data in binary form , Up to 4G |
| TEXT | Long text data , Up to 4G |
(4) Modify table
ALTER TABLE sentence
Use ALTER TABLE Statement can realize :
● Add columns to existing tables
● Modify columns in existing tables
● Delete columns from existing tables
● Rename columns in an existing table
Append a new column
ALTER TABLE emp
ADD job_id VARCHAR(15);


Modify a column
• You can modify the data type of the column , Dimensions and defaults
ALTER TABLE emp
MODIFY (job_id VARCHAR(30));
• Changes to the default value only affect future changes to the table
ALTER TABLE emp
MODIFY (salary double(9,2) default 1000);
Delete a column
Use DROP COLUMN Clause to delete columns that are no longer needed
ALTER TABLE emp
DROP COLUMN birthday;


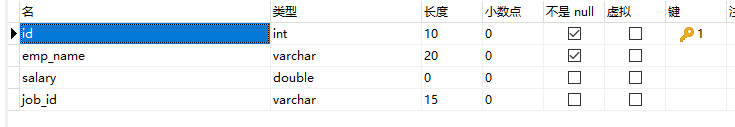
Rename a column
Use CHANGE old_column new_column dataType Clause renames the column
ALTER TABLE emp
CHANGE emp_id id int(10);


(5) Delete , Empty table and rename
Delete table
• Data and structures are deleted
• All running related transactions are committed
• All relevant indexes are deleted
• DROP TABLE Statement cannot be rolled back
DROP TABLE demo;

Clear the table
• TRUNCATE TABLE sentence :
– Delete all data in the table
– Free the storage space of the table
TRUNCATE TABLE demo1;

• TRUNCATE Statement cannot be rolled back
• have access to DELETE Statement delete data , You can roll back
• contrast :
DELETE FROM emp;
SELECT * FROM emp;
ROLLBACK;
SELECT * FROM emp;
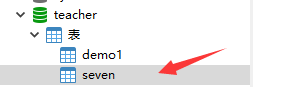
rename
• perform RENAME Statement change table , The name of the view
• Must be the owner of the object
ALTER table emp
RENAME TO seven;

边栏推荐
- 第十三届 蓝桥杯 嵌入式设计与开发项目 决赛
- Flutter mixed development exercise - large picture of collaborative loading of ever & method channel
- zcu102 PL端流水灯
- How to count the growth of daily business data from the database level?
- 老王说系列第六期:PHP程序员要建立自己的自信心
- Endeavouros installation configuration introduction!
- OpenCV调用usb摄像头出现“select timeout”解决方法
- Flutter之CustomPaint 绘制贝塞尔曲线图表(三)
- CVPR 2022 | 针对场景文本检测的视觉语言模型预训练
- 第十二届 蓝桥杯 嵌入式设计与开发项目 决赛
猜你喜欢

巨杉数据库荣获艾媒咨询2022年中国信创产业双项荣誉
Tis tutorial 01- installation

推荐一款M1芯片电脑快速搭建集群的虚拟机软件

ffmpeg将amr格式转成mp3格式

第十三届 蓝桥杯 嵌入式设计与开发项目 决赛

1961-Check If String Is a Prefix of Array(检查字符串是否为数组前缀)

Shutter & flame - tankcombat game console development (I)

4tb production database cannot be accessed due to disk rejecting i/o to offline device failure

Flutter版 仿.知乎列表的视差效果

Final of the 11th Blue Bridge Cup embedded design and development project
随机推荐
stm32 hal串口中断分析
PyCharm编写shell脚本无法运行
[game] Zhou Yu's skills
1961-Check If String Is a Prefix of Array(检查字符串是否为数组前缀)
【游戏】周瑜技巧
webrtc入门:11.Kurento中使用RtpEndpoint拉取rtp流在直播中做集群
Tianyi cloud explores a new idea of cloud native and edge computing integration
0007 reverse integer
Flutter -- realize the tabbar switching effect of Netease cloud music
查看gstreamer插件
SAP-ABAP-BAPI_GOODSMVT_CREATE创建物料凭证bapi的各种情况如何赋值
BSS应用程序云原生部署的8大挑战
第十二届 蓝桥杯 嵌入式设计与开发项目 决赛
Flutter之CustomPaint 绘制贝塞尔曲线图表(三)
Onnx survey
What is C language structure byte alignment and why?
ncnn的使用(初学必看)
Shutter & flame - tankcombat game console development (I)
access_token不到两个小时失效的处理办法
智龄语音+php