当前位置:网站首页>How to simplify a lot of if... Elif... Else code?
How to simplify a lot of if... Elif... Else code?
2022-06-11 17:22:00 【Python Programming Jacko】
In everyday code , We always face a lot of if…elif…else The problem of conditional branch selection . Tell the truth , In most cases, my first recommendation is to write honestly
if…elif, And try to extract the content under each branch into independent functions . The structure is clear , Intention understanding , It is very convenient for writing and reading . however , In some special circumstances , You can also use other more elegant ways , Like we shared before 《 Don't use
if-elif sentence , How to judge the rank of a number gracefully ?》, And this article to share today , You can broaden your thinking of coding .
In today's Github read EdgeDB[1] Code for , Found it dealing with a lot of if…elif…else When judging , Using a very clever decorator . Let's see what this method is .
Today is double eleven , Suppose we want to do a function , Judge the discount he can get according to the user's level . The conventional if … elif… This is how it is written :
def get_discount(level):
if level == 1:
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.1
elif level == 2:
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.2
elif level == 3:
discount = 0.3
elif level == 4:
discount = 0.4
elif level == 5:
discount = 0.5
elif level == 6:
discount = 3 + 2 - 5 * 0.1
else:
return ' Wrong level '
return discount
Everybody knows , So many if … elif… The code is very ugly , It's hard to maintain . And each if There is a lot of code inside . This function will be pulled very long .
Some students know , You can use a dictionary to rewrite this too long if Judge :
def parse_level_1():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.1
return discount
def parse_level_2():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.2
return discount
def parse_level_3():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.3
return discount
def parse_level_4():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.4
return discount
def parse_level_5():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.5
return discount
def parse_level_6():
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 3 + 2 - 5 * 0.1
return discount
discount_map = {
1: parse_level_1,
2: parse_level_2,
3: parse_level_3,
4: parse_level_4,
5: parse_level_5,
6: parse_level_6,
}
discount = discount_map.get(level, ' Wrong level ')
But the method I learned today , It's easier than using a dictionary . Let's first look at its effect :
@value_dispatch
def get_discount(level):
return ' Wrong level '
@get_discount.register(1)
def parse_level_1(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.1
return discount
@get_discount.register(2)
def parse_level_2(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.2
return discount
@get_discount.register(3)
def parse_level_3(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.3
return discount
@get_discount.register(4)
def parse_level_4(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.4
return discount
@get_discount.register(5)
def parse_level_5(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.5
return discount
@get_discount.register(6)
def parse_level_1(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 3 + 2 - 5 * 0.1
return discount
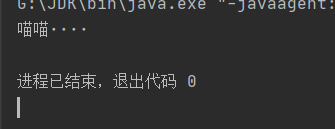
discount = get_discount(3)
print(f' Grade 3 Users of , The discount received is :{discount}')
The operation effect is shown in the figure below :

Write it like this , More intuitive than using a dictionary , It's better than using it directly if … elif… More concise .
that , This decorator value_dispatch How to achieve it ? The password is hidden in this open source project EdgeDB Of Source code [2] in , The core code is just 20 Multiple lines :

also , It can also implement or query . For example, the user level is 2 perhaps 3 When , Discounts are 0.2, Then the code can be written as :
@get_discount.register(2)
@get_discount.register(3)
def parse_level_2(level):
" A lot of calculation code "
discount = 0.2
return discount
The operation effect is shown in the figure below :

Its code can only implement equal queries at present . But in fact, as long as the code is slightly modified , We can achieve greater than 、 Less than 、 Greater than or equal to 、 Less than or equal to 、 It's not equal to 、in Wait, judge . If you are interested , Please leave a message at the bottom of the article , Let's talk about how to modify this code tomorrow , Realize more logical judgment .
Push inside the post 、 Exchange of learning
We need a lot of front-end jobs 、python Position 、Java Position 、Android and iOS Development position of , Workplace : Beijing byte , Welcome to the school recruitment agency to scan the QR code below Look for me to push inside
Python Information 、 technology 、 Course 、 answer 、 For consultation, you can also directly click on the business card below ,
Add official customer service Qi↓
边栏推荐
- LeetCode-384. Scramble array
- 用实际案例分析PMP与ACP应该考哪个?哪个更有用?
- Authing 背后的计算哲学
- 每周推荐短视频:菜鸟CEO谈未来物流新赛道
- Redis - learn five types of NoSQL
- LeetCode-1005. Maximized array sum after K negations
- TypeScript学习笔记(二)
- 信息安全数学基础 Chapter 2——同余
- Authing 双周动态:应用市场上线(5 .10 —5 .22 )
- Export data prompt -- solution to the problem of secure file priv option
猜你喜欢
子类继承了什么、多态、 向上转型

Katalon Studio Enterprise

vscode配置eslint自动格式化报错“The setting is deprecated. Use editor.codeActionsOnSave instead with a source“

Real time myth -- real-time RTOS multitask performance analysis

每周推荐短视频:菜鸟CEO谈未来物流新赛道

Redis - learn five types of NoSQL

Authing 双周动态:应用市场上线(5 .10 —5 .22 )
Tornado environment construction and basic framework construction -- familiar Hello World

vscode保存代码时自动eslint格式化

Bentley 使用 Authing 快速实现应用系统与身份的集成
随机推荐
Exception handling and exception usage in golang
Analysis report on sales status and supply and demand prospects of phosphoric acid fuel cell industry in the world and China 2022-2028 Edition
活动 | Authing 首次渠道合作活动圆满落幕
Environment configuration and pymysql installation
mysql 大表的拆分方式
How to store tree structure in database
启牛商学院给的证券账户是安全的吗?开户收费吗
从制造到“智造”,探索制造企业破局之道
Is the second-class cost engineer worth the exam? What is the development prospect?
信息安全数学基础 Chapter 1——整除
Export data prompt -- solution to the problem of secure file priv option
Oracle generates non duplicate string sys_ Guid() and MySQL generate unique values
Vscode configures eslint to automatically format an error "auto fix is enabled by default. use the single string form“
二级造价工程师值得考吗?发展前景如何?
Intranet penetration based on UDP port guessing
Pycharm使用小技巧 - 如何设置背景图片
Vscode configures eslint to automatically format with an error "the setting is deprecated. use editor.codeactionsonsave instead with a source“
Global and Chinese molten carbonate fuel cell industry outlook and market panoramic Research Report 2022-2028
vscode配置eslint自动格式化报错“Auto Fix is enabled by default. Use the single string form“
LeetCode-384. Scramble array