当前位置:网站首页>Balloon punching and Boolean operation problems (extremely difficult)
Balloon punching and Boolean operation problems (extremely difficult)
2022-07-04 04:30:00 【A boy in the mountains】
One . The biggest score of the big balloon
1. Corresponding letecode link
The maximum score of ballooning _ Niuke Tiba _ Cattle from (nowcoder.com)
2. Title Description :
3. Their thinking
Personally, I think this topic is extremely difficult : The main steps are as follows :
1. Preprocessing : For ease of handling , Can be found in nums Add a sentinel at both ends of the array 1, namely nums[0]= and nums[N]=1, among N Is the length of the array .
2. Define recursive functions func(vector<int>&nums,int L,int R) Its recursive meaning is nums[L........R] The maximum score that can be obtained in the range
3. We found that when we try the possibility, the score of each position is related to its left state and right state, which makes the possibility of trying very much, so . We can try this , We try to get the maximum score of each waste in the final explosion .
4. Be careful : Recursive function func We must ensure a subtext nums[L-1] The number of positions must not explode and nums[R+1] The number of positions is not explosive. You must obey it, or don't adjust this function
First, add one at the beginning and one at the end 1, This is to facilitate code implementation . Next we can generate possibilities
We try cur The position was finally blasted. Pay attention :( If an interval is (left,right) Then there is no balloon in this range ). We try this at every location. The final answer must be in it. We just need to update it .
4. The corresponding code :
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; // Submersible number arr[L-1] Location and arr[R+1] The position must not explode // Recursive meaning arr[L.....R] The maximum score in the range int func(vector<int>& arr, int L, int R) { if (L == R) { // Only one balloon explodes return arr[L] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; } // possibility 1: Finally explode arr[L] Balloon in position int p1 = func(arr, L + 1, R) + arr[L] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; // possibility 2: Finally explode arr[R] Balloon in position int p2 = func(arr, L, R - 1) + arr[R] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; int ans = max(p1, p2); for (int i = L + 1; i < R; i++) {// produce [L+1,R-1] The maximum score that can be obtained by the final explosion of each position in the range int left = func(arr, L, i - 1); // Blow up the left part int right = func(arr, i + 1, R); // Blow up the right part int cur = arr[i] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; // Blow up the current position ans = max(ans, cur + left + right);// Update answers } return ans; } int maxCoins(vector<int>& nums) { int N = nums.size(); vector<int>arr(N + 2); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { arr[i + 1] = nums[i]; } arr[0] = arr[N + 1] = 1; dp.resize(N + 1, vector<int>(N + 1, -1)); return func(arr, 1, N); } int main() { int N; cin >> N; vector<int>arr(N); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cin >> arr[i]; } cout << maxCoins(arr) << endl; return 0; }
2. Memorize search code :
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; vector<vector<int>>dp; // Submersible number arr[L-1] Location and arr[R+1] The position must not explode // Recursive meaning arr[L.....R] The maximum score in the range int func(vector<int>& arr, int L, int R) { if (L == R) { // Only one balloon explodes return arr[L] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; } if (dp[L][R] != -1) { return dp[L][R]; } // possibility 1: Finally explode arr[L] Balloon in position int p1 = func(arr, L + 1, R) + arr[L] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; // possibility 2: Finally explode arr[R] Balloon in position int p2 = func(arr, L, R - 1) + arr[R] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; int ans = max(p1, p2); for (int i = L + 1; i < R; i++) {// produce [L+1,R-1] The maximum score that can be obtained by the final explosion of each position in the range int left = func(arr, L, i - 1); // Blow up the left part int right = func(arr, i + 1, R); // Blow up the right part int cur = arr[i] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; // Blow up the current position ans = max(ans, cur + left + right);// Update answers } dp[L][R] = ans; return ans; } int maxCoins(vector<int>& nums) { if (nums.size() == 0) { return 0; } int N = nums.size(); vector<int>arr(N + 2); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { arr[i + 1] = nums[i]; } arr[0] = arr[N + 1] = 1; dp.resize(N + 1, vector<int>(N + 1, -1)); return func(arr, 1, N); } int main() { int N; cin >> N; vector<int>arr(N); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cin >> arr[i]; } dp.resize(N + 1, vector<int>(N + 1, -1)); cout << maxCoins(arr) << endl; return 0; }
Dynamic programming with strict location dependence :
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int maxCoins(vector<int>& nums) { if (nums.size() == 0) { return 0; } int N = nums.size(); vector<int>arr(N + 2); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { arr[i + 1] = nums[i]; } arr[0] = arr[N + 1] = 1; vector<vector<int>>dp(N + 2, vector<int>(N + 2)); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { dp[i][i] = arr[i] * arr[i - 1] * arr[i + 1]; } for (int L = N; L >= 1; L--) { for (int R = L + 1; R <= N; R++) { int ans = max(arr[L - 1] * arr[L] * arr[R + 1] + dp[L + 1][R], arr[L - 1] * arr[R] * arr[R + 1] + dp[L][R - 1]); for (int i = L + 1; i < R; i++) { int left = dp[L][i - 1]; int right = dp[i + 1][R]; int cur = arr[i] * arr[L - 1] * arr[R + 1]; ans = max(ans, left + right + cur); } dp[L][R] = ans; } } return dp[1][N]; } int main() { int N; cin >> N; vector<int>arr(N); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cin >> arr[i]; } cout << maxCoins(arr) << endl; return 0; }
Two . Boolean operation
1. Corresponding letecode link
Interview questions 08.14. Boolean operation - Power button (LeetCode)
2. Title Description :
3. Their thinking :
1. Try each symbol and finally calculate what you can get true perhaps false The number of ways .
2. Define recursive functions Info*func(str,L,R) Means str from [L......R] The scope is true and false The number of ways . also L and R The location is not 0 Namely 1, Please refer to the code for details.
4. The corresponding code
class Solution { public: struct Info { Info(int tr, int tf) { t = tr; f = tf; } int t;//t Representative for true The number of ways int f;// Representative for false The number of ways }; int countEval(string s, int result) { dp.resize(s.size(), vector<Info*>(s.size(), NULL)); Info* ret = func(s, 0, s.size() - 1); return result == 1 ? ret->t : ret->f; } //L......R Upper must L and R Not 0 Namely 1 Info* func(const string& str, int L, int R) { int t = 0; int f = 0; if (L == R) { t = str[L] == '1' ? 1 : 0; f = str[L] == '0' ? 1 : 0; } else { // Be sure to save the subtext of recursion L and R The location is not 0 namely 1 for (int Split = L + 1; Split < R; Split += 2) { // Try the number of methods that can get the result by the last operation of each symbol Info* leftInfo = func(str, L, Split - 1); Info* rightInfo = func(str, Split + 1, R); int a = leftInfo->t; int b = leftInfo->f; int c = rightInfo->t; int d = rightInfo->f; switch (str[Split]) { // Classify and calculate according to the last symbol case'&': t += a * c; f += b * c + b * d + a * d; break; case'|': t += a * c + a * d + b * c; f += b * d; break; case '^': t += a * d + b * c; f += a * c + b * d; break; } } } Info* ans = new Info(t, f); return ans; } };
Memory search :
class Solution { public: struct Info { Info(int tr, int tf) { t = tr; f = tf; } int t; int f; }; vector<vector<Info*>>dp; int countEval(string s, int result) { dp.resize(s.size(), vector<Info*>(s.size(), NULL)); Info* ret = func(s, 0, s.size() - 1); return result == 1 ? ret->t : ret->f; } //L......R Upper must L and R Not 0 Namely 1 Info* func(const string& str, int L, int R) { if (dp[L][R]) { return dp[L][R]; } int t = 0; int f = 0; if (L == R) { t = str[L] == '1' ? 1 : 0; f = str[L] == '0' ? 1 : 0; } else { cout << L << " " << R << endl; for (int Split = L + 1; Split < R; Split += 2) { Info* leftInfo = func(str, L, Split - 1); Info* rightInfo = func(str, Split + 1, R); int a = leftInfo->t; int b = leftInfo->f; int c = rightInfo->t; int d = rightInfo->f; switch (str[Split]) { case'&': t += a * c; f += b * c + b * d + a * d; break; case'|': t += a * c + a * d + b * c; f += b * d; break; case '^': t += a * d + b * c; f += a * c + b * d; break; } } } Info* ans = new Info(t, f); dp[L][R] = ans; return ans; } };
边栏推荐
- [microservice openfeign] @feignclient detailed explanation
- [webrtc] M98 Ninja build and compile instructions
- Redis: order collection Zset type data operation command
- Use NRM and NVM to manage your NPM source and node versions
- Redis:有序集合zset类型数据操作命令
- leetcode刷题:二叉树06(对称二叉树)
- (指针)编写函数void fun(int x,int *pp,int *n)
- Leetcode skimming: binary tree 04 (sequence traversal of binary tree)
- How to view installed r packages in R language
- 西部数据绿盘、蓝盘、黑盘、红盘和紫盘有什么区别
猜你喜欢

Leetcode skimming: binary tree 08 (maximum depth of n-ary tree)

Understand the principle of bytecode enhancement technology through the jvm-sandbox source code
Leetcode skimming: binary tree 04 (sequence traversal of binary tree)

leetcode:1314. 矩阵区域和【二维前缀和模板】

Redis:有序集合zset类型数据操作命令
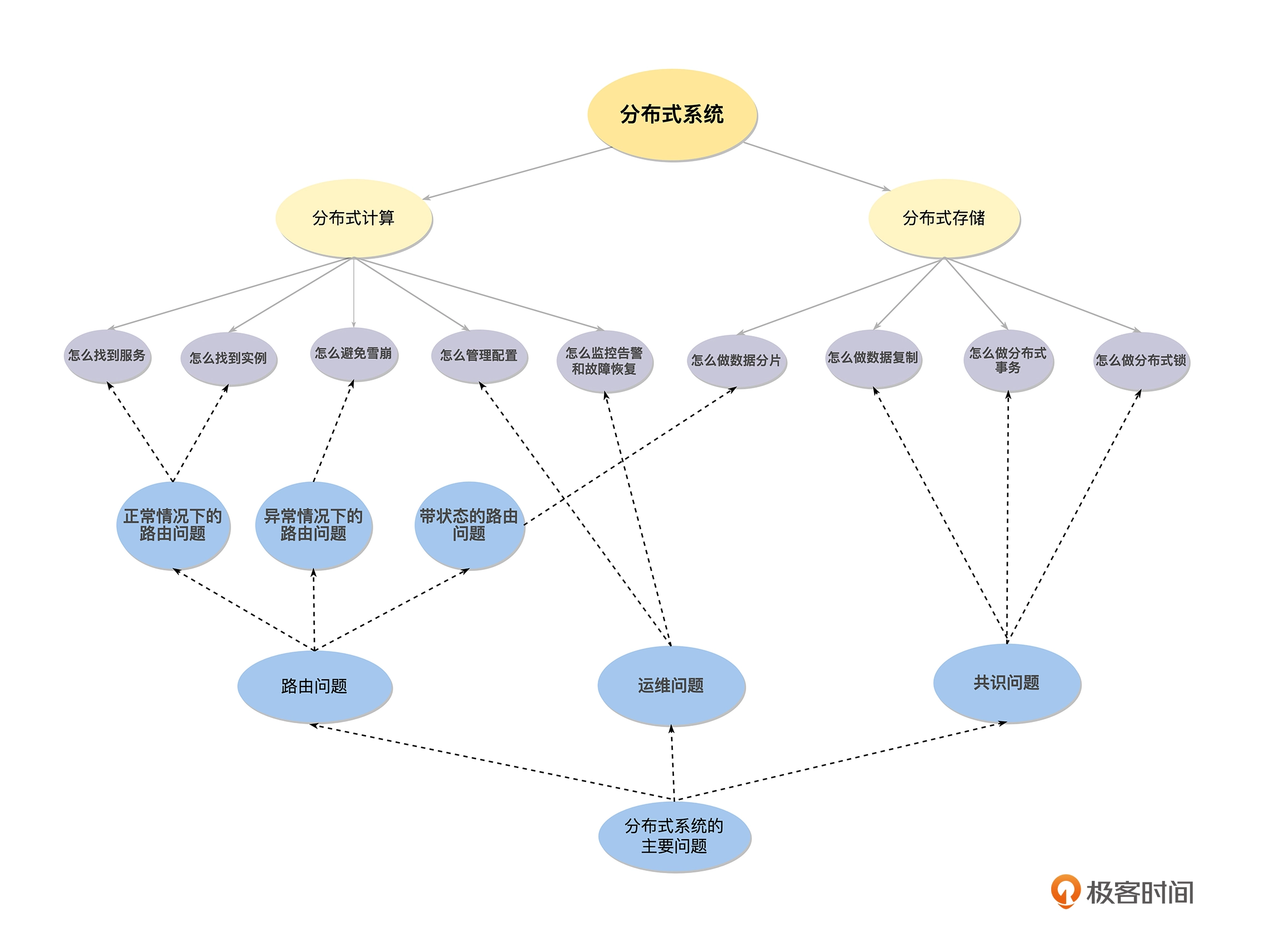
分布式系统:what、why、how
02 specific implementation of LS command
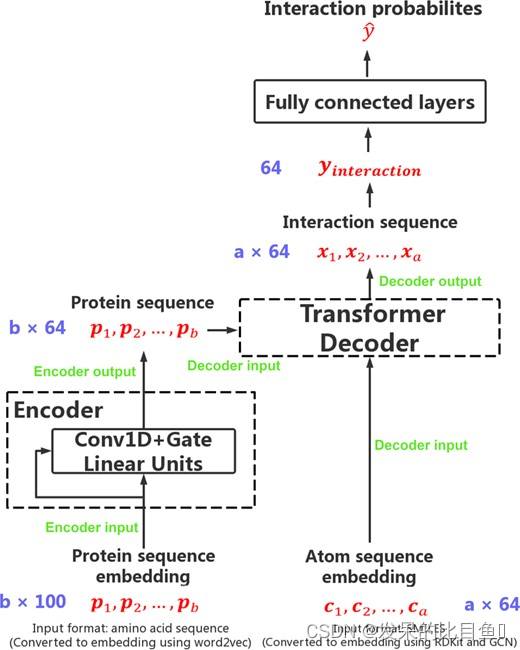
2020 Bioinformatics | TransformerCPI

Graduation project: design seckill e-commerce system

RPC技术
随机推荐
[microservices openfeign] two degradation methods of feign | fallback | fallbackfactory
RHCSA 06 - suid, sgid, sticky bit(待补充)
Emlog用户注册插件 价值80元
ROS2中CMake编译选项的设置
Programmers' telecommuting is mixed | community essay solicitation
Redis: order collection Zset type data operation command
dried food! Generation of rare samples based on GaN
C language bidirectional linked list first edition
Apple CMS imitation watermelon video atmospheric response video template source code
ModStartBlog 现代化个人博客系统 v5.2.0 源码下载
Touch and take you to implement an EventEmitter
Katalon uses script to query list size
leetcode:1314. 矩阵区域和【二维前缀和模板】
Lnk2038 detected a mismatch of "runtimelibrary": the value "md_dynamicrelease" does not match the value "mdd_dynamicdebug" (in main.obj)
NFT新的契机,多媒体NFT聚合平台OKALEIDO即将上线
C语言单向链表练习
5张图告诉你:同样是职场人,差距怎么这么大?
Common methods of threads
精品网址导航主题整站源码 wordpress模板 自适应手机端
什么是上下文?



