当前位置:网站首页>【深度学习】:《PyTorch入门到项目实战》第一天:数据操作和自动求导
【深度学习】:《PyTorch入门到项目实战》第一天:数据操作和自动求导
2022-07-28 16:02:00 【JoJo的数据分析历险记】
【深度学习】:PyTorch:数据操作和自动求导
- 本文收录于【深度学习】:《PyTorch入门到项目实战》专栏,此专栏主要记录如何使用
PyTorch实现深度学习笔记,尽量坚持每周持续更新,欢迎大家订阅! - 个人主页:JoJo的数据分析历险记
- 个人介绍:小编大四统计在读,目前保研到统计学top3高校继续攻读统计研究生
- 如果文章对你有帮助,欢迎
关注、点赞、收藏、订阅专栏
参考资料:本专栏主要以沐神《动手学深度学习》为学习资料,记录自己的学习笔记,能力有限,如有错误,欢迎大家指正。同时沐神上传了的教学视频和教材,大家可以前往学习。
文章目录
1.数据操作
# 导入torch
import torch
import numpy as np
1.1 张量创建
x = torch.arange(12)
y = np.arange(12)
x,y
(tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]),
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]))
tensor(张量)表示一个数值组成的数组,可以有多个维度,类似numpy中的n维数组,因此很多n维数组有的方法张量也有,下面我们来测试一下有哪些numpy中的方法可以在这里使用。要了解numpy可以看这篇文章:
Python数据分析大杀器之Numpy详解
# 查看形状
x.shape
torch.Size([12])
# 查看数量长度
len(x)
12
同样可以使用reshape函数转换数组
x = x.reshape(3,4)
x
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
zeros创建全为0的元素
x = torch.zeros(3,4)
x
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
ones创建全为1的元素
x = torch.ones(3,4)
x
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
eye创建对角矩阵
l = torch.eye(5)
l
tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
ones_like创建形状一致的全为1的元素矩阵
x = torch.ones_like(l)
x
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
randn创建随机矩阵
x = torch.randn((2,4))
x
tensor([[-0.2102, -1.5580, -1.0650, -0.2689],
[-0.5349, 0.6057, 0.7164, 0.4334]])
可以有多个维度,如下所示,创建两个维度的tensor,其中0表示外面的一层,1表示内部的一层
x = torch.tensor([[1,1,1,1],[1,2,3,4],[4,3,2,1]])
x
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[4, 3, 2, 1]])
张量还可以和numpy的数组之间相互转换,具体如下所示
y = x.numpy()
type(x),type(y)
(torch.Tensor, numpy.ndarray)
1.2 基本运算
在创建完张量之后,我们对如何计算这些张量感兴趣。和多维数组一样,张量也可以进行一些基本运算,具体代码如下所示
x = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4])
y = torch.tensor([2,3,4,5])
x+y,x-y,x*y,x/y
(tensor([3, 5, 7, 9]),
tensor([-1, -1, -1, -1]),
tensor([ 2, 6, 12, 20]),
tensor([0.5000, 0.6667, 0.7500, 0.8000]))
可以看出和numpy数组一样,也是对元素进行运算。下面看看求和操作
x = torch.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
x.sum(dim=0)#按行求和
tensor([12, 15, 18, 21])
y = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
y.sum(axis=0)#按行求和
array([12, 15, 18, 21])
从上面可以看出,tensor和array都可以按行或案列进行操作,但是在torch中,指定dim参数,numpy中,指定axis参数
1.3 广播机制
我们之前的numpy中介绍过广播机制,在两个数组纬度不同时,可以适当的复制元素来拓展一个纬度或者两个纬度的元素,我们接下来看看torch中是不是也支持广播机制
x = torch.tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
y = torch.tensor([1,1,1])
z = x + y
print('x:',x)
print('y:',y)
print('z:',z)
x: tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
y: tensor([1, 1, 1])
z: tensor([[2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7]])
通过上述代码可以发现,torch中也支持广播机制,并且和numpy中的使用基本一致
1.4 索引和切片
接下来我们来看看如何对tensor结果进行切片和索引,用法和numpy基本一致
x
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
# 选取第一列和第二列的数据
x[:,[0,1]]
tensor([[1, 2],
[4, 5]])
2.自动微分(求导)
线性代数部分大家可以看我的numpy文章,有具体的介绍,这里着重看一下如何求导数。
在深度学习中,对于很多层的神经网络而言,人工求导是一件很复杂的事情,因此在如何自动求导是一件很work的事情
这里我们假设要对 y = x T x y=x^Tx y=xTx进行求导。首先我们先初始化一个x值
x = torch.arange(4.0)
x
tensor([0., 1., 2., 3.])
下面我们在计算梯度之前,需要一个地方来存储梯度,就像我们在进行一些循环时,需要一个空列表来存储内容。下面我们来看如何使用requires_grad_来存储
x.requires_grad_(True)
print(x.grad)#默认是None,相当于这个时候是一个空列表
None
下面我们来计算y
y = torch.dot(x,x)
y
tensor(14., grad_fn=<DotBackward0>)
# 通过反向传播函数计算梯度
y.backward(retain_graph=False)
x.grad
tensor([0., 2., 4., 6.])
这里默认情况下,pytorch会保存梯度,因此当我们需要重新计算梯度时,首先要进行初始化,使用grad.zero_
x.grad.zero_()
# 重新计算y=x的梯度
y = x.sum()
y.backward()
x.grad
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1.])
上面我们都是先将y变为一个标量再求梯度,如果y不是标量呢?可以先将y求和转换为标量
x.grad.zero_()
y = x*x
y.sum().backward()
x.grad
tensor([0., 2., 4., 6.])
2.3 分离微分计算
这里沐神给出了一个这样的场景,y是关于x的函数,而z是关于y和x的函数,在我们对z求x偏导时,我们希望将y看做一个常数。这种方法在有的复杂的神经网络模型会很有效,具体通过detach()实现,将u为y的常量
具体代码如下:
x.grad.zero_()#初始化梯度
y = x * x#y对x的函数
u = y.detach()#将y分离处理
z = u * x#z对x的函数
z.sum().backward()#通过反向传播函数求梯度
x.grad
tensor([0., 1., 4., 9.])
上述结果是什么呢?我们根据求导法则:
d z d x = u \frac{dz}{dx} = u dxdz=u
下面我们来看看u是多少
u
tensor([0., 1., 4., 9.])
2.4 控制流梯度计算
使用自动微分有一个好处是,当我们的函数是分段的,其也会自动计算得到相应的梯度。下面我们来看一个线性控制流梯度计算案例:
def f(a):
if a.sum() > 0:
b = a
else:
b = 100 * a
return b
首先我们定义一个线性分段函数,如上所示:
f ( a ) = { a a.sum()>0 100 ∗ a else f(a) = \begin{cases} a& \text{a.sum()>0}\\ 100*a& \text{else} \end{cases} f(a)={ a100∗aa.sum()>0else
下面我们来看如何进行自动求导
a = torch.randn(12, requires_grad=True)
d = f(a)
d.backward(torch.ones_like(a))
a.grad == d / a
tensor([True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True])
练习与总结
1.重新设计一个求控制流梯度的例子,运行并分析结果。
在上面的案例中,沐神给了一个线性分段函数的例子,假设不是线性的呢,下面我们假设一个分段函数是这样的
f ( x ) = { x norm(x)>10 x 2 else f(x) = \begin{cases} x& \text{norm(x)>10}\\ x^2& \text{else} \end{cases} f(x)={ xx2norm(x)>10else
具体控制流代码如下:
def f(x):
if x.norm() > 10:
y = x
else:
y = x*x
return y
x = torch.randn(12,requires_grad=True)
y = f(x)
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x))
x.grad
tensor([ 0.3074, -2.0289, 0.5950, 1.2339, -2.2543, 0.5834, -2.3040, -1.9097,
0.9255, 1.6837, -1.4464, -0.3131])
2.绘制微分图
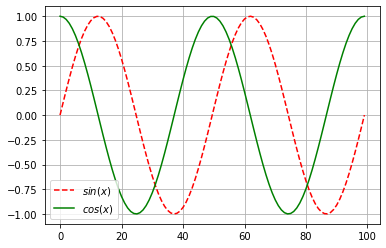
使 f ( x ) = s i n ( x ) f(x)=sin(x) f(x)=sin(x),绘制 f ( x ) f(x) f(x)和 d f ( x ) d x \frac{df(x)}{dx} dxdf(x)的图像,后者不使用 f ′ ( x ) = c o s ( x ) f'(x)=cos(x) f′(x)=cos(x),这里我们还需要使用matplotlib,想要了解的小伙伴可以看我这篇文章:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
x = torch.linspace(-2*torch.pi, 2*torch.pi, 100)
x.requires_grad_(True)
y = torch.sin(x)
y.sum().backward()
y = torch.detach(y)
plt.plot(y,'r--',label='$sin(x)$')
plt.plot(x.grad,'g',label='$cos(x)$')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.grid()
本章的介绍到此介绍,如果文章对你有帮助,请多多点赞、收藏、评论、关注支持!!
边栏推荐
- Sort 3-select sort and merge sort (recursive implementation + non recursive implementation)
- Sort 2 bubble sort and quick sort (recursive and non recursive explanation)
- Redis系列4:高可用之Sentinel(哨兵模式)
- asp.net大文件分块上传断点续传demo
- Brother Ali teaches you how to correctly understand the problem of standard IO buffer
- 有趣的 Kotlin 0x07:Composition
- Ansa secondary development - apps and ansa plug-in management
- IM即时通讯软件开发网络请求成功率的优化
- 阿里大哥教你如何正确认识关于标准IO缓冲区的问题
- 排序2-冒泡排序与快速排序(递归加非递归讲解)
猜你喜欢

Wake up after being repeatedly upset by MQ! Hate code out this MQ manual to help the journey of autumn recruitment
Text filtering skills

IM即时通讯软件开发网络请求成功率的优化

排序5-计数排序

Ansa secondary development - two methods of drawing the middle surface

Interesting kotlin 0x07:composition

Im im development optimization improves connection success rate, speed, etc

排序2-冒泡排序与快速排序(递归加非递归讲解)

What does it remote operation and maintenance mean? Which is the best remote operation and maintenance software?

排序4-堆排序与海量TopK问题
随机推荐
LwIP development | socket | UDP
Use js direct OSS to store files in Alibaba cloud and solve the limitation of large file upload server
微软100题-天天做-第16题
智慧园区是未来发展的趋势吗?
CRC16 data verification supports modelbus and XMODEM verification modes (C language)
"Wei Lai Cup" 2022 Niuke summer multi school training camp 3 a.ancestor lca+ violence count
Li Hongyi, machine learning 5. Tips for neural network design
Implementation of transfer business
LeetCode每日一练 —— 160. 相交链表
Geodetic coordinate system to Martian coordinate system
ANSA二次开发 - 界面开发工具介绍
Leetcode daily practice - the number of digits in the offer 56 array of the sword finger
Introduction and implementation of queue (detailed explanation)
Kubeedge releases white paper on cloud native edge computing threat model and security protection technology
Multiple commands produce ‘.../xxx.app/Assets.car‘问题
Implementation of paging
"Wei Lai Cup" 2022 Niuke summer multi school training camp 3 acfhj
What does it remote operation and maintenance mean? Which is the best remote operation and maintenance software?
Learn ABAQUS script programming script in an hour
LeetCode-学会对无序链表进行插入排序(详解)