当前位置:网站首页>Epoll principle and Application & ET mode and lt mode
Epoll principle and Application & ET mode and lt mode
2022-06-11 02:23:00 【Prison code department】
[Ⅰ] Epoll Principle and Application && ET Patterns and LT Pattern
- [Ⅱ] Epoll Reactor model The core principle && Code explanation
- [Ⅰ] Epoll Principle and Application && ET Patterns and LT Pattern
[Ⅱ] Epoll Reactor model The core principle && Code explanation
The second part is the article link : Epoll Reactor model The core principle && Code explanation
[Ⅰ] Epoll Principle and Application && ET Patterns and LT Pattern
epoll yes Linux Lower multiplexing IO Interface select/poll Enhanced version of , It can Significantly improve the system when the program is only a few active in a large number of concurrent connections CPU utilization , Because it reuses the collection of file descriptors to deliver results without forcing developers to prepare the collection of file descriptors to be listened to again before each event , Another reason is to get events , It does not have to traverse the entire set of descriptors being listened to , Just go through the kernel IO Events wake up asynchronously and join Ready The set of descriptors for the queue is enough .
at present epell yes linux Popular model of choice in large-scale concurrent network programs .
epoll In addition to providing select/poll That kind of IO The level of the event triggers (Level Triggered) Outside , It also provides edge trigger (Edge Triggered), This makes it possible for user-space programs to cache IO state , Reduce epoll_wait/epoll_pwait Call to , Improve application efficiency .
One 、 breakthrough 1024 File descriptor limit
1.1 View file descriptor limits
- have access to
catCommand to view the current computer ( Or virtual machines ) The maximum number of files that can be opened , Affected by hardware configuration .
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
- It can be used
ulimit -asee ,open file It indicates the maximum number of file descriptors that can be opened by the process under the current user by default , Default is 1024.
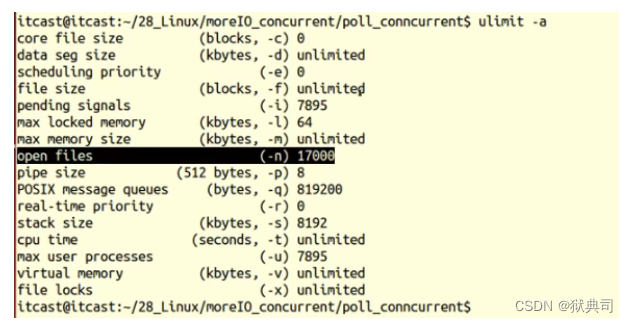
The image above open files The value is changed .
1.2 Modify file descriptor restrictions
① You can modify the upper limit by modifying the configuration file .
sudo vi /etc/security/limits.conf
Write the following configuration at the end of the file ,soft Soft limit ,hard Hard limit . As shown in the figure below :
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 100000

② soft The value can be modified by the command , But not more than hard value :
ulimit -n [ Modified soft value ]
Log off the user after the change , Make it effective .
Two 、Epoll Basics API
epoll Is characterized by a balanced binary tree ( The height difference between the left and right subtrees shall not exceed 1), More strictly, it is a red black tree ;
The listening tree is created by the kernel , And provide the user with access to API To add or delete query nodes .
2.1 epoll_create()
Create a epoll Handle , Parameters size The number of file descriptors used to tell the kernel to listen to , It's about memory size .
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_create(int size)
Parameters :
- size —— Number of listening text descriptors ( reference value , That is, the size is not limited , It can be dynamically expanded )
Return value :
- success —— Return the newly created root node that listens to the red black tree epfd
- Failure —— return -1 Juxtaposition errno
2.2 epoll_ctl()
Control someone epoll Events on the monitored file descriptor : register 、 modify 、 Delete .
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event)
Parameters :
int epfd—— epoll_create() The return value of , namely epoll Listen to the root node of the red black treeint op—— The specific operation of this monitoring red black tree , Defined by macro :EPOLL_CTL_ADD: add to fd To epoll Listen to the red and black treesEPOLL_CTL_MOD: modify fd stay epoll Monitor events on the red black treeEPOLL_CTL_DEL: Will a fd from epoll Listen to the red and black trees ( Cancel monitoring )
int fd—— File descriptor to be operatedstruct epoll_event *event—— Structure pointer ( Address ), Are incoming and outgoing parametersstruct epoll_event { __uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */ epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */ };struct epoll_eventIn structureeventsOn behalf of listening events , Value for :EPOLLIN : Indicates that the corresponding file descriptor can be read ( Including the end SOCKET Normally shut down ) EPOLLOUT: Indicates that the corresponding file descriptor can write EPOLLPRI: Indicates that the corresponding file descriptor has urgent data readability ( This should indicate that there is out-of-band data coming in ) EPOLLERR: Indicates that there is an error in the corresponding file descriptor EPOLLHUP: Indicates that the corresponding file descriptor is suspended ; EPOLLET: take EPOLL Set edge trigger (Edge Triggered) Pattern , This is relative to the horizontal trigger (Level Triggered) In terms of the EPOLLONESHOT: Listen for only one event , After listening to this event , If you need to keep listening to this socket Words , I have to do this again socket Add to EPOLL In the queuestruct epoll_eventUnion parameters in the structureepoll_data_t dataIt's an outgoing parameter :typedef union epoll_data { void *ptr; int fd; // The fd It's the introduction epoll_ctl() Of the corresponding listening event fd uint32_t u32; uint64_t u64; } epoll_data_t;
Return value :
- success —— return 0
- Failure —— return -1 Juxtaposition errno
2.3 epoll_wait()
Wait for an event to occur on the monitored file descriptor , Be similar to select() call .
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout)
Parameters :
int epfd—— epoll_create() The return value of , namely epoll Listen to the root node of the red black treestruct epoll_event *events—— Note here and the collection of events used to store the kernelBe careful Here and epoll_ctl() Functional
struct epoll_event *eventParameters ( A pointer to a structure , Incoming and outgoing parameters ) Dissimilarity , thereeventsIt's an outgoing parameter , And it's an array , Used to store a collection of satisfaction events .
int maxevents—— Tell the kernel this events How big is theFor example, the outgoing parameters are defined
struct epoll_event ret[1024], thatmaxeventsFill in the value of 1024, amount to buffer_size;But pay attention to this maxevents Value of cannot be greater than create epoll_create() At the time of the size( Generally take the same value ).
int timeout—— Set timeout-1: Blocking
0: Return immediately , Non blocking
> 0: Specify milliseconds
Return value :
- success —— Returns how many file descriptors are ready , If timing blocking or non blocking is set, the timeout returns 0
- error —— return -1
3、 ... and 、Epoll socket Basic use cases
3.1 Server
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define MAXLINE 8192
#define SERV_PORT 8000
#define OPEN_MAX 5000
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i, listenfd, connfd, sockfd;
int n, num = 0;
ssize_t nready, efd, res;
char buf[MAXLINE], str[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
socklen_t clilen;
struct sockaddr_in cliaddr, servaddr;
listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(listenfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt)); // Port multiplexing
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *) &servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
listen(listenfd, 20);
efd = epoll_create(OPEN_MAX); // establish epoll Model , efd Point to the root node of the red black tree
if (efd == -1)
perr_exit("epoll_create error");
struct epoll_event tep, ep[OPEN_MAX]; //tep: epoll_ctl Parameters //ep[] : epoll_wait Parameters
tep.events = EPOLLIN;
tep.data.fd = listenfd; // Appoint lfd The listening time is " read "
res = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listenfd, &tep); // take lfd And the corresponding structure set to the tree ,efd You can find the tree
if (res == -1)
perr_exit("epoll_ctl error");
for ( ; ; ) {
/*epoll by server Blocking listening Events , ep by struct epoll_event Type array , OPEN_MAX Is the array capacity , -1 The watch is permanently blocked */
nready = epoll_wait(efd, ep, OPEN_MAX, -1);
if (nready == -1)
perror("epoll_wait error");
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
if (!(ep[i].events & EPOLLIN)) // If not " read " event , Continue to cycle
continue;
if (ep[i].data.fd == listenfd) {
// Judge the satisfaction of the event fd Is it right? lfd
clilen = sizeof(cliaddr);
connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &clilen); // Accept link
printf("received from %s at PORT %d\n",
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &cliaddr.sin_addr, str, sizeof(str)),
ntohs(cliaddr.sin_port));
printf("cfd %d---client %d\n", connfd, ++num);
tep.events = EPOLLIN; tep.data.fd = connfd;
res = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connfd, &tep); // Join the red and black trees
if (res == -1)
perror("epoll_ctl error");
} else {
// No lfd,
sockfd = ep[i].data.fd;
n = read(sockfd, buf, MAXLINE);
if (n == 0) {
// Read 0, The client closes the link
res = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, sockfd, NULL); // Remove the file descriptor from the red black tree
if (res == -1)
perror("epoll_ctl error");
close(sockfd); // Close the link to the client
printf("client[%d] closed connection\n", sockfd);
} else if (n < 0) {
// error
perror("read n < 0 error: ");
res = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, sockfd, NULL); // Remove the node
close(sockfd);
} else {
// Number of bytes actually read
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
buf[i] = toupper(buf[i]); // Turn capitalization , Write back to the client
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n);
}
}
}
}
close(listenfd);
close(efd);
return 0;
}
3.2 Client
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define MAXLINE 8192
#define SERV_PORT 8000
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
char buf[MAXLINE];
int sockfd, n;
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET, "127.0.0.1", &servaddr.sin_addr);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
while (fgets(buf, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL) {
write(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf));
n = read(sockfd, buf, MAXLINE);
if (n == 0) {
printf("the other side has been closed.\n");
break;
}
else
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n);
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
Four 、ET and LT Event model
EPOLL There are two models of events :
Edge Triggered (ET) Edge trigger —— Only the arrival of data triggers , Whether there is data in the cache or not .
Level Triggered (LT) Level trigger —— As long as there is data, it will trigger .
Think about the following steps :
Suppose we have a file descriptor used to read data from the pipeline (RFD) Add to epoll The descriptor .
The other end of the pipe writes 2KB The data of
call epoll_wait, And it will return RFD, Indicates that it is ready for read operation
Read 1KB The data of
call epoll_wait……
In the process , There are two working modes :
4.1 ET Pattern
ET The pattern is Edge Triggered Working mode .
If we were in 1 Step by step RFD Add to epoll The descriptor was used EPOLLET sign , Then in the first place 5 Step call epoll_wait After that, it's possible to suspend , Because the rest of the data is still in the input buffer of the file , And the data sending end is still waiting for a feedback message for the sent data . Only when an event occurs on the monitored file handle ET Working mode will report the incident . So on the 5 When you walk , The caller may give up waiting for the remaining data that still exists in the file input buffer .epoll Working in ET In mode , Non blocking socket interface must be used , To avoid blocking read due to a file handle / Blocking writes starve the task of processing multiple file descriptors . It's best to call ET Mode epoll Interface , Avoiding possible defects will be described later .
Based on non blocking file handle
Only when read perhaps write return EAGAIN( Non blocking read , No data available ) When you need to suspend 、 wait for . But that's not to say every time read You need to read it in cycles , Until I read that it produced a EAGAIN I think that this incident has been handled , When read When the returned read data length is less than the requested data length , You can determine that there is no data in the buffer at this time , It can be considered that the event has been handled .

4.2 LT Pattern
LT The pattern is Level Triggered Working mode .
And ET The pattern is different , With LT Way to call epoll At the interface , It is equivalent to a relatively fast poll, Whether or not the following data is used .
LT(level triggered):LT It's the default way of working , And at the same time support block and no-block socket. In this way , The kernel tells you if a file descriptor is ready , Then you can be ready for this fd Conduct IO operation . If you don't do anything , The kernel will continue to inform you , therefore , This mode is less likely to make errors in programming . Conventional select/poll They are all representatives of this model .
ET(edge-triggered):ET It's a high-speed way of working , Only support no-block socket. In this mode , When the descriptor is never ready to be ready , The kernel passes through epoll Tell you . Then it assumes that you know the file descriptor is ready , And no more ready notifications will be sent for that file descriptor . Please note that , If it's not right all the time fd do IO operation ( So it becomes not ready again ), The kernel will not send any more notifications (only once).
4.3 ET Examples of patterns
In the following example code , The parent and child processes share an anonymous pipeline , Subprocesses every 5s write in 10 Bytes of data ;
Parent process passed epoll Listen to the anonymous pipeline , Each listening event is ready for the parent process to read 5 Bytes of data .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXLINE 10
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int efd, i;
int pfd[2];
pid_t pid;
char buf[MAXLINE], ch = 'a';
pipe(pfd); // Create anonymous pipes
pid = fork(); // Parent child process sharing pipeline
if (pid == 0) {
// Son Write
close(pfd[0]);
while (1) {
//aaaa\n
for (i = 0; i < MAXLINE/2; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//bbbb\n
for (; i < MAXLINE; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//aaaa\nbbbb\n
write(pfd[1], buf, sizeof(buf));
sleep(5);
}
close(pfd[1]);
} else if (pid > 0) {
// Father read
struct epoll_event event;
struct epoll_event resevent[10]; //epoll_wait Ready to return event
int nready, len;
close(pfd[1]);
efd = epoll_create(10);
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; // ET edge-triggered
//event.events = EPOLLIN; // LT Level trigger ( Default )
event.data.fd = pfd[0];
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, pfd[0], &event);
while (1) {
nready = epoll_wait(efd, resevent, 10, -1);
printf("res %d\n", nready);
if (resevent[0].data.fd == pfd[0]) {
len = read(pfd[0], buf, MAXLINE/2);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len);
}
}
close(pfd[0]);
close(efd);
} else {
perror("fork");
exit(-1);
}
return 0;
}
The code logic of the example is as follows :
If... Is used in ET Edge trigger mode , I'm using epoll_ctl() take fd When it is connected to the monitoring tree, it is set
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;, that epoll_wait() Only events on the rising edge will be captured , In short epoll_wait() Only return each time the child process writes data ( Whether or not there is data in the buffer );Compared with , If the default is used LT Flat edge trigger mode (
event.events = EPOLLIN; // LT Level trigger ( Default )), So as long as there is data left in the buffer , Will be considered as read event ready ,epoll_wait() Will return .The subprocess of the sample code writes to the pipeline every time 10 Bytes of data , Every time the parent process reads from the pipe 5 Bytes of data , But whether it's ET Mode or LT Pattern , The data read out by the parent process is read out in the order in which the child process writes data ;
In this example ,ET and LT The pattern difference is Every time a subprocess is written ,ET In mode epoll_wait() Only once back ,LT In mode epoll_wait() Will return twice .
【ET Detailed examples of patterns 】
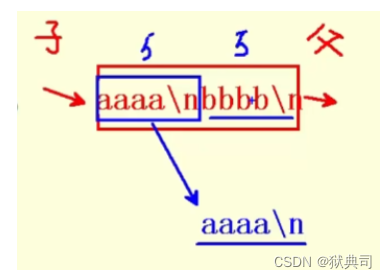
- Subprocess write aaaa\nbbbb\n;
- The parent process epoll_wait() return , The parent process reads aaaa\n, At this time, there are still bbbb\n A total of five bytes of data were not read ;
- Child process dormancy 5 Wake up in seconds , Continue writing to the pipeline cccc\ndddd\n;
- The parent process epoll_wait() return , Note that the parent process does not read cccc\n, It is bbbb\n; At this time, there are still cccc\ndddd\n The data of the cross section is not read ;
** Be careful :** The pipeline has no buffer overflow problem , If the buffer is full write It will block .
4.4 The Internet socket Medium ET / LT Pattern
The following code logic and 4.3 The sample code of is basically the same , The difference is that the two communication terminals are changed from the parent-child process to server End sum client End , Communication medium ( File descriptor ) from Linux The pipeline of the local system becomes the network socket.
But the real use epoll ET The non blocking mode is used in the , Here is a simple transition .
4.4.1 Server
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXLINE 10
#define SERV_PORT 9000
int main(void)
{
struct sockaddr_in servaddr, cliaddr;
socklen_t cliaddr_len;
int listenfd, connfd;
char buf[MAXLINE];
char str[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
int efd;
listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
listen(listenfd, 20);
struct epoll_event event;
struct epoll_event resevent[10];
int res, len;
efd = epoll_create(10);
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; /* ET edge-triggered */
//event.events = EPOLLIN; /* Default LT Level trigger */
printf("Accepting connections ...\n");
cliaddr_len = sizeof(cliaddr);
connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &cliaddr_len);
printf("received from %s at PORT %d\n",
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &cliaddr.sin_addr, str, sizeof(str)),
ntohs(cliaddr.sin_port));
event.data.fd = connfd;
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connfd, &event);
while (1) {
res = epoll_wait(efd, resevent, 10, -1);
printf("res %d\n", res);
if (resevent[0].data.fd == connfd) {
len = read(connfd, buf, MAXLINE/2); //readn(500)
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len);
}
}
return 0;
}
4.4.2 Client
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define MAXLINE 10
#define SERV_PORT 9000
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
char buf[MAXLINE];
int sockfd, i;
char ch = 'a';
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET, "127.0.0.1", &servaddr.sin_addr);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
while (1) {
//aaaa\n
for (i = 0; i < MAXLINE/2; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//bbbb\n
for (; i < MAXLINE; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//aaaa\nbbbb\n
write(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
sleep(5);
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
5、 ... and 、Epoll Of ET Non blocking model
The following code is in 4.4 Code for ET The non blocking polling mechanism is updated based on the pattern .
5.1 Server
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define MAXLINE 10
#define SERV_PORT 8000
int main(void)
{
struct sockaddr_in servaddr, cliaddr;
socklen_t cliaddr_len;
int listenfd, connfd;
char buf[MAXLINE];
char str[INET_ADDRSTRLEN];
int efd, flag;
listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
listen(listenfd, 20);
struct epoll_event event;
struct epoll_event res_event[10];
int res, len;
efd = epoll_create(10);
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; /* ET edge-triggered , The default is to trigger horizontally */
//event.events = EPOLLIN;
printf("Accepting connections ...\n");
cliaddr_len = sizeof(cliaddr);
connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, &cliaddr_len);
printf("received from %s at PORT %d\n",
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &cliaddr.sin_addr, str, sizeof(str)),
ntohs(cliaddr.sin_port));
// Set non-blocking ///
flag = fcntl(connfd, F_GETFL); /* modify connfd For non blocking read */
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(connfd, F_SETFL, flag);
/
event.data.fd = connfd;
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connfd, &event); // take connfd Join the monitoring red and black tree
while (1) {
printf("epoll_wait begin\n");
res = epoll_wait(efd, res_event, 10, -1); // most 10 individual , Blocking monitor
printf("epoll_wait end res %d\n", res);
if (res_event[0].data.fd == connfd) {
while ((len = read(connfd, buf, MAXLINE/2)) >0 ) // Non blocking read , polling
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len);
}
}
return 0;
}
The point is ET + Perform non blocking polling after listening returns
5.2 Client
/* client.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define MAXLINE 10
#define SERV_PORT 8000
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
char buf[MAXLINE];
int sockfd, i;
char ch = 'a';
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET, "127.0.0.1", &servaddr.sin_addr);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
while (1) {
//aaaa\n
for (i = 0; i < MAXLINE/2; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//bbbb\n
for (; i < MAXLINE; i++)
buf[i] = ch;
buf[i-1] = '\n';
ch++;
//aaaa\nbbbb\n
write(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
sleep(10);
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
The second part is the article link : Epoll Reactor model The core principle && Code explanation
边栏推荐
- Me11/me12 purchase information record and condition record creation and update bapi:me_ INFORECORD_ MAINTAIN_ MULTI
- aspects to consider for a recommendation letter
- SAP smartforms page feed printing automatic judgment
- Is it appropriate for a 27 - year-old girl to change her career from zero to software testing?
- The female programmer gives out a salary slip: the salary is high, but she feels she is 10 years old
- 腾讯测试开发岗面试上机编程题
- 浅析直播间海量聊天消息的架构设计难点
- MD61计划独立需求导入BAPI【按日维度/动态模板/动态字段】
- Web watermark
- [untitled]
猜你喜欢

力扣刷题篇——哈希表

Sword finger offer II 095 Longest common subsequence dynamic programming

Oracle收集统计信息

The diligent is the laziest

环糊精金属有机骨架(β-CD-MOF)装载二巯丁二酸/大黄素/槲皮素/三氯蔗糖/二氟尼柳/奥美拉唑(OME)

叶酸配体的金属有机骨架材料MOFs负载5-氟尿嘧啶,西达本胺,紫杉醇,阿霉素,柔红霉素,布洛芬,喜树碱,姜黄素,藤黄酸等小分子药物

The interviewer of Tencent said that who knows the internal module index principle and performance optimization idea of MySQL architecture?

查看Redis内数据,除了命令行和客户端,你还有第三种选择

adb 常用命令解析

Fb02 edit coding block field
随机推荐
CRS-5017
Tencent test development post interview programming questions
Talk about an annotation implementation interface retry
[3.delphi common components] 5 List class component
Orcale driver
The largest kth element in the array
The annual salary of testers in large factories ranges from 300000 to 8K a month. Roast complained that the salary was too low, but he was ridiculed by netizens?
Li Kou brushing questions - hash table
Record the actual record of my question brushing
贵金属白银和现货白银之间是什么关系
NFT insider 61:animoca brands holds US $1.5 billion of encrypted assets in 340 investments
Implementing queues with stacks
腾讯测试开发岗面试上机编程题
421. 数组中两个数的最大异或值
Oracle收集统计信息
QT database learning notes (I) basic concepts of database
Wechat automatic red envelope grabbing source code
[penetration test tool bee] how to install and use the XSS penetration test tool bee?
从测试零基础到测试架构师,这10年,他是这样让自己成才的
Me11/me12 purchase information record and condition record creation and update bapi:me_ INFORECORD_ MAINTAIN_ MULTI