当前位置:网站首页>Opencv learning notes 3
Opencv learning notes 3
2022-06-26 08:26:00 【Cloudy_ to_ sunny】
opencv Learning notes 3
import cv2 #opencv The reading format is BGR
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt#Matplotlib yes RGB
%matplotlib inline
def cv_show(img,name):
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img_rgb = cv2.merge((r,g,b))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.show()
def cv_show1(img,name):
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Histogram

cv2.calcHist(images,channels,mask,histSize,ranges)
- images: The original image format is uint8 or float32. When you pass in a function, you should Use brackets [] For example [img]
- channels: In the same way, it will tell us the function in brackets Like histogram . If the input image is a grayscale image, its value is [0] If it's a color image The parameters passed in to can be [0][1][2] They correspond to BGR.
- mask: mask image . The histogram of the whole image is taken as None. But like If you want to unify the histogram of an image, you make a mask image and Use it .
- histSize:BIN Number of . It should also be enclosed in brackets
- ranges: The range of pixel values is usually [0256]
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg',0) #0 Represents a grayscale image
hist = cv2.calcHist([img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
hist.shape
(256, 1)
plt.hist(img.ravel(),256);
plt.show()

img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg')
color = ('b','g','r')
for i,col in enumerate(color):
histr = cv2.calcHist([img],[i],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.plot(histr,color = col)
plt.xlim([0,256])

mask operation
# establish mast
mask = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], np.uint8)
print (mask.shape)
mask[100:300, 100:400] = 255
cv_show1(mask,'mask')
(414, 500)

img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg', 0)
cv_show1(img,'img')

masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img, img, mask=mask)# And operation
cv_show1(masked_img,'masked_img')

hist_full = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
hist_mask = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], mask, [256], [0, 256])
plt.subplot(221), plt.imshow(img, 'gray')
plt.subplot(222), plt.imshow(mask, 'gray')
plt.subplot(223), plt.imshow(masked_img, 'gray')
plt.subplot(224), plt.plot(hist_full), plt.plot(hist_mask)
plt.xlim([0, 256])
plt.show()

Histogram equalization


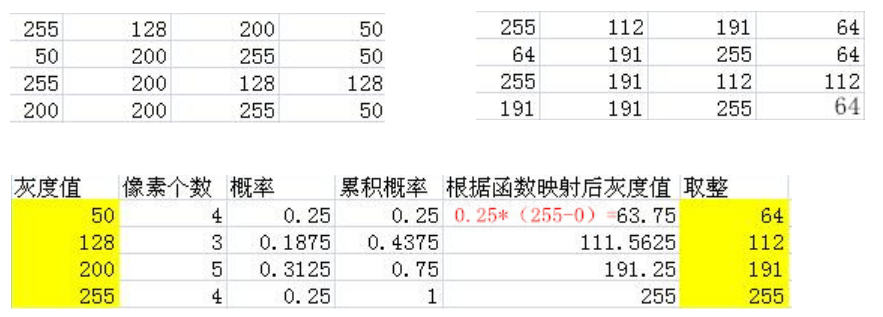
img = cv2.imread('clahe.jpg',0) #0 Represents a grayscale image #clahe
plt.hist(img.ravel(),256);
plt.show()

equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img)
plt.hist(equ.ravel(),256)
plt.show()

res = np.hstack((img,equ))
cv_show1(res,'res')

Adaptive histogram equalization
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8,8))
res_clahe = clahe.apply(img)
res = np.hstack((img,equ,res_clahe))
cv_show1(res,'res')

Template matching
Template matching is very similar to convolution , The template slides from the origin on the original image , Computing templates and ( Where the image is covered by the template ) The degree of difference , The calculation of the degree of difference is in opencv Are there in 6 Kind of , Then put the results of each calculation into a matrix , Output as a result . If the original figure is AxB size , And the template is axb size , Then the output matrix is (A-a+1)x(B-b+1)
# Template matching
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg', 0)
template = cv2.imread('face.jpg', 0)
h, w = template.shape[:2]
img.shape
(263, 263)
template.shape
(110, 85)
- TM_SQDIFF: The square is different , The smaller the calculated value , The more relevant
- TM_CCORR: Calculate correlation , The larger the calculated value , The more relevant
- TM_CCOEFF: Calculate the correlation coefficient , The larger the calculated value , The more relevant
- TM_SQDIFF_NORMED: Calculating the normalized square is different , The closer the calculated value is to 0, The more relevant
- TM_CCORR_NORMED: Calculate the normalized correlation , The closer the calculated value is to 1, The more relevant
- TM_CCOEFF_NORMED: Calculate the normalized correlation coefficient , The closer the calculated value is to 1, The more relevant
The formula :https://docs.opencv.org/3.3.1/df/dfb/group__imgproc__object.html#ga3a7850640f1fe1f58fe91a2d7583695d
methods = ['cv2.TM_CCOEFF', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCORR',
'cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED']
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_SQDIFF)
res.shape
(154, 179)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res) # The smaller the value, the better
min_val
39168.0
max_val
74403584.0
min_loc
(107, 89)
max_loc
(159, 62)
for meth in methods:
img2 = img.copy()
# The true value of the matching method
method = eval(meth)
print (method)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, method)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
# If it's a square difference match TM_SQDIFF Or normalized square difference matching TM_SQDIFF_NORMED, Minimum value
if method in [cv2.TM_SQDIFF, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED]:
top_left = min_loc
else:
top_left = max_loc
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + w, top_left[1] + h)
# Draw a rectangular
cv2.rectangle(img2, top_left, bottom_right, 255, 2)
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(res, cmap='gray')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) # Hide axis
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(img2, cmap='gray')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.suptitle(meth)
plt.show()
4

5

2

3

0

1

Match multiple objects
img_rgb = cv2.imread('mario.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
template = cv2.imread('mario_coin.jpg', 0)
h, w = template.shape[:2]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img_gray, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
threshold = 0.8
# The matching degree is greater than %80 Coordinates of
loc = np.where(res >= threshold)
for pt in zip(*loc[::-1]): # * The sign indicates an optional parameter
bottom_right = (pt[0] + w, pt[1] + h)
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, pt, bottom_right, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv_show(img_rgb,'img_rgb')

边栏推荐
- STM32 project design: an e-reader making tutorial based on stm32f4
- (vs2019 MFC connects to MySQL) make a simple login interface (detailed)
- Learn signal integrity from zero (SIPI) - (1)
- XXL job configuration alarm email notification
- STM32 project design: smart home system design based on stm32
- Golang JSON unsupported value: Nan processing
- First character that appears only once
- 51 single chip microcomputer project design: schematic diagram of timed pet feeding system (LCD 1602, timed alarm clock, key timing) Protues, KEIL, DXP
- Apple motherboard decoding chip, lightning Apple motherboard decoding I.C
- Oracle 19C download installation steps
猜你喜欢

Pychart connects to Damon database

Esp8266wifi module tutorial: punctual atom atk-esp8266 for network communication, single chip microcomputer and computer, single chip microcomputer and mobile phone to send data

STM32 project design: an e-reader making tutorial based on stm32f4

Idea automatically sets author information and date

Win11 open folder Caton solution summary

Quickly upload data sets and other files to Google colab ------ solve the problem of slow uploading colab files

MySQL practice: 1 Common database commands

Learning signal integrity from scratch (SIPI) -- 3 challenges faced by Si and Si based design methods

leetcode2022年度刷题分类型总结(十二)并查集

MySQL insert Chinese error
随机推荐
Learning signal integrity from scratch (SIPI) -- 3 challenges faced by Si and Si based design methods
Uniapp uses uviewui
X-VLM多模态模型解读
Getting started with idea
When loading view, everything behind is shielded
GHUnit: Unit Testing Objective-C for the iPhone
loading view时,后面所有东西屏蔽
MySQL practice: 2 Table definition and SQL classification
批量执行SQL文件
STM32 encountered problems using encoder module (library function version)
MySQL practice: 1 Common database commands
Cause analysis of serial communication overshoot and method of termination
Wifi-802.11 2.4G band 5g band channel frequency allocation table
STM32 porting mpu6050/9250 DMP official library (motion_driver_6.12) modifying and porting DMP simple tutorial
Application of wireless charging receiving chip xs016 coffee mixing cup
Assembly led on
Leetcode22 summary of types of questions brushing in 2002 (XII) and collection search
(2) Buzzer
[postgraduate entrance examination] group planning exercises: memory
(3) Dynamic digital tube