当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode 96. Different binary search trees
Leetcode 96. Different binary search trees
2022-06-10 12:56:00 【Changersh】
96. Different binary search trees
Give you an integer n , Seek just by n Composed of nodes with node values from 1 To n Different from each other Binary search tree How many kinds? ? Returns the number of binary search trees satisfying the meaning of the question .
Example 1: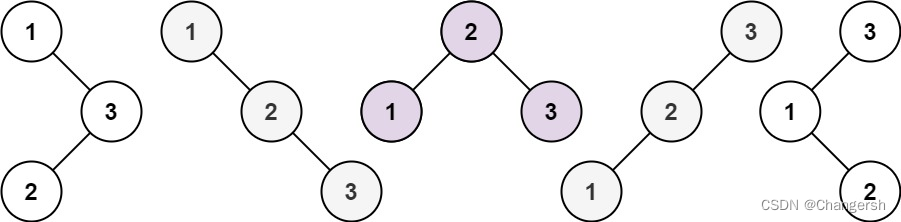
Input :n = 3
Output :5
Example 2:
Input :n = 1
Output :1
Tips :
1 <= n <= 19
Ideas
We can n = 1 2 3 All three cases are listed , Then we can find out :
n = 1 when , There is only one node , The value is 1, It can only form a binary search tree .
n = 2 when ,1 2 Sure 1 For the node , It's fine too 2 Root node , So there are two cases .
n = 3 when , This is the case in the above figure , There are five situations , It can be divided into three categories :
- 1 Root node : The rest are better than 1 Big , So the left subtree has 1 - 1 = 0 Nodes , Right subtree has 3 - 1 = 2 Nodes , Then the situation becomes two nodes of the right subtree , The left subtree has zero nodes . So the number of times = The left subtree 0 Number of types of nodes * Right subtree 2 Number of types of nodes
- 2 Root node : The left subtree 2 - 1 = 1 Nodes , Right subtree 3 - 2 = 1 Nodes , So the number of times = A node of the left subtree * A node of the right subtree
- 3 Root node : The left subtree 3 - 1 = 2 Nodes , Right subtree 3 - 3 = 0 Nodes , So the number of times = Two nodes of left subtree * A node of the right subtree
And we can also know , Whether the left subtree or the right subtree, the number of types of corresponding nodes is equal to dp[i] Value .
therefore dp[3] = dp[2] * dp[0] + dp[1] * dp[1] + dp[0] * dp[2];
For the first i Nodes , Consider starting from 1 To i As the root node , So you need to add up
Is the total i Nodes , For the root node j , here , Zuo Zi Shu you j - 1 Nodes , Right subtree has i - j Nodes
Code
class Solution {
public:
int numTrees(int n) {
int dp[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) dp[i] = 0;
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
dp[i] += dp[i - j] * dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
/* // For the first i Nodes , You need to consider 1 As the root node until i As the root node , So you need to add up // altogether i Nodes , For the root node j when , The number of nodes in the left subtree is j-1, The number of nodes in the right subtree is i-j */
/* Elements 1 The number of search trees for the head node = Right subtree has 2 Number of search trees of elements * Zuo Zi Shu you 0 Number of search trees of elements Elements 2 The number of search trees for the head node = Right subtree has 1 Number of search trees of elements * Zuo Zi Shu you 1 Number of search trees of elements Elements 3 The number of search trees for the head node = Right subtree has 0 Number of search trees of elements * Zuo Zi Shu you 2 Number of search trees of elements Yes 2 The number of search trees per element is dp[2]. Yes 1 The number of search trees per element is dp[1]. Yes 0 The number of search trees per element is dp[0]. therefore dp[3] = dp[2] * dp[0] + dp[1] * dp[1] + dp[0] * dp[2] */
边栏推荐
- 微信web开发工具使用教程,公司开发web
- Office technical lecture: punctuation - Chinese - vertical
- [mobile robot] principle of wheel odometer
- 技术分享| 快对讲,全球对讲
- VDMA commissioning summary
- 编写程序,计算2/1+3/2+5/3+8/5.....的值。要求计算前n项之和,保留2位小数(该序列从第二项起,每一项的分子是前一项分子与分母的和,分母是前一项的分子)
- Give root password for maintenace (or press Control-D to continue): solution
- 使用unique快速删除重复元素
- 【抬杠C#】如何实现接口的base调用
- ASP.NET 利用ImageMap控件设计导航栏
猜你喜欢

C # balanced weight distribution

Give root password for maintenace (or press Control-D to continue): solution

Daniel recommended and hanged the interviewer

微信web开发工具使用教程,公司开发web

Unity3d uses URP rendering pipeline to realize ar shadow (shadow casting and transparent ground)

(1) Pretreatment summary

阿里云ECS服务器搭建Mysql数据库

蔚来:“拿捏”了数据,“扭捏”着未来

Stm32f407 learning notes (1) -exti interrupt event and NVIC register

VDO-SLAM: A Visual Dynamic Object-aware SLAM System 论文阅读
随机推荐
Which EDA design software should Altium Allegro pads choose
Use unique to quickly remove duplicate elements
文档提升计划第二期|OceanBase 邀您一起进行文档共建
FM4057S单节锂电池线性充电芯片的学习
【Golang】创建有配置参数的结构体时,可选参数应该怎么传?
使用unique快速删除重复元素
Gimp - free and open source image processing software with powerful functions, known as an excellent substitute for Photoshop
IQR箱线图
How can the team be dissolved...
Technology sharing | quick intercom, global intercom
Vdo-slam: a visual dynamic object aware slam system paper reading
PCB learning notes (2) -3d packaging related
用C语言创建基本的栈与队列
Mr developed by unity3d realizes model occlusion and transparent ground receiving shadow
KITTI 相关信息汇总
VDMA commissioning summary
Can qiniu open an account? Can qiniu directly open the security of securities companies on the app
Give root password for maintenace (or press Control-D to continue):解决方法
UML类图
MySQL service evolution