当前位置:网站首页>Gbase 8C - SQL reference 6 SQL syntax (4)
Gbase 8C - SQL reference 6 SQL syntax (4)
2022-07-27 05:56:00 【aisirea】
Function description
Modify parameters of type .
Grammar format
ALTER TYPE name action [, ... ]
ALTER TYPE name OWNER TO { new_owner | CURRENT_USER | SESSION_USER }
ALTER TYPE name RENAME ATTRIBUTE attribute_name TO new_attribute_name [ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]
ALTER TYPE name RENAME TO new_name
ALTER TYPE name SET SCHEMA new_schema
ALTER TYPE name ADD VALUE [ IF NOT EXISTS ] new_enum_value [ { BEFORE | AFTER } neighbor_enum_value ]
ALTER TYPE name RENAME VALUE existing_enum_value TO new_enum_value
here action Is one of the following :
ADD ATTRIBUTE attribute_name data_type [ COLLATE collation ] [ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]
DROP ATTRIBUTE [ IF EXISTS ] attribute_name [ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]
ALTER ATTRIBUTE attribute_name [ SET DATA ] TYPE data_type [ COLLATE collation ] [ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]
Parameter description
- name: The name of the existing type that needs to be modified , Can be modified by patterns ;
- new_name: New name of this type ;
- new_owner: User name of the new owner ;
- new_schema: New mode of this type ;
- attribute_name: To add 、 Name of the changed or deleted attribute ;
- new_attribute_name: The new name of the attribute to be renamed ;
- data_type: The data type of the attribute to be added , Or the new type name of the attribute to be changed ;
- new_enum_value: Enumeration type new tag value , Need to be quoted in quotation marks ;
- neighbor_enum_value: An existing enumeration tag value , The new value should be added immediately before or after the enumeration value ;
- existing_enum_value: Existing enumeration value to rename , Need to be quoted in quotation marks ;
- CASCADE: Automatic cascading updates require updating types, associated records, and child tables that inherit them ;
- RESTRICT: If the type of linkage update is the associated record of the updated type , Then refuse to update , This is the default option ;
matters needing attention
Use ALTER TYPE Must be the owner of this type .
Example
ALTER TYPE compfoo RENAME TO g_compfoo;
ALTER TYPE
Grammar compatible
ALTER TYPE Adding and deleting are SQL Belong to SQL standard , Other parameters are PostgreSQL Expand .
Related to the grammar
Function description
Modify the attributes of database users .
Grammar format
ALTER USER role_specification [ WITH ] option [ ... ]
among option It can be :
SUPERUSER | NOSUPERUSER
| CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB
| CREATEROLE | NOCREATEROLE
| INHERIT | NOINHERIT
| LOGIN | NOLOGIN
| REPLICATION | NOREPLICATION
| BYPASSRLS | NOBYPASSRLS
| CONNECTION LIMIT connlimit
| [ ENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'password'
| VALID UNTIL 'timestamp'
ALTER USER name RENAME TO new_name
ALTER USER { role_specification | ALL } [ IN DATABASE database_name ] SET configuration_parameter { TO | = } { value | DEFAULT }
ALTER USER { role_specification | ALL } [ IN DATABASE database_name ] SET configuration_parameter FROM CURRENT
ALTER USER { role_specification | ALL } [ IN DATABASE database_name ] RESET configuration_parameter
ALTER USER { role_specification | ALL } [ IN DATABASE database_name ] RESET ALL
among role_specification It can be :
role_name
| CURRENT_USER
| SESSION_USER
matters needing attention
ALTER USER Now it is ALTER ROLE An alias for . See ALTER ROLE.
Grammar compatible
ALTER USER Sentence is a kind of PostgreSQL Expand .
Related to the grammar
CREATE USER, DROP USER, ALTER ROLE
Function description
Change various auxiliary properties of the view .
Grammar format
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name SET DEFAULT expression
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name ALTER [ COLUMN ] column_name DROP DEFAULT
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name OWNER TO { new_owner | CURRENT_USER | SESSION_USER }
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name RENAME TO new_name
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name SET SCHEMA new_schema
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name SET ( view_option_name [= view_option_value] [, ... ] )
ALTER VIEW [ IF EXISTS ] name RESET ( view_option_name [, ... ] )
Parameter description
- name: Existing view name , Can be decorated with patterns ;
- IF EXISTS: If the view does not exist, no error will be reported , Just prompt ;
- SET/DROP DEFAULT: Set or delete the default value of a column ;
- new_owner: User name of the new owner of the view ;
- new_name: New name of the view ;
- new_schema: New mode of view ;
- SET ( view_option_name [= view_option_value] [, ... ] ) | RESET ( view_option_name [, ... ] ): Specify an optional parameter for the view , Parameters can be chosen :
- check_option (string): Change the check options of the view , The optional value is local perhaps cascaded;
- security_barrier (boolean): Specify view row level security ;
matters needing attention
To use ALTER VIEW Must be the owner of this view .
To change the mode of the view , Users must have new models CREATE jurisdiction .
To change the owner of the view , The user must be a direct or indirect member of the new role , And this role must have view mode CREATE jurisdiction .
The administrator user can change the ownership of any view .
Example
ALTER VIEW g_view RENAME TO gc_view;
ALTER VIEW
Grammar compatible
ALTER VIEW It's a kind of PostgreSQL Of SQL Standard extension .
Related to the grammar
Function description
It is used to collect statistical information related to the contents of common tables in the database .
Grammar format
ANALYZE [ VERBOSE ] [ table_name [ ( column_name [, ...] ) ] ]
Parameter description
- VERBOSE: Enable the display of progress information ;
- table_name: The table name of the specific table that needs to be analyzed ( May bring the mode name ), If omitted , All tables in the database ( Except external table ) Analyze ;
- column_name: You need to analyze the column names of specific columns , Default to all columns .
matters needing attention
If no parameter is specified ,ANALYZE It will analyze each table and partition table in the current database .
Example
ANALYZE VERBOSE orders;
INFO: analyzing "public.orders" inheritance tree
INFO: analyzing "public.orders_history"
INFO: analyzing "public.orders_202003"
INFO: analyzing "public.orders_202004"
ANALYZE
Grammar compatible
SQL There is no in the standard ANALYZE sentence .
Related to the grammar
Function description
BEGIN Used to start a transaction .
Grammar format
BEGIN [ WORK | TRANSACTION ] [ transaction_mode [, ...] ]
among transaction_mode Is one of the following :
ISOLATION LEVEL { SERIALIZABLE | REPEATABLE READ | READ COMMITTED | READ UNCOMMITTED }
READ WRITE | READ ONLY
[ NOT ] DEFERRABLE
Parameter description
- WORK | TRANSACTION: Optional keywords , It does nothing but increase readability .
For the meanings of other parameters, please refer to SET TRANSACTION.
matters needing attention
START TRANSACTION With and BEGIN Same function .
Use COMMIT perhaps ROLLBACK To terminate a transaction block .
Issued when already in a transaction block BEGIN Will trigger a warning , At this time, the transaction status will not be affected . To nest transactions in a transaction block , You can use a savepoint (SAVEPOINT).
Due to backward compatibility , Successive transaction_modes The comma between can be omitted .
Example
Start a transaction :
BEGIN;
Grammar compatible
BEGIN yes PostgreSQL Language extension , Equivalent to SQL The standard START TRANSACTION.
Related to the grammar
COMMIT, ROLLBACK, END, START TRANSACTION, SAVEPOINT
Function description
checkpoint (CHECKPOINT) Is a point in the transaction log , All data files are updated at this point to reflect the information in the log , All data files will be flushed to disk .
Set transaction log checkpoints . Pre written logs (WAL) By default, a checkpoint is placed in the transaction log at intervals .
Grammar format
CHECKPOINT
matters needing attention
Only system administrators can call CHECKPOINT.
CHECKPOINT In the local CN And all DN Execution on node .
Example
CHECKPOINT;
CHECKPOINT
Grammar compatible
CHECKPOINT Command is a kind of PostgreSQL Language extension .
Function description
When there are exceptions in the database , Used to clean up database connections .
Grammar format
CLEAN CONNECTION TO { COORDINATOR ( nodename [, ... ] ) | NODE ( nodename [, ... ] ) | ALL {FORCE} }
[ FOR DATABASE dbname ]
[ TO USER username ]
Parameter description
- FORCE: Only when the node list is TO ALL You can specify , If this parameter is specified , Before cleaning up the connection, it will check whether the database is accessed by other session connections , This parameter is mainly used for DROP DATABASE Previous connection access check , If other session connections are found , Will report an error and stop deleting the database ;
- dbname: Delete the connection on the specified database , If not specified, delete the connection of all databases ;
- username: Delete the connection on the specified user , If not specified, delete all users' connections ;
- nodename: Delete the connection on the specified node , Three scenarios :
- Delete the specified CN Connections on ;
- Delete the specified DN When connecting on , You need to specify the DN Group name ;
- Delete connections on all nodes , Include CN and DN.
Example
CLEAN CONNECTION TO ALL FORCE FOR DATABASE gbase TO USER gbase1;
CLEAN CONNECTION
CLEAN CONNECTION TO NODE (dn2) TO USER gbase1;
CLEAN CONNECTION
Grammar compatible
CLEAN CONNECTION Do not conform to the SQL standard
Function description
Release all resources associated with a cursor .
Grammar format
CLOSE { name | ALL }
matters needing attention
When creating cursor transactions COMMIT or ROLLBACK After the termination , Every open cursor that cannot be held is implicitly closed .
When the transaction that creates the cursor passes ROLLBACK After you quit , Every cursor that can be held will be closed implicitly .
GBase 8c No cursor is explicitly opened OPEN sentence , Because a cursor is in use CURSOR It opens when the command is defined . You can query the system view pg_cursors See all available cursors .
Grammar compatible
CLOSE Completely obey SQL standard .CLOSE ALL It's a kind of PostgreSQL Expand .
Related to the grammar
Function description
Cluster and sort the table according to an index .
Grammar format
CLUSTER [VERBOSE] table_name [ USING index_name ]
CLUSTER [VERBOSE]
Parameter description
- table_name: The name of the table , Can be modified by patterns ;
- index_name: The index name ;
- VERBOSE: Print progress report when clustering the table .
matters needing attention
Only line deposit B-tree Index support CLUSTER operation .
If the user just randomly accesses the rows in the table , Then the actual storage order of the data in the table is irrelevant . however , If some data is accessed more than others , And there is an index that groups these data , So it's going to use CLUSTER Will help . If you request the value of a certain index range from a table , Or one index value corresponds to multiple rows ,CLUSTER It will also help to apply , Because if the index identifies the storage page where the first matching row is located , All other rows may already be in the same storage page , This saves disk access time , Speed up queries .
During clustering , The system first creates a temporary copy of the table established according to the index order . It also creates a temporary copy of each index on the table . therefore , You need enough free space on the disk , At least the sum of table size and index size .
because CLUSTER Memory gathers information , You can cluster tables manually for the first time , Then set a similar VACUUM Time for , In this way, the table can be automatically clustered periodically .
Because the optimizer records statistics about the sorting of tables , Therefore, it is recommended to run on the newly clustered table ANALYZE. otherwise , The optimizer may choose poor Query Planning .
CLUSTER It is not allowed to execute .
CLUSTER Will also be performed on all data nodes .
Example
CLUSTER customer USING gcustomer_idx;
CLUSTER
Grammar compatible
stay SQL There is no in the standard CLUSTER sentence .
Function description
Define or modify the annotation of an object .
Grammar format
COMMENT ON
{
ACCESS METHOD object_name |
AGGREGATE aggregate_name ( aggregate_signature ) |
CAST (source_type AS target_type) |
COLLATION object_name |
COLUMN relation_name.column_name |
CONSTRAINT constraint_name ON table_name |
CONSTRAINT constraint_name ON DOMAIN domain_name |
CONVERSION object_name |
DATABASE object_name |
DOMAIN object_name |
EXTENSION object_name |
EVENT TRIGGER object_name |
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER object_name |
FOREIGN TABLE object_name |
FUNCTION function_name ( [ [ argmode ] [ argname ] argtype [, ...] ] ) |
INDEX object_name |
LARGE OBJECT large_object_oid |
MATERIALIZED VIEW object_name |
OPERATOR operator_name (left_type, right_type) |
OPERATOR CLASS object_name USING index_method |
OPERATOR FAMILY object_name USING index_method |
POLICY policy_name ON table_name |
[ PROCEDURAL ] LANGUAGE object_name |
ROLE object_name |
RULE rule_name ON table_name |
SCHEMA object_name |
SEQUENCE object_name |
SERVER object_name |
TABLE object_name |
TABLESPACE object_name |
TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION object_name |
TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY object_name |
TEXT SEARCH PARSER object_name |
TEXT SEARCH TEMPLATE object_name |
TRANSFORM FOR type_name LANGUAGE lang_name |
TRIGGER trigger_name ON table_name |
TYPE object_name |
VIEW object_name
} IS 'text'
ACCESS METHOD object_name |
AGGREGATE aggregate_name ( aggregate_signature ) |
CAST (source_type AS target_type) |
COLLATION object_name |
COLUMN relation_name.column_name |
CONSTRAINT constraint_name ON table_name |
CONSTRAINT constraint_name ON DOMAIN domain_name |
CONVERSION object_name |
DATABASE object_name |
DOMAIN object_name |
EXTENSION object_name |
EVENT TRIGGER object_name |
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER object_name |
FOREIGN TABLE object_name |
FUNCTION function_name [ ( [ [ argmode ] [ argname ] argtype [, ...] ] ) ] |
INDEX object_name |
LARGE OBJECT large_object_oid |
MATERIALIZED VIEW object_name |
OPERATOR operator_name (left_type, right_type) |
OPERATOR CLASS object_name USING index_method |
OPERATOR FAMILY object_name USING index_method |
POLICY policy_name ON table_name |
[ PROCEDURAL ] LANGUAGE object_name |
PUBLICATION object_name |
ROLE object_name |
RULE rule_name ON table_name |
SCHEMA object_name |
SEQUENCE object_name |
SERVER object_name |
STATISTICS object_name |
SUBSCRIPTION object_name |
TABLE object_name |
TABLESPACE object_name |
TEXT SEARCH CONFIGURATION object_name |
TEXT SEARCH DICTIONARY object_name |
TEXT SEARCH PARSER object_name |
TEXT SEARCH TEMPLATE object_name |
TRANSFORM FOR type_name LANGUAGE lang_name |
TRIGGER trigger_name ON table_name |
TYPE object_name |
VIEW object_name
} IS 'text'
among aggregate_signature yes :
* |
[ argmode ] [ argname ] argtype [ , ... ] |
[ [ argmode ] [ argname ] argtype [ , ... ] ] ORDER BY [ argmode ] [ argname ] argtype [ , ... ]
Parameter description
- object_name: Object name ;
- relation_name.column_name: Definition / Modify the column name of the comment , Prefix with table name ;
- aggregate_name: The name of the aggregate function ;
- constraint_name: Definition / Modify the name of the annotated table constraint ;
- function_name: Definition / Modify the function name of the annotation ;
- operator_name: Operator name ;
- policy_name: Security policy name ;
- rule_name: Rule name ;
- trigger_name: Trigger Name .
- table_name: The name of the table
- domain_name: When in a constraint 、 trigger 、 When creating a comment on a rule or policy , These parameters specify the name of the table or field on which the object is defined
- source_type: Source data type of type conversion ;
- target_type: Target data type of type conversion ;
- argmode: Mode of function parameters , Optional parameters :IN、 OUT、INOUT perhaps VARIADIC, The default is IN;
- argname: The name of the function parameter ;
- argtype: The type of function argument ;
- large_object_oid: Definition / Modify the annotation of large objects OID value ;
- left_type | right_type: Data type of operation parameter , Can be modified by patterns , When the pre or post operator does not exist , Can increase NONE Options ;
- PROCEDURAL: Noise words ;
- type_name: The name of the data type to be converted ;
- lang_name: The name of the language to be converted ;
- text: notes .
matters needing attention
Currently, there is no security mechanism for annotation browsing : Any user connected to a database can see all the comments of the database object . Shared objects ( Like databases 、 role 、 Table space ) Comments for are stored globally , Any user connected to any database can see them . therefore , Do not store sensitive information related to security in comments .
Example
COMMENT ON TABLE customer IS 'This is my customer.';
COMMENT
Grammar compatible
SQL There is no in the standard COMMENT command .
边栏推荐
- GBASE 8C——SQL参考6 sql语法(10)
- Seektiger's okaleido has a big move. Will the STI of ecological pass break out?
- Which futures company has a low handling fee and a high refund?
- 6.维度变换和Broadcasting
- Rating and inquiry details of futures companies
- If you encounter oom online, how to solve it?
- Cap principle
- Minio fragment upload lifting fragment size limit - chunk size must be greater than 5242880
- MySQL limit分页查询优化实践
- Activity之应用进程创建流程简析
猜你喜欢
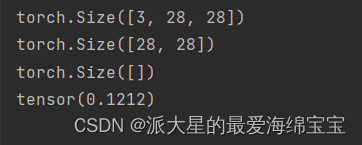
5.索引和切片
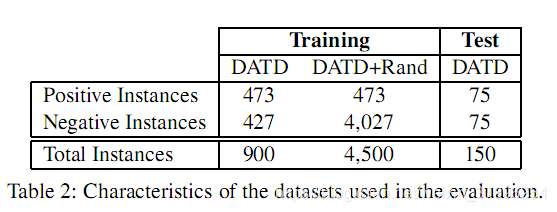
Day 7. Towards Preemptive Detection of Depression and Anxiety in Twitter
Count the quantity in parallel after MySQL grouping

Choose a qualified futures company to open an account

4.张量数据类型和创建Tensor

16.过拟合欠拟合
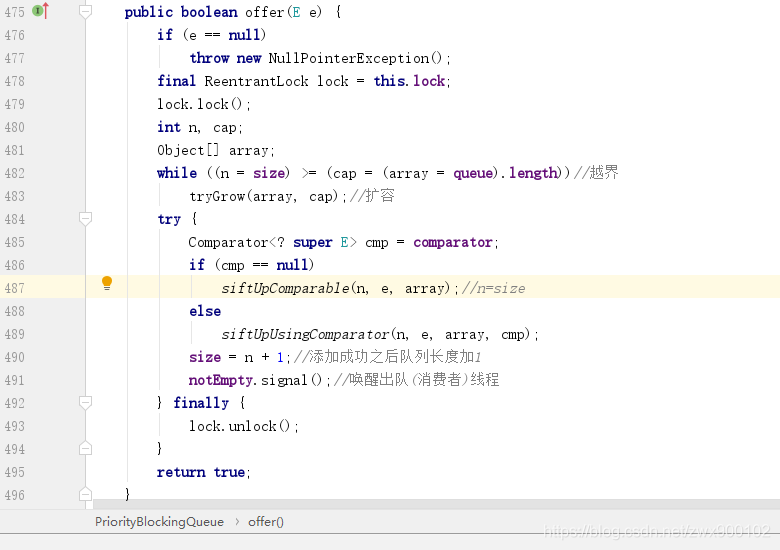
【并发编程系列9】阻塞队列之PriorityBlockingQueue,DelayQueue原理分析

Personal collection code cannot be used for business collection

Graph node deployment

Do you really know session and cookies?
随机推荐
你真的了解 Session 和 Cookie 吗?
Move protocol launched a beta version, and you can "0" participate in p2e
ES对比两个索引的数据差
How to open a general commodity futures account
Which futures company do you go to and how do you open an account?
php 定义数组使用逗号,
How can seektiger go against the cold air in the market?
Seektiger will launch STI fusion mining function to obtain Oka pass
【好文种草】根域名的知识 - 阮一峰的网络日志
If you encounter oom online, how to solve it?
Day 3. Suicidal ideation and behavior in institutions of higher learning: A latent class analysis
Social media user level psychological stress detection based on deep neural network
GBASE 8C——SQL参考6 sql语法(10)
Mysql5.7版本如何实现主从同步
Minimum handling charges and margins for futures companies
Day 4.Social Data Sentiment Analysis: Detection of Adolescent Depression Signals
andorid检测GPU呈现速度和过度绘制
Day14. 用可解释机器学习方法鉴别肠结核和克罗恩病
Docker部署redis单机版本 - 修改redis密码和持久化方式
Graph node deployment