当前位置:网站首页>Pytoch (I) -- basic grammar
Pytoch (I) -- basic grammar
2022-07-01 04:46:00 【CyrusMay】
Pytorch( One ) —— Basic grammar
- 1. Basic data type
- 2 Tensor Common operations for creating
- 2.1 Judge whether there are available for this machine GPU resources
- 2.2 CPU Type data to GPU Type data
- 2.3 obtain Tensor The shape of the
- 2.4 take numpy Format data into Tensor Format
- 2.4 take List Format data into Tensor Format
- 2.5 Create uninitialized Tensor
- 2.6 Set up Tensor The default format for
- 2.7 Create uniform distribution and pure integer Tensor
- 2.8 Create a normal distribution Tensor
- 2.9 Create elements that are all the same Tensor
- 2.10 torch.arange()
- 2.10 torch.linespace()
- 2.10 torch.logspace()
- 2.11 torch.ones / .zeros / eye
- 2.12 Break up randomly
- 3. Index and slice
- 4. Dimensional transformation
- 5 Tensor The merger and split of
- 6. Mathematical operations
- 7. Tensor Statistical calculation of
- 8. where and gather function
1. Basic data type
1.1 torch.FloatTensor And torch.cuda.FloatTensor
- torch.FloatTensor by CPU Data type on
- torch.cuda.FloatTensor by GPU Data type on

1.2 torch.DoubleTensor And torch.cuda.DoubleTensor

1.3 torch.IntTensor And torch.cuda.IntTensor

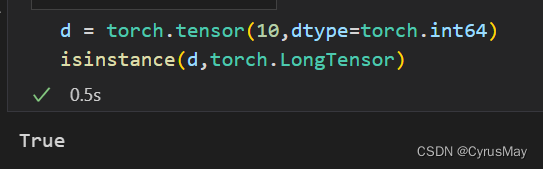
1.4 torch.LongTensor And torch.cuda.LongTensor
1.5 torch.BoolTensor And torch.cuda.BoolTensor

2 Tensor Common operations for creating
2.1 Judge whether there are available for this machine GPU resources

2.2 CPU Type data to GPU Type data
- Using data .cuda() Method

2.3 obtain Tensor The shape of the
- Use .shape attribute
- Use .size() Method

2.4 take numpy Format data into Tensor Format

2.4 take List Format data into Tensor Format

2.5 Create uninitialized Tensor
- torch.empty()
- torch.FloatTensor(d1,d2,d3)

2.6 Set up Tensor The default format for
- torch.set_default_tensor_type

2.7 Create uniform distribution and pure integer Tensor
- Uniform distribution :torch.rand() / torch.rand_like()
- Pure integers : torch.randint() / torch.randint_like()

2.8 Create a normal distribution Tensor
- torch.randn()
- torch.normal()


2.9 Create elements that are all the same Tensor
- torch.full()

2.10 torch.arange()

2.10 torch.linespace()

2.10 torch.logspace()
- Create a log even 1 dimension Tensor

2.11 torch.ones / .zeros / eye

2.12 Break up randomly
- torch.randperm Randomly disrupt a sequence of numbers

3. Index and slice
3.1 Index the specified dimension
- Tensor.index_select()

3.2 Use … Index

3.3 Use masked_select Index
- torch.masked_select()
- Tensor.ge() Whether it is greater than a certain value

4. Dimensional transformation
4.1 torch.view() / reshape()
- torch.view() Show us the data in some sort of arrangement , Do not change the real data in the storage area , Just change the header area , Data storage is not continuous and cannot be used view() Methodical .
- torch.reshape(), When tensor When continuity requirements are met ,reshape() = view(), And original tensor Shared storage When tensor; When the continuity requirements are not met ,reshape() = **contiguous() + view(), A new storage area will be generated tensor, With the original tensor Do not share storage .


4.2 Add a dimension torch.unsqueeze()

4.3 Reduce one dimension torch.squeeze()

4.4 broadcasting: Use expand Method
- The function will not allocate new memory for the returned tensor , That is, return the read-only view on the original tensor , The returned tensor memory is discontinuous

4.4 Memory copy : Use repeat Method
- And torch.expand The difference is torch.repeat The returned tensor is continuous in memory

4.5 Dimension exchange and transpose : Use transpose and permute Method
- .t() Transpose for a two-dimensional matrix
- .transpose() Exchange the order of any two dimensions
- .permute() Any exchange dimension order

5 Tensor The merger and split of
5.1 Merge
- torch.cat() Merge on existing dimensions
- torch.stack() Create a new dimension and merge
a = torch.randn(4,28,64)
b = torch.randn(4,28,64)
print(torch.cat([a,b],dim=0).size())
print(torch.stack([a,b],dim=0).size())
torch.Size([8, 28, 64])
torch.Size([2, 4, 28, 64])
5.2 Split
- torch.split() Split according to the given length
- torch.chunk() Split according to the given number of copies
a = torch.rand(9,28,28)
print([i.size() for i in a.split([4,5],dim=0)])
print([i.size() for i in a.chunk(2,dim=0)])
[torch.Size([4, 28, 28]), torch.Size([5, 28, 28])]
[torch.Size([5, 28, 28]), torch.Size([4, 28, 28])]
6. Mathematical operations
6.1 Basic operation
- +、-、*、/
a = torch.rand(64,128)
b = torch.rand(128)
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a+b,torch.add(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a-b,torch.sub(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a/b,torch.div(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a*b,torch.mul(a,b))))
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
6.2 Matrix operations
- torch.mm() Applicable to two-dimensional tensor Matrix multiplication between
- torch.matmul() Applicable to 2D and larger tensor Matrix multiplication between
- @ And .matmul() The usage of the method is the same
x = torch.rand(100,32)
w = torch.rand(32,64)
print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
print(([email protected]).size())
torch.Size([100, 64])
torch.Size([100, 64])
torch.Size([100, 64])
x = torch.rand(128,64,100,32)
w = torch.rand(32,64)
print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
print(([email protected]).size())
print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
torch.Size([128, 64, 100, 64])
torch.Size([128, 64, 100, 64])
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-15-df2761074153> in <module>
3 print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
4 print(([email protected]).size())
----> 5 print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
RuntimeError: self must be a matrix
6.3 Power operation
- .pow() Power operation
- .sqrt() Open root operation
- .rsqrt() Open root and then find reciprocal operation
a = torch.full([3,3],3.)
print(a)
print(a.pow(2))
print(a.sqrt())
print((a**2).rsqrt())
tensor([[3., 3., 3.],
[3., 3., 3.],
[3., 3., 3.]])
tensor([[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.]])
tensor([[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321],
[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321],
[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321]])
tensor([[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333]])
6.4 Exponential and logarithmic operations
- torch.exp()
- torch.log()
a = torch.exp(torch.full([2,2],3.))
print(a)
print(torch.log(a))
## With 3 Base logarithm operation
print(torch.log(a)/torch.log(torch.tensor(3.)))
tensor([[20.0855, 20.0855],
[20.0855, 20.0855]])
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[2.7307, 2.7307],
[2.7307, 2.7307]])
6.5 Approximate calculation
- torch.floor() Rounding down
- torch.ceil() Rounding up
- torch.round() rounding
- torch.trunc() Take the whole part
- torch.frac() Take out the decimal part
a = torch.tensor(3.14)
b = torch.tensor(3.54)
print(a.floor())
print(a.ceil())
print(a.round())
print(b.round())
print(a.trunc())
print(a.frac())
tensor(3.)
tensor(4.)
tensor(3.)
tensor(4.)
tensor(3.)
tensor(0.1400)
6.6 Gradient clipping calculation
- torch.clamp()
| min, if x_i < min
y_i = | x_i, if min <= x_i <= max
| max, if x_i > max
grad = torch.rand(3,3)*30
print(grad)
print(grad.clamp(0,10))
tensor([[ 0.5450, 3.1299, 0.0786],
[22.1880, 27.4744, 2.3748],
[10.4793, 5.7453, 20.6413]])
tensor([[ 0.5450, 3.1299, 0.0786],
[10.0000, 10.0000, 2.3748],
[10.0000, 5.7453, 10.0000]])
7. Tensor Statistical calculation of
7.1 Norm calculation
- Tensor.norm§ Conduct p Norm calculation
a = torch.randn(8)
b = a.view(2,4)
c = a.view(2,2,2)
print(a.norm(1),b.norm(1),c.norm(1))
print(a.norm(2),b.norm(2),c.norm(2))
print(b.norm(2,dim=1))
print(c.norm(2,dim=0))
tensor(5.4647) tensor(5.4647) tensor(5.4647)
tensor(2.1229) tensor(2.1229) tensor(2.1229)
tensor([1.6208, 1.3711])
tensor([[1.1313, 0.8043],
[1.2935, 0.9523]])
7.2 Calculation of statistical indicators
- Tensor.sum() Sum up
- Tensor.min() / .max() Find the minimum and maximum
- Tensor.argmin() / .Tensor.argmax() Find the index corresponding to the minimum or maximum value
- Tensor,prod() Find the result of cumulative multiplication
- Tensor.mean() Find the mean
- It can be done to keepdim Keyword assignment , To determine whether the calculation result should maintain the original dimension
a = torch.rand(3,4)
print(a)
print(a.mean(),a.max(),a.min(),a.prod())
print(a.argmax(),a.argmin())
print(a.argmin(dim=1))
print(a.argmin(dim=1,keepdim=True))
tensor([[0.7824, 0.4527, 0.4538, 0.6727],
[0.2269, 0.9950, 0.9010, 0.2681],
[0.3563, 0.2929, 0.5285, 0.6461]])
tensor(0.5480) tensor(0.9950) tensor(0.2269) tensor(0.0002)
tensor(5) tensor(4)
tensor([1, 0, 1])
tensor([[1],
[0],
[1]])
7.3 Before calculation k Value or number k Small value
- Tensor.topk() Before calculation k Minimum or maximum values
- Tensor.kthvalue() Back to page k Small value
a = torch.rand(3,4)
print(a)
print(a.topk(2,dim=0,largest=True))
print(a.kthvalue(3,dim=0))
tensor([[0.9367, 0.3146, 0.6258, 0.2656],
[0.8911, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946],
[0.4879, 0.5836, 0.0198, 0.2136]])
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[0.9367, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946],
[0.8911, 0.5836, 0.6258, 0.2656]]),
indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 0, 0]]))
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.9367, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946]),
indices=tensor([0, 1, 1, 1]))
8. where and gather function
8.1 torch.where()
torch.where(condition,a,b) -> Tensor
Return... If conditions are met a, Otherwise return to b
condition = torch.rand(2,2)
a = torch.full([2,2],1)
b = torch.full([2,2],0)
print(condition)
print(a)
print(b)
print(torch.where(condition>= 0.5,a,b))
tensor([[0.5827, 0.1495],
[0.8753, 0.6246]])
tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 1]])
tensor([[0, 0],
[0, 0]])
tensor([[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
8.1 torch.gather()
- Used for table lookup
- torch.gather(input,dim,index)
- Query by index for the specified dimension
- index In addition to specifying the size of the dimension and input It can be inconsistent , Others shall be consistent
prob = torch.rand(5,10)
index = prob.topk(3,dim=1,largest=True)[1]
print(index)
table = torch.arange(150,160).expand(5,10)
print(table)
print(torch.gather(table,dim=1,index=index))
tensor([[8, 7, 3],
[2, 0, 1],
[4, 3, 2],
[8, 4, 0],
[0, 6, 1]])
tensor([[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159]])
tensor([[158, 157, 153],
[152, 150, 151],
[154, 153, 152],
[158, 154, 150],
[150, 156, 151]])
by CyrusMay 2022 06 28
Most profound The story of Most eternal The legend of
however It's you Is my can Ordinary life
—————— May day ( Because of you So I )——————
边栏推荐
- LM小型可编程控制器软件(基于CoDeSys)笔记二十:plc通过驱动器控制步进电机
- 2022 tea master (intermediate) examination question bank and tea master (intermediate) examination questions and analysis
- Pytorch(三) —— 函数优化
- CF1638E. Colorful operations Kodori tree + differential tree array
- 2022 a special equipment related management (elevator) simulation test and a special equipment related management (elevator) certificate examination
- Thoughts on the construction of Meizhou cell room
- Shell之分析服务器日志命令集锦
- LeetCode_35(搜索插入位置)
- LM small programmable controller software (based on CoDeSys) note 19: errors do not match the profile of the target
- Registration for R2 mobile pressure vessel filling test in 2022 and R2 mobile pressure vessel filling free test questions
猜你喜欢

Dual Contrastive Learning: Text Classification via Label-Aware Data Augmentation 阅读笔记

Section 27 remote access virtual private network workflow and experimental demonstration

分布式架构系统拆分原则、需求、微服务拆分步骤

Sorting out 49 reports of knowledge map industry conference | AI sees the future with wisdom

OdeInt與GPU

2022 question bank and answers for safety production management personnel of hazardous chemical production units

Pytorch(三) —— 函数优化

解决:拖动xib控件到代码文件中,报错setValue:forUndefinedKey:this class is not key value coding-compliant for the key

How to use common datasets in pytorch

OdeInt与GPU
随机推荐
无器械健身
Ten wastes of software research and development: the other side of research and development efficiency
CF1638E. Colorful operations Kodori tree + differential tree array
Simple implementation of slf4j
分布式架构系统拆分原则、需求、微服务拆分步骤
2022-02-15 (399. Division evaluation)
Difficulties in the development of knowledge map & the importance of building industry knowledge map
STM32扩展板 温度传感器和温湿度传感器的使用
js解决浮点数相乘精度丢失问题
Pytorch convolution operation
[ue4] event distribution mechanism of reflective event distributor and active call event mechanism
Dede collection plug-in does not need to write rules
LeetCode_28(实现 strStr())
Leecode records the number of good segmentation of 1525 strings
C read / write application configuration file app exe. Config and display it on the interface
Dual contractual learning: text classification via label aware data augmentation reading notes
STM32 extended key scan
STM32扩展板 数码管显示
LeetCode_35(搜索插入位置)
STM32 光敏电阻传感器&两路AD采集