当前位置:网站首页>Test manager defines and implements test metrics
Test manager defines and implements test metrics
2022-06-12 07:11:00 【Snow falls on the devil's land】
There is a famous saying in management , The work of measurement will be effectively implemented . conversely , Because it is easy to ignore the work that is not measured , So work that is not measured is usually not performed effectively . therefore , For any activity including testing , It is important to establish appropriate metrics .
Test metrics can be divided into one or more of the following types :
Project measurement , Against established project export guidelines , Such as test case execution rate 、 Pass rate and failure rate , Measure project progress
Product metrics , Measure some attributes of the product , Such as test degree and defect density
Process measurement , Ability to measure the testing or development process , E.g. percentage of defects found by testing
Personnel measurement , Measure the ability of an individual or group , Such as the implementation of test cases within a given time
Any given metric falls into the above two categories 、 Three 、 Even four types . for example , The trend chart showing the daily defect detection rate can be related to the following : Export guidelines ( No new defects have been found for a week )、 product quality ( Testing can no longer find defects in the product )、 And test process capability ( A large number of defects were found in the early stage of testing ).
People measurement is particularly sensitive . Test managers sometimes mistake process measurement for personnel measurement , This leads people to take some actions to make the measurement more beneficial to them , Have disastrous consequences .
Our main concern is to use metrics to measure the progress of testing work , Such as project measurement . The use of metrics allows testers to report results consistently , And you can track test progress consistently . Test managers are often asked to present measurement data at various meetings , Participants in these meetings may include stakeholders at all levels, from technical personnel to executive management . Because sometimes these metrics are also used to determine the overall success of a project , When deciding what to track 、 The frequency of reporting and the manner in which this information is presented need special attention . It's important to note that , The test manager must consider the following :
Definition of measurement : A limited set of useful metrics should be defined . Metrics are defined according to the project 、 Process and / Or the specific objectives of the product . Balance should be taken into account when defining metrics , Because a single measurement can mislead the impression of a state or trend . The interpretation of these defined metrics must be accepted by all stakeholders , Avoid confusion when discussing these metrics . It often happens that too many metrics are defined without focusing on the most relevant metrics
Tracking of metrics : Measurement reporting and aggregation should be automated as much as possible , To shorten the time of collecting and processing measurement data . Over time , Specific measurement data may reflect information that is different from the interpretation agreed in the measurement definition phase . The test manager should be prepared , Carefully analyze the possible deviations of these measurement data and expectations , And the reasons for the deviation
Reporting of metrics : The purpose is to help the management quickly understand the information obtained . A measure of a period of time should be presented “ snapshot ” Or measuring change over time , In this way, trend analysis can be carried out
The effectiveness of measurement : The test manager must also verify the reported information . The data collected for a measure may not reflect the reality of the project or may convey an overly optimistic or pessimistic trend . Before presenting data , The test manager must review the data on both the accuracy of the data and the information that may be conveyed
The progress of supervision and testing is mainly in the following five aspects :
product ( quality ) risk
defects
test
coverage
confidence
In projects and businesses , Product risk 、 defects 、 Testing and coverage can , And usually measured and reported in a specific way . If these metrics relate to the exit criteria defined in the test plan , They can be used as objective criteria to judge whether the test work is completed . Confidence can be measured by surveys or by using coverage as an alternative measure , However, confidence is often reported in a subjective way .
Measures related to product risk include :
Percentage of risks fully covered ( All the tests passed (Pass))
Percentage of risks partially covered ( Some tests or many tests fail )
The percentage of risks that have not been fully tested ( Some tests have not been completed yet )
Percentage of risk covered by risk category
Percentage of risks identified after initial quality risk analysis
Defect related metrics include :
It has been reported that ( Find out ) The comparison of the total number of defects has been solved ( Repair ) Total number of defects
Mean time between failures and failure occurrence rate
The number or percentage of defects counted according to the following categories o Specific test items or components o The root cause o The source of the defect is ( Such as requirements and specifications 、 new function 、 Regression, etc ) o Test release o introduce 、 The stage of finding and removing defects o priority / severity o Rejected or repeated defect reports
Trend in time from reporting defects to fixing defects
Introduced new defects ( Sometimes called sub defect ) Number of defects repaired
Test related metrics include :
Planned 、 Has specified ( Implemented ) Of 、 Has run 、 Adopted 、 The failure of the 、 Total number of tests that could not be executed and skipped not to be executed
Regression testing and validation testing status , Including the total number of trend and failed regression tests and the total number of failed validation tests
The planned daily test duration is compared with the actual daily test duration
Test the usability of the environment ( The percentage of test environments available to the preparation test team for the planned test duration )
Measures related to test coverage include :
Coverage of requirements and design elements
Risk coverage
Environmental Science / Configure coverage
Code coverage
It is important that test managers know how to interpret and use coverage metrics , In order to understand and report the test status . For higher level tests , Such as system test 、 System integration test and acceptance test , The main test basis is usually the requirements specification 、 Design specifications 、 Use cases 、 A user story 、 Product risk 、 Support environment, support configuration and other work products . Structured code coverage metrics are more appropriate for lower level tests , Like unit testing ( Such as statement and branch coverage ) And component integration testing ( Such as interface coverage ). The test manager may use the measurement data of code coverage to measure the extent to which the test covers the system under test , But when reporting high-level test results , Code coverage metrics are not usually mentioned . Besides , Test managers should know that even if unit tests and component integration tests achieve the goal of structural coverage 100%, Defects and quality risks still need to be dealt with at a higher level of testing .
Metrics can also be linked to activities in the basic testing process . During the whole test process , You can compare the project objectives with the test process itself , Use metrics to monitor the testing process itself and progress toward project goals .
Metrics related to monitoring test plans and control activities include :
risk 、 Coverage of requirements and other test basis elements
Defect discovery
The planned time for developing test pieces and executing test cases is compared with the actual time
Metrics related to monitoring test analysis activities include :
Number of test conditions identified
Number of defects found in the test analysis ( For example, identify risks or other test conditions by using test basis )
Metrics related to monitoring test design activities include :
Percentage of test conditions covered by test cases
Number of defects found in the test design ( For example, the development test is based on the comparison test )
Metrics related to monitoring test implementation activities include :
Percentage of test environment configuration
Percentage of test data records loaded
Percentage of test case Automation
Metrics related to monitoring test execution activities include :
perform 、 The percentage of tests that passed and failed that were scheduled
perform ( and / Or through ) Percentage of test conditions covered by the test case of
Planned versus actual reporting / Comparison of defects solved
Comparison between planned coverage and actual coverage
Monitor the measurement of test progress and test completion activities, including milestones 、 Entry criteria and exit criteria ( Defined and approved in the test plan ) Mapping , It may include the following :
Planned test conditions 、 The number of test cases or test specifications and the test conditions executed according to whether the test passes or not 、 The number of test cases or test specifications
Total number of defects , Usually by severity 、 priority 、 Current state of 、 Affected subsystem or other classified statistics
Required 、 Accepted 、 Number of changes carried out and tested
Planned cost vs. actual cost
The planned construction period is compared with the actual construction period
The planned date of the test milestone is compared with the actual date
Project milestones for testing ( Such as code freezing ) Compare the planned date with the actual date
product ( quality ) Risk status 、 Generally, the risk is divided into mitigated and unmitigated risks , Major risk areas 、 Classification and statistics of new risks found after test and analysis
The amount of testing effort due to blocking events or planned changes 、 Percentage of cost or time lost
Confirm and regression test status
Measures related to surveillance test closure activities include :
Performed during test execution 、 Adopted 、 The failure of the 、 Percentage of test cases that could not be executed and skipped not to be executed
Percentage of test cases included in the reusable test case library
Percentage of automated test cases or planned vs. actual automated test cases Percentage of test cases incorporated into regression testing
resolved / Percentage of outstanding defect reports not resolved
Percentage of test work products identified and archived
in addition , Standard project management techniques , Such as work breakdown structure , It is usually used to supervise the testing process . In an agile team , Testing is part of the evolution of the user story on the burn out chart . When using lean management techniques , The test progress is based on a series of stories , It is usually monitored by the status of the user story card moving on the Kanban diagram .
Given a set of metrics , Measurement data can be presented orally 、 In the form of numerical values in the table , Or use graphics to report . Measurement data can have many uses , Include :
analysis , Find out the trends and reasons that can be observed from the test results
report , Inform interested project participants and stakeholders of the test results
control , Change the process of the whole test or project and supervise the results of the process correction
collect 、 The appropriate way to analyze and report these test metrics depends on the specific information needs 、 Goals and personal ability to use these metrics . in addition , The specific content of the test report should also vary according to different readers .
To test the need for control , It is very important that the measurement data be available to the test manager about the entire test process ( After the test plan is completed ) Information about , And can guide the test manager to successfully complete the test task 、 Implement test strategy and achieve test objectives . Therefore, information needs must be taken into account when planning , Monitoring must include collecting any required work product metrics . The amount of information required and the amount of work required to collect information depend on various project factors , Including project scale 、 Complexity and risk .
Test control must respond to the information generated by the test and the changing environment in which the project or activity exists . for example , If the dynamic test finds a defect group in some areas where it is considered impossible to have many defects , Another example is that the test execution cycle is shortened due to the delay of test start time , The risk analysis and plan must be modified . Doing so may require resetting the test priorities and reassigning the remaining test execution work .
If deviation from the test plan is found through the test progress report , Test control shall be performed . The purpose of test control is for the project and / Or test redirection to a more likely direction of success . When the control of the project depends on or is affected by the test results , The following needs to be considered :
Modify the quality risk analysis 、 Test priority and / Or test plan
Increase resources or project or test workload
Postpone the release date
Relax or strengthen test exit guidelines
Change the scope of the project ( Functional or non functional )
Implementation of these often requires consensus among project or business stakeholders , And obtain the consent of the project or business manager .
The information published in the test report should largely depend on the target audience , For example, the information needs of project management personnel or business management personnel . The project manager is most likely interested in the details of the defect , The business manager may be most concerned about the status of product risk .
边栏推荐
- Kotlin plug-ins kotlin Android extensions
- Meituan won the first place in fewclue in the small sample learning list! Prompt learning+ self training practice
- 8086/8088 instruction execution pipeline disconnection reason
- d的扩大@nogc
- 库里扛起了勇士对凯尔特人的第四场
- TypeScript基础知识全集
- Day 6 of pyhon
- 最近面了15个人,发现这个测试基础题都答不上来...
- 新知识:Monkey 改进版之 App Crawler
- Kali and programming: how to quickly build the OWASP website security test range?
猜你喜欢

Dynamic coordinate transformation in ROS (dynamic parameter adjustment + dynamic coordinate transformation)

8 IO Library
![Leetcode: offer 60 Points of N dice [math + level DP + cumulative contribution]](/img/2b/41bd6a213892062f4c12721b5d4e8d.png)
Leetcode: offer 60 Points of N dice [math + level DP + cumulative contribution]

Lambda function perfect use guide
(14) The software version number is displayed in the flash window of blender source code analysis

New knowledge: monkey improved app crawler

Pyhon的第六天
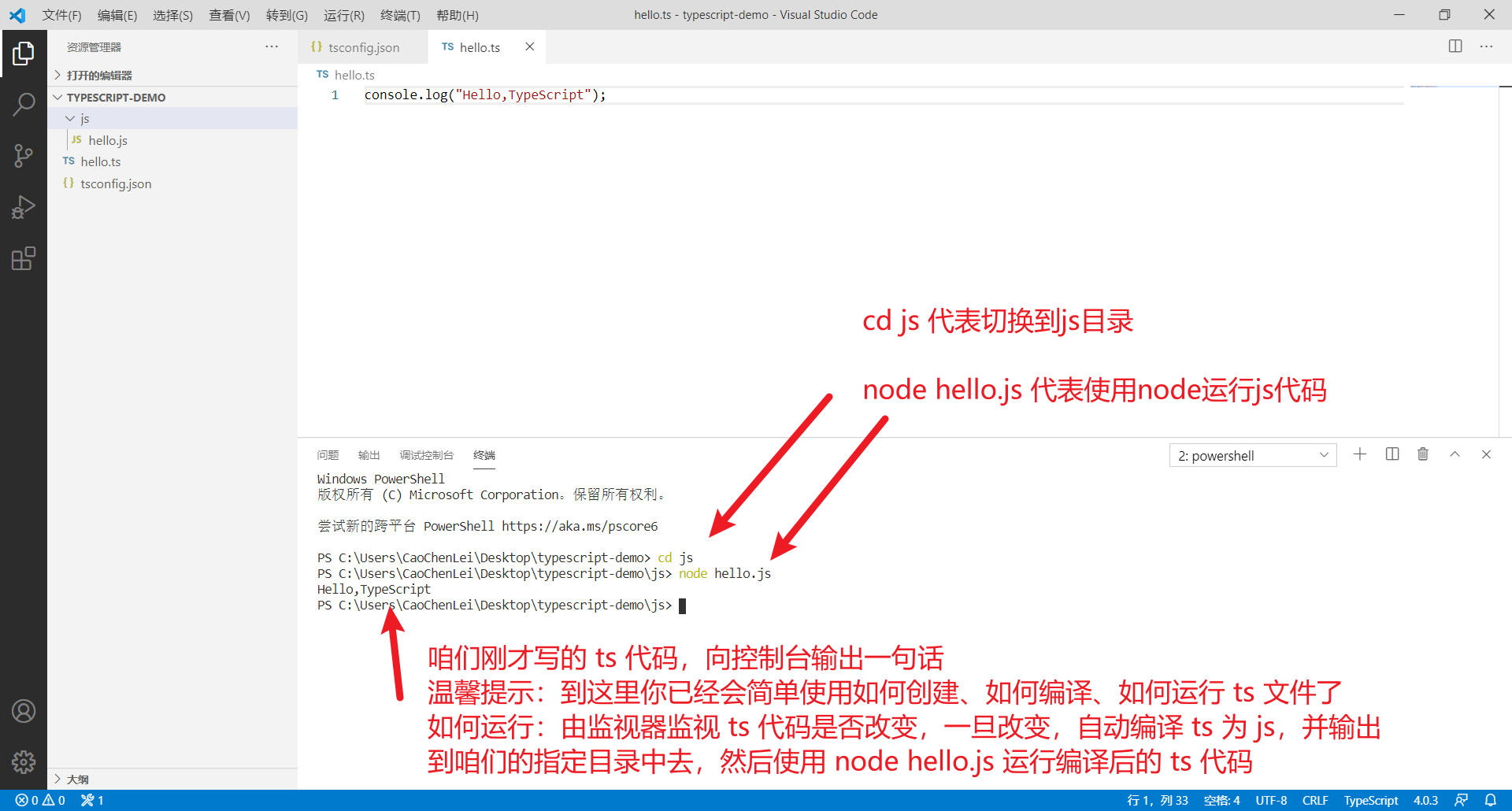
TypeScript基础知识全集

JDE 对象管理工作平台介绍及 From 的使用

Throw away the ugly toast. The movable toast is more interesting
随机推荐
Vscode outline preview cannot find file symbol
sql server2019安装到这步无法进行下一步了,如何解决?
Problems encountered in learning go
RT thread studio learning (VIII) connecting Alibaba cloud IOT with esp8266
5 ROS simulation modeling (4-navigation navigation simulation)
Scons compiling imgui
5、 El expression & JSTL tag library
五、EL 表达式& JSTL 标签库
sql server 2019安装出现错误,如何解决
Summary from November 29 to December 5
[image denoising] image denoising based on partial differential equation (PDE) with matlab code
Putty installation and use
d的自动无垃集代码.
d不能用非常ctfe指针
New knowledge: monkey improved app crawler
8. form label
【图像去噪】基于非局部欧几里德中值 (NLEM) 实现图像去噪附matlab代码
ROS dynamic parameter configuration: use of dynparam command line tool (example + code)
node:打不开/node:已拒绝访问
网络丢包问题排查