当前位置:网站首页>Explain the garbage collection mechanism (GC) in JVM
Explain the garbage collection mechanism (GC) in JVM
2022-06-29 08:07:00 【Blue and white porcelain secretly tapping code】
List of articles
1. What is a garbage collection mechanism (GC)
In the early days of computer languages , such as C and C++, Developers need to track memory manually , The advantages of this mechanism yes The efficiency of memory allocation and release is very high . however It also has its disadvantages , If a programmer accidentally forgets to free memory , Thus causing memory leakage
Memory leak : After applying for memory , Forgot to release Lead to Less and less content is available , Eventually no memory is available
New programming language , such as JAVA,Go,Python,PHP… Most of the major programming languages on the market today , Have adopted a plan , That's it “ Garbage collection mechanism ”, The runtime itself runs the corresponding garbage collection mechanism . Programmers only need to request memory , There is no need to pay attention to the release of memory . Garbage collector (GC) Will in due course Variables whose lifecycles have been terminated To free up the memory .
1.1 Advantages and disadvantages of garbage collection mechanism
GC The advantages of :
- It greatly simplifies the complexity of application layer development ( There is no need for developers to track memory manually )
- Reduces the risk of memory leaks
GC The shortcomings of :
- Consume extra expenses ( More resources are consumed )
- Will affect the smooth operation of the program
2. What memory needs to be recycled
JVM The memory structure consists of four areas :1. Program counter 2. Stack ( Virtual machine stack , Native Method Stack )3. Pile up 4. Method area

for instance , In any organization , Everyone has three factions ,1. Activists 2. Negatives 3. Middle swing , Pictured , For the above three factions , What is to be reclaimed to free memory ?
In memory objects in use representative Activists
No longer use , But objects in memory that have not been reclaimed On behalf of the negative
The middle single part is the middle swing 
Recycling is required to release resources : Negatives
Why don't the swing center reclaim and free memory ? For this part still in use , Some objects that are not in use , On the whole, it is not released ! Wait until the object is completely unused , To really release !!
Be careful :
The basic unit of garbage collection is “ object ”, instead of “ byte ”
3. How does garbage collection work
There are two stages :
- Look for trash / Judging garbage
- Recycling waste ( Free memory )
3.1 Look for trash / Judging garbage
How to find The garbage / Judging garbage ? The current mainstream thinking , There are two options :
- Based on reference count ( No Java The scheme adopted in , This is another language , image Python The plan adopted )
- Based on reachability analysis ( This is Java The plan adopted )
3.11 Based on reference count
What is based on reference counting : Simply speaking , For each object , Will introduce a small additional memory , Save how many references this object has to it
for instance
1.Test t = new Test();, here new An object , Then we will introduce a small additional memory , here t A reference to this object , therefore Reference count Add 1

2.Test t2 = t; here t and t2 Are references to this object , At this point, the reference count from 1 Turn into 2
3.
void func() {
Test t = new Test();
Test t2 = t;
}
func()// During method call , You create an object ( Allocate memory ), During method execution , The import count quantity is 2, When method execution ends , because t and t2 All local variables , It is released along with the stack frame , This release causes the reference count to be 0 了 ( There is no reference to this object , No code can access this object ), At this point, the object is considered to be garbage !
Be careful : The reference count is 0 When , It's no longer in use , This memory is no longer used , It's released ( Pave the way for later understanding )
3.12 Advantages and disadvantages of reference counting
Quoting Technology , Simple, reliable and efficient , But there are two fatal flaws !!
- Low space utilization , Every new All the objects must be matched with Counter , The counter assumes 4 Bytes , If the object itself is large ( Hundreds of bytes ), Come out more 4 Bytes , It's nothing , But if the object itself is small ( I just 4 Bytes ), More 4 Bytes , Equivalent to half the space being wasted
- There's a problem with circular references
Circular quotation problem : Write a code example for understanding
// First create a class
class Test {
// Member variables
Test t = null;
}
// Create examples
Test t1 = new Test();
Test t2 = new Test();
Draw the memory layout :

t1.t = t2;// hold t2 Assigned to t1 Inside t attribute , At this point the object 2 There are two references
Quote count plus 1, Turn into 2

t2.t = t1// hold t1 Assign a value to t2 Inside t attribute , At this point the object 1 There are two references
Quote count plus 1, Turn into 2

Next , Brain burning link :
t1 = null
t2 = null
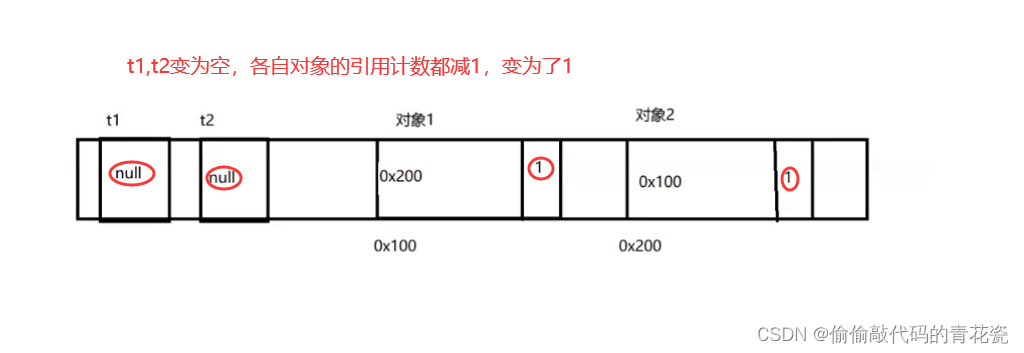
At the moment , Reference count of two objects , Not for 0, So it's impossible to release , But because references grow on each other , External code can not access these two objects , At the moment , These two objects , You can't use it , Can not release , And that's what happened “ Memory leak ” The problem of .
therefore , image Python,PHP in GC It's not just reference counting , It also relies on other mechanisms to cooperate , however Java Accessibility analysis can be used directly , To judge garbage
3.13 Based on reachability analysis
Based on reachability analysis : In a nutshell , Through additional threads , Regularly scan objects in the entire memory space , There are some starting positions ( be called GCRoots), It would be like Depth first traversal , Mark all the accessible objects ( A marked object is a reachable object ), Objects that are not marked , It's just not reachable , It's rubbish !
What is it GCRoots
- Local variables on the stack
- The object pointed to by the reference in the constant pool
- The object pointed to by the static member in the method area
Give me a chestnut , such as : Write a code , Construct a binary tree 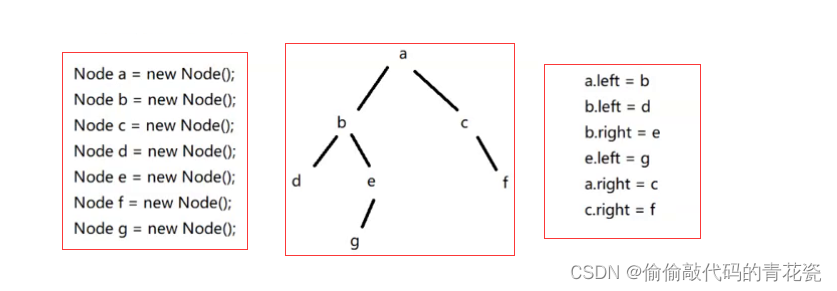
If we're outside the code
Node root = a
Just get... In the code Trees The root node , You can master all the nodes , Any node on the tree , Both can pass a direct / Get... Indirectly
let me put it another way ,GC When performing reachability analysis , When GC Scan to a When , It will a All the elements that can be accessed are accessed once , And mark it , Marked nodes Express Are not The garbage
If in the code , Write the following code
c.right = null
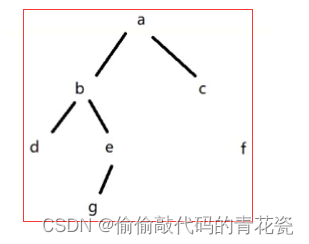
Then this means , from a set out , Can't access f,f Namely Unreachable ,f It's garbage ,f It should be recycled
If in the code
a.right = null

At that moment, from a set out ,c and f It's all unreachable , It will be marked as garbage !
From the above points we can see , Reachability analysis is to traverse every object , If there are too many objects in memory , This traversal will be very slow , therefore GC It still consumes time and system resources !
3.14 Advantages and disadvantages of reachability analysis
advantage :
- Two disadvantages of reference counting are overcome :
- Low space utilization
- Circular reference
shortcoming :
- The system costs a lot , Traversal may be slow
tips:
Look for trash , The core is to confirm whether the object will be used in the future , What counts as no use ? There is no reference , I will not use
After knowing who is garbage , The next step is to recycle garbage !
3.2 Recycling waste ( Free memory )
3.21 Recycling waste ( Free memory ) Three basic strategies
Mark - eliminate
Pictured : This is a piece of memory , It is divided into many small pieces , Some of them are garbage ( Hooked )

there Mark , It is the process of reachability analysis
eliminate , Is to release memory directly , The gray area represents the free memory

At this time, if you directly release , Although the memory is still returned to the system , But the memory released is discrete ( Not continuous )
The problem with decentralization is :“ Memory fragments ”, This problem actually affects the execution of the program !
Memory fragments : such as , Free memory , There's a lot of , Suppose the total is 1G, If you want to apply 500M Memory , It is also possible that the application fails , Because I have to apply for 500M Of memory It has to be continuous , Every time you apply , Are all contiguous memory spaces requested , And here it is 1G It could be multiple The pieces add up only 1G, Not much is available
In order to solve memory fragmentation, we introduce a replication algorithm !
Copy algorithm
Pictured : A piece of memory , Split in two , There are many objects in the left half , The tick is marked as garbage , On the right is The left is not garbage , Copy it over

Then mark the left side as garbage ( gray ), Release them all , We can guarantee , The space on both sides is continuous
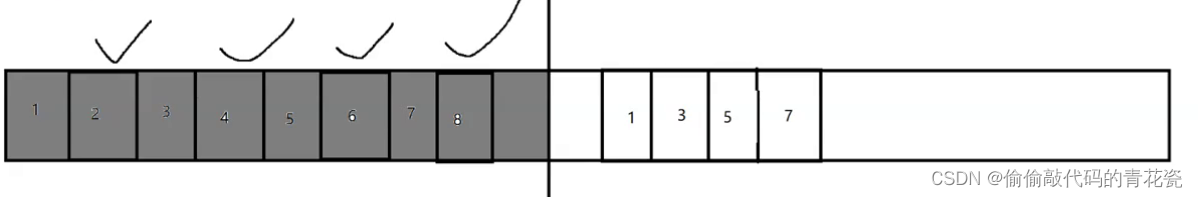
At this point, the memory fragmentation problem is solved !
Be careful : The problems of replication algorithm are as follows
- Low memory space utilization ( You can only use ordinary space )
- If there are many objects to keep , There are fewer objects to release , At this point, the replication cost is very high
We improve the replication algorithm !–》 Mark - Arrangement
Mark - Arrangement
Pictured : Or a piece of memory , There are some objects on it , Some of them are marked as garbage ( Hooked )

How to mark - Sorting out ?
It is similar to deleting intermediate elements in a sequence table , There is a handling operation , We will 3 Carry to 2 , then 5 Carry to 3 , And then 7 Carry to 4 Then release the following parts as a whole
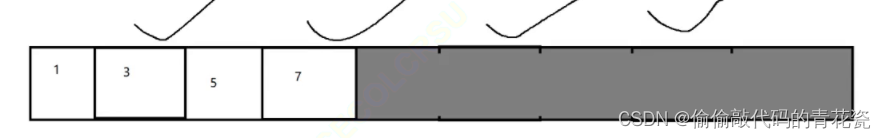
The space utilization rate of this scheme is high , But replication is still not resolved / The problem of high overhead in moving elements ~
3.22 Generational recycling
The three schemes mentioned above , Although it can solve the problem of recycling garbage , But they all have defects , actual JVM In the implementation of , Be able to combine various schemes and use them together , This idea is called “ Generational recycling ”

Our object , How he went back and forth in this area rotary What about ?
- The newly created object , Just in Eden
- If the object of Eden survives a round GC scanning , Will be copied to Survival zone ( Eden To Survival zone Replication algorithm is applied )
- In subsequent rounds GC in , The objects in the surviving area are copied back and forth between the two surviving areas ( Copy algorithm ), A wave of survivors will be eliminated in each round
- After several rounds , The object finally , Into the old age , There is a characteristic of the old age , The objects inside are all older ( Older students ), So old age GC The scanning frequency is much lower than that of the Cenozoic . The old generation uses the way of marking and sorting for recycling !
The above process is a classic interview question !!! We must master the key points !
Be careful :
Be careful !!!
Generation by generation recycling , There is another special case , There is a class of objects that can directly enter the elderly generation ( Big object , Objects that occupy too much memory ), Copying large objects is expensive , Replication algorithms are not suitable !
4. Garbage collector
Look for garbage , And release garbage , It's all about algorithmic thinking , It is not a concrete implementation , stay JVM in , The module that really implements the above algorithm is called “ Garbage collector ”


summary
“ The best time to plant a tree was ten years ago , The second is now ”
therefore ,
“ Let's work together , Go to higher and farther mountains and seas ”
If there is an error , Welcome to correct
If you feel full of harvest , You can move your hands , A little bit of praise , Support
Take dreams as horses , Not to lose time

边栏推荐
- 产品经理应该学习墨刀还是Axure?
- Explanation of swing transformer theory
- SQL Server enable CDC
- Line features & surface features of vSLAM features
- What are the organizational structure and job responsibilities of product managers in Internet companies?
- MySQL enable logging
- Robotframework learning notes: introduction to robot framework and browserlibrary (playwright)
- Basic syntax - bit operation
- Protobuf 二进制文件学习及解析
- js:Array. Reduce cumulative calculation and array consolidation
猜你喜欢
C实战——高配版贪吃蛇游戏设计
电检码配置

After crossing, she said that the multiverse really exists

SQL injection bypass (6)

Explanation of swing transformer theory

C mqtt subscription message

Common MySQL errors and solutions summarized painstakingly (II)

征文投稿丨使用轻量应用服务器搭建博客环境
![[repair collection function, update login interface] knowledge payment applet, blog applet, full version open source code, resource realization applet, with 299 whole station resource data](/img/77/328bd10e97d1d78708464c5d59153a.png)
[repair collection function, update login interface] knowledge payment applet, blog applet, full version open source code, resource realization applet, with 299 whole station resource data

Protobuf binary file learning and parsing
随机推荐
【量化投资系统】问题记录及解决方法
SQL Server 开启cdc
Simulation time and bag operation in ROS
After crossing, she said that the multiverse really exists
Reflection - project management thinking of small and medium-sized companies - make the products first and the functions first
Electric check code configuration
基础知识 - 语法标准(ANSI C、ISO C、GNU C)
Basic syntax - bit operation
征文投稿丨使用轻量应用服务器搭建博客环境
ROS2中的行为树 BehaviorTree
Pointer reference array element
【修复收藏功能、更新登录接口】知识付费小程序、博客小程序、完整版开源源码、资源变现小程序,带299整站资源数据
【6G】算力网络技术白皮书整理
498. diagonal traversal (simulation)
SQL Server enable CDC
[量化投资系统]Django从数据库中实现筛选及分页
C编译器 - 隐式函数声明
C mqtt subscription message
Little white battle pointer (Part 1)
Linear regression with one variable