当前位置:网站首页>[hard ten treasures] - 2 [basic knowledge] characteristics of various topological structures of switching power supply
[hard ten treasures] - 2 [basic knowledge] characteristics of various topological structures of switching power supply
2022-07-01 04:46:00 【Siege lion and duck】
List of articles
- 1、 Basic terms
- 2、Buck step-down
- 3、Boost boost
- 4、Buck-Boost step-down - boost
- 5、Flyback Flyback
- 6、Forward Forward excitation
- 7、Two-Transistor Forward Dual transistor forward
- 8、Push-Pull push-pull
- 9、Half-Bridge Half bridge
- 10、Full-Bridge Full bridge
- 11、SEPIC Single ended primary inductive converter
- 12、C’uk(Slobodan C’uk Patents )
- 13、 Details of circuit operation
- 14、Buck- Step down regulator - Continuous conduction
- 15、Buck- Step down regulator - Critical conductivity
- 16、Buck- Step down regulator - Discontinuous conduction
- 17、Boost Boost regulator
- 18、 Transformer operation ( Including the role of primary inductance )
- 19、 Flyback transformer
- 20、Forward Forward converter transformer
- 21、 summary
- Return directory 【 Hard ten treasures 】
1、 Basic terms
Common basic topologies
■ Buck step-down
■ Boost boost
■ Buck-Boost step-down - boost
■ Flyback Flyback
■ Forward Forward excitation
■ Two-Transistor Forward Dual transistor forward
■ Push-Pull push-pull
■ Half Bridge Half bridge
■ Full Bridge Full bridge
■ SEPIC
■ C’uk
Basic pulse width modulation waveform
These topologies are related to switching circuits .
The basic pulse width modulation waveform is defined as follows :
2、Buck step-down

characteristic
■ Reduce the input to a lower voltage .
■ Probably the simplest circuit .
■ inductance / The capacitor filter filters out the square wave after the switch .
■ The output is always less than or equal to the input .
■ The input current is discontinuous ( Chopping ).
■ The output current is smooth
3、Boost boost

** characteristic **
■ Raise the input to a higher voltage .
■ Same as depressurization , But rearranged the inductance 、 Switches and diodes .
■ The output ratio is always greater than or equal to the input ( Ignore the forward voltage drop of the diode ).
■ Input current is smooth .
■ The output current is discontinuous ( Chopping ).
4、Buck-Boost step-down - boost

characteristic
■ inductance 、 Another arrangement of switches and diodes .
■ It combines the disadvantages of step-down and step-up circuits .
■ The input current is discontinuous ( Chopping ).
■ The output current is also discontinuous ( Chopping ).
■ The output is always opposite to the input ( Pay attention to the polarity of the capacitor ), However, the amplitude can be less than or greater than the input .
■ “ Flyback ” The converter is actually buck - Boost circuit isolation ( Transformer coupling ) form .
5、Flyback Flyback

characteristic
■ Such as reducing blood pressure - The boost circuit works the same , But the inductor has two windings , And as both transformer and inductor .
■ The output can be positive or negative , Determined by the polarity of the coil and diode .
■ The output voltage can be greater than or less than the input voltage , Determined by the turns ratio of the transformer .
■ This is the simplest of the isolated topologies
■ Multiple outputs can be obtained by adding secondary windings and circuits .
6、Forward Forward excitation

characteristic
■ Transformer coupling form of step-down circuit .
■ Discontinuous input current , Smooth output current .
■ Because of the transformer , The output can be greater or less than the input , It can be any polarity .
■ Multiple outputs can be obtained by adding secondary windings and circuits .
■ The transformer core must be demagnetized in each switching cycle . The common practice is to add a winding with the same number of turns as the primary winding .
■ The energy stored in the primary inductor during the switch on phase , During the switch off phase, it is released through another winding and diode .
7、Two-Transistor Forward Dual transistor forward

characteristic
■ Both switches work at the same time .
■ When the switch is off , The energy stored in the transformer reverses the polarity of the primary , Turn on the diode .
The main advantages :
■ The voltage on each switch will never exceed the input voltage .
■ There is no need to reset the winding track .
8、Push-Pull push-pull

characteristic
■ switch (FET) The driving phases are different , Pulse width modulation (PWM) To adjust the output voltage .
■ Good transformer core utilization — Power is transmitted in both half cycles .
■ Full wave topology , Therefore, the output ripple frequency is twice the frequency of the transformer .
■ Imposed on FET The voltage on the is twice the input voltage .
9、Half-Bridge Half bridge

characteristic
■ High power converters are very common topologies .
■ switch (FET) The driving phases are different , Pulse width modulation (PWM) To adjust the output voltage .
■ Good transformer core utilization — Power is transmitted in both half cycles . Moreover, the utilization rate of primary winding is better than that of push-pull circuit .
■ Full wave topology , Therefore, the output ripple frequency is twice the frequency of the transformer .
■ Imposed on FET The voltage on the is equal to the input voltage .
10、Full-Bridge Full bridge

characteristic
■ Higher power converters are the most commonly used topology .
■ switch (FET) Drive in the form of diagonal pairs , Pulse width modulation (PWM) To adjust the output voltage .
■ Good transformer core utilization — Power is transmitted in both half cycles .
■ Full wave topology , Therefore, the output ripple frequency is twice the frequency of the transformer .
■ Imposed on FETs The voltage on the is equal to the input voltage .
■ At a given power , The primary current is half that of the half bridge .
11、SEPIC Single ended primary inductive converter

characteristic
■ The output voltage can be greater than or less than the input voltage .
■ Same as boost circuit , Input current is smooth , But the output current is discontinuous .
■ Energy is transferred from the input to the output through a capacitor .
■ Need two inductors .
12、C’uk(Slobodan C’uk Patents )
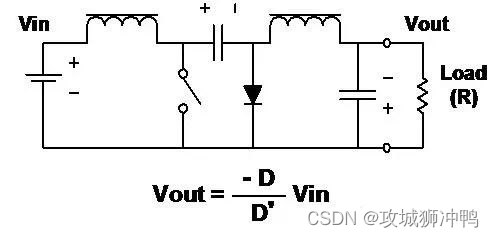
characteristic
■ Output inverting
■ The amplitude of the output voltage can be greater or less than the input voltage .
■ The input current and output current are smooth .
■ Energy is transferred from the input to the output through a capacitor .
■ Need two inductors .
■ Inductors can be coupled to obtain zero ripple inductor current .
13、 Details of circuit operation
The following explains the working details of several topologies
■ Step down regulator :
Continuous conduction
Critical conductivity
Discontinuous conduction
■ Boost regulator ( Continuous conduction )
Transformer operation
Flyback transformer
Forward transformer
14、Buck- Step down regulator - Continuous conduction

characteristic
■ The inductive current is continuous .
■ Vout Is its input voltage (V1) The average of .
■ The output voltage is the input voltage multiplied by the load ratio of the switch (D).
■ On , Inductive current flows out of the battery .
■ When the switch is off, current flows through the diode .
■ Ignore losses in switches and inductors , D Independent of load current .
The characteristics of the step-down regulator and its derived circuit are :
■ The input current is discontinuous ( Chopping ), The output current is continuous ( smooth ).
15、Buck- Step down regulator - Critical conductivity

■ The inductive current is still continuous , Only when the switch is turned on again “ achieve ” zero .
This is known as “ Critical conductivity ”.
The output voltage is still equal to the input voltage multiplied by D.
16、Buck- Step down regulator - Discontinuous conduction

■ under these circumstances , The current in the inductor is zero for a period of time in each cycle .
■ The output voltage remains ( Throughout ) yes v1 Average value .
■ The output voltage is not the input voltage multiplied by the load ratio of the switch (D).
■ When the load current is below the critical value ,D Varies with load current ( and Vout remain unchanged ).
17、Boost Boost regulator

■ The output voltage is always greater than ( Or equal to ) Input voltage .
■ The input current is continuous , The output current is discontinuous ( As opposed to the step-down regulator ).
■ Output voltage to load ratio (D) The relationship is not as simple as in the step-down regulator . In the case of continuous conduction :
V o = V i n ( 1 1 − D ) Vo =Vin ( \frac {1} {1-D}) Vo=Vin(1−D1)
In this case ,Vin = 5,Vout = 15,and D = 2/3,Vout = 15,D = 2/3.
18、 Transformer operation ( Including the role of primary inductance )

■ The transformer is regarded as an ideal transformer , Its primary ( magnetization ) The inductor is connected in parallel with the primary .
19、 Flyback transformer

■ The primary inductance here is very low , Used to determine peak current and stored energy . When the primary switch is off , Energy is transferred to the secondary .
20、Forward Forward converter transformer

■ The primary inductance is very high , Because there is no need to store energy .
■ Magnetizing current (i1) inflows “ Magnetizing inductance ”, Demagnetize the magnetic core after the primary switch is disconnected ( The voltage is reversed ).
21、 summary
■ The most common circuit topologies in switching mode power supply conversion are reviewed here .
■ There are also many topologies , But most of them are combinations or deformations of the topologies described here .
■ Each topology contains unique design tradeoffs :
The voltage applied to the switch
Chopping and smoothing input and output current
Utilization of windings
■ Choosing the best topology requires research :
Input and output voltage range
Current range
Cost and performance 、 The ratio of size to weight
Return directory 【 Hard ten treasures 】
边栏推荐
- Pytorch(四) —— 可视化工具 Visdom
- 数据加载及预处理
- Dede collection plug-in does not need to write rules
- 扩展-Fragment
- Common UNIX Operation and maintenance commands of shell
- Leecode records the number of good segmentation of 1525 strings
- Basic exercise of test questions hexadecimal to decimal
- 科研狗可能需要的一些工具
- RuntimeError: “max_pool2d“ not implemented for ‘Long‘
- Leecode question brushing record 1310 subarray XOR query
猜你喜欢

2022 polymerization process test questions and simulation test

2022 Shanghai safety officer C certificate examination question simulation examination question bank and answers
STM32扩展板 数码管显示

【硬十宝典】——1.【基础知识】电源的分类

Extension fragment
2022 tea master (intermediate) examination question bank and tea master (intermediate) examination questions and analysis

Question bank and online simulation examination for special operation certificate of G1 industrial boiler stoker in 2022

CF1638E. Colorful operations Kodori tree + differential tree array

Software testing needs more and more talents. Why do you still not want to take this path?

The index is invalid
随机推荐
Seven crimes of counting software R & D Efficiency
One click shell to automatically deploy any version of redis
Caijing 365 stock internal reference | the first IPO of Beijing stock exchange; the subsidiary of the recommended securities firm for gambling and gambling, with a 40% discount
Pytest automated testing - compare robotframework framework
LM小型可编程控制器软件(基于CoDeSys)笔记十九:报错does not match the profile of the target
2022 G2 power station boiler stoker examination question bank and G2 power station boiler stoker simulation examination question bank
LeetCode_28(实现 strStr())
Announcement on the list of Guangdong famous high-tech products to be selected in 2021
【硬十宝典目录】——转载自“硬件十万个为什么”(持续更新中~~)
LeetCode_ 58 (length of last word)
Pytorch convolution operation
Tencent has five years of testing experience. It came to the interview to ask for 30K, and saw the so-called software testing ceiling
科研狗可能需要的一些工具
STM32扩展板 温度传感器和温湿度传感器的使用
[FTP] the solution to "227 entering passive mode" during FTP connection
最长递增子序列及最优解、动物总重量问题
VIM easy to use tutorial
Kodori tree board
数据加载及预处理
【硬十宝典】——2.【基础知识】开关电源各种拓扑结构的特点