当前位置:网站首页>Graph theory (tree diameter)
Graph theory (tree diameter)
2022-06-23 23:26:00 【D αī s ч】
One 、 Basics
The distance between the two farthest nodes in a tree is called the diameter of the tree , The path connecting these two points is called the longest chain of the tree ( Also called diameter )
Two 、 Twice traversal to find the diameter
1、 Starting from any node , adopt bfs perhaps dfs Traverse the tree once , Find the node farthest from the starting point , Write it down as p, This is the diameter end of the tree
2、 From the node p set out , adopt bfs and dfs Traverse the tree again , Work out with p The farthest node , Write it down as q
3、 that p To q The path of is a diameter of the tree , because p It must be the end of the diameter , Otherwise, a longer chain will always be found . In the second step of traversal , You can record the precursor node of each point when it is accessed for the first time , Finally from the q Go back to p The specific scheme of diameter can be obtained
4、 notes : The problem of negative edge weight cannot be solved by searching
int to[maxn << 1], nex[maxn << 1], edge[maxn << 1], head[maxn];
int cnt, n, m, r;
ll dis[maxn], maxd, maxv;
void add(int u, int v, int w)
{
to[++cnt] = v;
edge[cnt] = w;
nex[cnt] = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
}
void dfs(int u, int fa)
{
if (maxd < dis[u])
{
maxd = dis[u];
maxv = u;
}
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = nex[i])
{
int v = to[i];
if (fa == v)
continue;
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i];
dfs(v, u);
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
add(u, v, w);
add(v, u, w);
}
dfs(1, 0);
maxd = 0;
dis[maxv] = 0;
dfs(maxv, 0);
cout << maxd;
}3、 ... and 、 Tree form dp Find the diameter
1、 set up d[x] Represents a slave node x Set out to x Root subtree , The distance of the farthest node that can be reached , namely x The longest chain that goes down , Obviously there is
![d[x]=\underset {1\leq i \leq t}{max}\{d[y_i]+w(x,y_i)]\}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/23/202206232006247781_0.gif)
2、 So we can think about finding each point through x The length of the longest chain f[x], Then the diameter of the whole tree is the largest f[x]. about x Any two nodes of yi,yj, Through the nodes x The length of the longest chain consists of four parts , as follows
![f[x]=\underset {1\leq j<i\leq t}{max}\{d[y_i]+d[y_j]+w(x,y_i)+w(x,y_j)\}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/23/202206232006247781_3.gif)
3、 When child nodes are enumerated to i when ,d[x] Just saved from x Departure direction yi Is the distance of the farthest node that can be reached by the subtree of the root , This distance is ![\underset {1\leq j<i}{max}\{d[y_j]+w(x,y_j)\}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/23/202206232006247781_1.gif) , So let's use
, So let's use ![d[x]+d[y_i]+w(x,y_i)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/23/202206232006247781_4.gif) to update f[x], Reuse
to update f[x], Reuse ![d[y_i]+w(x,y_i)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/23/202206232006247781_2.gif) to update d[x] that will do
to update d[x] that will do
int to[maxn << 1], nex[maxn << 1], edge[maxn << 1], head[maxn];
int vis[maxn];
int cnt, n, m, r;
ll ans = 0, d[maxn];
void add(int u, int v, int w)
{
to[++cnt] = v;
edge[cnt] = w;
nex[cnt] = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
}
void dp(int u)
{
vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = nex[i])
{
int v = to[i];
if (vis[v])
continue;
dp(v);
ans = max(ans, d[u] + d[v] + edge[i]);
d[u] = max(d[u], d[v] + edge[i]);
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
add(u, v, w);
add(v, u, w);
}
dp(1);
cout << ans << '\n';
}边栏推荐
- Practice of issuing vouchers for Tiktok payment of 100000 TPS traffic
- Deserialization - PHP deserialization
- The national post office and other three departments: strengthen the security management of personal information related to postal express delivery, and promote the de identification technology of per
- C#/VB.NET Word转Text
- 国家邮政局等三部门:加强涉邮政快递个人信息安全治理,推行隐私面单、虚拟号码等个人信息去标识化技术
- C WinForm custom progress bar ProgressBar
- 【设计】1359- Umi3 如何实现插件化架构
- AndroidKotlin全面详细类使用语法学习指南
- Data interpretation! Ideal L9 sprints to "sell more than 10000 yuan a month" to grab share from BBA
- 什么是免疫组织化学实验? 免疫组织化学实验
猜你喜欢

Talking about the knowledge of digital transformation

How can wechat video numbers be broadcast live on a PC?
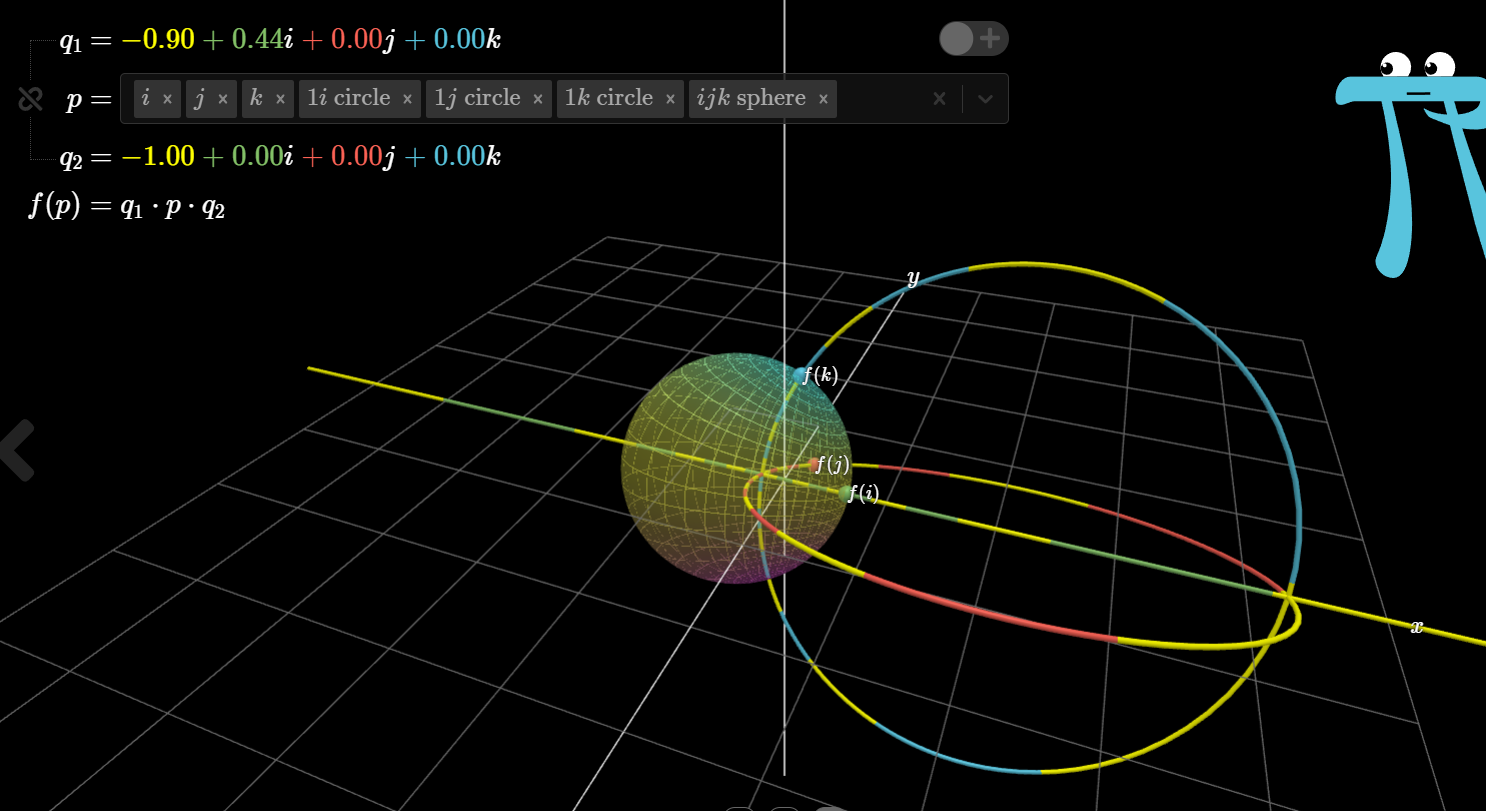
详解四元数
Several cases of index invalidation caused by MySQL
Flutter中的GetX状态管理用起来真的那么香吗?
Androidkotlin comprehensive and detailed class usage grammar learning guide

Bilibili × Blue bridge cloud course | online programming practice competition is new!

CS5213 HDMI转VGA带音频信号输出方案

Cause analysis and Countermeasures for FANUC robot srvo-050 collision detection alarm (available for personal test)
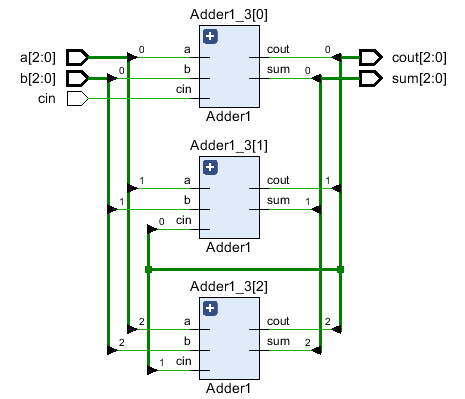
HDLBits-&gt; Circuits-&gt; Arithmetic Circuitd-&gt; 3-bit binary adder
随机推荐
Is the geTx status management in the flutter really so good to use?
2022 cloud consulting technology series storage & CDN special sharing meeting
TDP "spark" plan - the third phase of new recruitment is launched
Giants end up "setting up stalls" and big stalls fall into "bitter battle"
SQL Server common SQL
PHP curl function extension basic usage
迪赛智慧数——柱状图(基本柱状图):2022年父亲节过节的方式
Apache log4j 2 reported high-risk vulnerability, coding teamed up with Tencent to protect software security
Micro build low code tutorial - Application creation
Production of labels for table products
Summary of some indicators for evaluating and selecting the best learning model
2022云顾问技术系列之存储&CDN专场分享会
The 12 SQL optimization schemes summarized by professional "brick moving" old drivers are very practical!
微信视频号如何用 PC 电脑做直播?
C WinForm custom progress bar ProgressBar
The principle of async and await
Urgent! Tencent cloud container security supports the detection of Apache log4j2 vulnerabilities for the first time. It is in free trial
HDLBits-&gt; Circuits-&gt; Arithmetic Circuitd-&gt; 3-bit binary adder
How can manufacturing enterprises go to the cloud?
PostgreSQL怎么创建分区表详解

