当前位置:网站首页>Geospatial search: implementation principle of KD tree
Geospatial search: implementation principle of KD tree
2022-06-25 12:45:00 【Wenxiaowu】
Previous review :
Suppose we now have a data set , When given a new instance , The simplest and crudest way is to calculate its distance from all points , And then find k The nearest neighbor , Finally, judge the class of this instance according to the rule of majority voting .
But if there are many and intensive training examples in this dataset , And an instance has many features , Then you have to calculate thousands of distances , The amount of computation is extremely huge .
At this time , We can use a faster calculation method ——kd Trees .
What is? kd Trees
kd Trees look fundamentally , It's a binary tree structure , According to this structure k Continuous division of dimensional space , Each node represents k Dimension super rectangle area .
A two-dimensional (k=2) The rectangular area of :

The three dimensional (k=3) The rectangular area of :

Be careful ,kd The tree here k Represents the number of features , That is, the dimension of data , and k In the neighborhood k It refers to the closest to the new instance point k A neighbor .
How to construct kd Trees
principle
Input : k Dimensional data sets :
xi=(xi(1),xi(2),...,xi(k))T,xi(l) The superscript of represents the th l Eigenvalues
Output : kd Trees
1. Start : Construct the root node .
Select an optimal feature at the root node for cutting , It is generally determined by comparing the variance of each feature , The feature with the largest variance is what we want to choose Axis .
If we choose x(1), Take it as the coordinate axis , Find the syncopation point , Cut the super rectangular area into two sub areas . Usually selected x(1) The median of the data in the direction is used as the cut-off point , The depth generated from the root node is 1 Left and right child nodes of , The coordinates of the left node are smaller than the tangent point , The coordinate of the right node is greater than the tangent point .
2. repeat : Selection and cutting of residual features
Continue to the depth of j The node of , choice x(1) Is the tangent axis ,l=j(mod k)+1, Take all instances in the node area x(1) The median of the coordinates is used as the tangent point , The region is continuously divided into two sub regions .
3. stop it : obtain kd Trees
Stop segmentation until there are no instances in the two sub regions , That is to get a tree kd Trees .
Example explanation
Input :
Output : kd Trees
For convenience , Mark the data points in the data set for visual display :
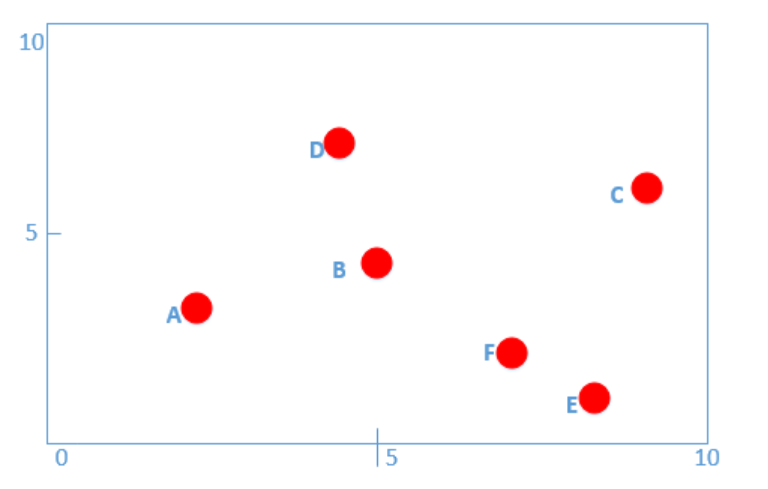
1. For the first time
Because the dimension of the training data set is 2, Then select any feature . Choose x(1) For the axis , take x(1) The data in is sorted from small to large , Namely :2,4,5,7,8,9
The median might as well choose 7, namely With (7,2) Is the root node , Slice the whole area .

On the left is less than 7 The child node of , The one on the right is larger than 7 The child node of .
2. Second slice
Divide the area again :
Add... To the first feature 1, With x(2) For the axis .
For the left area after the first segmentation , take x(2) The data in is sorted from small to large , Namely :2,3,4,7
The median is 4, The coordinates of the syncopation point are (5,4), Draw another horizontal line for the second segmentation .
similarly , For the right area after the first segmentation , take x(2) The data in is sorted from small to large , Namely :1,6
Because there are only two points , Choose 6 As a syncopation point , The coordinates of the tangent point in the right area are (9,6) , Draw a horizontal line for the second segmentation .

3. Continue to cut
The second feature adds 1, With x(3) For the axis , And only here x(1) and x(2), So only for x(1) division . Or directly calculate 2(mod 2)+1=1 You can get the selected feature .
It's obvious that A(2,3),D(4,7),E(8,1) The three instance points have not been segmented yet , Then take these points as root nodes and draw a line perpendicular to x(1) Cut the line of the axis .

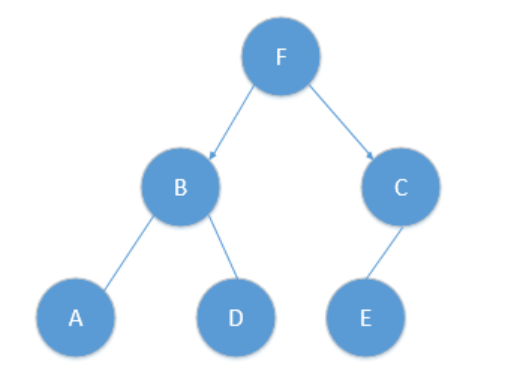
4. draw kd Trees
The root nodes in these divisions are :
first stage :(7,2)
Level second :(5,4),(9,6)
Level third :(2,3),(4,7),(8,1)
Draw... According to this level kd Trees :
How to search kd Trees
principle
Input : Constructed kd Trees , The target point is x
Output : x The nearest neighbor of
seek “ The nearest point at the moment ”: Starting from the root node , Recursive access kd Trees , Find out include x Leaf nodes of , This leaf node is “ The nearest point at the moment ”
to flash back : Take the target point and ” The nearest point at the moment “ Backtracking and iteration along the root of the tree , The current nearest point must exist in the region corresponding to a child node of the node , Check whether there is a closer point in the area corresponding to another child node of the parent node of the child node .
When you go back to the root node , End of the search , final ” The nearest point at the moment “ That is to say x The nearest neighbor of .
Example explanation
The tree generated above kd Trees, for example :

Case 1
Input : kd Trees , The target point x=(2.1,3.1)
Output : The nearest neighbor of the target

Find the nearest point : Start at root ,x=(2.1,3.1) At the root node (7,2) In the left sub region of , Continue to (5,4) In the determined left sub region , Continue to (2,3) In the right sub region of ,(2,3) Is the nearest neighbor .
to flash back : With (2.1,3.1) For the center of a circle , Draw a circle with its distance from the determined nearest neighbor as the radius , There are no other points in this area , That proves (2,3) yes (2.1,3.1) The nearest neighbor of .
Case 2
Input : kd Trees , The target point x=(2,4.5)
Output : The nearest neighbor of the target point

Find the nearest point : Start at root ,x=(2,4.5) At the root node (7,2) In the left sub region of , Continue to (5,4) Within the determined upper sub region , Continue to (4,7) In the left sub region of ,(4,7) Is the nearest neighbor .
to flash back : We use (2,4.5) For the center of a circle , With (2,4.5) To (4,7) The distance between two points draws a circle for the radius , There are two nodes in this area , Namely (2,3) and (5,4), By calculation (2,4.5) The distance to these two points , Come to (2,3) The closest , that (2,3) Is the nearest point . Then with (2,4.5) For the center of a circle , With (2,4.5) To (2,3) The distance between two points draws a circle for the radius , There are no other nodes in the circle , The description can confirm (2,3) Namely (2,4.5) The nearest neighbor of .
边栏推荐
- Penetration tool environment - Installation of sqlmap
- Wait for the end of the network request in the uniapp Onshow method before executing the subsequent code content
- Penetration tool environment - installing sqli labs in centos7 environment
- Huikan source code -- Huikan app system secondary development source code sharing
- ECSHOP whole site custom URL supports directory type
- Ramda rejects objects with null and empty object values in the data
- An example of using dynamic datalist
- Methods of strings in JS charat(), charcodeat(), fromcharcode(), concat(), indexof(), split(), slice(), substring()
- JS picture switching (simple and practical)
- 微信全文搜索技术优化
猜你喜欢

3+1保障:高可用系统稳定性是如何炼成的?
![Select randomly by weight [prefix and + dichotomy + random target]](/img/84/7f930f55f8006a4bf6e23ef05676ac.png)
Select randomly by weight [prefix and + dichotomy + random target]

How to implement a high-performance load balancing architecture?

为何数据库也云原生了?

Jeecgboot startup popup configuration is still incorrect

ECSHOP video list_ ECSHOP uploading video, video classification, video list playing video function

高性能负载均衡架构如何实现?

Optimal solution for cold start

PPT绘图之AI助力论文图
The drop-down box renders numbers instead of the corresponding text. How to deal with it
随机推荐
Go novice exploration road 1
flutter 收到推送后自动消失问题
Foreach method of array in JS
Three jobs! You can learn this from me (attached with graduation vlog)
Match regular with fixed format beginning and fixed end
yolov5训练使用的负样本图片
Guess Tongyuan B
mysql FIND_ IN_ Set function
ECSHOP product attribute color specification size stock item No. automatic combination
How can we differ LEFT OUTER JOIN vs Left Join [duplicate]
Figure explanation of fiborache sequence
(2) Pyqt5 tutorial -- > using qtdesigner to separate interface code
thinkphp3.2.5 GIF. class. php for php7.4
Matlab simulation of m-sequence
list.replace, str.append
Optimal solution for cold start
Yunfan mall -- Yunfan mall system development source code sharing
Summary of common MySQL database commands (from my own view)
ECSHOP video list_ ECSHOP uploading video, video classification, video list playing video function
Initialize the project using the express framework