当前位置:网站首页>Massive log collection tool flume
Massive log collection tool flume
2022-06-26 06:54:00 【Dregs and dregs】
List of articles
- Massive log collection tool ——Flume
- One 、Flume An introduction to the
- Two 、Flume Architecture of
- 3、 ... and 、Flume Installation
- Four 、Flume Deployment of
- 5、 ... and 、 Case presentation
- 6、 ... and 、 Use of interceptors
- 7、 ... and 、 Use of selectors
Massive log collection tool ——Flume
One 、Flume An introduction to the
1.1、 Big data processing flow
In the enterprise , The processing flow of big data is generally :
Data collection
data storage
Data cleaning
Data analysis
Data presentation
Refer to the below :
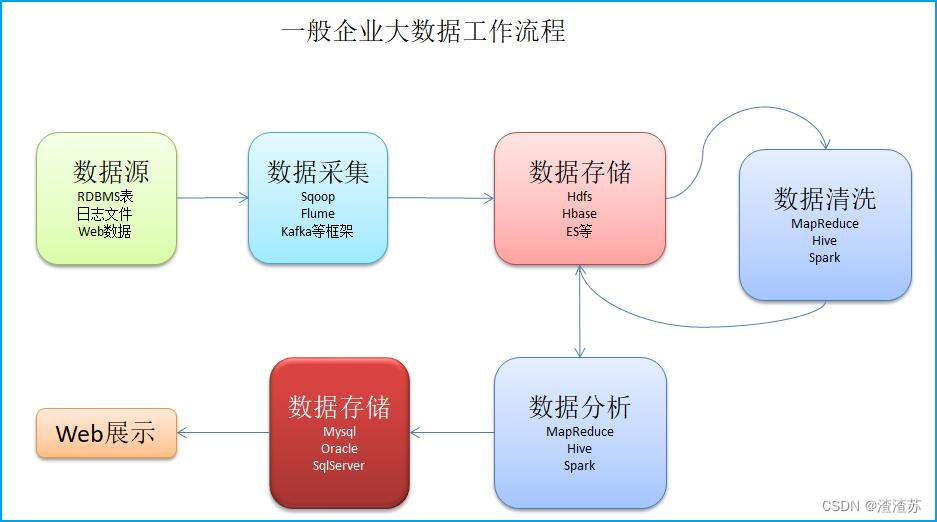
In the tools of data collection and collection ,Flume The framework occupies a certain market share .
1.2、Flume An introduction to the
Flume It's a distribution 、 Reliable and available services , For efficient collection 、 Aggregate and move large amounts of log data . It has a simple and flexible architecture based on stream data flow . It has an adjustable reliability mechanism and many fail over and recovery mechanisms , It has robustness and fault tolerance . It uses a simple and extensible data model that allows online analysis applications .
Refer to the official website : http://flume.apache.org/
Flume is a distributed, reliable, and available service for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of log data. It has a simple and flexible architecture based on streaming data flows. It is robust and fault tolerant with tunable reliability mechanisms and many failover and recovery mechanisms. It uses a simple extensible data model that allows for online analytic application.
flume From the beginning cloudera Development of real-time log collection system , It has been recognized and widely used in the industry . But as the flume The expansion of function ,flume Our code engineering is bloated 、 The design of core components is unreasonable 、 Shortcomings such as non-standard core configuration are gradually exposed , Especially in the release version 0.9.4 in , The instability of log transmission is especially serious .
To solve these problems ,2011 year 10 month 22 Number ,cloudera Yes Flume A milestone change has been made : Refactor the core components 、 Core configuration and code architecture , And will Flume Included in the apache its , from cloudera Flume Renamed as Apache Flume.
1.3、 Version difference
To distinguish from previous versions , The reconstructed version is called Flume NG(next generation), The versions before refactoring are collectively referred to as Flume OG(original generation),Flume At present, only Linux System startup script , No, Windows Environment startup script .
Two 、Flume Architecture of
2.1、 Introduction to architecture
Flume The core of operation is Agent.Flume In order to agent It is the smallest independent operation unit . One agent It's just one. JVM. It is a complete data collection tool , There are three core components , Namely source、 channel、 sink. Through these components , Event It can flow from one place to another . As shown in the figure below :

2.2、 Components and their functions
- Client:
client ,Client The production data , Run in a separate thread
- Event:
A data unit , Message header and message body .(Events It could be logging 、 avro Object etc. .)
- Flow:
Event The abstraction of the migration from the source to the destination .
- Agent:
An independent Flume process , Running on the JVM in , Contains the components Source、 Channel、 Sink.
Each machine runs one agent, But one agent Can contain more than one sources and sinks.
- Source:
Data collection component .source from Client collecting data , Pass to Channel
- Channel:
The Conduit , Responsible for receiving source End data , Then push the data to sink End .
- Sink:
In charge of from channel End pull data , And push it to the persistence system or the next Agent.
- selector:
Selectors , Act on source End , Then decide which target to send the data to .
- interceptor:
Interceptor ,flume Allow interceptors to intercept data . Interceptor chains are allowed , Act on source and sink Stage .
3、 ... and 、Flume Installation
3.1、 Install and configure environment variables
3.1.1、 Prepare the package
take apache-flume-1.8.0-bin.tar.gz Upload to linux In the system /root/soft/ Directory
3.1.2、 Unzip package
[[email protected] soft]# pwd
/root/soft
[[email protected] soft]# tar -zxvf apache-flume-1.8.0-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
3.1.3、 Rename operation
[[email protected] soft]# cd /usr/local/
[[email protected] local]# mv apache-flume-1.8.0-bin/ flume
3.1.4、 Configure environment variables
[[email protected] local]# vi /etc/profile
........ Omit ..........
export FLUME_HOME=/usr/local/flume
export PATH=$FLUME_HOME/bin:$PATH
# Load environment variables
[roo[email protected] apps]# source /etc/profile
3.1.5、 Verify environment variables
[[email protected] local]# flume-ng version
Flume 1.8.0
Source code repository: https://git-wip-us.apache.org/repos/asf/flume.git
Revision: 99f591994468633fc6f8701c5fc53e0214b6da4f
Compiled by denes on Fri Sep 15 14:58:00 CEST 2017
From source with checksum fbb44c8c8fb63a49be0a59e27316833d
3.2、 The configuration file
[[email protected] local]# cd flume/conf/
[[email protected] conf]# ll # Check to see if there is a flume-env.sh.template file
[[email protected] conf]# cp flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh
[[email protected] conf]# vim flume-env.sh
........ Omit ..........
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
........ Omit ..........
Four 、Flume Deployment of
4.1、 Data model
- Single data model
- Multi data flow model
4.1.1、 Single data model
In a single Agent It consists of a single Source, Channel, Sink Build a single data flow model , As shown in the figure below , The whole data flow is
Web Server --> Source --> Channel --> Sink --> HDFS.

4.1.2、 Multi data flow model
**1)** many Agent Serial transmission data flow model

**2)** many Agent Aggregation data flow model

**3)** single Agent Multi channel data flow model

**4)**Sinkgroups Data flow model

4.1.3、 A small summary
stay flume In the data flow model provided , Several principles are important .
Source--> Channel
1. Single Source Components can work with multiple Channel Combine to establish data flow , You can replicating and multiplexing.
2. Multiple Sources You can write a single Channel
Channel-->Sink
1. Multiple Sinks It can be combined into Sinkgroups from Channel Get data in , You can loadbalancing and failover Mechanism .
2. Multiple Sinks It can also be from a single Channel Take data from .
3. Single Sink Only from a single Channel Take data from
Based on the above 5 Principles , You can design a data flow model that meets your needs .
4.2、 Configuration is introduced
4.2.1、 Define component name
To define a flow in a single agent , You need to link the source and receiver through the channel . You need to list the sources for a given agent , Receiver and channel , Then point the source and receiver to a channel . A source instance can specify multiple channels , However, a receiver instance can only specify one channel . The format is as follows :
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
<Agent>.sources = <Source>
<Agent>.sinks = <Sink>
<Agent>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2>
# set channel for source
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.channels = <Channel1> <Channel2> ...
# set channel for sink
<Agent>.sinks.<Sink>.channel = <Channel1>
The case is as follows :
# list the sources, sinks and channels for the agent
agent_foo.sources = avro-appserver-src-1
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-sink-1
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for source
agent_foo.sources.avro-appserver-src-1.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for sink
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-sink-1.channel = mem-channel-1
4.2.2、 Configure component properties
# properties for sources
<Agent>.sources.<Source>.<someProperty> = <someValue>
# properties for channels
<Agent>.channel.<Channel>.<someProperty> = <someValue>
# properties for sinks
<Agent>.sources.<Sink>.<someProperty> = <someValue>
The case is as follows :
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source
agent_foo.sinks = hdfs-Cluster1-sink
agent_foo.channels = mem-channel-1
# set channel for sources, sinks
# properties of avro-AppSrv-source
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.type = avro
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.bind = localhost
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source.port = 10000
# properties of mem-channel-1
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.type = memory
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.capacity = 1000
agent_foo.channels.mem-channel-1.transactionCapacity = 100
# properties of hdfs-Cluster1-sink
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink.type = hdfs
agent_foo.sinks.hdfs-Cluster1-sink.hdfs.path = hdfs://namenode/flume/webdata
#...
4.3、 frequently-used source and sink species
4.3.1、 frequently-used flume sources
# Avro source:
avro
# Syslog TCP source:
syslogtcp
# Syslog UDP Source:
syslogudp
# HTTP Source:
http
# Exec source:
exec
# JMS source:
jms
# Thrift source:
thrift
# Spooling directory source:
spooldir
# Kafka source:
org.apache.flume.source.kafka,KafkaSource
.....
4.3.2、 frequently-used flume channels
# Memory Channel
memory
# JDBC Channel
jdbc
# Kafka Channel
org.apache.flume.channel.kafka.KafkaChannel
# File Channel
file
4.3.3、 frequently-used flume sinks
# HDFS Sink
hdfs
# HIVE Sink
hive
# Logger Sink
logger
# Avro Sink
avro
# Kafka Sink
org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink
# Hbase Sink
hbase
5、 ... and 、 Case presentation
Configuration reference :https://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.10.0/FlumeUserGuide.html
5.1、 Case presentation :avro+memory+logger
Avro Source: Listen to a specified Avro port , adopt Avro The port can obtain Avro client Sent files , That is, as long as the application passes Avro Port send file ,source Component can get the contents of the file , The output position is Logger
5.1.1、 Write the acquisition scheme
[[email protected] flume]# mkdir flumeconf
[[email protected] flume]# cd flumeconf
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi avro-logger.conf
# Define the name of each component
a1.sources=avro-sour1
a1.channels=mem-chan1
a1.sinks=logger-sink1
# Definition sources Component related properties
a1.sources.avro-sour1.type=avro
a1.sources.avro-sour1.bind=master
a1.sources.avro-sour1.port=9999
# Definition channels Component related properties
a1.channels.mem-chan1.type=memory
# Definition sinks Component related properties
a1.sinks.logger-sink1.type=logger
a1.sinks.logger-sink1.maxBytesToLog=100
# Binding between components
a1.sources.avro-sour1.channels=mem-chan1
a1.sinks.logger-sink1.channel=mem-chan1
5.1.2、 start-up Agent
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./avro-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5.1.3、 Test data
Start another window test
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir flumedata
[[email protected] ~]# cd flumedata/
[[email protected] flumedata]#
[[email protected] flumedata]# date >> test.data
[[email protected] flumedata]# cat test.data
2019 year 11 month 21 Japan Thursday 21:22:36 CST
[[email protected] flumedata]# ping master >> test.data
[[email protected] flumedata]# cat test.data
.... Omit ....
[[email protected] flumedata]# flume-ng avro-client -c /usr/local/flume-1.6.0/conf/ -H master -p 9999 -F ./test.dat
5.2、 Real time acquisition ( Listening files ):exec+memory+hdfs
Exec Source: Listen for a specified command , Get the result of a command as its data source
# What is commonly used is tail -F file Instructions , That is, as long as the application logs ( file ) Write data in it ,source Component can get the log ( file ) The latest content inmemory: The transmission of data Channel by Memory
hdfs Yes, the output target is Hdfs
5.2.1、 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vim exec-hdfs.conf
# Definition sources Properties of
a1.sources=r1
a1.sources.r1.type=exec
a1.sources.r1.command=tail -F /root/flumedata/test.data
# Definition sinks Properties of
a1.sinks=k1
a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/tailout/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix=events
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue=10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=3
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=20
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=5
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize=1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
# Definition channels Properties of
a1.channels
channels=c1
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# Binding between components
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
5.2.2、 start-up Agent
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./exec-hdfs.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5.2.3、 Test data
[[email protected] flumedata]# ping master >> test.data
5.3、 Real time acquisition ( Monitor Directory ):spool+ mem+logger
spool: Source From the directory , If a file enters the directory, it will be ingested .
mem: Transfer data through memory
logger: Is to transfer data to the log
5.3.1、 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi spool-logger.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = s1
a1.sources.r1.type=spooldir
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /home/flume/spool
a1.sources.r1.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED
a1.sources.r1.deletePolicy=never
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader=false
a1.sources.r1.fileHeaderKey=file
a1.sources.r1.basenameHeader=false
a1.sources.r1.basenameHeaderKey=basename
a1.sources.r1.batchSize=100
a1.sources.r1.inputCharset=UTF-8
a1.sources.r1.bufferMaxLines=1000
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.sinks.s1.type=logger
a1.sinks.s1.maxBytesToLog=100
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
5.3.2、 start-up agent
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./spool-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5.3.3、 test
[[email protected] ~]# for i in `seq 1 10`; do echo $i >> /home/flume/spool/$i;done
5.4、 Case presentation :http+ mem+logger
http: Indicates that the data source is http Network protocol , Generally, the received requests are get or post request . be-all http The request will be made in plug-in format Handle Turn into a flume Of Event data .
mem: Indicates the memory transfer channel
logger: Indicates that the output format is Logger Format
5.4.1、 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi http-logger.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = s1
a1.sources.r1.type=http
a1.sources.r1.bind = master
a1.sources.r1.port = 6666
a1.sources.r1.handler = org.apache.flume.source.http.JSONHandler
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.sinks.s1.type=logger
a1.sinks.s1.maxBytesToLog=16
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
5.4.2、 start-up agent Service for
[[email protected] ~]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./http-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
5.4.3、 test
[[email protected] ~]# curl -X POST -d '[{"headers":{"name":"zhangsan","pwd":"123456"},"body":"this is my content"}]' http://master:6666
6、 ... and 、 Use of interceptors
stay Flume In operation ,Flume Have the ability to modify... At run time / Delete Event, This is through interceptors (Interceptors) To achieve . The interceptor has the following characteristics :
Interceptors need to implement org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor Interface .
The interceptor can modify or delete events based on any condition selected by the developer in the selector .
The interceptor adopts the responsibility chain mode , Multiple interceptors can intercept in a specified order .
The list of events returned by an interceptor is passed to the next interceptor in the chain .
If an interceptor needs to delete an event , It only needs to include no events to be deleted in the returned event set .
6.1、 Common interceptors :
- Timestamp Interceptor : Time stamp interceptor , Stamp the current time ( millisecond ) Add to events header in ,key The name is :timestamp, The value is the current timestamp . Not a lot
- Host Interceptor: Hostname interceptor . Will run Flume agent The host name or IP Add the address to events header in ,key The name is :host( You can also customize )
- Static Interceptor: Static interceptors , Used in events header Add a set of static key and value.
6.2、 Case presentation :Syslogtcp+mem+hdfs
Through the time interceptor , Data source is SyslogTcp, The channel mode of transmission is FileChannel, The destination of the final output is HDFS
6.2.1 Configuration scheme :
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi ts.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = s1
a1.sources.r1.type=syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host=master
a1.sources.r1.port=6666
a1.sources.r1.interceptors=i1 i2 i3
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type=timestamp
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.preserveExisting=false
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type=host
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.preserveExisting=false
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.useIP=true
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.hostHeader=hostname
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.type=static
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.preserveExisting=false
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.key=hn
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.value=master
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/%H%M
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=%{hostname}
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
6.2.2 start-up agent Service for :
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./ts.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
6.2.3 test :
[[email protected] ~]# echo "hello world hello qiangeng" | nc master 6666
6.3、 Case presentation :regex+Syslogtcp+mem+hdfs
Interceptors are regular expression interceptors , Data source is Syslogtcp Format , The transmission channel is MemChannel, The destination of the last transmission is HDFS
6.3.1 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi regex-ts.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = s1
a1.sources.r1.type=syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host = master
a1.sources.r1.port = 6666
a1.sources.r1.interceptors=i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type=regex_filter
# Don't wrap regular in quotation marks
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.regex=^[0-9].*$
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.excludeEvents=false
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
a1.channels.c1.keep-alive=3
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacityBufferPercentage=20
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacity=800000
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/%H%M
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=%{hostname}
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
6.3.2、 start-up agent Service for :
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./regex-ts.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
6.3.3、 test :
[[email protected] ~]# echo "hello world hello qiangeng" | nc master 6666
[[email protected] ~]# echo "123123123 hello world hello qiangeng" | nc master 6666
6.4、 Custom interceptors
6.4.0 demand :
In order to improve the Flume Scalability , Users can define an interceptor by themselves
take event Of body Data in , Begin with a number , Stored as hdfs://master:8020/flume/number.log s1
take event Of body Data in , Start with a letter , Stored as hdfs://master:8020/flume/character.log s2
take event Of body Data in , Others start with , Stored as hdfs://master:8020/flume/other.log s3
6.4.1 pom.xml
You can refer to /code/pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flume/flume-ng-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
6.4.2 Code
Specific code can refer to code/MyInterceptor
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private static final String LOCATION_KEY = "location";
private static final String LOCATION_NUM = "number";
private static final String LOCATION_CHAR = "character";
private static final String LOCATION_OTHER = "other";
@Override
public void initialize() {
}
/** * When intercepting a single Event Called when * @param event This is blocked Event * @return This interceptor sent out Event */
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
// Yes, the intercepted event Of header Add the specified key value pair to the
// 1. Get the intercepted event Of body
byte[] body = event.getBody();
// 2. Verify that it starts with a number
if (body[0] >= '0' && body[0] <= '9') {
// In this event Add a key value pair to the header of , To identify this event Which one to put in channel in
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_NUM);
}
else if (body[0] >= 'a' && body[0] <= 'z' || body[0] >= 'A' && body[0] <= 'Z') {
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_CHAR);
}
else {
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_OTHER);
}
return event;
}
/** * Batch interception to Event * @param list Storage Event Set * @return After processing Event aggregate */
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> list) {
for (Event event : list) {
intercept(event);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
/** * Design a class to get the interceptor object */
public static class MyBuilder implements Builder {
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}
6.4.3 Package and upload
Use maven Pack the interceptor , Then the package and the dependent fastjson Upload to flume lib Under the table of contents
6.4.4 Write a plan
a1.sources=r1
a1.channels=c1 c2 c3
a1.sinks=s1 s2 s3
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 c2 c3
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.s2.channel=c2
a1.sinks.s3.channel=c3
# Set up source Properties of
a1.sources.r1.type=syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host=master
a1.sources.r1.port=12345
# Set up interceptors
a1.sources.r1.interceptors=i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type=com.qf.MyInterceptor$MyBuilder
# Set the properties of the selector
a1.sources.r1.selector.type=multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header=location
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.number=c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.character=c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.other=c3
# Set up channel Properties of
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c2.type=memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c3.type=memory
a1.channels.c3.capacity=1000
# Set up sink Properties of
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s1/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s2.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s2/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s3.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s3/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
6.4.5 start-up agent
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf/ -f ./mytest.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
6.4.6 test :
7、 ... and 、 Use of selectors
7.1、 explain
Flume Medium Channel Selectors act on source Stage , It's a decision Source To which... The specific event accepted is written Channel The components of , They told Channel processor , Write it to the event Channel.
Agent Interaction of various components in
because Flume Not a two-stage submission , Events are written to a Channel, Then the event is written to the next Channel Submitted before , If you write a Channel Something unusual happened , So it has been written to other Channel The same event cannot be rolled back . When such an exception occurs ,Channel Processor throw ChannelException abnormal , Transaction failure , If Source Trying to write the same event again ( Most of the time , Will be written again , Only Syslog,Exec etc. Source Cannot retry , Because there is no way to generate the same data ), Duplicate events will be written to Channel in , The previous submission was successful , In this way Flume There is repetition in .
Channel The selector is configured through Channel The processor completes ,Channel Selectors can specify a set of Channel Is a must , Another set of optional .
Flume Sort two selectors , If Source Selector... Is not specified in the configuration , Then copy will be used automatically Channel Selectors .
- replicating: This selector copies each event to pass through Source Of Channels All of the Channel in .
- multiplexing: Is a method specially used for dynamically routing events Channel Selectors , By selecting which... The event should be written to Channel, Route based on the value of a specific event header
7.2、 Case presentation :replicating selector
7.2.1 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi rep.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = s1 s2
a1.sources.r1.type=syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host = master
a1.sources.r1.port = 6666
a1.sources.r1.selector.type=replicating
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c2.type=memory
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/rep
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=s1sink
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s2.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/rep
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.filePrefix=s2sink
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 c2
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.s2.channel=c2
7.2.2 start-up agent Service for :
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./rep.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
7.2.3 test :
[[email protected] ~]# echo "hello world hello qianfeng" | nc master 6666
7.3、 Case presentation :Multiplexing selector
7.3.1 Configuration scheme
[[email protected] flumeconf]# vi mul.conf
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = s1 s2
a1.sources.r1.type=http
a1.sources.r1.bind = master
a1.sources.r1.port = 6666
a1.sources.r1.selector.type=multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = state
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.USER = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.ORDER = c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c1
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c2.type=memory
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/mul
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=s1sink
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s2.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/%Y/%m/%d/mul
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.filePrefix=s2sink
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileSuffix=.log
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.inUseSuffix=.tmp
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollInterval=60
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollSize=1024
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollCount=10
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.idleTimeout=0
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.batchSize=100
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.round=true
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.roundValue=1
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.roundUnit=second
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 c2
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.s2.channel=c2
7.3.2 start-up agent Service for :
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf -f ./mul.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
7.3.3 test :
[[email protected] ~]# curl -X POST -d '[{"headers":{"state":"ORDER"},"body":"this my multiplex to c2"}]' http://master:6666
[[email protected] ~]# curl -X POST -d '[{"headers":{"state":"ORDER"},"body":"this is my content"}]' http://master:6666
7.4、 Custom interceptors
7.4.0、 demand :
In order to improve the Flume Scalability , Users can define an interceptor by themselves
take event Of body Data in , Begin with a number , Stored as hdfs://qianfeng01:8020/flume/number.log s1
take event Of body Data in , Start with a letter , Stored as hdfs://qianfeng1:8020/flume/character.log s2
take event Of body Data in , Others start with , Stored as hdfs: //qianfeng01:8020/flume/other.log s3
7.4.1、pom.xml
You can refer to /code/pom. xml
<!-- https: //mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flume/flume-ng-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
7.4.2、 Code
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private static final String LOCATION_KEY = "location";
private static final String LOCATION_NUMBER = "number";
private static final String LOCATION_CHARACTER = "character";
private static final String LOCATION_OTHER = "other";
/** * When intercepting a single Event Called when * * @param event Intercepted Event * @return This interceptor sent out Event, If you return null, Then this Event Will be discarded */
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
// 1. Get interceptor to intercept Event Of body part
byte[] body = event.getBody();
// 2. Verify that it starts with a number
if (body[0] > '0' && body[0] <= '9') {
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_NUMBER);
} else if (body[0] >= 'a' && body[0] <= 'z' || (body[0] >= 'A' && body[0] <= 'Z')) {
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_CHARACTER);
} else {
event.getHeaders().put(LOCATION_KEY, LOCATION_OTHER);
}
return event;
}
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> list) {
for (Event event : list) {
intercept(event);
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void initialize() {
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
public static class MyBuilder implements Builder {
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}
7.4.3、 Package and upload
Use maven Pack the interceptor , Then the package and the dependent fastjson Upload to flume lib Under the table of contents
7.4.4、 Write a plan
a1.sources=r1
a1.channels=c1 c2 c3
a1.sinks=s1 s2 s3
a1.sourres.r1.channels=c1 c2 c3
a1.sinks.s1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.s2.channel=c2
a1.sinks.s3.channel=c3
# Set up source Properties of
a1.sources.r1.type=syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host=master
a1.sources.r1.port=12345
# Set up interceptors
a1.sources.r1.interceptors=i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type=com.qf.flume.MyInterceptor$MyBuilder
# Set the properties of the selector
a1.sources.r1.selector.type=multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header=location
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.number=c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.character=c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.other=c3
# Set up channel Properties of
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c2.type=memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c3.type=memory
a1.channels.c3.capacity=1000
# Set up sink Properties of
a1.sinks.s1.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s1/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
ai.sinks.s1.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s2.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s2/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s2.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.s3.type=hdfs
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.path=hdfs://master:8020/flume/customInterceptor/s3/%Y-%m-%d-%H
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.filePrefix=regex
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1,sinks.s3.hdfs.rollSize=102400
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.rollCount=30
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.s3.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
6.4.5、 start-up agent
[[email protected] flumeconf]# flume-ng agent -c ../conf/-f ./mytest.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INF0,console
test
边栏推荐
- LabVIEW arduino TCP / IP Remote Intelligent Home System (Project section - 5)
- China imported wine circulation and investment market survey and Future Development Trend Outlook report 2022-2027
- SHOW语句用法补充
- Professional course - Code question record
- 浅析一道经典题
- Go language learning notes 1.1
- Number of connections server database message: error number 2003can't connect to MySQL server on 'server address' (10061)
- 【路径规划】基于改进人工势场实现机器人路径规划附matlab代码
- [micro service series] protocol buffer dynamic analysis
- When vs code uses prettier to format JS, there is a space between the name of the function definition and the parentheses, and ESLIt does not allow this space
猜你喜欢

在公司逮到一个阿里10年的测试开发,聊过之后大彻大悟...

MATLAB线性规划模型学习笔记

Reasons why MySQL indexes are not effective

STM 32 使用cube 生成TIM触发ADC并通过DMA传输的问题

Container with the most water
Bugku exercise ---misc--- prosperity, strength and democracy

Web technology sharing | webrtc recording video stream

Phantom star VR equipment product details II: dark battlefield

直播预告丨消防安全讲师培训“云课堂”即将开讲!

Analyse d'un problème classique
随机推荐
Turris omnia: an open source router technology favored by hackers
Mysql操作数据库
同步通信和异步通信的区别以及优缺点
MATLAB线性规划模型学习笔记
【图像融合】基于梯度能量、局部能量、 PCA三种融合规则实现MRI-CT图像融合附matlab代码
Market development status analysis and investment risk outlook report of China's battery industry 2022-2027
Closure problem C Lua
Six stones Management: exaggerating the achievements, whether the parties themselves know
Simple use of typescript's class interface
China's wind farm operation industry's "fourteenth five year plan" planning direction and investment risk prediction report 2022-2027
MySQL (III)
JS download pictures
Matlab linear programming model learning notes
Live broadcast Preview - fire safety instructor training "cloud class" is about to start!
What is deadlock
STM 32 uses cube to generate Tim to trigger ADC and transmit through DMA
MySQL delete in without index
Mysql delete in 不走索引的
Numpy learning challenge level 5 - create array
NumPy学习挑战第一关-NumPy的下载与安装