当前位置:网站首页>FPGA timing constraint sharing 04_ Output delay constraint
FPGA timing constraint sharing 04_ Output delay constraint
2022-07-27 14:42:00 【MDYFPGA】
This article discusses FPGA The temporal input delay constraint , The content of this article , From mingdeyang's time series constraint special course video .
《FPGA Timing constraint sharing 01_ Four steps of constraint 》 Give a general introduction to The four steps of timing constraints , The temporal constraints are classified , And get a classification table .
《FPGA Timing constraint sharing 02_ Clock constraint 》 The constraints on the clock are introduced in detail , According to the clock source, it can be divided into input clock constraints 、PLL And other derived clock constraints and their own frequency division clock constraints . These three types of constraint methods are different , Readers need to know how to distinguish .
this paper , The author will introduce the input delay in detail (input delay) The concept of 、 Scene classification 、 Constraint parameter acquisition method and constraint method .
Hello everyone , Welcome to the series of video tutorials on minimalist design launched by mingdeyang . In this lesson, we continue with the third step of timing constraints ,output delay One of the settings for . I'm my video lecturer, Mr. Pan . Speaking of this video, before this step , Let's take a look at our steps . This picture , Our third step is output delay Of . When we look at this step, we need to look at three situations , One is system synchronization , One is source synchronization . Source synchronization is divided into SDR and DDR These two kinds , So to sum up, we have three situations . These three cases will have different settings . The materials we need to refer to this time , It's still us PDF Documentation , We offer you a PDF file . good , Let's take a look at the title , We will talk about these steps in this course , The first output is the original concept . The second is that we use two measurement methods to get our timing parameters , Then go and constrain . After that , The third one is our different situation , The first is system synchronization , The second is source synchronization . Source synchronization is divided into SDR and DDR These two kinds .
The first 1 section : Output delay concept
The goal is : Give Way FPGA Adjust the timing , Make the timing meet the requirements of downstream devices .max Used to consider the establishment time : Follow positive numbers , Indicates that the data arrives before the sampling edge of the clock . The formula : Maximum board level delay +TSUmin Used to consider holding time : Negative number after , It indicates that the data remains for a period of time after the sampling edge of the clock . The formula : Minimum board level delay -TH If the board level delay is 0, be max It is the downstream device “TSU”;min It is the downstream device “-Th”.
good , Let's look at the first concept of output delay . First, we set the output delay , Why output delay ? Our goal is to make way for fpga Adjust the timing of its own output , Make our output timing meet a requirement of downstream devices . In this way, our downstream devices can correctly collect our timing , So the goal is like this . Remember that the goal is to collect downstream devices correctly , Therefore, you should ensure that your output is correct , So we have to adjust ourselves . So we are also telling fpga, What are the requirements of our downstream devices , We told us fpga What are the requirements during the downstream period , We know this requirement according to , I'll adjust the timing myself . This is our goal of output delay . ah , remember fpga It's output , To this offline is to input . good , Our output delay also has two parameters , One is max, One is min Of , One is the largest , One is the minimum delay , Maximum delay . Why use it ? You can use it to think like this , It is used to consider the establishment time , They usually follow positive numbers , A positive number means that the data arrived before the sampling edge of the clock , How did we get this value in our formula , This maximum board delay plus this TSU ah ,TSU It's about setting up time . Whose establishment time , It's the establishment time of downstream devices , That is to say, the delay of my board plus the identification time required by him during your downstream is me max ah . And this min What is it ? The minimum is used to consider holding time , Whose holding time is the holding time in the downstream period , Followed by a negative number means that the data has remained for a period of time after using the sampling edge , It means , And what about our formula ? It is the smallest board level delay , Is the delay minus TH ah , This keeps time . Where does this parameter come from ? From the requirements of downstream devices , For example, my board delay is the delay on the circuit board minus your request , Keeping time is one of my most min For a minimum delay of, note that generally, this value is relatively small , And this is a big one minus it becomes a negative number . For example, our board delay is zero , If the board is in an ideal situation , I haven't had any delay now , Anyway, the delay is zero , This is also a very common situation , Anyway, it is zero . This is the downstream period TSU ah , This is the establishment time requirement during the downstream period . And this side is the downstream device . Keep the minus sign of time , Negative click TH This is also . This is the time , The smallest one is a negative number . This is our concept of input delay . What you should remember in this is the formula , The maximum board delay plus your identification time requirements , It's mine. max ah , The delay of the minimum board minus TH Is that you keep time ,, Is my minimum time requirement .
The first 2 section : Constraint statement
The first 3 section : Purpose of output delay
The first 4 section : Two methods of parameter acquisition
good , Second, let's look at two measurement methods . about . our output delay There are also two measurement methods .
4.1 Parameters of downstream devices ( recommend )
The first is based on the parameters of downstream devices , That is to say, we, er, must have data manuals from downstream devices . Its data book will definitely tell you the requirements of establishment time and holding time . After we get its parameters from the build time and save time , You can set it , It's bound .
4.2 The oscilloscope measures
The second method is to use a microwave absorber to measure an input port of our downstream devices , Go to see the timing information to get it . What timing information can we get ? It's the one who got it , For example, it delays such information , But we don't usually use this . What we recommend is to use this method , This requires us to standardize the hardware , This is better , Don't say that the delay comes and goes . So generally, we talked about a way of parameters of downstream devices .
The first 5 section : Constraint methods in various application scenarios
good , Let's have a look , Let's discuss how to restrict this kind of situation in different situations .
5.1 System synchronization 
good , Third , We'll do it according to different situations , The first one we need to configure is called system synchronization . As for system synchronization, we talked about it last class , Namely fpga It shares the same clock with downstream devices . We can think that the delay of this clock is equal to zero, ah, equal to zero . good , And he fpga Send this data , It has a certain delay , Send it to the downstream device . The downstream device has its own set-up time retention requirements . We will get such parameters from the data manual. Before it is built, it is 2 Thousands of seconds , It's this TH Namely 1 Nanosecond , Its identification time retention requirements . Here, it is possible that my delay is in line with my jitter . Time delay here we pass a er measurement , Or the calculation method can get . For example, its way is ah, not its jitter is 0.5, Sometimes it's 0.3, The minimum is 0.3.ok What about after you get it like this , Next, we will know how to configure it . For example, what is its maximum delay , This is my biggest board level delay , Plus my establishment time requirement is 2 add 0.5, This is my biggest delay . ah , And what is the smallest ? This is my youngest 0.3, This is also minus my holding time requirements , This is this. 1 nanosecond , That is 0.3 Minus one , Then negative 0.7, This is the requirement . We're here PDF130 Page also has the concept of describing this process , Please have a look , We see this constraint . The first is to generate a clock. Ah, this must be available , Each port has a clock . so what , We will tell him about this clock , What is the maximum delay of this clock ? yes 2.5 ah , Its object is this DOUT, This is this. DOUT. And its minimum delay is -0.7. good , This is the case of system synchronization . System synchronization means that the clock is shared fpga Share one with downstream devices .
5.2 Source synchronization SDR
good , Next, let's look at source synchronization , Which means it's fpga While sending data , Also send the clock to the next module , Clock and data are sent together . Among them, we will follow SDR and DDR.SDR It refers to the rising edge of the edge to sample ,SDR It means that both the rising point and the falling point are sampled .
So let's take a look at SDR Is that so? ?SDR It is the way of sampling on the upper edge . ah , The same way , We can also get a result of it . It is the same as system synchronization , Its method is the same , It also gets my appraisal time by checking the data manual , The requirement of keeping it can also know how much the jitter of my delay is . For example, we get the jitter after measurement , After getting the maximum jitter and the minimum jitter , I can configure . This formula is also mentioned , The biggest one refers to my maximum delay plus my setup time requirements , And the minimum refers to my minimum delay minus my, er, retention time requirements , Is my youngest
5.3 Source synchronization -DDR( Check the manual )
then DDR Well ,DDR It means that the rising edge and the falling edge are synchronous , All are sampled . So it samples like this , Samples will be taken here and here , They'll sample . We can do it in one way ? For example, let's check this manual , We can also check the manual to get his request . For example, how long will he ask you to set up this , How long does it last , And how long is the establishment time here , How long is the guarantee . For example, we have an example here , For example, his business appraisal time requirement is 0.7. For example, this is 0.7, This is 0.3, This is 0.6 And this is 0.4 ah . Therefore, we need to configure it ,outlay Ah, we can see that the clock generates, generates a clock . Okay , Let's take a look at its biggest delay, which is zero 7. For it, the biggest is 0.7, What is the smallest ? ah ,0 subtract 0.3. Let's check and accept the board at this time , It's considered to be zero .0 subtract 0.3. And at this moment , We are the biggest is 0.6, The minimum is zero minus 0.4, That's it . Negative 0.4 ah , Notice our for At the falling edge , Add this clock for Ah Jia I Bar ADD delay. good , Add this sentence , This is our right way . Among them, this, for example, may not be necessary , This one in the middle is different . We are mainly talking about the following four parts , The front part is the same as our clock . For example, we clock in ahead , And this one, we need this one behind . Suppose we configure output delay Ha , Plus the following four sentences . This is us. DDR A way of .
Okay , Some students said our input delay What is an edge ? Also called center aligned . Why don't we have it here , Because everyone knows that we input delay That's by measurement , And our way is to check the data manual , Check the data book . Then at this point on his edge , He can't shake, it can't shake . He will definitely establish . When you are on the falling edge , You will be stable before , How long is it stable , How long will it stabilize , So he must be so stable in such a situation , He will give you the actual parameter requirements , So we don't have a case of edge alignment and center alignment . ah , We can find these parameters from the data manual , Then configure it . Another point is for our board level delay in general , If our hardware makes a good board , This matter does not need to be considered . That means ours output delay Generally, it is to set its identification time , That is to get the two parameters of identification time and shelf life from the manual . Then according to its formula, you can directly configure it , So it output delay The way is relatively simple .
The first 6 section : Summary and suggestions
good , Let's summarize , We still follow our experience , Is to index according to the previous order , Find the corresponding situation , Constrain as required . For example, which of the above three cases does my current port belong to , If so , You can configure and constrain according to which one .
ah , The second is that we still follow the front input delay It was emphasized when input delay 、output delay Is to tell the tool my current actual situation . For example, I told me fpga What are the requirements during the downstream period , Tell this result directly fpga That's it . You don't have to worry fpga How can he move , How much does he want to move , You don't even care , Just tell him the reality . then fpga He can calculate automatically , Finally, I decide how much time sequence I want to offset . Then there is a similar , That is, if we have a person named offset in /out This kind of thing , Just tell you how much you offset before , How much is the offset , So as to meet the time sequence like this , We have to calculate this by ourselves. In this step, there is no need to calculate . ah , This is our output delay A configuration method , Relatively simple . good , This video is about here , thank you .
The above is the relevant knowledge in Ming Deyang's serial course of time sequence constraints , Students who want to obtain information about timing constraints can ( Add W:MDYfpga003 ) Mr. Chen
边栏推荐
- SLAM综述阅读笔记六:基于图像语义的SLAM调研:移动机器人自主导航面向应用的解决方案 2020
- HDU1422 重温世界杯【DP】
- Electronic bidding procurement mall system: optimize traditional procurement business and speed up enterprise digital upgrading
- Lesson 3: reverse word order
- The difference between [x for X in list_a if not np.isnan (x)] and [x if not np.isnan (x) else none for X in list_a]
- @Detailed explanation of repository
- 进程间通信
- Failed to connect to ResourceManager
- Forward proxy and reverse proxy
- Basic exercises of C language
猜你喜欢
![[popular science] the difference and connection between accuracy and resolution](/img/12/efcce1f6b8801d8d8b08b79818632c.png)
[popular science] the difference and connection between accuracy and resolution
Architecture - the sublimation of MVC
自动化配置SSH免密登录和取消SSH免密配置脚本

基于企业知识图谱的企业关联关系挖掘

Chapter 3 business function development (view clue details)

Windows10 installing SQL Server 2019
Research on Chinese idiom metaphorical knowledge recognition and relevance based on transfer learning and text enhancement

文献翻译__基于自适应全变差L1正则化的椒盐图像去噪

Utnet hybrid transformer for medical image segmentation
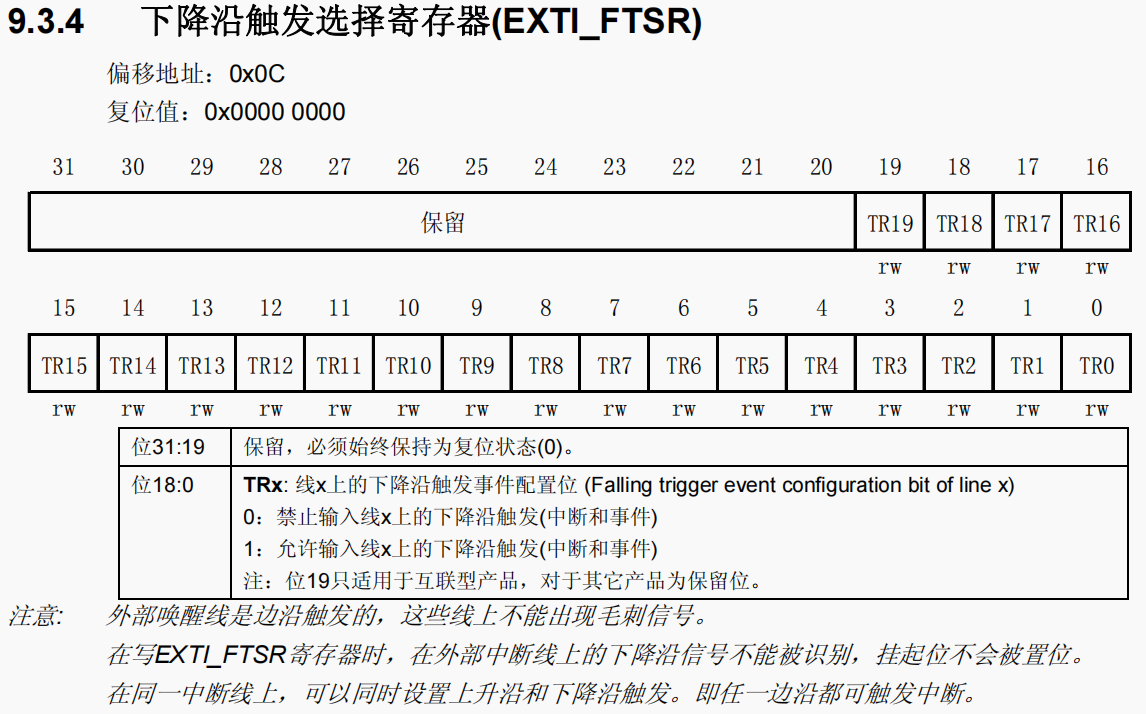
【STM32】EXTI
随机推荐
JS epidemic at home, learning can't stop, 7000 word long text to help you thoroughly understand the prototype and prototype chain
Chinese character style transfer --- antagonistic discriminative domain adaptation (L1)
spark job 使用log4j appender 追加日志到本地文件或者mysql
2022年中国网络视频市场年度综合分析
Docker实践经验:Docker 上部署 mysql8 主从复制
Airport cloud business sign analysis
[related contents of multithreading]
Mining enterprise association based on Enterprise Knowledge Map
Detoxify! After Harbin Institute of technology was disabled MATLAB, domestic industrial software fought back domineering
Import the virtual machine officially made by Kali Linux into Oracle VirtualBox
Research on automatic classification of electronic medical records based on unbalanced data
log4j2 jdbc appender
RTL8762DK 环境搭建(一)
Getting started for beginners: build your own blog with WordPress
万字详解 Google Play 上架应用标准包格式 AAB
开源版思源怎么私有部署
线程知识总结
Chapter 3 business function development (add clues and remarks, and automatically refresh the added content)
Construction and empirical research of post talent demand analysis framework based on recruitment advertisement
Carla notes (04) - client and world (create client, connect world, batch object, set weather, set lights, world snapshots)