当前位置:网站首页>Task07: double pointer
Task07: double pointer
2022-06-11 01:59:00 【JxWang05】
Task07: Double pointer
1. Video title
1.1 Reverse a linked list
1.1.1 describe
Here's the head node of the list head , Please reverse the list , And return the inverted linked list .
Example 1:
Input :head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output :[5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input :head = [1,2]
Output :[2,1]
Example 3:
Input :head = []
Output :[]
Tips :
The number range of nodes in the linked list is [0, 5000]
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Advanced : The linked list can be inverted by iteration or recursion . Can you solve the problem in two ways ?
1.1.2 Code
Create a linked list of another leading node , Then use the head insertion method , The new element is inserted from the header
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode()
while head:
temp = head.next
head.next = dummy.next
dummy.next = head
head = temp
return dummy.next
1.1.3 summary
Because it is a reverse linked list , So use the head insertion method
1.2 Delete the last of the linked list N Nodes
1.2.1 describe
I'll give you a list , Delete the last of the linked list n Nodes , And return the head node of the list .
Example 1:
Input :head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output :[1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input :head = [1], n = 1
Output :[]
Example 3:
Input :head = [1,2], n = 1
Output :[1]
Tips :
The number of nodes in the list is sz
1 <= sz <= 30
0 <= Node.val <= 100
1 <= n <= sz
Advanced : Can you try a scan implementation ?
1.2.2 Code
Linked list title , First create an empty header node , Then start from here . Wise remark of an experienced person , Generally, it works very well
To delete the penultimate n Nodes , It is to find two intervals n Double pointer . Be careful , Yes, the interval is n
One arrives at the last node , That is to say .next==null, The other is the previous node of the deleted node
So make slow Pointer to slow.next.next, That is, skip the deleted slow.next that will do
Then it is found that this method is applicable to the boundary conditions as in the example 2 and 3 All applicable , Directly
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode()
dummy.next = head
fast = dummy
while n>0 and fast:
fast = fast.next
n -= 1
slow = dummy
while fast.next:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
1.2.3 summary
This question proves once again , When you encounter a linked list problem, first create a new header node
Then is , To delete a node of the linked list , Generally, the previous node is operated
And that is , Be sure to pay attention to the spacing , This is not the same concept as length , The difference between the two is 1
2. Assignment topic
2.1 Delete duplicate elements from the sort list
2.1.1 describe
Given the header of a sorted linked list head , Delete all duplicate elements , Make each element appear only once . return Sorted linked list .
Example 1:
Input :head = [1,1,2]
Output :[1,2]
Example 2:
Input :head = [1,1,2,3,3]
Output :[1,2,3]
Tips :
The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range [0, 300] Inside
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
The title data ensures that the linked list has been in ascending order array
2.1.2 Code
Directly judge whether the value of the next node of the current node is the same as that of the current node
If the same, skip the node , The current pointer . Point to .next.next
What needs attention is the judgment of conditions , The current pointer is not empty to prevent the linked list from being empty
If the next node is not empty, it is because the value of the next node needs to be taken for judgment
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode()
dummy.next = head
while head and head.next:
if head.val == head.next.val :
head.next = head.next.next
else:
head = head.next
return dummy.next
2.1.3 summary
This question proves once again , When you encounter a linked list problem, first create a new header node
Then is , To delete a node of the linked list , Generally, the previous node is operated
2.2 Circular list
2.2.1 describe
Give you a list of the head node head , Judge whether there are links in the list .
If there is a node in the linked list , It can be done by continuously tracking next The pointer reaches again , Then there is a ring in the linked list . To represent a ring in a given list , The evaluation system uses an integer pos To indicate where the end of the list is connected to the list ( Index from 0 Start ). Be careful :pos Not passed as an argument . Just to identify the actual situation of the linked list .
If there are rings in the list , Then return to true . otherwise , return false .
Example 1: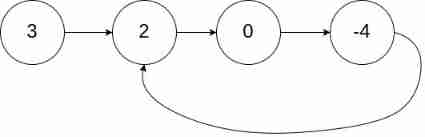
Input :head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output :true
explain : There is a link in the list , Its tail is connected to the second node .
Example 2: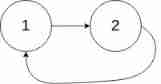
Input :head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output :true
explain : There is a link in the list , Its tail is connected to the first node .
Example 3:

Input :head = [1], pos = -1
Output :false
explain : There are no links in the list .
Tips :
The number range of nodes in the linked list is [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos by -1 Or one of the lists Valid index .
Advanced : You can use O(1)( namely , Constant ) Does memory solve this problem ?
2.2.2 Code
Judge into a ring , The classic fast and slow pointer problem , Two steps at a time , Slow pointer one step
If the two meet, it proves that there must be a ring , Whenever it appears None It is proved that there is no ring and to the end
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if head and head.next:
fast = head.next.next
else:
fast = None
slow = head
while fast and slow and fast.next:
if fast != slow:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
else:
return True
return False
2.2.3 summary
involves next Make sure that the node is not empty , Otherwise, the reference value is invalid
in other words , We need to make sure that references .next and .val The node of is not empty
Especially if the reference itself contains other references , That is to say .next.next The situation of
2.3 Sort list
2.3.1 describe
Here's the head of the list head , Please press Ascending Arrange and return to Sorted list .
Example 1:
Input :head = [4,2,1,3]
Output :[1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input :head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output :[-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input :head = []
Output :[]
Tips :
The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range [0, 5 * 104] Inside
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
Advanced : You can O(n log n) Under time complexity and constant space complexity , Sort the linked list ?
2.3.2 Code
At the beginning O(n log n) I thought of a quick row , Then it feels too complicated , Use insert sort instead
And then … It's overtime , The title doesn't say O(n log n) Is it advanced ? Then I found that this is the requirement of the topic …
According to this time complexity limit , Consider that linked lists are different from arrays , The solution to the problem is to merge and sort
There are two steps to divide and merge , Division is simply division , Merge is to merge two ordered linked lists
So recursively jump out of the condition , Is to finally divide into two single elements , Then sort by size in the merge
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def sortFunc(head: ListNode, tail: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return head
# If it is empty, return , It could be an empty list
if head.next == tail:
head.next = None
return head
# With only two elements , Return to the former
# Because last time mid It is passed into the left and right parts at the same time
# So the default here is... On the right mid Is valid and the left is invalid
slow = fast = head
while fast != tail:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
if fast != tail:
fast = fast.next
# fast Always one step faster
mid = slow
# fast To the end ,slow Namely mid
return merge(sortFunc(head, mid), sortFunc(mid, tail))
def merge(head1: ListNode, head2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummyHead = ListNode(0)
# The head node of the new list
temp, temp1, temp2 = dummyHead, head1, head2
# The temporary pointer is used to move
while temp1 and temp2:
if temp1.val <= temp2.val:
temp.next = temp1
temp1 = temp1.next
else:
temp.next = temp2
temp2 = temp2.next
# Select the smaller ones and add them to the new linked list
temp = temp.next
# Update the temporary pointer of the new linked list
if temp1:
temp.next = temp1
elif temp2:
temp.next = temp2
# If there is still something left , Add a new linked list directly
return dummyHead.next
return sortFunc(head, None)
2.3.3 summary
Merge sort has two steps of dividing and merging , Division is simply division , Merge is to merge two ordered linked lists
So recursively jump out of the condition , Is to finally divide into two single elements , Then sort by size in the merge
边栏推荐
- [leetcode] different binary search trees (recursion - recursion + memory search optimization - dynamic programming)
- AI fanaticism | come to this conference and work together on the new tools of AI!
- Px4 from abandonment to mastery (twenty four): customized model
- Lazy singleton mode
- MATLAB数组其他常见操作笔记
- Leetcode 1116 print zero even odd (concurrent multithreading countdownlatch lock condition)
- [leetcode] ordered linked list transformation binary search tree
- Threejs: how to get the boundingbox of geometry?
- Elsevier ---elseviewer--- preprint online publishing notice
- Win11画图工具没了怎么重新安装
猜你喜欢

Leetcode 2054 two best non overlapping events

从解读 BDC 自动生成的代码谈起,讲解 SAPGUI 的程序组成部分试读版

字节北京23k和拼多多上海28K,我该怎么选?
![[leetcode] reverse linked list](/img/b9/4d8e47d2b4bb1f6b5b9b4dfad30dca.jpg)
[leetcode] reverse linked list

Deep exploration of functions with indefinite parameters in C language
Task01: be familiar with the basic process of news recommendation system

今日睡眠质量记录80分

面试官:介绍一下你简历中的项目,细讲一点,附项目实战

Method of using dism command to backup driver in win11 system

Threejs: how to get the boundingbox of geometry?
随机推荐
MeterSphere教程:接口返回结果为空时如何进行断言
Lazy singleton mode
【MATLAB】图像增强(幂次变换、直方图规定化处理方法、平滑、锐化滤波)
Leetcode 1248 count number of nice subarrays
---Arrange numbers---
Method of using dism command to backup driver in win11 system
LeetCode 1609 Even Odd Tree (bfs)
2021-07-18 ROS notes - basics and communication
[leetcode] flat multi-level bidirectional linked list
Well paid test development programmers, why are you leaving? Kill each other with products until the sky is dark
小鱼儿的处理
C语言 深度探究具有不定参数的函数
【MATLAB】MATLAB图像处理基本操作
2021-07-18 ROS笔记-基础和通讯
(已解决)Latex--取消正文中参考文献引用的上标显示(gbt7714-2015会导致默认上角标引用)(上角标&平齐标混合使用教程)
数据库概述
Leetcode 1567 maximum length of subarray with positive product
Threejs: how to get the boundingbox of geometry?
逻辑漏洞 / 业务漏洞
How to change the theme of win11 touch keyboard? Win11 method of changing touch keyboard theme