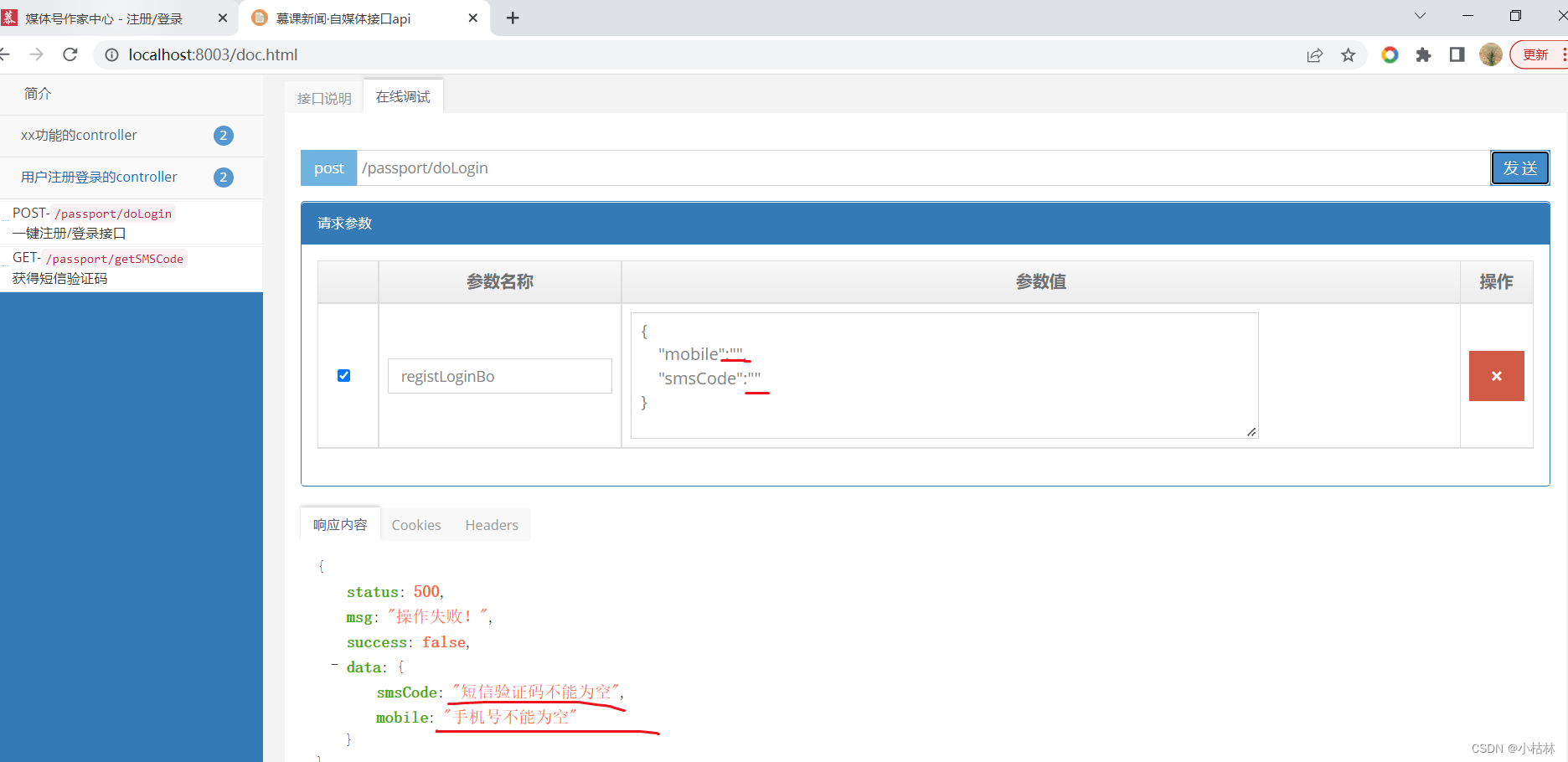
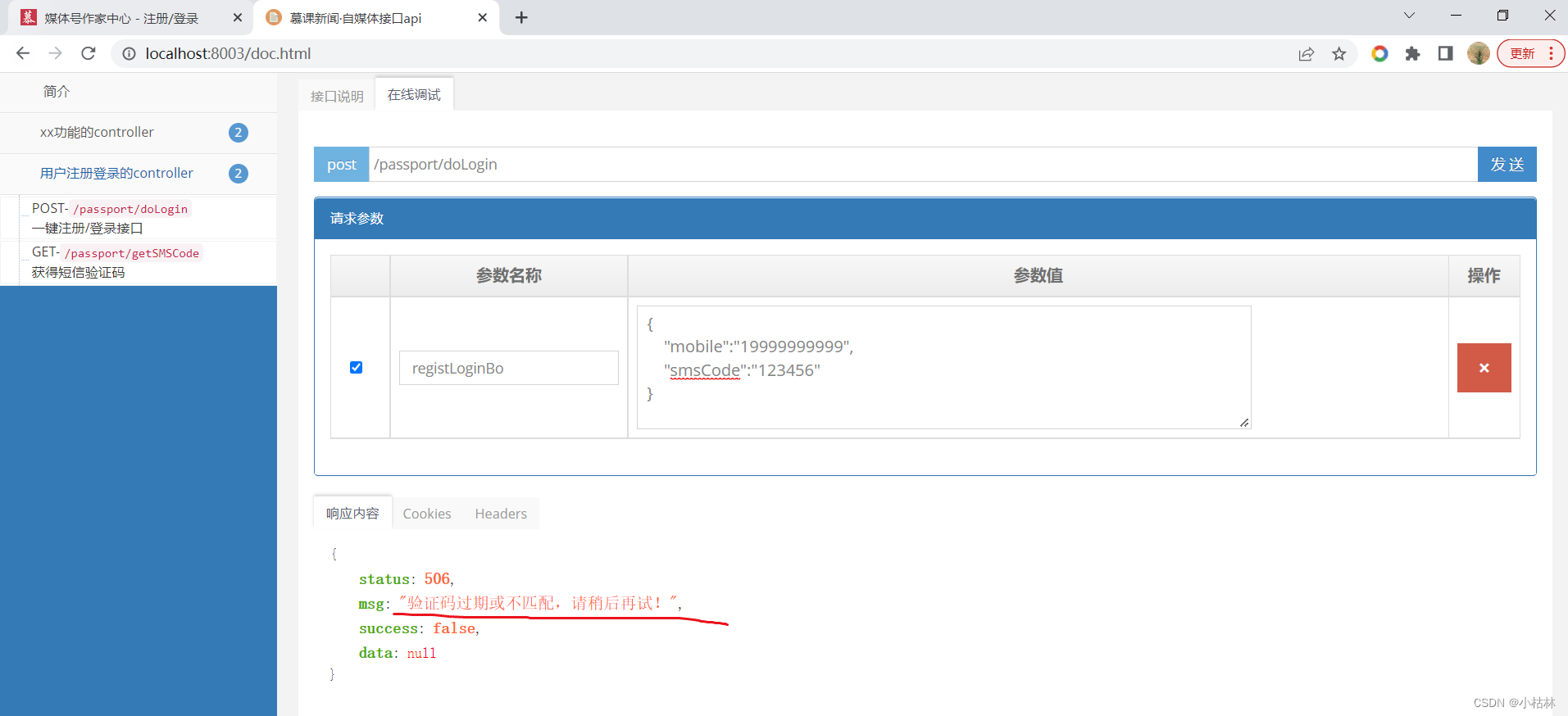
当前位置:网站首页>25: Chapter 3: developing pass service: 8: [registration / login] interface: receiving and verifying "mobile number and verification code" parameters; (it is important to know the application scenario
25: Chapter 3: developing pass service: 8: [registration / login] interface: receiving and verifying "mobile number and verification code" parameters; (it is important to know the application scenario
2022-06-30 20:10:00 【Small withered forest】
explain :
(1) The content of this blog : Start developing 【 One click registration / Sign in 】 Interface ;
● then , The development part of this blog is : The user is clicking 【 One click registration / Sign in 】 After button , The back end will verify 【 Whether the user has entered the mobile phone number or verification code 】、【 Whether the verification code entered by the user matches 】;
(2) The points needing attention in this blog :
● Created BO Entity class , To accept the data submitted by the front-end form ;
● Used 【@Valid annotation 】 Parameter checking ;
● Some common methods , Can be defined in 【imooc-news-dev-service-api】 Interface Engineering BaseController Class ;
● Pay attention to the overall process of parameter verification ;
Catalog
1. stay 【imooc-news-dev-service-api】 Interface Engineering PassportControllerApi Interface , Definition 【 register / Sign in 】 Interface ;
/** * 【 One click registration / Sign in , Interface 】 * @param registLoginBo * @param result * @return */ @ApiOperation(value = " One click registration / Login interface ", notes = " One click registration / Login interface ", httpMethod = "POST") // The request interface on the front end is already “getSMSCode” 了 , So I am writing back-end interface url When , Don't write ; @PostMapping("/doLogin") public GraceJSONResult doLogin(@RequestBody @Valid RegistLoginBo registLoginBo, BindingResult result);explain :
(1) The interface request mode is POST, Because the front end is actually a form , The corresponding form submission generally uses POST The way ;
(2) Generally speaking , When receiving form data , We can use objects to take parameters ;
● So we are 【imooc-news-dev-model】 In model engineering , establish bo package , establish RegistLoginBo Entity class ;(BO It means , Objects passed from the page view layer , It can also be understood as Bussiness Object)( In this project ,BO Entity classes are passed from the front end to the back end ,VO Entity classes are passed from the back end to the front end )
package com.imooc.bo; import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; /** * BO Entity class : Undertaking 【 One click registration / Sign in 】 Interface parameters ; */ public class RegistLoginBo { @NotBlank(message = " Cell phone number cannot be empty ") private String mobile; @NotBlank(message = " SMS verification code cannot be empty ") private String smsCode; public String getMobile() { return mobile; } public void setMobile(String mobile) { this.mobile = mobile; } public String getSmsCode() { return smsCode; } public void setSmsCode(String smsCode) { this.smsCode = smsCode; } @Override public String toString() { return "RegistLoginBo{" + "mobile='" + mobile + '\'' + ", smsCode='" + smsCode + '\'' + '}'; } }● Here we use 【@Valid annotation 】 Parameter checking ; You can refer to 【Spring Boot E-commerce projects 24: Commodity classification module III : Use 【@Valid annotation 】 Check the input parameters ;】;
● among 【@NotNull】 annotation , Only the completely empty case can be verified , If the front-end input a value such as 【" "】 Empty string for , This annotation cannot be verified ;;; and 【@NotBlank】 The annotation can not only check the case that it is completely empty , It can also be verified as 【" "】 Empty string for ;
● then , Remember in the interface RegistLoginBo There are parameters , To use 【@Valid】 annotation , To enable parameter verification ;
● If we use... On entity classes lombok After the comments , You can omit get and set Such method ;;; however , Many companies do not recommend using lombok Of ( Because when it is combined with some third-party libraries , There may be some small bug)
● then , If we use bean When receiving parameters , Need to use 【@RequestBody】 annotation ;;; The main meaning of this note is 【 From the front JSON】 and 【 hinder RegistLoginBo registLoginBo】 Is the corresponding , In order to accept parameters ;
● Once the verification fails , There is an error message , We can go through 【BindingResult result】 To get the corresponding error information ; therefore , Here in the parameter , It has also been introduced. 【BindingResult result】;
● The content here , I've met before N Time , It's not particularly complicated , It's just a little more ;
2. stay 【imooc-news-dev-service-user】 User microservices PassportController Class , Realization 【 register / Sign in 】 Interface ;
/** * 【 One click registration / Sign in , Interface 】 * @param registLoginBo * @param result * @return */ @Override public GraceJSONResult doLogin(@Valid RegistLoginBo registLoginBo, BindingResult result) { //0. Judge BindingResult Whether the error message of validation failure is saved in , If there is , It indicates that there is a problem with the input of the front end ( Mobile phone number or verification code , At least one has not been entered ); // that , We get this error message , And build a GraceJSONResult Unified return object , return ; if (result.hasErrors()) { Map<String, String> map = getErrorsFromBindingResult(result); return GraceJSONResult.errorMap(map); } //1. Check whether the verification code matches ; //1.1 Get the mobile phone number and verification code entered by the user in the front end ; String mobile = registLoginBo.getMobile(); String smsCode = registLoginBo.getSmsCode(); //1.2 According to the mobile phone number entered by the user in the front end , Try to go redis Get the corresponding verification code in ; String redisSMSCode = redisOperator.get(MOBILE_SMSCODE + ":" + mobile); //1.3 If the verification code entered by the front end , stay redis Does not exist in the ( explain : We are not targeting 【 The mobile phone number entered by the user 】 Sent verification code ; // Or after the user receives the verification code text message , After that 30min Before use ,redis The verification code stored in the has expired ), // Or the front-end input verification code and redis The difference between ( explain : The user's verification code is entered incorrectly ); // that , Go back to the corresponding , With error messages GraceJSONResult Unified return object ; // among , Here we use 【org.apache.commons.lang3】 Medium StringUtils The utility class isBlank() Method to judge the null ; if (StringUtils.isBlank(redisSMSCode) || !redisSMSCode.equals(smsCode)) { return GraceJSONResult.errorCustom(ResponseStatusEnum.SMS_CODE_ERROR); } return GraceJSONResult.ok(); }explain :
(1) Judge 【 Parameter checking 】 whether OK;
● We are 【imooc-news-dev-service-api】 Interface Engineering BaseController in , Defines a method getErrorsFromBindingResult(): from BindingResult Extract error information from ;( This method , Later in other places , It will also be used )
(2) Check whether the verification code matches ;
● explain 1;
● explain 2;
3. effect ;
(1) overall situation install Look at the whole project ;
(2) start-up 【imooc-news-dev-service-usr】 Main startup class of user microservice ;
(3) We are 【http://localhost:8003/doc.html】Swagger2 On the page , To test the interface ;
● Failure situation ;
● OK The situation of ;
边栏推荐
- Spark - 一文搞懂 Partitioner
- Advanced skills of testers: a guide to the application of unit test reports
- 如何使用robots.txt及其详解
- 25:第三章:开发通行证服务:8:【注册/登录】接口:接收并校验“手机号和验证码”参数;(重点需要知道【利用redis来暂存数据,获取数据的】的应用场景)(使用到了【@Valid注解】参数校验)
- discuz 论坛提速之删除data/log下的xxx.php文件
- 微信小程序开发实战 云音乐
- exness:流动性系列-流动性清洗和反转、决策区间
- 如何做好测试用例设计
- RP原型资源分享-购物类App
- Cv+deep learning network architecture pytoch recurrence series basenets (backbones) (I)
猜你喜欢

qt中toLocal8Bit和toUtf8()有什么区别

CADD course learning (2) -- target crystal structure information

Why must we move from Devops to bizdevops?

A necessary tool for testing -- postman practical tutorial
Source code analysis of redis ziplist compressed list

Enterprise middle office planning and it architecture microservice transformation

文件包含&条件竞争

Lambda 表达式原理分析学习(2022.06.23)
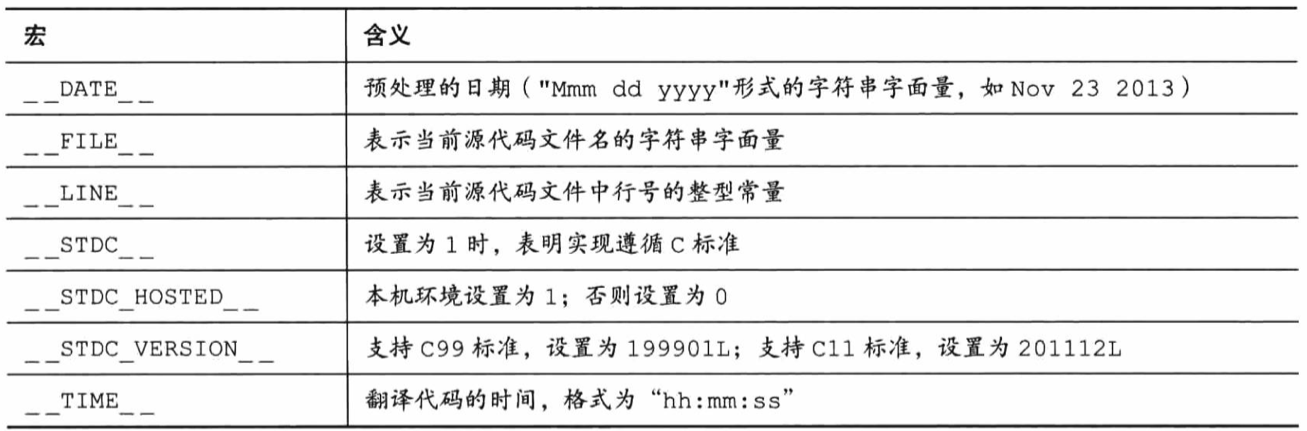
Conditional compilation

RP原型资源分享-购物类App
随机推荐
Exness: liquidity series - liquidity cleaning and reversal, decision interval
PostgreSQL heap堆表 存储引擎实现原理
数据智能——DTCC2022!中国数据库技术大会即将开幕
Ten percent of the time, the tar command can't parse the English bracket "()" when decompressing the file
如何使用robots.txt及其详解
PS2手柄-1「建议收藏」
Smarter! Airiot accelerates the upgrading of energy conservation and emission reduction in the coal industry
为什么数字化转型战略必须包括持续测试?
WeakSet
Application of JDBC in performance test
arthas调试 确定问题工具包
Warmup预热学习率「建议收藏」
CADD课程学习(1)-- 药物设计基础知识
腾讯会议应用市场正式上线,首批入驻超20款应用
Wechat applets - basics takes you to understand the life cycle of applets (2)
yolo 目标检测
更智能!AIRIOT加速煤炭行业节能减排升级
8 - function
Unity 如何拖拉多个组件中的一个
Enterprise middle office planning and it architecture microservice transformation