当前位置:网站首页>Descscheduler secondary scheduling makes kubernetes load more balanced
Descscheduler secondary scheduling makes kubernetes load more balanced
2022-06-12 06:43:00 【Chenshaowen's website】
1. Why do I need secondary scheduling
Kubernetes The role of the scheduler is to Pod Bind to an optimal node . In order to achieve this function , The scheduler will need to perform a series of screening and scoring .
Kubernetes The scheduling of is based on Request, But every one of them Pod The actual use value of is dynamic . After a period of operation , The load on the nodes is not balanced . Some nodes are overloaded 、 However, the utilization rate of some nodes is very low .
therefore , We need a mechanism , Give Way Pod Can be healthier 、 More balanced dynamic distribution on cluster nodes , Instead of being fixed on a host after one-time scheduling .
2. descheduler Several operation modes of
descheduler yes kubernetes-sigs Sub projects under , First, clone the code locally , Enter project directory :
| |
If the operating environment cannot be pulled gcr Mirror image , Can be k8s.gcr.io/descheduler/descheduler Replace with k8simage/descheduler.
- Disposable Job
Only once
| |
- Timing task CronJob
The default is */2 * * * * every other 2 Once per minute
| |
- Permanent mission Deployment
The default is --descheduling-interval 5m every other 5 Once per minute
kubectl create -f kubernetes/base/rbac.yamlkubectl create -f kubernetes/base/configmap.yamlkubectl create -f kubernetes/deployment/deployment.yaml- CLI Command line
First, generate a policy file locally , And then execute descheduler command
| |
descheduler Yes --help Parameter to view relevant help documents .
| |
3. Test scheduling effect
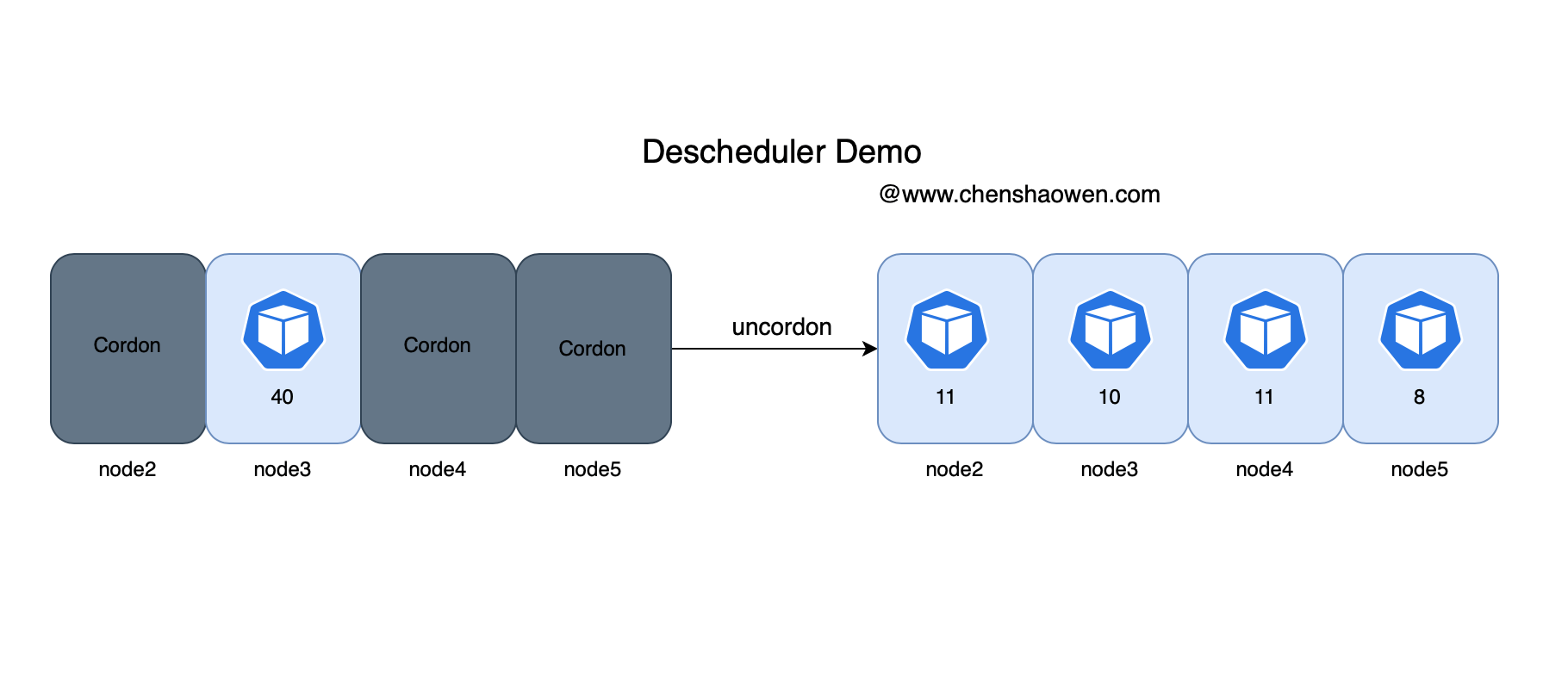
- cordon Some nodes , Only one node is allowed to participate in scheduling
| |
- Run one 40 Application of the number of copies
You can observe that all copies of this application are node3 Node .
kubectl get pod -o wide|grep nginx-645dcf64c8|grep node3|wc -l 40- Deployment in cluster descheduler
What we use here is Deployment The way .
| |
- Release node scheduling
Before dispatching , All copies are centralized in node3 node
| |
Release node scheduling
| |
- see descheduler Related logs
When the timing requirements are met ,descheduler Will begin to expel according to the strategy Pod.
| |
- After the second scheduling Pod Distribution
Node load ,node3 falling , Other nodes have risen a little .
| |
Pod Distribution on nodes , This is done without configuring any affinity 、 In the anti affinity scenario .
| node | Pod Number ( common 40 copy ) |
|---|---|
| node2 | 11 |
| node3 | 10 |
| node4 | 11 |
| node5 | 8 |
Pod The quantity distribution of is very balanced , among node2-4 The virtual machine configuration is the same ,node5 Low configuration . The following figure shows the whole process :
4. descheduler Scheduling strategy
View the default policy configuration recommended by the official warehouse :
| |
The default is on RemoveDuplicates、RemovePodsViolatingInterPodAntiAffinity、LowNodeUtilization Strategy . We can configure it according to the actual scenario .
descheduler At present, the following scheduling strategies are provided :
- RemoveDuplicates
Evict multiple nodes on the same node Pod
- LowNodeUtilization
Find low load nodes , Evict from other nodes Pod
- HighNodeUtilization
Find high load nodes , Get rid of the above Pod
- RemovePodsViolatingInterPodAntiAffinity
Expulsion violation Pod Anti affinity Pod
- RemovePodsViolatingNodeAffinity
Expulsion violation Node Anti affinity Pod
- RemovePodsViolatingNodeTaints
In violation of the NoSchedule Stained Pod
- RemovePodsViolatingTopologySpreadConstraint
Expel those that violate the topology domain Pod
- RemovePodsHavingTooManyRestarts
Evict those who restart too many times Pod
- PodLifeTime
Eviction operation time exceeds the specified time Pod
- RemoveFailedPods
Banish the state of failure Pod
5. descheduler What are the applicable scenarios
descheduler Our perspective is dynamic , It includes two aspects :Node and Pod.Node Dynamic means ,Node The label of 、 The stain 、 To configure 、 When the quantity, etc. changes .Pod Dynamic means ,Pod Actual resource usage value of 、 stay Node The distribution on is not constant .
According to these dynamic characteristics , The following applicable scenarios can be summarized :
- New node added
- After the node restarts
- Modify the node topology domain 、 After the stain , Hope that the stock of Pod It can also satisfy the topological domain 、 The stain
- Pod There is no balanced distribution among different nodes
If it's because Pod The actual use value of is far more than Reqeust value , A better way is to adjust Request value , Rather than let Pod Rescheduling .
6. Reference resources
边栏推荐
- LeetCode-1303. Team size
- LeetCode-997. Find the town judge
- C language pointer
- 【图像检测】基于深度差分和PCANet实现SAR图像变化检测附matlab代码
- Leetcode January 13 daily question 747 At least twice the maximum number of other numbers
- Redis configuration (IV) -- cluster
- [easyexcel] easyexcel checks whether the header matches the tool class encapsulated in easyexcel, including the field verification function. You can use validate to verify
- 如何更新 Kubernetes 证书
- Opencv_ 100 questions_ Chapter V (21-25)
- Node. Detailed installation tutorial of CPM and cnpm (including error resolution)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
LeetCode-884. Unusual words in two sentences
leetcode:剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数【模拟 + 分割 +讨论】
An error occurred while downloading the remote file The errormessage
leetcode.39 --- 组合总和
Host computer development (firmware download software requirement analysis)
June training day 6 - sliding window
Codeforces Round #793 (Div. 2) A B C
Category 7
The first day of June training - array
Solution: unsatisfieddependencyexception: error creating bean with name 'authaspect':
5 statement
SQL注入原理即sqli-labs搭建,sql注入简单实战
Leetcode: offer 60 Points of N dice [math + level DP + cumulative contribution]
Multithreading (IV) -- no lock (IV) -- unsafe
The fifth day of June training - double pointer
SQL注入——联合查询union
LeetCode-1078. Bigram participle
Tomato learning notes -seq2seq
Redis configuration (IV) -- cluster
Redis problem (I) -- cache penetration, breakdown, avalanche