当前位置:网站首页>- heavy OpenCV 】 【 mapping
- heavy OpenCV 】 【 mapping
2022-08-04 01:04:00 【I love to learn】
1、重映射的概念
重映射是把一幅图像中某位置的像素放置到另一个图片指定位置的过程.In order to complete the heavy mapping process,需要获得一些插值为非整数像素的坐标,Because the source image and the target image pixel coordinates is not one-to-one.如下:
g ( x , y ) = f ( h ( x , y ) ) g(x,y)=f(h(x,y)) g(x,y)=f(h(x,y))
g()是目标图像,f()是源图像,而h(x,y)是作用于(x,y)的映射方法函数.
2、实现重映射:remap()函数
remap()函数会根据指定的映射形式,将源图像进行重映射几何变换:
d s t ( x , y ) = s r c ( m a p x ( x , y ) , m a p y ( x , y ) ) dst(x,y)=src(mapx(x,y),mapy(x,y)) dst(x,y)=src(mapx(x,y),mapy(x,y))
void remap(InputArray src,OutputArray dst,InputArray map1,InputArray map2,int interpolation,intborderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT,const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
- 第一个参数:输出图像
- 第二个参数:函数调用后的运算结果存在这里,即这个参数用于存放函数调用后的输出结果,需和源图片有一样的尺寸和类型
- 第三个参数:InputArray类型的 map1,有两种可能的表示对象
- 表示点(x,y)The first mapping
- 表示CV_16SC2,CV_32FC1,CV_32FC2类型的X值
- 第四个参数:InputArray类型的 map2,有两种可能的表示对象
- 若map1表示点(x,y)时,这个参数不代表任何值
- 表示CV_16UC1,CV_32FC1类型的Y值
- 第五个参数:int 类型的interpolation,插值方式,The selected interpolation method is as follows:
- INTER_NEAREST——最近邻插值
- INTER_LINEAR——双线性插值(默认值)
- INTER_CUBIC——双三次样条插值
- INTER_LANCZOS4——Lanczos插值
- 第六个参数:边界模式
- 第七个参数:const Scalar&类型的borderValue,When there is a constant boundary value used,其默认值Scalar(),即默认值为0
3、基本重映射
说明:The following is streamlined toremapFunction as the core of the sample program
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat srcImage, dstImage;
Mat map_x, map_y;
//载入原始图像
srcImage = imread("E:\\Pec\\car.jpg", 1);
imshow("【原始图】", srcImage);
//创建和原始图一样的效果图,x重映射图,y重映射图
dstImage.create(srcImage.size(), srcImage.type());
map_x.create(srcImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
map_y.create(srcImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
//双层循环,遍历每一个像素点,改变map_x和Map_y
for (int j = 0; j < srcImage.rows; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < srcImage.cols; i++)
{
//通过at获取像素值
map_x.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(i);
map_y.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(srcImage.rows-j);
}
}
//进行重映射
remap(srcImage, dstImage, map_x, map_y, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
imshow("【效果图】", dstImage);
waitKey(0);
}

4、To realize the multiple mapping
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
#define WINDOW_NAME "【程序窗口】"
Mat g_srcImage, g_dstImage;
Mat g_map_x, g_map_y;
int update_map(int key);
static void ShowHelpText();
int main()
{
system("color 2F");
ShowHelpText();
//载入原始图像
g_srcImage = imread("E:\\Pec\\car.jpg", 1);
imshow("【原始图】", g_srcImage);
//创建和原始图一样的效果图,x重映射图,y重映射图
g_dstImage.create(g_srcImage.size(), g_srcImage.type());
g_map_x.create(g_srcImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
g_map_y.create(g_srcImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
namedWindow(WINDOW_NAME, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(WINDOW_NAME, g_srcImage);
while (1)
{
int key = waitKey(0);
if ((key & 255) == 27)
{
cout << "程序退出......" << endl;
break;
}
update_map(key);
//According to press the keyboard keys to updatemap_x & map_y的值,然后调用remap()进行重映射
remap(g_srcImage, g_dstImage, g_map_x, g_map_y, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
imshow(WINDOW_NAME, g_dstImage);
}
return 0;
}
int update_map(int key)
{
//双层循环,遍历每一个像素点,改变map_x和Map_y
for (int j = 0; j < g_srcImage.rows; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < g_srcImage.cols; i++)
{
switch (key)
{
case '1'://按键1按下,For the first mapping operation
if (i > g_srcImage.cols*0.25&&i<g_srcImage.cols*0.75&&j>g_srcImage.rows*0.25&&j < g_srcImage.rows*0.75)
{
g_map_x.at<float>(j, i) = 2 * (i - g_srcImage.cols*0.25) + 0.5;
g_map_y.at<float>(j, i) = 2 * (j - g_srcImage.rows*0.25) + 0.5;
}
else
{
g_map_x.at<float>(j, i) = 0;
g_map_y.at<float>(j, i) = 0;
}
break;
case '2': //按键2按下,For the second mapping operation
g_map_x.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(i);
g_map_y.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(g_srcImage.rows - j);
break;
case '3':
g_map_x.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(g_srcImage.cols-i);
g_map_y.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(j);
break;
case '4':
g_map_x.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(g_srcImage.cols - i);
g_map_y.at<float>(j, i) = static_cast<float>(g_srcImage.rows - j);
break;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
static void ShowHelpText()
{
cout << "\n\n\n\t欢迎来到重映射示例程序\n";
cout << "\n\n\n\tKeystrokes as follows:" ;
cout << "\n\n\n\t键盘按下【ESC】-退出程序" ;
cout << "\n\n\n\t键盘按下【1】-第一种映射方式,缩小2倍" ;
cout << "\n\n\n\t键盘按下【2】-第二种映射方式,y方向翻转" ;
cout << "\n\n\n\t键盘按下【3】-第三种映射方式,x方向反转" ;
cout << "\n\n\n\t键盘按下【4】-第四种映射方式,x,y方向反转" ;
}
第一种映射方式,缩小2倍
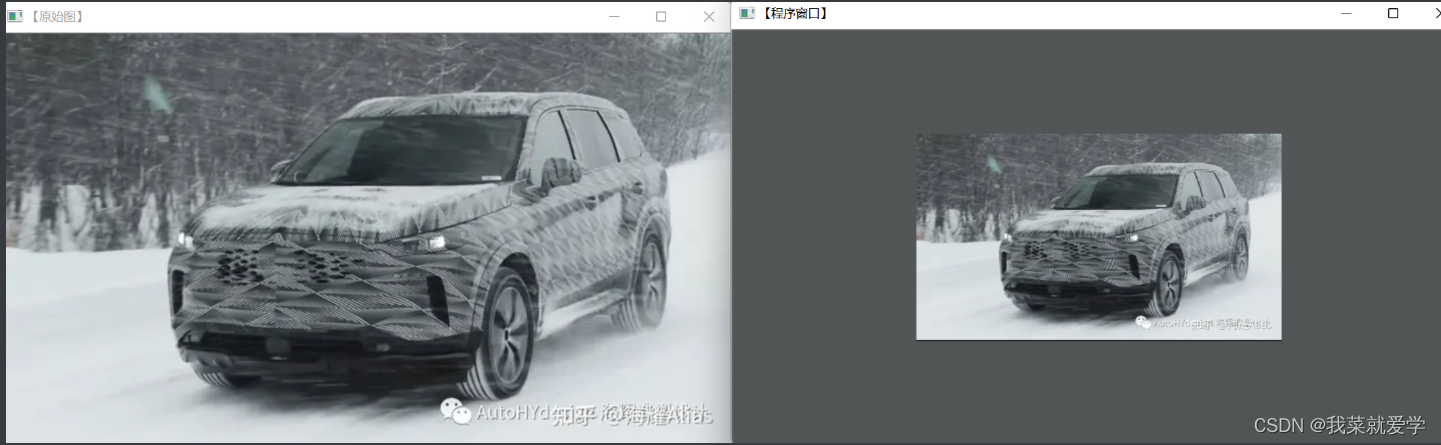
第二种映射方式,y方向翻转

第三种映射方式,x方向反转
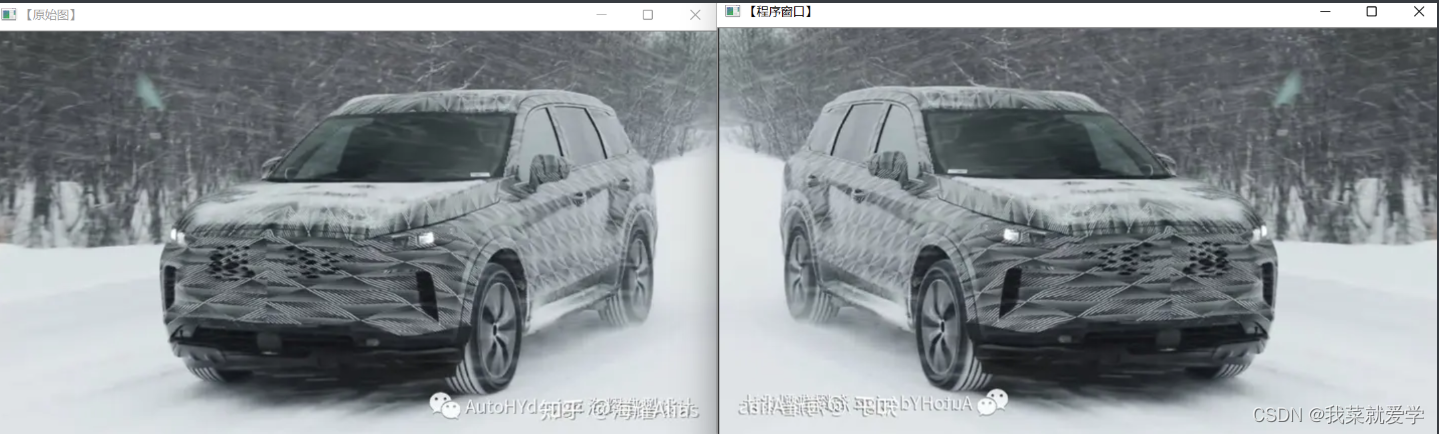
第四种映射方式,x,y方向反转

边栏推荐
- .NET Static Code Weaving - Rougamo Release 1.1.0
- Apache DolphinScheduler新一代分布式工作流任务调度平台实战-中
- What warehouse management problems can WMS warehouse management system solve in the electronics industry?
- The 600MHz band is here, will it be the new golden band?
- nodejs 安装多版本 版本切换
- 【详细教程】一文参透MongoDB聚合查询
- c语言分层理解(c语言操作符)
- Analysis of usage scenarios of mutex, read-write lock, spin lock, and atomic operation instructions xaddl and cmpxchg
- 无代码7月热讯 | 微软首推数字联络中心平台;全球黑客马拉松...
- nodejs+npm的安装与配置
猜你喜欢
面试必问的HashCode技术内幕
轻量级网络整理及其在Yolov5上的实现
GraphQL背后处理及执行过程是什么

Web3 security risks daunting?How should we respond?
Vant3 - click on the corresponding name name to jump to the next page corresponding to the location of the name of the TAB bar

谁说程序员不懂浪漫,表白代码来啦~

typescript50 - type specification between cross types and interfaces
因为一次bug的教训,我决定手撕Nacos源码(先撕客户端源码)
![Please refer to dump files (if any exist) [date].dump, [date]-jvmRun[N].dump and [date].dumpstream.](/img/10/87c0bedd49b5dce6fbcd28ac361145.png)
Please refer to dump files (if any exist) [date].dump, [date]-jvmRun[N].dump and [date].dumpstream.
typescript55-泛型约束
随机推荐
GeoAO:一种快速的环境光遮蔽方案
Jmeter cross-platform operation CSV files
【QT小记】QT中信号和槽的基本使用
LeetCode third topic (the Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters) trilogy # 3: two optimization
分析:Nomad Bridge黑客攻击的独特之处
jmeter跨平台运行csv等文件
jmeter分布式压测
【虚拟化生态平台】虚拟化平台esxi挂载USB硬盘
【虚拟化生态平台】虚拟化平台搭建
Web3 安全风险令人生畏?应该如何应对?
nodejs+npm的安装与配置
如何通过API接口从淘宝(或天猫店)复制宝贝到拼多多接口代码对接教程
【性能优化】MySQL性能优化之存储引擎调优
《The Google File System》新说
typescript51 - basic use of generics
虚拟机CentOS7中无图形界面安装Oracle
typescript53-泛型约束
How to find the cause of Fiori Launchpad routing errors by single-step debugging
nodejs+express实现数据库mysql的访问,并展示数据到页面上
Shell编程之循环语句(for、while)