当前位置:网站首页>Multithreaded instance code (Demo)
Multithreaded instance code (Demo)
2022-06-21 21:05:00 【if you never leave me, i will be with you till death do us apart】
What is multithreading ?
When introducing multithreading , We first need to know what threads are , And to understand threads, you have to understand processes .
1. process : One of the programs being executed , Each process execution has an execution order , This sequence is an execution path , Or a control unit .
2. Threads : An independent control unit in the process , Threads are controlling the execution of processes . At least one thread in a process .
3. Multithreading : There is more than one thread in a process .
eg: For example, we drive from Beijing to Shanghai , The process can be understood as we are on our way to Shanghai , Going by plane is equivalent to a process , We can not only fly but also take high-speed rail , Self driving, etc. This is the multithreading we mentioned above .
principle :
Multithreading is to apply the principle of concurrent execution mechanism in the operating system to a program , Divide a program into several subtasks , Multiple subtasks are executed concurrently , Every task is a thread .
Multithreading is a concurrent execution mechanism .
advantage
1、 Convenient communication and data exchange
2、 Make more efficient use of CPU
3、 The difference between thread and process
Threads Is an execution path in the process , Share a memory space , You can switch between threads freely , Concurrent execution . One process is the least There is a thread , Threads are actually further divided on the basis of processes , After a process starts , Several execution paths inside can be divided into several threads .
process An application running in memory , Each process has a separate memory space
Why should we use multithreading ?
In order to make better use of CPU Resources for , If there is only one thread , When we have multiple tasks, we must wait for the last task to be completed . Multithreading can perform other tasks while the main thread executes without waiting .
Data cannot be shared between processes , however Threads can .
The system creation process needs to reallocate system resources for this process , Creating threads is less expensive .
Java Language built-in multithreading support , To simplify the Java Multithreaded programming .
CompletionService What is it? ?
Callable+Future Can achieve more than one task Parallel execution , But if you encounter the previous task When the execution is slow, you need to block and wait for the previous task After execution task To achieve results .
CompletionService Its main function is to generate tasks on one side , While getting the return value of the task . Separate the two things , Tasks don't block each other , You can get the first result after the first execution , No longer rely on task order .
He has only one implementation class :ExecutorCompletionService
CompletionService principle
Internally through the blocking queue +FutureTask, The task is completed first, and the priority can be obtained , That is, the results are sorted according to the order of completion , There is a first in first out blocking queue inside , Used to save completed execution of Future, By calling its take Method or poll Method can get a completed execution of Future, And then by calling Future Interface implementation class get Method to get the final result .
CompletionService Application scenarios of
When you need to submit asynchronous tasks in batch, we suggest that you use CompletionService:CompletionService Put thread pool Executor And blocking queues BlockingQueue It's a combination of functions , It can make the management of batch asynchronous tasks easier .
CompletionService It can make the execution results of asynchronous tasks orderly : First of all, execute the first in the blocking queue , Take advantage of this feature , You can easily achieve the order of subsequent processing , Avoid unnecessary waiting , At the same time, it can also quickly realize such as Forking Cluster Such a need .
Thread pool isolation :CompletionService Support to create thread pools by yourself , This isolation avoids the risk of several particularly time-consuming tasks dragging down the entire application .
Although the use of thread pool improves the overall execution efficiency , But traverse these Future, call Future Interface implementation class get Method is blocked , This and the present Future When the associated computing task is actually completed ,get Method to return the result , If the current calculation task is not completed , And there are others Future The associated calculation task has been executed , A lot of waiting time will be wasted , So it's best to get the first result when traversing , This saves a lot of waiting time .
and ExecutorCompletionService Can achieve this effect , It has a first in, first out blocking queue inside , Used to save completed execution of Future, By calling its take Method or poll Method can get a completed execution of Future, And then by calling Future Interface implementation class get Method to get the final result
ExecutorCompletionService Realized CompletionService Interface , stay CompletionService The following methods are defined in the interface :
Future submit(Callable task): To submit a Callable Types of tasks , And return the task execution results associated with Future;
Future submit(Runnable task,V result): To submit a Runnable Types of tasks , And return the task execution results associated with Future;
Future take(): Get and remove the first completed task from the internal blocking queue , Blocking , Until something's done ;
Future poll(): Get and remove the first completed task from the internal blocking queue , If not, return null, Don't block ;
Future poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit): Get and remove the first completed task from the internal blocking queue , The blocking time is timeout, If not, return null;
package com.example.yanwc;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Deadlock {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// Creating a thread pool
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// establish CompletionService
CompletionService<Integer> cs = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executor);
// Turn on 5 A mission
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cs.submit(new CompletionTask());
}
// Asynchronously save the inquiry result to the database
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Get task results :" + cs.take().get());
}
}
}
/** * Custom tasks */
class CompletionTask implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
// Get the random world
int randomSleepTime = new Random().nextInt(10) * 1000;
// Start execution
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Start execution , The current task needs to wait " + randomSleepTime + " millisecond ");
// Thread waiting , Simulation is in progress
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(randomSleepTime);
// End to perform
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " End to perform , The current task needs to wait " + randomSleepTime + " millisecond ");
// Return to the time he waited
return randomSleepTime;
}
}
E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\bin\java.exe -javaagent:D:\idea\idea20203pj_186103\lib\idea_rt.jar=51798:D:\idea\idea20203pj_186103\bin -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\charsets.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\deploy.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\javaws.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\jce.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\jfr.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\jfxswt.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\jsse.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\plugin.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\resources.jar;E:\JAVA-JIHE\JDK\java\jdk1.8.0_162\jre\lib\rt.jar;F:\IDEA_gulimall\Login_Register\yanwc\target\classes;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-autoconfigure\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-logging\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-logging-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\ch\qos\logback\logback-classic\1.2.3\logback-classic-1.2.3.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\ch\qos\logback\logback-core\1.2.3\logback-core-1.2.3.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\apache\logging\log4j\log4j-to-slf4j\2.12.1\log4j-to-slf4j-2.12.1.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\apache\logging\log4j\log4j-api\2.12.1\log4j-api-2.12.1.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\slf4j\jul-to-slf4j\1.7.30\jul-to-slf4j-1.7.30.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\jakarta\annotation\jakarta.annotation-api\1.3.5\jakarta.annotation-api-1.3.5.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\yaml\snakeyaml\1.25\snakeyaml-1.25.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\thymeleaf\thymeleaf-spring5\3.0.11.RELEASE\thymeleaf-spring5-3.0.11.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\thymeleaf\thymeleaf\3.0.11.RELEASE\thymeleaf-3.0.11.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\attoparser\attoparser\2.0.5.RELEASE\attoparser-2.0.5.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\unbescape\unbescape\1.1.6.RELEASE\unbescape-1.1.6.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\slf4j\slf4j-api\1.7.30\slf4j-api-1.7.30.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\thymeleaf\extras\thymeleaf-extras-java8time\3.0.4.RELEASE\thymeleaf-extras-java8time-3.0.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-web\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-web-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-json\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-json-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\core\jackson-databind\2.10.2\jackson-databind-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\core\jackson-annotations\2.10.2\jackson-annotations-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\core\jackson-core\2.10.2\jackson-core-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\datatype\jackson-datatype-jdk8\2.10.2\jackson-datatype-jdk8-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\datatype\jackson-datatype-jsr310\2.10.2\jackson-datatype-jsr310-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\jackson\module\jackson-module-parameter-names\2.10.2\jackson-module-parameter-names-2.10.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-tomcat\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-tomcat-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\apache\tomcat\embed\tomcat-embed-core\9.0.30\tomcat-embed-core-9.0.30.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\apache\tomcat\embed\tomcat-embed-el\9.0.30\tomcat-embed-el-9.0.30.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\apache\tomcat\embed\tomcat-embed-websocket\9.0.30\tomcat-embed-websocket-9.0.30.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\boot\spring-boot-starter-validation\2.2.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-starter-validation-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\jakarta\validation\jakarta.validation-api\2.0.2\jakarta.validation-api-2.0.2.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\hibernate\validator\hibernate-validator\6.0.18.Final\hibernate-validator-6.0.18.Final.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\jboss\logging\jboss-logging\3.4.1.Final\jboss-logging-3.4.1.Final.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\com\fasterxml\classmate\1.5.1\classmate-1.5.1.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-web\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-web-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-beans\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-beans-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-webmvc\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-webmvc-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-aop\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-aop-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-context\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-context-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-expression\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-expression-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\projectlombok\lombok\1.18.10\lombok-1.18.10.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-core\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-core-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar;D:\maven\apache-maven-3.5.3-bin\repository\org\springframework\spring-jcl\5.2.3.RELEASE\spring-jcl-5.2.3.RELEASE.jar com.example.yanwc.Deadlock
pool-1-thread-4 Start execution , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
pool-1-thread-3 Start execution , The current task needs to wait 0 millisecond
pool-1-thread-3 End to perform , The current task needs to wait 0 millisecond
pool-1-thread-2 Start execution , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
pool-1-thread-5 Start execution , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
pool-1-thread-1 Start execution , The current task needs to wait 7000 millisecond
main Get task results :0
pool-1-thread-2 End to perform , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
pool-1-thread-4 End to perform , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
pool-1-thread-5 End to perform , The current task needs to wait 2000 millisecond
main Get task results :2000
main Get task results :2000
main Get task results :2000
pool-1-thread-1 End to perform , The current task needs to wait 7000 millisecond
main Get task results :7000
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class DeadLock2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Integer i = 1;
Integer ii = 2;
Integer iii = 3;
Integer iiii = 4;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Pass relevant parameters into list aggregate
list.add(i);
list.add(ii);
list.add(iii);
list.add(iiii);
System.out.println(" Before conversion " + list);
// The thread returns the object
List<Future<Integer>> l = new ArrayList<>();
// Create a thread pool waiting queue
BlockingQueue q = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
// Create a thread pool and set up related parameters
// Creating thread objects Enable multithreading
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,6,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS,q);
// Threads To carry out a task
CompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService(executor);
//for loop
for (Integer integer : list) {
Future<Integer> future = completionService.submit(wc(integer));
l.add(future);
}
List<Integer> ll = new ArrayList<>();
// Instantiate data
for (Future<Integer> future : l) {
ll.add(future.get());
}
System.out.println(" After the transformation " + ll);
}
private static Callable<Integer> wc(Integer integer) {
Callable<Integer> callable = new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return integer + 1;
}
};
return callable;
}
}
Running results :
Before conversion [1, 2, 3, 4]
After the transformation [2, 3, 4, 5]
Construction method analysis :
CompletionService Construction method of source code analysis
/**
- Construction method of incoming thread pool
*/
public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor) {
// Thread pool is null, Throw an exception directly
if (executor == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// Assign a value to the thread pool used
this.executor = executor;
// Judgment is not AbstractExecutorService Subclasses of
this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ?
(AbstractExecutorService) executor : null;
// Default only LinkedBlockingQueue Store the results
this.completionQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Future<V>>();
}
/** * The construction method of incoming thread pool and the queue used */
public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor,
BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue) {
// Thread pool is null Or the queue used is empty , Throw an exception directly
if (executor == null || completionQueue == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// Assign a value to the thread pool used
this.executor = executor;
// Judgment is not AbstractExecutorService Subclasses of
this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ?
(AbstractExecutorService) executor : null;
// Use the incoming queue to store the results
this.completionQueue = completionQueue;
}
CompletionService Of submit Method source code analysis
/** * CompletionService Task submission method */
public Future<V> submit(Runnable task, V result) {
// Task is empty , Throws a null pointer exception
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// Create a specific task
RunnableFuture<V> f = newTaskFor(task, result);
// Perform this task : Encapsulate the , Rewrote done Method , Put the running results in the queue .
executor.execute(new QueueingFuture(f));
// Return the result of execution
return f;
}
/** * QueueingFuture class : He rewrote it done Method */
private class QueueingFuture extends FutureTask<Void> {
QueueingFuture(RunnableFuture<V> task) {
super(task, null);
this.task = task;
}
// Execute the completed method : Put the running results into the queue .
protected void done() { completionQueue.add(task); }
private final Future<V> task;
}
CompletionService Of take Method source code analysis
/** * CompletionService Out of the team take Method : Directly call the blocking out method of the queue . */
public Future<V> take() throws InterruptedException {
return completionQueue.take();
}
边栏推荐
- Analysis of ${} string splicing in JS
- Idea has this class but can't find it
- Book list given by Wu Jun to college students
- FM5012D小风扇集成ic方案
- 全新混合架构iFormer!将卷积和最大池化灵活移植到Transformer
- Get the openharmony source code: get it from the deveco marketplace (1)
- Flutter PageView组件
- JVM的类加载过程
- 决策树(Decision Tree)学习笔记
- 互联网协议入门详解--五层模型
猜你喜欢
![[专利与论文-19]:江苏省南京市2022年电子信息申报通知(中、高级)](/img/a5/47c1b189cfd4bee6edb68c266a3816.png)
[专利与论文-19]:江苏省南京市2022年电子信息申报通知(中、高级)
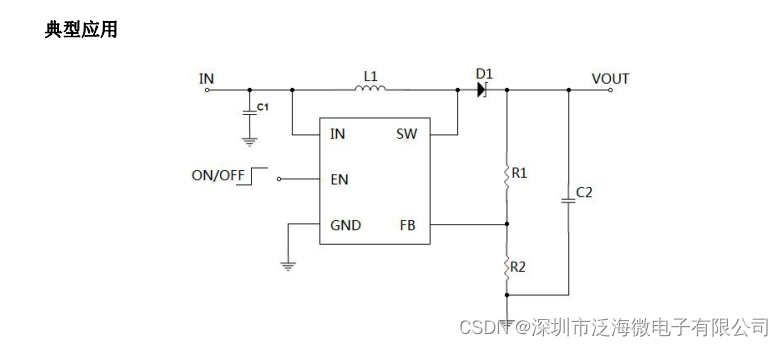
TC3608H高效率 1.2MHz DC-DC 升压器 IC

行业首家!极氪APP获中国网络安全审查技术与认证中心权威认证

纵横网络靶场社区-Modbus协议

Get the openharmony source code: get it from the deveco marketplace (1)

Shutter input box assembly
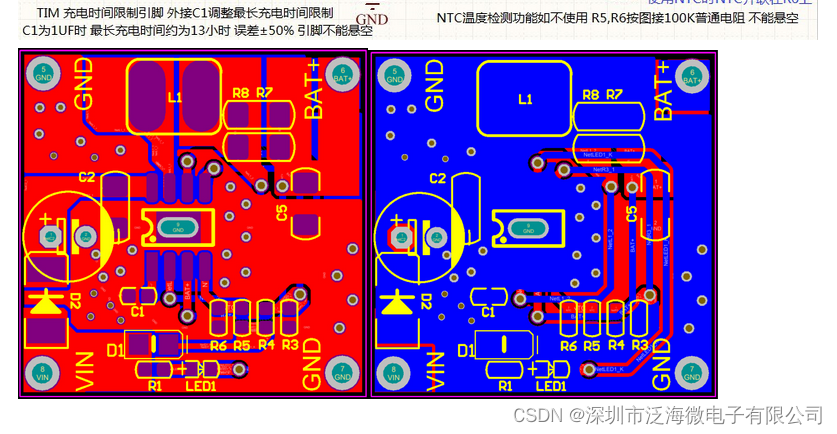
YB5212A充电IC充电芯片sop8

AB打包有的Shader没有触发IPreprocessShaders的回调

What noteworthy technologies of gold: the importance of fund management

Cocoapods安装(Xcode8.0之后,无限卡在Setting up CocoaPods master repo)
随机推荐
What noteworthy technologies of gold: the importance of fund management
MediaCodec的数据类型和使用方式
Random forest learning notes
LeeCode70 爬楼梯
产品创新 | 物极必反,回归真实生活的创新社交APP
决策树(Decision Tree)学习笔记
[专利与论文-19]:江苏省南京市2022年电子信息申报通知(中、高级)
Advanced algebra_ Chapter 9: linear mapping
pc 电商平台----search模块
Alibaba cloud ack one and ACK cloud native AI suite have been newly released to meet the needs of the end of the computing era
The Summer Challenge realizes a standard layout of Huawei app with openharmony ETS
Take off, annual salary: 400000+
M3608升压ic芯片High Efficiency 2.6A Boost DC/DC Convertor
Adum1401arwz-rl adenault digital signal isolation module
Show you how to distinguish several kinds of parallelism
[parallel and distributed computing] 10B_ MapReduce GFS Implementation
FM5012D小风扇集成ic方案
Quartus II 18.0软件安装包和安装教程
Flutter 输入框组件
同步升压 DC/DC 转换器FS3400同步SOT23-6小电流500MA升压ic