当前位置:网站首页>About log traffic monitoring and early warning small project | flask
About log traffic monitoring and early warning small project | flask
2022-06-11 00:53:00 【Smelly Nian】
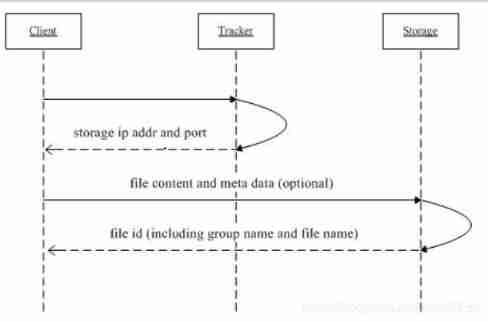
The first half of the architecture has been implemented In the second part

Filebeat Mounted on nginx Inside the machine
Version used :![]()
Nginx The website is just to simulate the environment Generate log
flask: yes python It's famous web frame
It mainly depends on the direction of data packets
Browser developer tools


Web Services are all based on http Agreed
http( Hypertext transfer protocol )(hyper text transfer protocol) The transmission is hypertext ( The hypertext here is the source code ) The source code is transmitted Local operation after local acquisition
http agreement :
1991 Release the first version 0.9 edition only one git command
1996 year , Released http1.0 edition Introduced post head Wait for the order
1997 year Released http1.1 Introduced persistent connections ( It is still the mainstream version )
2015 year http/2.0 Release Introduced ( Multiplexing , Binary is introduced In the form of frames and streams )-- The transmission rate will be much faster
Web Processing flow of application :
- Browser send http request
- The server receives the request , Generate a HTML file
- Server handle HTML Document as HTTP Respond to body Send data to browser
- Browser received HTTP Respond to , from HTTP body The inside out HTML Document and display
The server Accept the request Send a response
Nginx Only static pages can be provided So it is often used as a reverse proxy
wsgi:web server gateway interface
yes python Defined by language web A simple and general interface specification between server and program framework
gunicorn uwsgi ( These two are the same as nginx A level one )
Specialized python web Server to help you deal with the original tcp Connect ,http Original request and response
The underlying code has a special server implementation


finish writing sth. flask To give gunicorn To run (gunicorn drive flask function )
The user requests access directly gunicorn
Inside nginx The cluster is specialized in reverse proxy Load balancing


flask be based on jinja Module and werkzeug WSGI Suite development
flask Characteristics of :
flask very “ light ”,“ Microframets ”
flask More flexible free High scalability
flask Easy entry
flask Very suitable api( Application program interface ) Development
flask and django Is not the same :
django It is a relatively heavyweight framework , Will automatically match things , But we have to follow its ( Even the front end has a general framework You don't need to write your own front end )
Django Many have been written , But customizing what you want is cumbersome , It's too redundant , It's easy to make mistakes , But it's easy to operate ,flask You can customize the functions you want , Very flexible ,Django You can render templates , The front-end province writes
Assembled desktop (Flask) With a laptop (Django) The difference between
Django Feed the rice to your mouth flask Start by buying vegetables and make your own
Python common web frame :
Tornado,flask,twisted,django( What we use more is flask and django)
front end : The content of the page you can see Interacting with users
The architecture of the browser is B(brower browser )/S( The server ) framework : Use the browser to drive the page display
For convenience We usually separate the front and rear ends :

So our project is mainly about the separation of front and back ends of applications
pip and pip3 No difference between
path Just one of the environment variables There are many environment variables
A virtual environment :
Virtual environment a project a room
Keep the environment of the project clean They don't influence each other
Create a new virtual environment :

The code line creates the virtual environment
1.(python call venv Module to create a virtual environment )python -m venv Virtual environment name
![]()
- Script Is the script
![]()
It contains the of virtual environment pip and python And we use the system pip In the future, we need to use the virtual environment pip and python
3. Load virtual environment
Enter this command every time you enter the virtual environment Can be used pip and python
![]()
(source Commands are also called “ Click command ”, It's a dot symbol (.), yes bash The internal order of )


Role of virtual environment ?
Project depends on Library version environment isolation , Keep the project clean
pip freeze: Displays the installed libraries and versions of this program
requirements.txt file ( It is commonly called this name ):
It generally stores which libraries need to be installed for the normal operation of the current project And the corresponding library version
such When the project moves Directly in accordance with the requirements.txt Install the version and library specified in the file
Generate reqirements.txt:
Every project has requirements.txt Put the installed library into this file
![]()
according to requirements.txt File to install :
When our project moves to a new environment You can directly install the things in the dependency file
![]()
If this is not in a virtual environment , But in a global context , that requirements.txt There will be many useless libraries in the library , So virtual environment is to ensure purity
Create the first one flask project :
from flask import Flask
# As a program that runs directly __name__==‘__main__’
# To instantiate an object, you need to give a string , Usually use __name__ Value
# This name will serve as flask Identification of the core object
# The core object is through flask Examples come out of app
app=Flask(__name__) (Flask It's a class , This step is to instantiate )
app.run() (flask Bring a small web The server , This is only used in test development environments , Don't use it in a production environment )
stay pycharm Running is OK But this is a small one that comes with it web server Environmental Science Cannot be used in production environment ( So we have to use gunicate replace )

Flask In the definition :

Parameter name :( Desired type )
# The first function page ( I wrote an interface )
from flask import Flask
app=Flask(__name__)
# You need to use the decorator to add functions
@app.route("/index/") ( If you are visiting /index/ route Let the decorated function handle it )
def index():
return '{"key1":1,"key2":2}'
app.run()
Direct access does not Add one index Yes

We type in 127.0.0.1:5000 The default access is the root (/)
127.0.0.1 - - [19/Jan/2022 17:10:25] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 404 –
http://127.0.0.1:5000/index/ This is equivalent to writing an interface , Interfaces generally return json Format string , This returns a dictionary like json Interface
You can also add routes to it without decorators , The following can achieve the same effect
def index2():
return "gogogo"
app.add_url_rule("/",view_func=index2)
app.add_url_rule():
stay flask Inside , Each core object maintains two tables One is for url_map One is for view_functions
url_map: The maintenance is url and endpoint The mapping relation of
view_functions: The maintenance is endpoint and function The mapping relation of

endpoint If there is no obvious definition , Will use the decorated function name as endpoint

endpoint Is to put url and function Decoupled middle layer
endpoint stay view_function The table needs to be globally unique ( Which corresponds to the only one function), The function name can be repeated Because it corresponds to endpoint only
A function can also correspond to multiple endpoint
however endpoint It can correspond to different routes
@app.route("/index/") The bottom layer of this is actually called app.add_url_rule()
introduce endpoint url and function decoupling
File splitting
![]()
Set to debug After debugging mode ,
There is no need to restart the application for code modification , It will reload
There is an error , The log output will be more detailed
127.0.0.1 Local return address , There are... On every machine
![]()
Not set up host When The default is 127.0.0.1 No one else can access
and host=127.168.0.25 As long as you can follow 127.168.0.25 All correspondents can visit the website I wrote
![]()
Ports can also be changed If not set The default is 5000
Project split : Building big projects
Models are generally related to databases
View : Is the data returned to the user

The configuration file : Parts that the user is allowed to modify Give users a choice
A configuration file is a file that stores variables Configuration items inside ( Variable ) Capitalization ( Because what is defined in the source code is to judge whether it is capitalized If it is in upper case, it can be read out )

![]()
Generally, the source program startup will be packaged into a script So modify the configuration file directly You can start it directly
The configuration file should be consistent with app Combining core objects
# Load profile Inside pass python Module path
app.config.from_object('config.setting') ( This module will be imported here )
app.config It is essentially a dictionary
from_object() It is a new function added on this basis
This line of code is to put setting The attributes in the module are put into app.config In this dictionary
So don't import setting 了
Once the code is written :

All the loaded configurations are placed in app.config In the dictionary
The data generated by the test is dirty data Can't sync to the line Therefore, the configuration of the test environment is different from that of the online environment

Both test and online environments have /opt/config
So we put each environmental opt Inside config Are assigned to environment variables FLASK_CONF
![]()
All programs start with the main program
server Inside app Is the core object of the whole program
So what we need for the view app Namely server Inside app
So we need to view Import from the program app
stay server Inside ( The context here represents app Where is the memory )

stay app Inside

And again server.py It is necessary to introduce router Inside view( It must be pushed to the stack before it can be imported view)

Context is expressed in cpu The status saved during operation is the above The state after coming out is called the following
Flask The core object of this project is app Is the main content
The blueprint :blueprint ( Make routing management more modular )( This is equivalent to the routing view and app Middleware between )

Tied to the blueprint No longer need to write all paths all the time Never mind endpoint 了

Then the blueprint should be consistent with app combination :
So in router New in __init__.py

(init_app It doesn't have to be app It can also be current_app As long as it means the current app Just fine )
And app The relevant ones are put in app.py Inside

such server Import inside study.py No need to wait
Import represents execution
The blueprint will help you to revise endpoint
# Blueprint and endpoint
# After registration through blueprint study_bp==>endpoint It becomes study.index


postman: Tools that simulate client interface requests Is used to do testing software
see preview: It is displayed in the form of web pages
request object :


Tell the back end I gave you username and passwd
And then up there url Will automatically help fill in the information we fill in This is a url The ginseng :![]()
url Transmission parameter information :url ? Parameters 1& Parameters 2& Parameters 3
Get the interface

Everything related to the request is put in flask.request Inside
request object : Everything in the request is request In the object , For example, you requested url Parameters cookies http Header field
request Several common properties :
request.path Get the requested resource path -str type
request.args obtain url In the parameters of the – Dictionary type
request.form obtain body Form parameters carried in – Dictionary type
request.json Get what's passed on json Format data , And convert to object
request.method Get the requested method
request.url Get the requested url
Our parameters can be placed in url Inside It can also be placed in body In the data (form There is one form Forms )
Put it in url The data is obtained by request.args[]

Pass... Through form parameters :
The data obtained is request.form[]
For setting post request And the default is get request So we need to set the method




http Methods :
methods:
increase post
Delete delete
Change put
check get get This method browser is not allowed to have body
Many of them are conventional things
It can also be used. jison Format (request Object will do the following to the string json Handle , Turn to object )


You can also construct dynamic url To get the parameters : The view function needs to define relevant formal parameters
If there is no method defined now It's used get Method

We can also use put Method , Even support multiple methods
![]()


Structural dynamics url Is to put the parameter directly in url Inside adopt url Pass reference to ? Compare the parameters with url separate
Flask You can also return to the web page
How to edit a page ?
static Put pictures
A render function is required to return to the page render_template
Page rendering is the dynamic generation of web pages
Rendering is dynamic generation html
Jinja The grammar of :
![]() A variable name in two parentheses means that such a variable or expression needs to be passed
A variable name in two parentheses means that such a variable or expression needs to be passed
![]()
![]()
Reverse parsing url: there static It means endpoint, Not in the catalog static
url_for():( Reverse resolution ) The view function adopt endpoint Look for url
These things are all based on core objects app, To take effect ( Because the running time is app.run())
![]()
and flask The bottom layer specifies a static picture folder called “static” html Folder name “templates”
Templates and data are combined to form pages
边栏推荐
- [network counting] 1.4 network delay, packet loss and throughput
- The JVM determines whether an object can be recycled
- 阻塞隊列 — DelayedWorkQueue源碼分析
- 海贼oj#146.字符串
- 对象作为点(Objects as Points) 个人总结
- Dynamic programming classical topic triangle shortest path
- 【无标题】
- SLAM卡尔曼滤波&&非线性优化
- The mystery of number idempotent and perfect square
- compiler explorer
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
[network counting] 1.4 network delay, packet loss and throughput
[go language learning] - Concurrent Programming
[network planning] 2.4 DNS: directory service of the Internet
非重叠矩形中的随机点
What are absolute and relative paths, and what are their advantages and disadvantages?
阻塞隊列 — DelayedWorkQueue源碼分析
如何在office2016(word2016)中安装mathtype6.9及相关问题解决方案
亿级搜索系统(优酷视频搜索)的基石,如何保障实时数据质量?v2020
On the quality assurance system of youzan search V2021
市值215亿,这个四川80后会让电视机成为历史?
Dual wing layout
With a market value of 21.5 billion yuan, will the post-80s generation in Sichuan make TV history?
twelve billion three hundred and twenty-four million two hundred and forty-three thousand two hundred and forty-two
Detailed decomposition of the shortest path problem in Figure
333333
Ts+fetch to upload selected files
UUID quick explanation
[network planning] 1.5 seven layer network model and five layer network model
qt程序插件报错plugin xcb
图的最短路径问题 详细分解版

![[untitled] test](/img/6c/df2ebb3e39d1e47b8dd74cfdddbb06.gif)