当前位置:网站首页>【二叉树先导】树的概念和表示方法
【二叉树先导】树的概念和表示方法
2022-07-24 09:55:00 【摆烂的神】
前言
对于大量的数据而言,链表的线性访问时间太慢,不宜使用。本章节将会介绍一种简单的数据结构:树(tree),其大部分操作的运行时间平均为O(logN)。在数据结构中树是非常有用的抽象概念,在本篇中我们将讨论树的基本概念和表示方法,为后续二叉树及高阶搜索树打下基础。
一、树的概念
树形结构和线性结构最大的区别就是:线性结构是一对一的关系,而树是一对多的关系。

形如上图所示,就是一棵一般的树;而很明显我们可以看出:
- 一棵树是n个节点组成的集合,这个集合可以是空集;
- 若非空,则一棵树由称作根(root)的节点 r 和0个或者多个非空子树T1、T2...组成;
- 这些子树中的每一个根都被 根节点 r 的一条有向边(edge)所连接;
- 对于每一棵子树根所连接的节点称作根的孩子(child),而根则是孩子的父亲(parent);
- 没有孩子的节点称为叶子(leaf)。
用类似的定义方法,我们可以把具有相同父节点的节点互相称为兄弟(sibling),对于父亲的兄弟可以称为叔叔(uncle),同样的我们还可以定义爷爷(grandparent)和孙子(grandchild)。

同时我们还要了解一些也很重要的概念:
- 一个节点拥有子树的数量,称之为节点的度(degree)如上图中节点A的度是3而节点B的度是0;
- 其中最大的节点的度,就是树的度;
- 树的深度和高度:深度是从上往下数的、高度是从下往上数的,它们表示都是树的层数,如上图树的深度是3。
二、树的表示法
1、基本存储结构
树的表示法(存储结构)多样,每一种方法都是为了解决某些特定情况下的问题而使用的,不存在绝对方法!
①双亲表示法
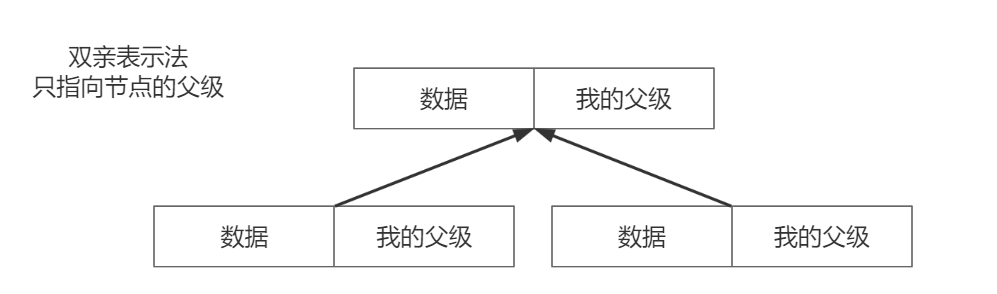
如图所示,双亲表示法就是每个节点通过存储指向父节点去寻找父节点;任何一种算法脱离不开两种书写的方式,一种是顺序存储,一种是链式存储,而实现这个结构我们用顺序存储非常简单(但是链式存储同样可以,还是那句话只要功能实现复杂度差不多就行了)

代码的操作和链表、顺序表操作一样,就不细说了:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//双亲表示法
typedef struct TreeNode
{
int data;
int parent;
}Node;
typedef struct TreeStruct
{
Node* node[5];//顺序结构
int size;//当前的大小
int capacity;//最大容量
}Tree;
//初始化
void init(Tree* tree)
{
tree->size = 0;
tree->capacity = 5;
}
//添加根节点
void addRoot(Tree* tree, int key)
{
Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建新的节点
newnode->data = key;
newnode->parent = -1;
tree->node[tree->size] = newnode;
tree->size++;
}
int findFatherNode(Tree* tree, int parentNode)
{
for (int i = 0; i < tree->size; i++)
{
if (tree->node[i]->data == parentNode)
{
return i;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
}
//添加孩子
void addChild(Tree* tree, int key, int parentNode)
{
if (tree->size == tree->capacity)
{
//满了就提示或者扩容
printf("FULL\n");
}
else
{
//先找有没有这个父节点
int parentIndex = findFatherNode(tree, parentNode);
if (parentIndex == -1)
{
printf("NOT FIND\n");
}
else
{
Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建新的节点
newnode->data = key;
newnode->parent = parentIndex;
tree->node[tree->size] = newnode;
tree->size++;
}
}
}显而易见的,我们通过双亲表示法寻找父节点非常容易,但是没办法寻找兄弟和孩子。而假如现在我们想知道某一节点和它父亲的关系,同时也想知道和兄弟的关系,我们该如何去做呢?这时我们可以再添加一个指针指向节点最近的兄弟的下标就可以了;

(还是那句话:存储结构的设计,侧重什么就加什么,非常灵活)
②孩子表示法

由于我们不知道一个节点可能有几个孩子,显然单独的链式结构或者顺序结构不方便实现,所以我们可以采用数组+链表的形式(这种方法在往后的数据结构中十分常见)
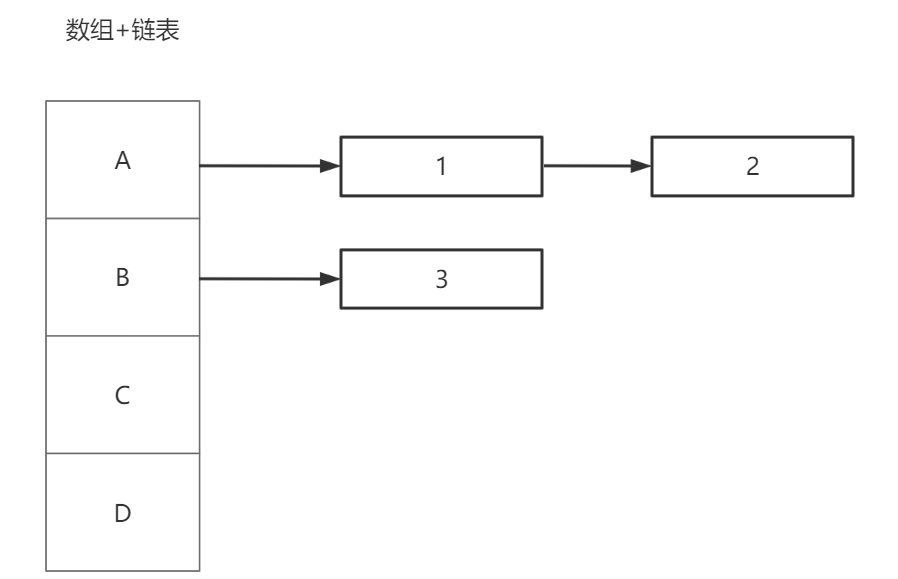
实现起来也很简单:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//孩子表示法
typedef struct LinkList
{
int data;//数据域
struct LinkList* next;//指向下一个的指针
}ListNode;
typedef struct Child
{
int data;//数据域
struct LinkList* first;//指向下一个的指针
}Node;
Node* array[20];
int size;
int capacity;
//创建根节点的过程
void init(int key)
{
size = 0;
capacity = 20;
array[size] = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
array[size]->data = key;
array[size]->first = NULL;
size++;
}
int findParent(int parent)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (array[i]->data == parent)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void creatTree(int parent, int key)
{
//先找有没有父节点
int parentIndex = findParent(parent);
if (parentIndex == -1)
{
printf("NOT FIND\n");
}
else
{
//先将新的节点插入到数组中
if (size == capacity)
{
printf("ERR\n");
}
else
{
array[size] = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
array[size]->data = key;
array[size]->first = NULL;
//再创造链表节点
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newnode->data = parentIndex;
newnode->next = array[parentIndex]->first;
array[parentIndex]->first = newnode;
size++;
}
}
}③ 孩子兄弟表示法
孩子兄弟表示法和在上述的父亲兄弟表示法的思想其实是一样的;

它的便利性在于遍历孩子非常简单,只需要从第一个孩子开始按照链表的方法访问孩子的兄弟就行了。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//孩子兄弟表示法
typedef struct ChildBro
{
int key;//数据域
struct ChildBro* child;//孩纸指针
struct ChildBro* sibling;//兄弟指针
}Node;
void init(Node** root, int key)
{
*root = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
(*root)->key = key;
(*root)->child = NULL;
(*root)->sibling = NULL;
}
Node* findNode(Node* node, int key)
{
static Node* temp = NULL;
if (node->key == key)
{
temp = node;
}
if (node->sibling)
{
findNode(node->sibling, key);
}
if(node->child)
{
findNode(node->child, key);
}
return temp;
}
void insert(Node** root, int key, int parent)
{
//定位节点 递归
Node* temp = findNode(*root, parent);
if (temp == NULL)
{
//没有这个节点
printf("没有这个节点\n");
}
else
{
if (temp->child == NULL)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->key = key;
node->child = NULL;
node->sibling = NULL;
temp->child = node;
}
else
{
temp = temp->child;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->key = key;
node->child = NULL;
node->sibling = temp->sibling;
temp->sibling = node;
}
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = NULL;
init(&root, 0);
insert(&root, 1, 0);
insert(&root, 2, 0);
insert(&root, 3, 2);
insert(&root, 4, 0);
printf("%d %d %d %d %d", root->key, root->child->key, root->child->sibling->sibling->key, root->child->sibling->sibling->child->key, root->child->sibling->key);
return 0;
}2、递归
除此之外我们还需要学习递归:
递归就是自己调用自己的函数,通常使用递归可以把大问题可以实现拆分成重复的小问题;

值得注意的是:我们必须严格定义递归的边界条件即递归函数出口,不然代码就会跑死;
这里实现一个1+2+3+4+5的递归计算:
int add(int n)
{
if(n == 1)
return n;
else
return n + add(n - 1);
}具体的实现过程是下面这样的:

递归占用内存大的主要原因就是运行一个函数并且进入下一个函数时,这个运行的函数其实并没有结束,只是挂起作为等待的状态,为了优化递归占用内存大的问题,出现了尾递归来优化递归操作
int add(int n,int sum)
{
if(n == 1)
return sum;
else
add(n - 1,sum + n);
}尾递归是递归的一种特殊形式,由于在尾部调用,没有需要等待(归)的过程,所以进入下一个函数时,这个运行的函数就会结束,于是不会有挂起的函数占用内存。
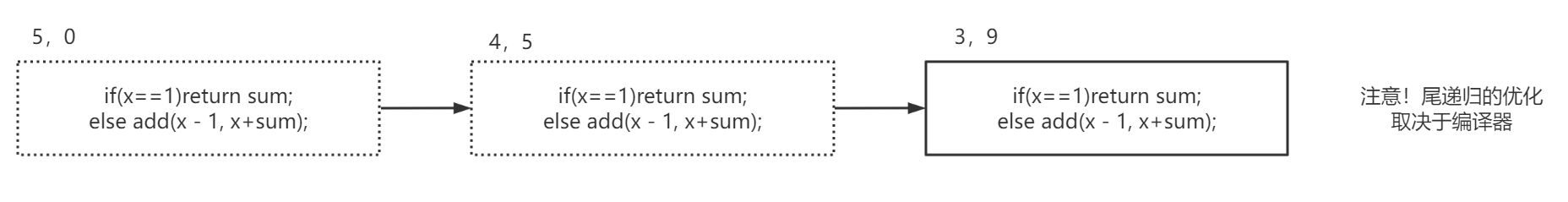
注意!尾递归的优化取决于编译器,不是所有的编译器都能对尾递归做优化,有些老的编译器是不能优化尾递归的。
边栏推荐
- Hands on deep learning (VII) -- bounding box and anchor box
- Common evaluation indexes of medical image segmentation
- What if path is deleted by mistake when configuring system environment variables?
- 力扣300-最长递增子序列——动态规划
- [don't bother to strengthen learning] video notes (IV) 1. What is dqn?
- This article takes you to understand the dynamic memory allocation of C language
- Simple parsing JSON strings with regular expressions
- JS bind simulation
- [STM32 learning] (7) use of serial port 2 (usart2)
- MySQL Basics (I) -- SQL Basics
猜你喜欢

Vscode failed to use SSH Remote Connection (and a collection of other problems)

Detailed LinkedList

Raspberry Pie:: no space left on device

Embedded development: Tools - optimizing firmware using DRT

It's eleven again. Those jokes about nagging programmers going home for blind dates
![[STM32 learning] (18) STM32 realizes LCD12864 display - parallel implementation of 8-bit bus](/img/6b/b49b9e7fff62026a4818561d79fe3f.png)
[STM32 learning] (18) STM32 realizes LCD12864 display - parallel implementation of 8-bit bus

07 Jason module
![[STM32 learning] (15) STM32 realizes DHT11 temperature and humidity acquisition and display](/img/f2/6fcd4b2e747b4ceb52a52eda0c1af4.png)
[STM32 learning] (15) STM32 realizes DHT11 temperature and humidity acquisition and display

Jenkins deploys the project and prompts that the module package defined by him cannot be found

The most complete solution for distributed transactions
随机推荐
cannot unpack non-iterable NoneType object
String sort
Installation UMI tutorial (error reporting and solutions)
Spark Learning: compile spark source code in win10
Get the historical quotation data of all stocks
聚集日志服务器
An article takes you to understand the operation of C language files in simple terms
PHP Basics - PHP types
JS, the return statement used in the for loop should be placed in the function to terminate the loop, similar to the invalid return problem in break & foreach
How to improve office efficiency through online collaborative documents
Where is the bitbucket clone address
[STM32 learning] (8) stm32f1 general timer configuration
Android Version Description security privacy 13
Spark Learning: Spark implementation of distcp
Opencv learning Day5
It is reported that the prices of some Intel FPGA chip products have increased by up to 20%
Firewalld firewall related commands
Home raiding III (leetcode-337)
Gin framework uses session and redis to realize distributed session & Gorm operation mysql
What is the cloud native mid platform business architecture?