当前位置:网站首页>File IO (1)
File IO (1)
2022-06-23 10:03:00 【Snail is also persistent】
(1) file IO:
- Open file
function :open
The header file :
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
The function prototype :
int open(const char *pathname, int flags); ------》 Suitable for opening files in read-only mode
function : Used to open a file
Parameters :
Parameters 1: Open file name ( Can include path )
Parameters 2: How to open a file
There are three ways : Main sign ( Mutually exclusive )
O_RDONLY
O_WRONLY
O_RDWR
Secondary sign :O_CREAT O_TRUNC
Return value :
Successfully returned a file descriptor ( Nonnegative integers )
Failure returns -1(errno is set)
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);---》 Suitable for opening files in write only mode
function : Used to open a file
Parameters :
Parameters 1: Open file name ( Can include path )
Parameters 2: How to open a file
There are three ways : Main sign ( Mutually exclusive )
O_RDONLY
O_WRONLY
O_RDWR
Secondary sign :O_CREAT O_TRUNC
Parameters 3: jurisdiction -----》 It can be expressed in octal
Return value :
Successfully returned a file descriptor ( Nonnegative integers )
Failure returns -1(errno is set)

- Operation file
2-1 Writing documents :
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
function :
Used to write data to the specified open file
Parameters :
Parameters 1: The file descriptor after successfully opening the file
Parameters 2: A buffer that stores data to be written
Parameters 3: The number of data elements to be written
Return value :
Success returns the number of successfully written data
Failure returns -1( It's set up errno Value )
2-2 Reading documents :
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
function :
Read data from the specified open file
Parameters :
Parameters 1: The file descriptor after successfully opening the file
Parameters 2: A buffer that stores the read content
Parameters 3: The number of data elements to be read
Return value :
Success returns the number of successfully read data
Failure returns -1( It's set up errno Value )
The return value is equal to 0, The representative has finished reading
- Close file
#include <unistd.h>
int close(int fd);
Parameters : The file descriptor after successfully opening the file
Case study 1: Realize the use of four functions in combination
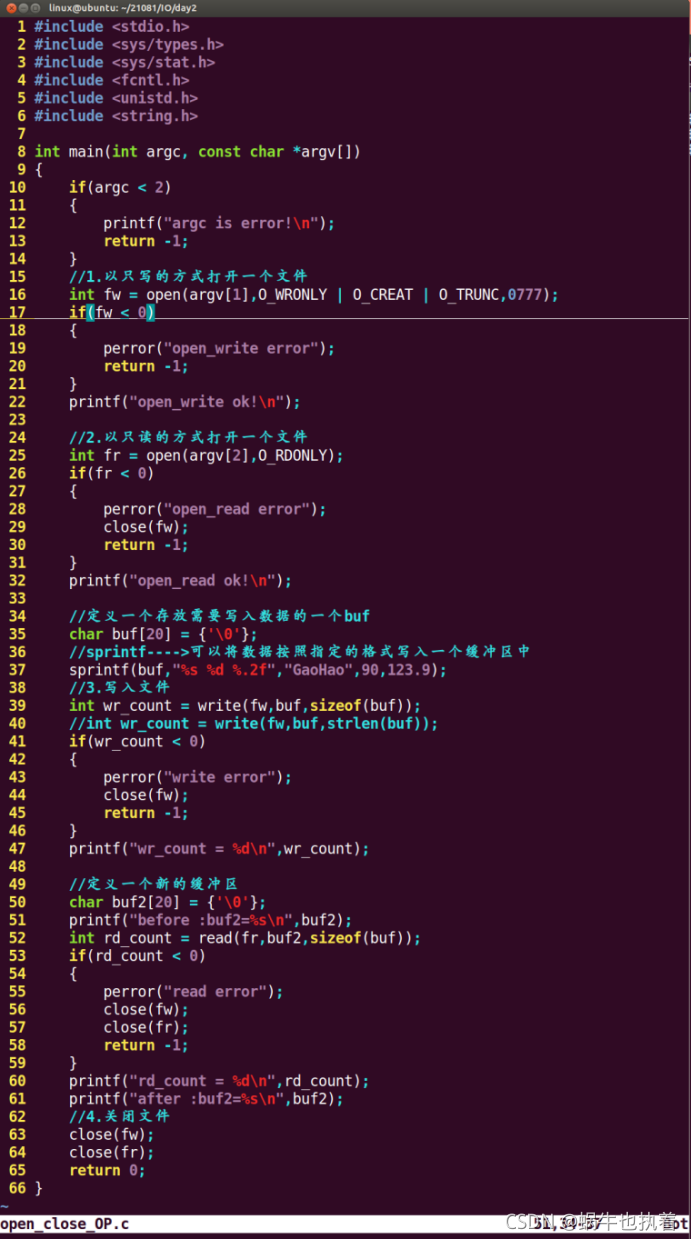
Case study 2: Utilization of documents IO Realization CP command

- location
The name of the function :lseek
The header file :
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
The function prototype :
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
function : Realize jump
Parameters :
Parameters 1: The file descriptor after successfully opening the file
Parameters 2: Offset
Parameters 3: Base point position relative to offset
SEEK_SET At the beginning of the file
SEEK_CUR File current location
SEEK_END End of file
Return value : If successful, the current displacement of the file will be returned .
Failure returns -1;

Case study : verification lseek What is the return value of ?

summary :lseek The return value of represents the current number of bytes successfully offset !
- Empty files
5-1. What is an empty file ?

5-2. How to create an empty file ?

The code implementation process is as follows :( file IO Realized ), Standards can also be used IO Realization

- Catalog related
- Open Directory
The header file :
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
The function prototype :
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
function : Open a directory
Parameters :
Name of the directory to be opened ( You can take the path )
Return value :
Success returns a directory pointer
Failure returns NULL
- Read the table of contents
#include <dirent.h>
The function prototype :
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
function : Used to read the contents of the directory
Parameters : The return value of successfully opening the directory
Return value :
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
off_t d_off; /* offset to the next dirent */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported
by all file system types */
char d_name[256]; /* filename */
};
Case study 1: Realization ls -a command
Case study 2: Realization ls command
Learn how to test file properties ?
function :stat/lstat/fstat
The header file
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
The function prototype :
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
Be careful : The above three functions can test the properties of the file .
among :
about fstat for : The first parameter of this function is the file descriptor of a file that has been opened , We don't usually take this approach .
about stat and lstat for : These two parameters are the same , But its nature is slightly different .
stat: It is called a trace function or a penetration function , It means if you use stat Function to test file properties , The first parameter passed in is a soft link file , This means that the function tests the source file pointed to by the linked file , Not the linked file itself .
lstat: Not tracking ( through ) function , This means that when the first parameter passed in is a linked file , The test attribute is also the attribute of the linked file itself .
Analysis function : With lstat For example :
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
function : The implementation can test the properties of the specified file
Parameters :
Parameters 1: File name to be tested ( Path taking )
Parameters 2: An address information structure for storing file attributes
Return value : Successfully returns 0, Failure to return -1
Be careful :lstat The address information structure of the second parameter is as follows :
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated*/
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};
- Close directory
The header file :
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
The function prototype :
int closedir(DIR *dirp);
function : Close the open directory
Parameters :opendir The return value of ( Directory pointer )
Return value : Successfully returns 0, Failure to return -1
、
边栏推荐
- J. Med. Chem. | RELATION: 一种基于靶标结构的深度学习全新药物设计模型
- What is BFC? What problems can BFC solve
- Go unit test
- 2022 gdevops global agile operation and maintenance summit - essence playback of Guangzhou station (with PPT download)
- Three methods to find the limit of univariate function -- lobida's rule and Taylor's formula
- SQL教程之 5 个必须知道的用于操作日期的 SQL 函数
- 2022 Gdevops全球敏捷运维峰会-广州站精华回放(附ppt下载)
- [SUCTF 2019]CheckIn
- 有没有人,计划开源一套工业级“秒杀”系统架构?
- 漫画 | Code Review快把我逼疯了!
猜你喜欢

UEFI learning 3.6 - ACPI table on ARM QEMU
Nuxt.js spa与ssr的区别

数学分析_笔记_第2章:实数与复数

RPC kernel details you must know (worth collecting)!!!

什么是BFC?BFC可以解决什么问题

IPv6 的速度比 IPv4 更快?
![[SUCTF 2019]CheckIn](/img/0e/75bb14e7a3e55ddc5126581a663bfb.png)
[SUCTF 2019]CheckIn

文件IO(1)

马斯克 18 岁儿子请愿改名,欲断绝父子关系

Liujinhai, architect of zhongang Mining: lithium battery opens up a Xintiandi for fluorine chemical industry
随机推荐
【CTF】bjdctf_ 2020_ babyrop
MySQL optimistic lock and pessimistic lock
Comic | code review is driving me crazy!
[MRCTF2020]Ez_bypass
正则表达式
Successful experience of postgraduate entrance examination in materials and Chemical Engineering (metal) of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics in 2023
Go 单元测试
Game of life of leetcode topic analysis
2021-04-12 链表第一次实现!!!
马斯克 18 岁儿子请愿改名,欲断绝父子关系
高性能算力中心 — InfiniBand — Overview
[MRCTF2020]Ez_ bypass
薄膜干涉数据处理
利用华为云ECS服务器搭建安防视频监控平台
web--信息泄漏
thymeleaf中如何给onclick事件传值的方法
ThinkPHP 2. X/3.0 vulnerability recurrence
Year end answer sheet! Tencent cloud intelligent comprehensive strength ranks first in China!
RPC kernel details you must know (worth collecting)!!!
高性能算力中心 — RDMA — 实现技术