当前位置:网站首页>Another way of understanding the essence of Hamming code
Another way of understanding the essence of Hamming code
2022-07-28 14:22:00 【Today is also a day to study hard】
Another way to understand the essence of Hamming code
Preface
It has been a long time since we learned computer composition , The forgotten Savior is coming , I read Haiming code in the process of Review , At that time, I knew a little about Haiming code , Review again, although you can solve problems , But I can't understand its principle : Why can we correct , Why can we detect errors , After thinking for a long time, I got nothing , In a trance, I thought of a way of understanding , So it was recorded , I won't go into details about Haiming code .
One 、 The distance between string and binary string
In this article, we only discuss the distance of strings with the same length . The distance between strings with the same length refers to modifying characters at least times and trying to make two strings equal , for example “ABC“ and ”ABD“ A distance of 1,”ABCD“ and ”ABBB“ A distance of 2. Similarly, when the characters are only ‘0’ and ‘1’ when , You can define the distance between binary strings , Such as
1000 and 1001 The distance to 1,1111 and 0000 The distance to 4, The distance here is not a numerical difference
Two 、 Hamming code is just a series of processed data
Hamming code contains original data , But we always ignore that Hamming code itself is also a kind of data , Hamming code and source code have many to one mapping relationship .
Two 、 analysis
Distance of binary string and undirected graph
Briefly analyze the distance of a set of binary strings , Set the length to K Binary string of , Let's know that the distance between them is 1 The binary string of is K individual , for example 000 There are three strings with a distance of one :100、010,001. The maximum distance between two binary strings is K, For example, 0000 The biggest distance is 1111.
Since there is a distance , I have to think of pictures , As you can imagine , A binary string is a dot , A distance of 1 The strings of are directly connected : such as 3 The graph of the graph corresponding to the bit binary string :
( No, cad Use window Draw a picture , Although only the topology of the graph does not specify the definite style , But I still paint it as a cube )
At this time, we can say that a jump is to move from a point on the graph to another nearby point , such as :
001---->101;
For ordinary odd or even parity check , Have an error detection ability , If we also want to implement in this graph or cube , Then the distance from the effective point is 1 All points of are invalid points , Such points can be found casually 4 individual :001,010,100,111, These four points can be used to represent the effective value , Any bit error can be detected ,( This is the last code of odd number validation ), Map... Separately 1,2,3,4, Of course, if you like , It can be mapped to any four different values
At this time, we think about coding with one bit error correction ability , Suppose that an error free binary string is called the center point , A wrong point is that the distance between the center points is 1 The point of , Call it effective , Then the effective point and the center point represent the same data , So presumably , The central point is always surrounded by the effective point , The distance between the two centers is at least 3. Find the distance in this cube is 2 Two points of , You can know that these are the two farthest endpoints , for example {000,111},{001,110} etc. , We know {001} and {111}, It's three Hamming codes without total validation code , When there is an error, you can still know the correct value .
Read here , I believe you have roughly understood this idea , Coding with error correction capability , Completely correct coding is like a lighthouse ,, When moving not too far away ( Move a bit ), Can still walk back to the right lighthouse , If you go too far ( That is, there are twoorthree bit errors ) Go to the light of other lighthouses , At this time, no mistakes can be found , For codes with error detection capability , Error codes are like black areas without light , It is impossible to find the right lighthouse ( The value of the original ), But I can know that something wrong happened .
If the length of the binary string is K, I hope to encode a code so that it can correct one digit , Then there are K Effective points ,K+1 Points represent a value , Altogether 2^ K A little bit , Then it can store at most n= 2^K/(1+k) Data , When K=3,n=2;K=7,n=2 ^5, That's exactly what it is. 3 Bit and 7 The data size that bit Hamming code can store , about K!= 2 ^i-1(i=1,2,3,4) Value , Presumably a little wasteful . There are invalid points , Invalid points = All points - Center point - Effective points .
Although mathematics is not good, it is impossible to deduce how many central points there are , But it can be inferred through Hamming code , The data bits of Hamming code have
K − ⌊ log 2 K ⌋ − 1 K -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{K} \right \rfloor -1 K−⌊log2K⌋−1
Then the central point is
2 K − ⌊ log 2 K ⌋ − 1 2^{ K -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{K} \right \rfloor -1 } 2K−⌊log2K⌋−1
The effective points are
K ∗ 2 K − ⌊ log 2 K ⌋ − 1 K*2^{ K -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{K} \right \rfloor -1 } K∗2K−⌊log2K⌋−1
Invalid points are
2 K − 2 K − ⌊ log 2 K ⌋ − 1 − K ∗ 2 K − ⌊ log 2 K ⌋ − 1 2^{K}-2^{ K -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{K} \right \rfloor -1 }-K*2^{ K -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{K} \right \rfloor -1 } 2K−2K−⌊log2K⌋−1−K∗2K−⌊log2K⌋−1
When K=2^i-1(i=1,2,3,…) Time invalid point :
2 2 i − 1 − 2 2 i − 1 − ⌊ log 2 2 i − 1 ⌋ − 1 − ( 2 i − 1 ) ∗ 2 2 i − 1 − ⌊ log 2 2 i − 1 ⌋ − 1 2^{2^{i} -1}-2^{ 2^{i} -1 -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{2^{i} -1} \right \rfloor -1 }-(2^{i} -1)*2^{ 2^{i} -1 -\left \lfloor \log_{2}{2^{i} -1} \right \rfloor -1 } 22i−1−22i−1−⌊log22i−1⌋−1−(2i−1)∗22i−1−⌊log22i−1⌋−1
2 2 i − 1 − 2 2 i − i − 1 − ( 2 i − 1 ) ∗ 2 2 i − i − 1 2^{2^{i} -1}-2^{ 2^{i} -i -1 }-(2^{i} -1)*2^{ 2^{i} - i-1 } 22i−1−22i−i−1−(2i−1)∗22i−i−1
2 2 i − 1 − 2 2 i − i − 1 − ( 2 i ∗ 2 2 i − i − 1 + ∗ 2 2 i − i − 1 ) 2^{2^{i} -1}-2^{ 2^{i} -i -1 }-(2^{i}* 2^{ 2^{i} - i-1 }+*2^{ 2^{i} - i-1 }) 22i−1−22i−i−1−(2i∗22i−i−1+∗22i−i−1)
0 0 0
So Dangdang K=2^i-1(i=1,2,3,…) Time efficiency is the highest, and there is no invalid point , Although it is deduced from Hamming code , But it can be believed that if a big man can calculate the number of central points from the figure, it should also be the same .
In this way, other error correction and detection codes are also similar , If you want two correction , It is necessary to find a distance of 5 The point of . because K At least for 5 There can be two points , We can 00000 representative 0, take 11111 representative 1, Then this coding two bit error can still be corrected , Of course, there are many points like this , such as 11110,00001, It doesn't matter what value it maps to , Data can be stored as long as there are multiple states .
3、 ... and , The successor of binary string graph
Bit length of binary string K,K=1 Diagram of time binary string ( Don't mark the value )
K=2
K=3
K=4.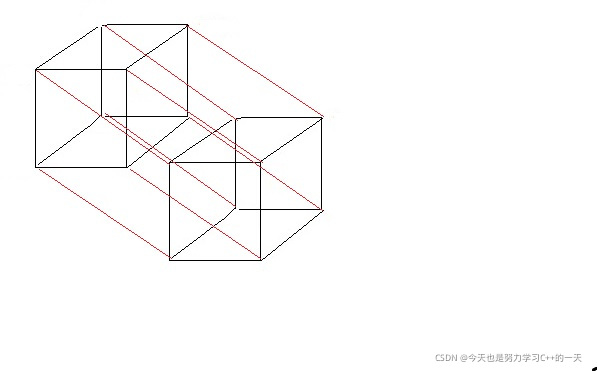
It can be seen that , about K+1 The figure of bit is K The graph of bits is copied and the copied points are connected , Because binary string x1,x2,x3…1 and x1,x2,x3…0(xi=0 or 1,i=1,2,3…) The distance is always 1. about K=4, We cannot find three pairwise distances greater than or equal to 3 The point of , therefore 4 Bit Hamming code can only store 1 A data ,
If you put K As a dimension , Maybe it can simulate a beautiful model , Or lay all the points on a sphere , As you can imagine , Because every point has K The adjacent point of , The distribution of these points is uniform and symmetrical , to want to 1 Bit error correction , Find a point on the ball with a distance of more than or equal to two 3 The center of , to want to 1 Bit error correction , You two check the error , Find a point on the ball with a distance of more than or equal to two 4 The point of , The distance from each center point is 2 The point of is invalid , If it works CG Make animation to find some 、 Error detection 、 The process of error correction , And center point 、 Effective point 、 Invalid dots are made into different colors , Then we can more intuitively understand the deep principle of Hamming code , I hope interested and capable bosses can make it .
( Level co., LTD. , Please point out the mistake ).
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
LeetCode 0142.环形链表 II

Career planning of Software Test Engineer

MySQL development skills - View

阿里、京东、抖音:把云推向产业心脏

As a programmer, how to manage time efficiently?

JMeter installation tutorial and login add token

成为绿色数据中心新样板,东莞华为云数据中心是怎样炼成的?

Recommended super easy-to-use mobile screen recording software

超好用的手机录屏软件推荐

Multithreading and high concurrency (III) -- source code analysis AQS principle
随机推荐
JMeter installation tutorial and login add token
[translation] salt companies come to linkerd for load balancing, and stay for efficiency, reliability and performance
解决uniapp微信小程序canvas不能引入字体的问题
软件测试的发展与定义
UFIDA BiP CRM new product launch enables large and medium-sized enterprises to grow their marketing
Docker deploys Mysql to realize remote connection [easy to understand]
数据库优化 理解这些就够了
【Utils】CookieUtil
线程阻塞的三种情况。
创建线程池的四种方式
Xcode编写SwiftUI代码时一个编译通过但导致预览(Preview)崩溃的小陷阱
QML picture preview
These three online PS tools should be tried
[try to hack] hfish honeypot deployment
【Try to Hack】HFish蜜罐部署
Revised version | target detection: speed and accuracy comparison (faster r-cnn, r-fcn, SSD, FPN, retinanet and yolov3)
一文读懂如何部署具有外部数据库的高可用 K3s
如何有效进行回顾会议(上)?
朗镜科技(Trax中国)“机器人+AI”开启中国零售元宇宙时代
【Utils】ServletUtil