One 、Programming Languages system

Static program analysis yes programing language in application A subdivision under the level , It is a very important core content .
- In the theoretical part , Consider how to design the syntax and semantics of a language , How to design the type system of language and so on . In the past decade , The core of the language has hardly changed
- With the grammar of language 、 After the semantic and type systems , We need to support the language . therefore , In the environment section , You need to consider how to provide a runtime environment for running programs —— How to design a compiler , What support is needed at runtime ( Such as memory allocation management ) wait . The language hosting environment is in a stage of slow improvement , It mainly focuses on hardware equipment and high-performance programming optimization
- The biggest change is program analysis , Because with IT、 Cloud computing 、 Software SaaS Rapid development of , The scale of software has become larger 、 The structure is more complicated 、 More . How to ensure the reliability of the system 、 Security and other commitments , How to automatically synthesize a degree , It has become an increasingly popular research and engineering field
Two 、Static Analysis Definition
Static analysis analyzes a program P to reason about its behaviors and determines whether it satisfies some properties before running P.
- Does P contain any private information leaks?
- Does P dereference any null pointers?
- Are all the cast operations in P safe?
- Can v1 and v2 in P point to the same memory location?
- Will certain assert statements in P fail?
- Is this piece of code in P dead (so that it could be eliminated)?
- …

The two answers in the above figure are both correct in the static analysis semantics , They represent two solutions respectively :
- Branch exhaustion : Time consuming , But precise
- Symbol execution : Fast , But not so precise
Static Analysis: ensure (or get close to) soundness, while making good trade-offs between analysis precision and analysis speed.
Two Words to Conclude Static Analysis:
Static Analysis = Abstraction + Over-approximation
Take a specific example : Through static analysis , Judge a paragraph PHP Whether the code can have the risk of executing any external parameter , That is, whether it is Webshell. To complete this static analysis process , The following processing is required :
- Abstraction
- Over-approximation
- Transfer functions
- Control flows
The original code is as follows :
<?php v1 = 1; v2 = 2; v3 = $_POST[1]; v4 = $_POST[2]; v5 = v3 == 1 ? v3 : 5; $$_POST[3] = $_POST[4]; // $_POST[4] = v6 if(v3 == 1){ eval(v5); } echo "hello world"; ?>
Let's see first Abstraction abstract ,

To understand in a popular way Abstraction abstract , Is to change the program from the original 、 High dimensional source code space , Mapping to an abstract 、 Low dimensional symbolic space . After symbolization , Subsequent optimizations 、 analysis 、 It will be more convenient to handle .
Let's look at Over-approximation: Transfer Functions Transformation function ,
- In static analysis, transfer functions define how to evaluate different program statements on abstract values.
- Transfer functions are defined according to “analysis problem” and the “semantics” of different program statements.
The transformation function defines the operation result of abstract symbols , It should be noted that , The transformation function is related to the specific semantics and the problem to be analyzed .

It should be noted that , Because in Abstraction In the process of abstraction, the dimension of the range space is reduced , So in the transformation function mapping , Between the results of static symbolic execution and dynamic actual implementation , There are differences , It's inevitable .

Let's look at Over-approximation: Control Flows control flow ,

As it’s impossible to enumerate all paths in practice, flow merging (as a way of over-approximation) is taken for granted in most static analyses.
In static analysis , Branch flow merging is a common branch inference technique , Promoted Soundness At the same time , Also led to Completeness The fall of , This leads to inevitable false positives .
3、 ... and 、Why we need Static Analysis
- In recent years , The complexity of the program is getting higher and higher , Reliability and security are increasingly difficult to guarantee
- Null pointer dereference, memory leak, etc.
- Null pointer references and memory leaks : Almost every programmer has been troubled by these two problems
- For program reliability 、 Security analysis
- Private information leak, injection attack, etc.
- Disclosure of privacy information : This problem is common in mobile applications
- Injection attack : This is a very common topic in network security
- Provide basic technology for compilation optimization
- Dead code elimination, code motion, etc.
- Dead code elimination : In the machine independent optimization of the compiler , Code that will not affect the results of program execution ( Dead code ) Delete .
- Loop invariant code moves : In the machine independent optimization of the compiler , Under the condition that the program execution results are not affected , Move a specific statement in a loop out of the loop , Reduce the number of statements executed when the program is running . For a more detailed explanation, please refer to StackOverFlow The answer on .
- Program understanding ( The call stack 、 Automatic completion, etc )
- IDE call hierarchy, type indication, etc.
- Help with the functionality of the integrated development environment : When you use VS/Idea/Clion/Eclipse/Android Studio wait IDE when , Hover over the code ,IDE It can dynamically analyze and prompt the relevant information of the hovering object , The technology behind this is static program analysis .
- A deeper understanding of the syntax and semantics of programming languages
- Writing naturally is more reliable 、 Security 、 Efficient procedures
Four 、Rice’s Theorem -- Limitations of static analysis
Any non-trivial property of the behavior of programs in a r.e.(recursively enumerable) language is undecidable.”
non-trivial properties:
- ~= interesting properties
- ~= the properties related with run-time behaviors of programs


According to Rice's law ,「 Perfect static analysis 」 There are two core features :
- Sound( Full coverage )
- Complete( To infer exactly )
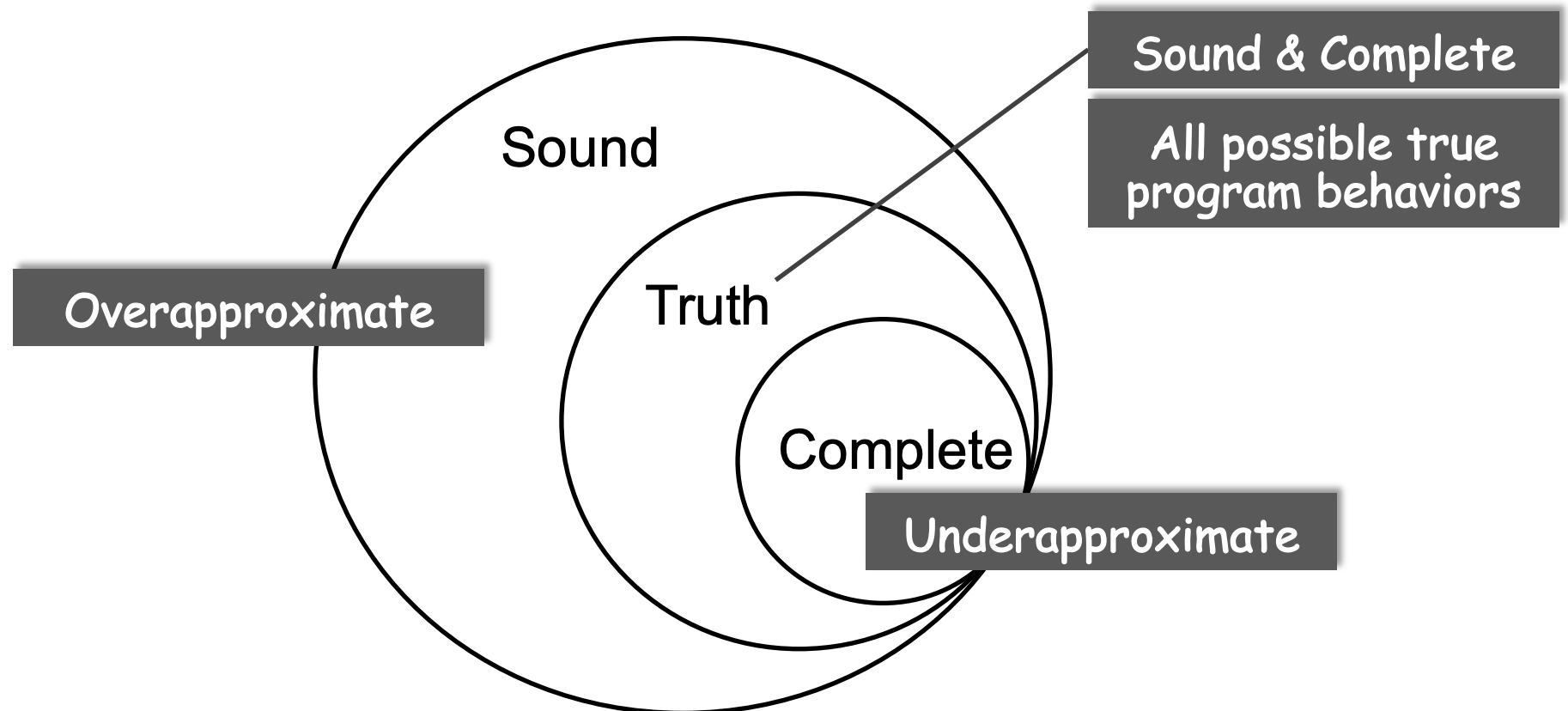
If a program is “non-trivial” Of , There is no perfect static analysis program , Can satisfy at the same time Sound and Complete features . In industrial terms, it is , False positives and false negatives cannot be achieved at the same time 100%.
In practical use , We are not pursuing 「 Perfect static analysis 」, It's about pursuing 「 Useful static analysis 」, That is, it meets the following two core characteristics :
- Compromise soundness (false negatives, Compromise under reporting control )
- Compromise completeness (false positives, Compromise false alarm control )

In a real industrial scenario ,Soundness It is often a priority , We use Webshell Static code analysis as an example .

If you pursue Sound The goal of , During static code analysis , integrity / coverage / High detection is often a priority . per contra , Relative false positives are inevitable .
5、 ... and 、 Comparison between static program analysis and similar techniques
Static program analysis
- advantage :
- Under the selected precision, no bug
- shortcoming :
- The academic threshold is relatively high . At present, only Peking University is known to have public course materials in domestic universities , Nanjing University , National Defense University , Jilin University , There are few easy to understand textbooks . As a senior elective course of computer major , It is difficult to get started and improve .
Dynamic software testing
- advantage :
- It is widely used in engineering , And it works . Implement a simple , Easy to automate .
- shortcoming :
- There is no guarantee that there is no bug. This is the inevitable result of not being able to traverse all possible program inputs .
- In today's concurrent environment brought about by multi-core and network applications, its role is limited . Some bug May only occur under certain circumstances , Therefore, it is difficult to reproduce stably .
Formal semantic validation
- advantage :
- Because the program is abstracted by mathematical method , Can guarantee that there is no bug.
- shortcoming :
- The academic threshold is high , Learners must have a good foundation in mathematics to get started .
- The cost of verification is high , Generally speaking, very important projects will use this method to ensure program quality . Even in software as important as the operating system , Not necessarily .