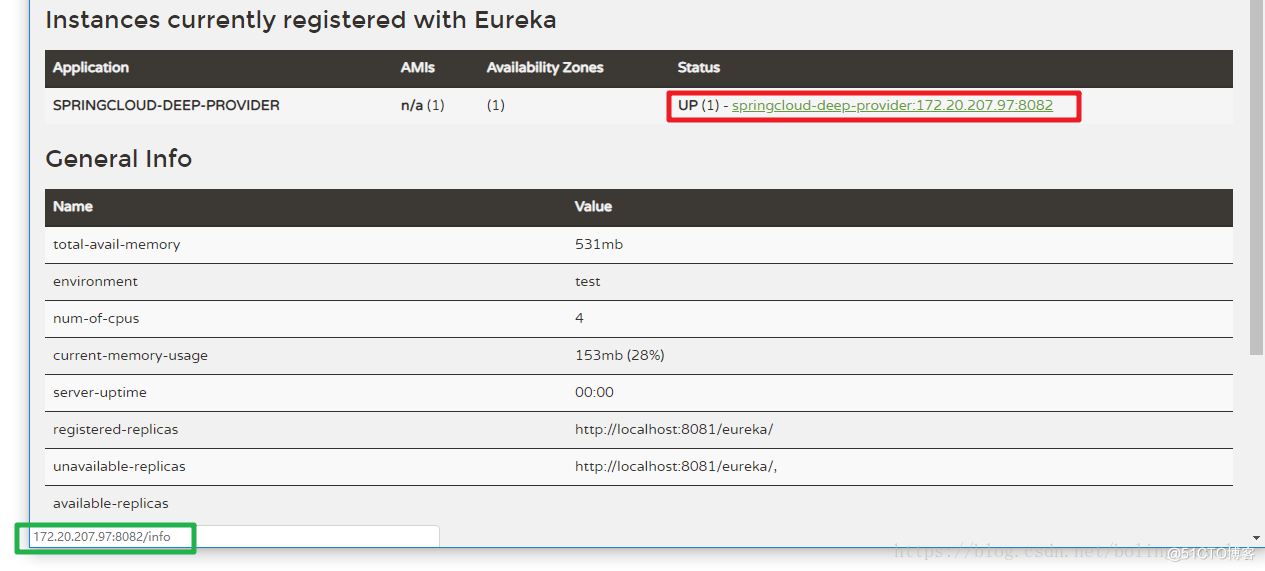
summary
OpenAPI 3.0 Specification by 8 Root objects :
- openapi
- info
- servers
- paths
- components
- security
- tags
- externalDocs
OpenAPI The rest of our functionality is based on this 8 The root object is extended , If it contains the above objects and the extension is json,yaml The file of , We can regard it as conforming to OpenAPI Specification description file , You can :API Editor Online editor To verify your OpenAPI Whether the document meets the specification , Here we will mainly introduce 8 How to use and extend root objects
openapi object
openapi Is the simplest and most basic attribute , We are OpenAPI Add the first root object attribute , Specify the version of the specification to use :
openapi: "3.0.2"
Then continue to add information
openapi: "3.0.2"
info:
title: openAPI Demo
version: '1.0'
paths: {}
A minimalist OpenAPI The document was born , It is displayed as follows :

- It's gray 1.0 I mean you server Version of
- OAS3 It refers to the OpenAPI Version of the specification
info object
The root node of the info The object mainly contains the following information :
- title: title
- description: API describe
- version: Version number
- license: License information
- contact: Contact information
- terms of service: Terms of service
Here are info Examples of objects and attributes :
openapi: "3.0.2"
info:
title: openAPI Demo
description: "This is an API program for teaching"
version: '1.1'
termsOfService: "https://openweathermap.org/terms"
contact:
name: "api developer"
url: "http://myblog.cn"
email: "[email protected]"
license:
name: "Apache 2.0"
url: "http://springdoc.org"
paths: {}
The preview effect of the above content is as follows :

If you feel description Too simple , It also supports Markdown Syntax display , The effect is as follows :

As agreed description The following information should be presented to the user :
- Describe the whole API And how to use it
- Provide users with test accounts and data
- Any other information that users need can be provided through it
servers object
servers It mainly refers to the basic path to access the server , This parameter will be carried before accessing the interface , Examples are as follows :
servers:
- url: 'http://localhost:8080/webapi'

servers Object supports multi parameter configuration , You can specify multiple servers ( Development , test , Generation, etc ) Of URL, From the drop-down box, the user can select a server that is not used URL Initiate request , The configuration and preview effects are as follows :
servers:
- url: https://localhost:8080/webapi
description: develop server
- url: http://test-server:8080/webapi
description: test server
- url: http://product-server:8080/webapi
description: product server

paths object
paths Object contains the real API information content , Each of its items contains an actionable endpoint Action object , Each operation object contains our common GET/POST/PUT/DELETE Other methods , Take a simple example :
paths:
/pet:
get:
The above information describes a /pet Of endpoint , It contains only one get Action object , similar get Action object ( Also known as Operation Objects) It also contains the following properties :
tags: Used to deal with endpoint Group name to groupsummary: Summary information of the operation object , It's better to limit it to 5-10 Within words , It is mainly presented as an overviewdescription: Description of the operation object , Be as detailed as possible , Show detailsoperationId: Unique of the operation object IDparameters: The request parameter object of the endpoint , Described below ,(requestBodyDescription does not include the family genus in this column )- name: Parameter name
- in: Where the parameter appears , Usually
header,path,query,cookie - description: Description of parameters ( Support markdown)
- required: mandatory
- deprecated: Whether to discard
- allowEmptyValue: Allow null values to be submitted
- style: Parameter serialization mode
- explode: Array related parameters
- schema: Parameter model
- example: Examples of media types
requestBody: Description of the request body , It can also contain a point tocomponentsOf$refThe pointerresponse: Description of the response body , Standard... Is usually used HTTP Status code , Can contain points tocomponentsOf$refThe pointercallbacks: Description of callback object and callback information , Rare , But more about itdeprecated: Identify thepathWhether it has been abandonedsecurity: Only used to override the global security authorization methodservers: Only used to override the global server access object
In most cases, you don't need to declare so many attributes , Here is an endpoint of operation object Common descriptive information , as follows :
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
summary:
description:
operationId:
externalDocs:
parameters:
responses:
parameters object
parameters Example usage of ( Containing a parameter get Method ):
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "Call current weather data for one location."
description: "^_^"
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- name: q
in: query
description: "^_^"
schema:
type: string
responses object
responses Response object used to describe the interface , Can directly describe , as follows :
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
title: Sample
type: object
properties:
placeholder:
type: string
description: Placeholder description
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
You can Swagger UI See the following example effect in :

components object
stay components You can mainly define reusable objects in , For other objects to use $ref Keyword direct reference and declaration
stay parameters Reuse objects in
We can put just now to parameters The description of moves to components In the to , as follows :
components:
parameters:
q:
name: q
in: query
description: "………………"
schema:
type: string
id:
name: id
in: query
description: "…………"
schema:
type: string
lat:
name: lat
in: query
description: "………………"
schema:
type: string
Then we can go to paramters It's directly quoted in , as follows :
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "………………"
description: "………………."
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/q'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/id'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lat'
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
title: Sample
type: object
properties:
placeholder:
type: string
description: Placeholder description
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
Above , Make good use of components Component reuse can be achieved + The effect of reducing space
stay reponses Reuse objects in
We can also go straight in reponses Reference the declared object in , as follows :
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/200'
It's in yaml The description in is as follows :
components:
schemas:
200:
title: Successful response
type: object
properties:
base:
type: string
description: Internal parameter
example: cmc stations
visibility:
type: integer
description: Visibility, meter
example: 16093
dt:
type: integer
description: Time of data calculation, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435658272
id:
type: integer
description: City ID
format: int32
example: 2172797
name:
type: string
example: Cairns
cod:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 200
It's in Swagger UI The display effect is as follows :
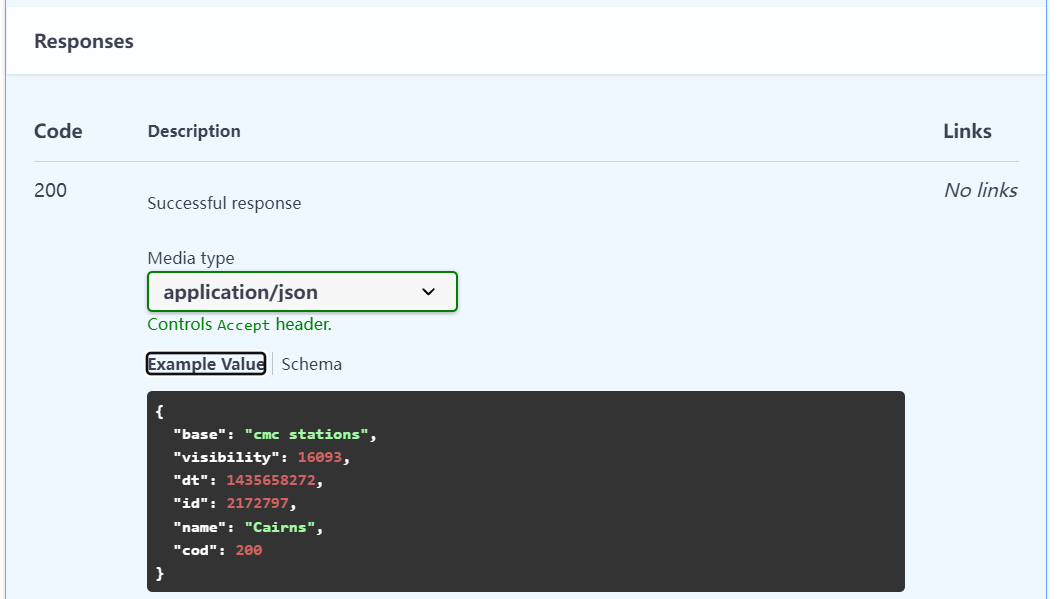
stay schemas Show in
adopt components The defined objects will be in Swagger UI Down through Schemas To display , as follows :

security object
Except in part Demo Show exceptions , Most of Web Services can only be accessed through identity authentication ,security It's used to describe API Security information and access authorization protocol ,OpenAPI Support the four most common authorization schemes , as follows :
- API key
- HTTP
- OAuth 2.0
- Open ID Connect
Here we use the most common API Key As a demonstration , stay OpenAPI Add security objects to the root directory of the document :
security:
- app_id: []
So all paths will use security Description of the app_id Safety method , But usually in components Add security object , Such description information will be more detailed , as follows :
components:
...
securitySchemes:
app_id:
type: apiKey
description: API key to authorize requests.
name: appid
in: query
security Property content of the object :
- type: License agreement , Enumeration values are :
apiKey、http、oauth2、openIdConnect - description: Description of the safety method , Be as detailed as possible , Contains usage examples
- name: Security key
apiKeystay HTTP Header Name in request - in: Security key
apiKeystay HTTP Location in transmission , Enumeration values are :query,header,cookie - …………
After adding the above description ,Swagger UI Any safety related signs will be displayed , as follows :

Click on Authorize More security information will be displayed :

When you are in Value When entering your access key ,Swagger Will be visiting API When , Access your... According to your settings API, as follows :

tags object
This object is mainly for OpenAPI Multiple access paths in the , So as to have a more comprehensive view API Information , An example is as follows :
We add... For a request path tags Information :
paths:
/pets:
get:
summary: List all pets
operationId: listPets
tags:
- pets
This indicates that the request path belongs to pets grouping , Then we add... At the root level tags attribute , To describe the grouping information :
tags:
- name: pets
description: "Chimelong Animal Happy World"
And then let's see Swagger UI For the presentation of grouping information , as follows :

externalDocs object
This object is not commonly used , Mainly add references to external documents , To supplement the current document , For example, you can add this attribute to the root directory , as follows :
externalDocs:
description: externalDocs API Documentation
url: https://openweathermap.org/api
It will be in you Swagger A link address is shown in the description of , as follows :

You can also API In the request path of , Add a description of an external reference , as follows :
paths:
/pets:
get:
summary: List all pets
externalDocs:
description: externalDocs API Documentation
url: https://openweathermap.org/api
Swagger UI In the description of the request path , Add an external link as a supplement to the description , as follows :

summary
The above is a complete OpenAPI Instructions for use of normative documents
Reference material :
- OpenAPI tutorial using Swagger Editor and Swagger UI: Overview OpenAPI Good tutorial
- OpenApi Openweathermap Example File complete OpenAPI Specification documents
- Swagger Editor Swagger Online editing provided OpenAPI File tools


![[JS] free API to judge holidays, working days, Saturdays and Sundays](/img/e1/8b742082385bb5e60f74beb3b81c7d.png)