当前位置:网站首页>Zheng Qing freshmen school competition and middle-aged engineering selection competition
Zheng Qing freshmen school competition and middle-aged engineering selection competition
2022-08-04 14:37:00 【51CTO】
A:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:Can pass with or without line breaks
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
int
n;
while(
scanf(
"%d",
&
n)
!=
EOF)
{
switch(
n)
{
case
1:
printf(
"You are the ukulele under the beach\n");
break;
case
2:
printf(
"Your hair is like snow\n");
break;
case
3:
printf(
"我喜欢的样子你都有\n");
break;
case
4:
printf(
"You are an angel's magic warm and kind\n");
break;
case
5:
printf(
"Your tenderness is like a feather\n");
break;
case
6:
printf(
"One day you will have your own day\n");
break;
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
B:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:比较2个数的大小
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
double
a,
b,
c;
while(
scanf(
"%lf%lf%lf",
&
a,
&
b,
&
c)
!=
EOF)
{
double
d
= (
a
+
b)
*
c
/
10;
double
e
=
min(
a,
d);
printf(
"%.2lf\n",
e);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
C:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:简单模拟
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
char
a[
7][
20]
= {
"c",
"java",
"php",
"html",
"phython",
"javascript",
"mysql"};
int
main()
{
int
t,
i,
j;
char
x,
y;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
getchar();
while(
t
--)
{
scanf(
"%c%c",
&
x,
&
y);
getchar();
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
7;
i
++)
{
int
sum
=
0;
for(
j
=
0;
a[
i][
j]
!=
'\0';
j
++)
{
if(
a[
i][
j]
==
x)
{
sum
++;
}
if(
a[
i][
j]
==
y)
{
sum
++;
}
if(
sum
==
2)
{
printf(
"%s\n",
a[
i]);
break;
}
}
if(
sum
==
2)
break;
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
D:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:模拟
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
a[
30];
int
main()
{
int
t,
i;
int
n,
k;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
scanf(
"%d%d",
&
n,
&
k);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
n;
i
++)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
a[
i]);
}
sort(
a,
a
+
n);
bool
flag
=
true;
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
n;
i
++)
{
if(
a[
i]
>=
k
&&
!
flag)
{
printf(
" %d",
a[
i]);
}
if(
a[
i]
>=
k
&&
flag)
{
printf(
"%d",
a[
i]);
flag
=
false;
}
}
printf(
"\n");
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
E:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:DP
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
dp[
30];
int
a[
30];
int
main()
{
int
i,
j;
int
t,
n;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
n);
dp[
1]
=
0;
for(
i
=
2;
i
<=
n;
i
++)
{
dp[
i]
=
100;
}
for(
i
=
1;
i
<=
n;
i
++)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
a[
i]);
}
for(
i
=
1;
i
<
n;
i
++)
{
for(
j
=
i
+
1;
j
<=
i
+
a[
i];
j
++)
{
dp[
j]
=
min(
dp[
j],
dp[
i]
+
1);
}
}
if(
dp[
n]
!=
100)
{
printf(
"%d\n",
dp[
n]);
}
else
{
printf(
"-1\n");
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
F:
题目地址“: 点击打开链接
思路:模拟
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
int
t,
n,
i;
double
x;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
double
sum
=
0;
scanf(
"%d",
&
n);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
n;
i
++)
{
scanf(
"%lf",
&
x);
sum
+=
x;
}
double
cf
=
2
*
3.1415926
*
sum
- (
n
-
1)
*
0.5;
printf(
"%.3lf\n",
cf);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
G:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:2种方法,The first comparison times,The second kind of thinking is a bit moving,和HDU1058类似
AC代码1:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
a[
10010];
void
cf()
{
int
i;
memset(
a,
0,
sizeof(
a));
for(
i
=
2;
i
<=
10000;
i
++)
{
int
l
=
i;
while(
l
%
2
==
0)
{
l
/=
2;
}
while(
l
%
3
==
0)
{
l
/=
3;
}
while(
l
%
7
==
0)
{
l
/=
7;
}
if(
l
!=
1)
{
continue;
}
l
=
i;
if(
l
%
3
!=
0)
{
continue;
}
l
=
i;
int
sum
=
0;
while(
l)
{
if(
l
%
10
==
4
||
l
%
10
==
6)
{
sum
++;
}
l
/=
10;
}
if(
sum
==
0)
continue;
a[
i]
=
1;
}
}
int
main()
{
int
t,
l,
r,
i;
cf();
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
int
sum;
while(
t
--)
{
sum
=
0;
scanf(
"%d%d",
&
l,
&
r);
for(
i
=
l;
i
<=
r;
i
++)
{
sum
+=
a[
i];
}
printf(
"%d\n",
sum);
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
AC代码2:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
lol[
10010];
int
dp[
10010];
void
cf()
{
int
i;
memset(
dp,
0,
sizeof(
dp));
lol[
1]
=
1;
int
a2
=
1,
a3
=
1,
a7
=
1;
int
temp,
k
=
2;
while(
1)
{
temp
=
min(
lol[
a2]
*
2,
min(
lol[
a3]
*
3,
lol[
a7]
*
7));
if(
temp
>
10000)
break;
lol[
k
++]
=
temp;
dp[
temp]
=
1;
if(
temp
==
lol[
a2]
*
2)
a2
++;
if(
temp
==
lol[
a3]
*
3)
a3
++;
if(
temp
==
lol[
a7]
*
7)
a7
++;
}
for(
i
=
2;
i
<=
10000;
i
++)
{
if(
!
dp[
i])
continue;
if(
i
%
3
!=
0)
{
dp[
i]
=
0;
continue;
}
int
l
=
i;
int
sum
=
0;
while(
l)
{
if(
l
%
10
==
4
||
l
%
10
==
6)
{
sum
++;
}
l
/=
10;
}
if(
sum
==
0)
{
dp[
i]
=
0;
}
}
}
int
main()
{
int
t,
l,
r,
i;
cf();
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
int
sum;
while(
t
--)
{
sum
=
0;
scanf(
"%d%d",
&
l,
&
r);
for(
i
=
l;
i
<=
r;
i
++)
{
sum
+=
dp[
i];
}
printf(
"%d\n",
sum);
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
- 74.
- 75.
- 76.
- 77.
- 78.
- 79.
- 80.
- 81.
- 82.
- 83.
H:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:My own fault,队友写 的题解
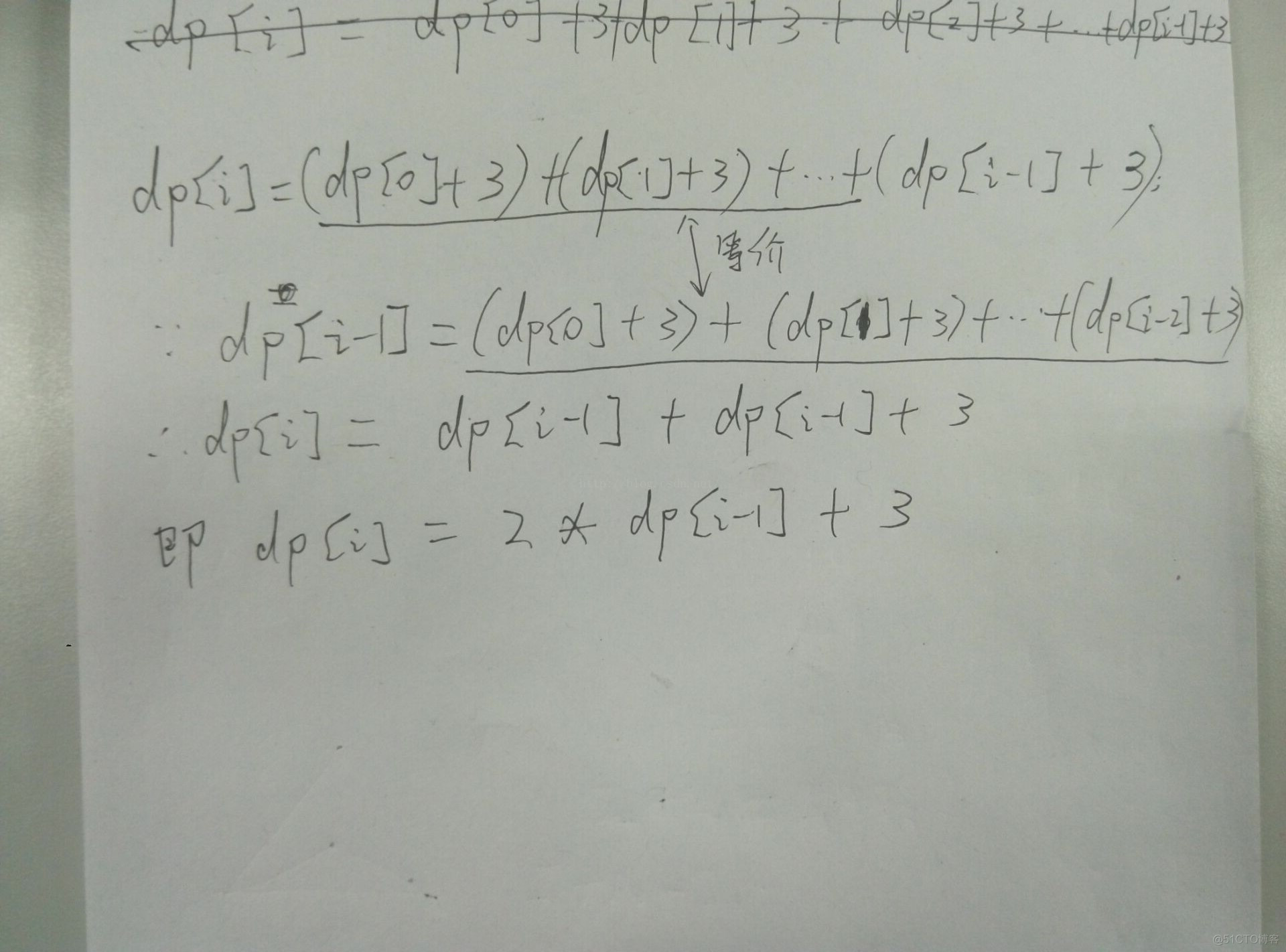
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using
namespace
std;
int
dp[
1000005];
int
main()
{
dp[
0]
=
1;
dp[
1]
=
4;
for (
int
i
=
2;
i
<=
1000000;
i
++)
{
dp[
i]
=
dp[
i
-
1]
*
2
+
3;
if (
dp[
i]
>
2333)
dp[
i]
%=
2333;
}
int
t;
cin
>>
t;
while (
t
--)
{
int
n;
cin
>>
n;
cout
<<
dp[
n]
<<
endl;
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
错误代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
dp[
100010];
void
cf()
{
int
i;
int
sum
=
0;
memset(
dp,
0,
sizeof(
dp));
dp[
0]
=
1;
for(
i
=
1;
i
<=
100000;
i
++)
{
sum
+=
dp[
i
-
1];
sum
%=
2333;
sum
+= ((
i
*
3)
%
2333);
sum
%=
2333;
dp[
i]
=
sum;
}
}
int
main()
{
int
t,
n;
cf();
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
n);
printf(
"%d\n",
dp[
n]);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
I:
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:模拟
AC代码:
Freshman Trials
斐波那契字符串
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:Use a structure to save the firstncharacters includedstr[0]和str[1]的数量,Just add it at the end
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
struct
node
{
int
a;
int
b;
}
a[
1000];
char
c[
1000];
char
b[
1000];
int
cf[
30];
int
lol[
30];
int
main()
{
int
t,
k,
i;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
memset(
cf,
0,
sizeof(
cf));
memset(
lol,
0,
sizeof(
lol));
a[
0].
a
=
1;
a[
0].
b
=
0;
a[
1].
a
=
0;
a[
1].
b
=
1;
scanf(
"%s",
c);
scanf(
"%s",
b);
scanf(
"%d",
&
k);
int
n
=
strlen(
c);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
n;
i
++)
{
cf[
c[
i]
-
'a']
++;
}
int
m
=
strlen(
b);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
m;
i
++)
{
lol[
b[
i]
-
'a']
++;
}
for(
i
=
2;
i
<=
k;
i
++)
{
a[
i].
a
=
a[
i
-
1].
a
+
a[
i
-
2].
a;
a[
i].
b
=
a[
i
-
1].
b
+
a[
i
-
2].
b;
}
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
26;
i
++)
{
cf[
i]
*=
a[
k].
a;
}
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
26;
i
++)
{
lol[
i]
*=
a[
k].
b;
lol[
i]
+=
cf[
i];
}
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
26;
i
++)
{
printf(
"%c:%d\n",
'a'
+
i,
lol[
i]);
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.
- 73.
AC代码2:(written by freshman)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
int
n,
m,
c,
i,
j,
k;
char
a[
32],
b[
32],
d;
int
s[
42][
30];
cin
>>
n;
while(
n
--)
{
cin
>>
a
>>
b
>>
k;
m
=
strlen(
a);
c
=
strlen(
b);
memset(
s,
0,
sizeof(
s));
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
m;
i
++)
{
s[
0][
a[
i]
-
'a']
++;
}
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
c;
i
++)
{
s[
1][
b[
i]
-
'a']
++;
}
for(
i
=
2;
i
<=
k;
i
++)
{
for(
j
=
0;
j
<
26;
j
++)
{
s[
i][
j]
=
s[
i
-
1][
j]
+
s[
i
-
2][
j];
}
}
for(
j
=
0;
j
<
26;
j
++)
{
d
=
j
+
'a';
cout
<<
d
<<
':'
<<
s[
k][
j]
<<
endl;
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
AC代码3:(队友写的)
Use a rolling array to keep taking the remainder
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<stack>
#include<cctype>
using
namespace
std;
int
main()
{
long
long
s[
3][
26];
int
t;
cin
>>
t;
while (
t
--)
{
string
a,
b;
int
n;
cin
>>
a
>>
b
>>
n;
memset(
s,
0,
sizeof(
s));
for (
int
i
=
0;
i
<
a.
length();
i
++)
s[
2][
a[
i]
-
'a']
++;
for (
int
i
=
0;
i
<
b.
length();
i
++)
s[
0][
b[
i]
-
'a']
++;
for (
int
i
=
1;
i
<=
n
-
1;
i
++)
{
for (
int
j
=
0;
j
<
26;
j
++)
{
s[
i
%
3][
j]
=
s[(
i
+
2)
%
3][
j]
+
s[(
i
+
1)
%
3][
j];
}
}
int
i_end;
if (
n
==
0)
i_end
=
2;
else
i_end
= (
n
-
1)
%
3;
for (
int
i
=
0;
i
<
26;
i
++)
{
cout
<<
char(
'a'
+
i)
<<
':'
<<
s[
i_end][
i]
<<
endl;
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
求解m值问题
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:Use the tablelong long存,不然会死循环
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
ll
a[
20];
void
cf()
{
int
i,
j;
ll
sum
=
0,
sum1
=
1;
for(
i
=
1;
i
<=
13;
i
++)
{
sum1
=
1;
for(
j
=
1;
j
<=
i;
j
++)
{
sum1
*=
j;
}
sum
+=
sum1;
a[
i]
=
sum;
}
}
int
main()
{
int
t,
n,
i;
cf();
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
n);
if(
n
<=
1)
{
printf(
"-1\n");
continue;
}
for(
i
=
1;
i
<=
13;
i
++)
{
if(
a[
i]
>=
n)
{
printf(
"%d\n",
i
-
1);
break;
}
}
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
Insert elements are queued
题目地址: 点击打开链接
思路:Because the number is not given, it can be input by character or by string
AC代码1:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
a[
10010];
char
b[
50020];
int
main()
{
int
t,
k,
l,
i;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
getchar();
//Eat the remaining carriage returns in the stream,不然会被gets吃掉
while(
t
--)
{
l
=
0;
gets(
b);
scanf(
"%d",
&
k);
//输入k,When I press enter again, there is a carriage return in the stream
getchar();
//Eat the remaining carriage returns in the stream,Otherwise, it will be cycled the next timegets()吃掉
int
sum
=
0;
bool
flag
=
false;
for(
i
=
0;
b[
i]
!=
'\0';
i
++)
{
if(
b[
i]
==
'-')
//This takes into account the case of negative numbers
{
flag
=
true;
}
else
if(
b[
i]
!=
' ')
{
sum
=
sum
*
10
+
b[
i]
-
'0';
}
else
{
if(
flag)
//Multiply if negative-1
sum
*=
-
1;
a[
l
++]
=
sum;
flag
=
false;
sum
=
0;
}
}
a[
l
++]
=
sum;
a[
l
++]
=
k;
sort(
a,
a
+
l);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
l
-
1;
i
++)
{
printf(
"%d ",
a[
i]);
}
printf(
"%d\n",
a[
l
-
1]);
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
AC代码2:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
typedef
long
long
ll;
using
namespace
std;
int
a[
10010];
int
main()
{
int
t,
l,
i;
scanf(
"%d",
&
t);
while(
t
--)
{
l
=
0;
int
b;
char
c;
while(
1)
{
scanf(
"%d",
&
b);
a[
l
++]
=
b;
c
=
getchar();
//获得一个字符
if(
c
==
'\n')
//Eject when the end of the line is reached
break;
}
scanf(
"%d",
&
b);
a[
l
++]
=
b;
sort(
a,
a
+
l);
for(
i
=
0;
i
<
l
-
1;
i
++)
{
printf(
"%d ",
a[
i]);
}
printf(
"%d\n",
a[
l
-
1]);
}
return
0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
边栏推荐
- 基于 Next.js实现在线Excel
- js深拷贝和浅拷贝具体使用区别_es6深拷贝和浅拷贝
- Oracle database user creation, restart, import and export
- 集合划分差最小问题(01背包)
- leetcode: 253. How many meeting rooms are required at least
- 1403. Minimum Subsequence in Non-Increasing Order
- 用了TCP协议,就一定不会丢包吗?
- AOSP内置APP特许权限白名单
- X射线掠入射聚焦反射镜
- Google plug-in. Download contents file is automatically deleted after solution
猜你喜欢

centos7安装mysql急速版
化繁为简,聊一聊复制状态机系统架构抽象
用了TCP协议,就一定不会丢包吗?
![[LeetCode] 38. Appearance sequence](/img/d6/092796b57844d5d30f3ed123a1b98a.png)
[LeetCode] 38. Appearance sequence

【Web技术】1401- 图解 Canvas 入门

Centos7 install mysql version rapidly
Basic Introduction for PLSQL
数据库恢复
Crawler - basic use of selenium, no interface browser, other uses of selenium, cookies of selenium, crawler cases
并发程序的隐藏杀手——假共享(False Sharing)
随机推荐
世间几乎所有已知蛋白质结构,都被DeepMind开源了
vim 常用操作命令
G.登山小分队(暴力&dfs)
C# winforms 输入颜色转换颜色名
Hangzhou electric the competition team arrangement (ACM)
vim common operation commands
16、学习MySQL 正则表达式
G. Mountaineering Squad (violence & dfs)
【剑指offer59】队列的最大值
ASA归因:如何评估关键词的投放价值
CCF GLCC officially opened | Kyushu Cloud open source experts bring generous bonuses to help universities promote open source
开发者独立搭建一个跨模态搜索应用有多难?
leetcode:251. 展开二维向量
基于 Next.js实现在线Excel
砺夏行动|九州云章津楠:开源不是少数人的运动,大众化才是源泉
leetcode: 253. How many meeting rooms are required at least
在腾讯,我的试用期总结!
1375. 二进制字符串前缀一致的次数-前序遍历法
【问题解决】QT更新组件出现 “要继续此操作,至少需要一个有效且已启用的储存库”
Almost all known protein structures in the world are open sourced by DeepMind