当前位置:网站首页>Regular expressions: Syntax
Regular expressions: Syntax
2022-06-27 02:16:00 【Live up to your youth】
Regular expressions are made up of ordinary characters ( Such as character a To z) And special characters ( be called " Metacharacters ") The composition of the text pattern . Pattern describes one or more strings to match when searching for text . Regular expression as a template , Match a character pattern to the string being searched .
The way to construct a regular expression is the same as the way to create a mathematical expression . That is, you can combine small expressions with many metacharacters and operators to create larger expressions . A regular expression component can be a single character 、 Character set 、 character in range 、 Choice between characters or any combination of all these components .
Ordinary character
Normal characters include all printable and nonprintable characters that are not explicitly specified as metacharacters . This includes all uppercase and lowercase letters 、 All figures 、 All punctuation and some other symbols .
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| x|y | matching x or y. for example ,'z |
| [xyz] | Character set . Match any character contained . for example ,“[abc]” matching “plain” Medium “a”. |
| [^xyz] | Reverse character set . Match any characters that are not included . for example ,“[^abc]” matching “plain” Medium “p”. |
| [a-z] | character in range . Matches any character in the specified range . for example ,“[a-z]” matching “a” To “z” Any lowercase letter in the range . |
| [^a-z] | Reverse range character . Matches any characters that are not in the specified range . for example ,“[^a-z]” Match any not in “a” To “z” Any character in the range . |
| \d | Number character matching . Equivalent to [0-9]. |
| \D | Non numeric character matching . Equivalent to [^0-9]. |
| \w | Match any word character , Include underline . And “[A-Za-z0-9_]” equivalent . |
| \W | Match any non word character . And “[^A-Za-z0-9_]” equivalent . |
| \xn | matching n, Here n Is a hex escape code . Hex escape code must be exactly two digits long . for example ,“\x41” matching “A”.“\x041” And “\x04”&“1” equivalent . Allow in regular expressions ASCII Code . |
| \num | matching num, Here num Is a positive integer . Reverse reference to capture match . for example ,“(.)\1” Match two consecutive identical characters . |
| \n | Identifies an octal escape code or reverse reference . If \n At least in front n Capture subexpressions , that n Is a reverse reference . otherwise , If n Is an octal number (0-7), that n Is octal escape code . |
| \nm | Identifies an octal escape code or reverse reference . If \nm At least in front nm Capture subexpressions , that nm Is a reverse reference . If \nm At least in front n Capture , be n Is a reverse reference , Followed by characters m. If neither of the preceding conditions exists , be \nm Match octal value nm, among n and m It's octal (0-7). |
| \nml | When n Is an octal number (0-3),m and l Is an octal number (0-7) when , Match octal escape code nml. |
| \un | matching n, among n Is represented by four hexadecimal numbers Unicode character . for example ,\u00A9 Match copyright symbol (). |
Nonprinting characters
Nonprinting characters can also be part of regular expressions .
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| \cx | Match by x Control characters indicated . |
| \f | Match a page break . Equivalent to \x0c and \cL. |
| \n | Match a line break . Equivalent to \x0a and \cJ. |
| \r | Match a carriage return . Equivalent to \x0d and \cM. |
| \s | Matches any whitespace characters , Including Spaces 、 tabs 、 Page breaks and so on . Equivalent to [ \f\n\r\t\v]. |
| \S | Matches any non-whitespace characters . Equivalent to [^ \f\n\r\t\v]. |
| \t | Match a tab . Equivalent to \x09 and \cI. |
| \v | Match a vertical tab . Equivalent to \x0b and \cK. |
Special characters
Special characters , Just some characters with special meanings . To match these special characters , You must first make the characters " escape ", namely , Put the backslash character () Put it in front of them .
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| $ | Matches the end of the input string . If set RegExp Object's Multiline attribute , be $ Also match ‘\n’ or ‘\r’. |
| ( ) | Mark the beginning and end of a subexpression . Subexpressions can be obtained for later use . To match these characters , Please use ( and ). |
| * | Match previous subexpression zero or more times . To match * character , Please use \ *. |
| + | Match previous subexpression one or more times . To match + character , Please use \ +. |
| . | Match break \n Any single character other than . To match ., Please use \ .. |
| [ | Mark the beginning of a bracket expression . To match [, Please use \ [. |
| ? | Match previous subexpression zero or once , Or indicate a non greedy qualifier . To match ? character , Please use \ ?. |
| \ | Mark next character as or special character 、 Or literal character 、 Or back reference 、 Or octal escape character . |
| ^ | Matches the start of the input string , Unless used in a bracket expression , In this case, it means that the character set is not accepted . To match ^ Character itself , Please use \ ^. |
| { | Mark the beginning of a qualifier expression . To match {, Please use \ {. |
| | | Indicate a choice between the two . To match |, Please use \ |. |
qualifiers
Qualifiers are used to specify how many times a given component of a regular expression must appear to satisfy a match . Yes * or + or ? or {n} or {n,} or {n,m} common 6 Kind of .
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| * | Match previous subexpression zero or more times . for example ,zo* Can match “z” as well as “zoo”.* Equivalent to {0,}. |
| + | Match previous subexpression one or more times . for example ,‘zo+’ Can match “zo” as well as “zoo”, But can't match “z”.+ Equivalent to {1,}. |
| ? | Match previous subexpression zero or once . for example ,“do(es)?” Can match “do” 、 “does” Medium “does” 、 “doxy” Medium “do” .? Equivalent to {0,1}. |
| {n} | n Is a non negative integer . Matched definite n Time . for example ,‘o{2}’ Can't match “Bob” Medium ‘o’, But it matches “food” Two of them o. |
| {n,} | n Is a non negative integer . Match at least n Time . for example ,‘o{2,}’ Can't match “Bob” Medium ‘o’, But it can match. “foooood” All in o.‘o{1,}’ Equivalent to ‘o+’.‘o{0,}’ Is equivalent to ‘o*’. |
| {n,m} | m and n All non negative integers , among n <= m. Least match n Times and at most m Time . for example ,“o{1,3}” Will match “fooooood” Top three in o.‘o{0,1}’ Equivalent to ‘o?’. Please note that there cannot be spaces between commas and two numbers . |
Locator
Locators enable you to fix regular expressions to the beginning or end of a line . Locators are used to describe the boundaries of strings or words ,^ and $ Refers to the beginning and end of a string ,\b Describe the front or back boundary of a word ,\B Indicates a non word boundary .
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| ^ | Matches where the input string starts . If set RegExp Object's Multiline attribute ,^ Also with \n or \r Position matching after . |
| $ | Matches the position of the end of the input string . If set RegExp Object's Multiline attribute ,$ Also with \n or \r Previous position match . |
| \b | Matches a word boundary , That is, the position between words and spaces . |
| \B | Non word boundary matching . |
choice
Use parentheses () Enclose all the options , Use... Between adjacent options | Separate .() Represents the capture group ,() The matching values in each group are saved .
Using parentheses can have a side effect , Make the relevant match cached , Available at this time ?: Put the first option forward to eliminate this side effect .
among ?: Is one of the non capture elements , Two other non capture elements are ?= and ?!, These two have more meanings , The former is positive preview , Match the search string at any position that begins to match the regular expression pattern in parentheses , The latter is negative preview , Match the search string at any position that does not initially match the regular expression pattern .
1. exp1(?=exp2): lookup exp2 Ahead exp1.
2. (?<=exp2)exp1: lookup exp2 hinder exp1.
3. exp1(?!exp2): It's not exp2 Of exp1.
4. (?<!exp2)exp1: Not the front look exp2 Of exp1.
backreferences
The simplest way to reverse reference 、 One of the most useful applications , It provides the ability to find a match between two identical adjacent words in the text . A back reference can also refer to a generic resource indicator (URI) Break down into its components .
边栏推荐
- dat. gui. JS star circle track animation JS special effect
- Sword finger offer 𞓜: stack and queue (simple)
- Consumers pursue the iPhone because its cost performance exceeds that of domestic mobile phones
- perl语言中 fork()、exec()、waitpid() 、 $? >> 8 组合
- Oracle/PLSQL: Substr Function
- Oracle/PLSQL: Soundex Function
- Look! In June, 2022, the programming language ranking list was released! The first place is awesome
- Reading a book in idea is too much!
- 剑指Offer || :栈与队列(简单)
- d的appendTo包装
猜你喜欢
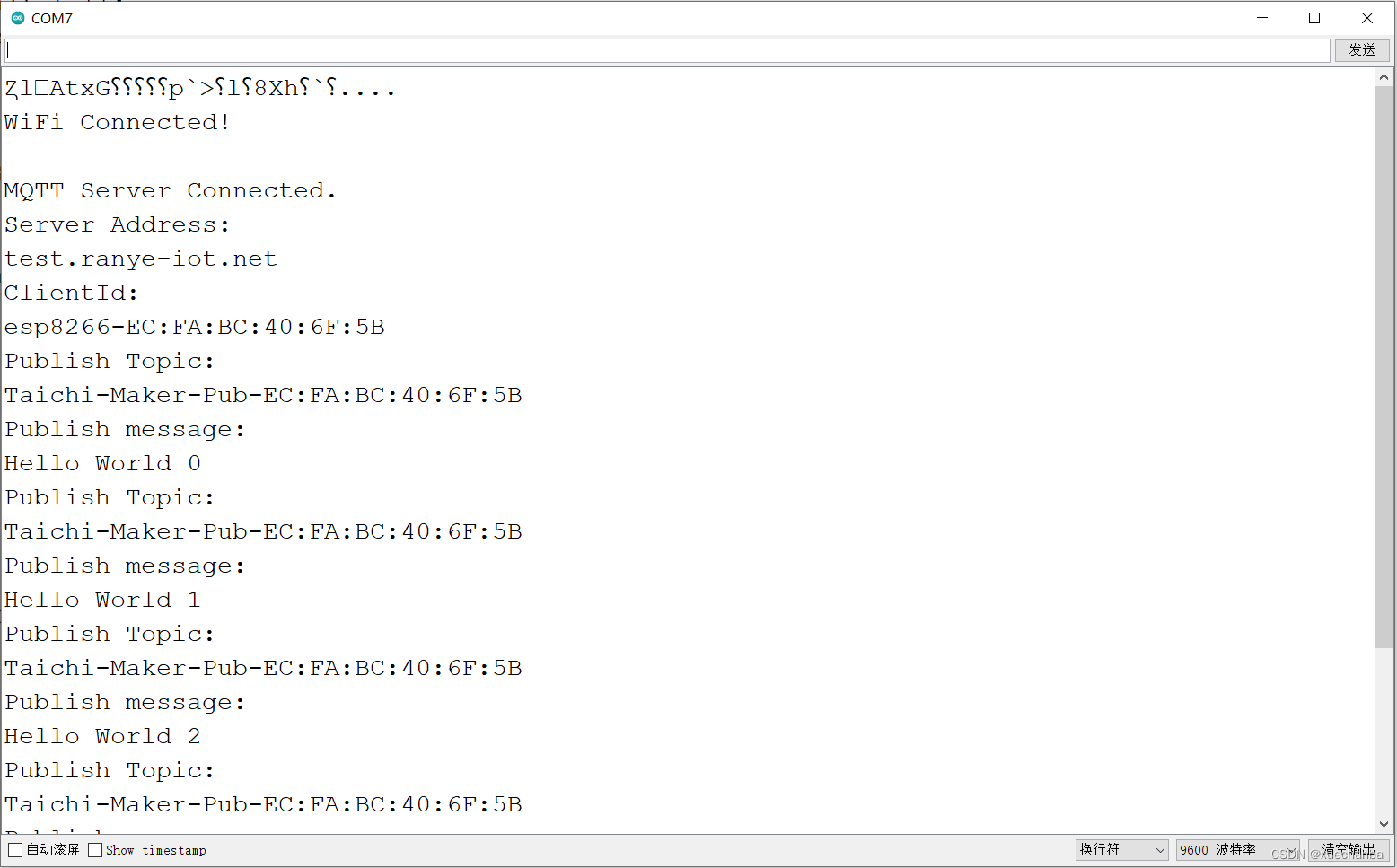
学习太极创客 — MQTT(六)ESP8266 发布 MQTT 消息
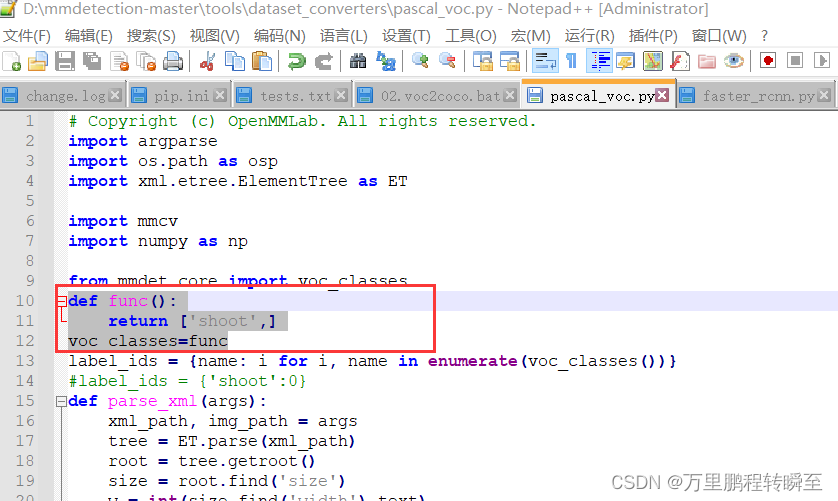
mmdetection ValueError: need at least one array to concatenate解决方案

Summer planning for the long river
Canvas particles: mouse following JS effect

Flink学习3:数据处理模式(流批处理)
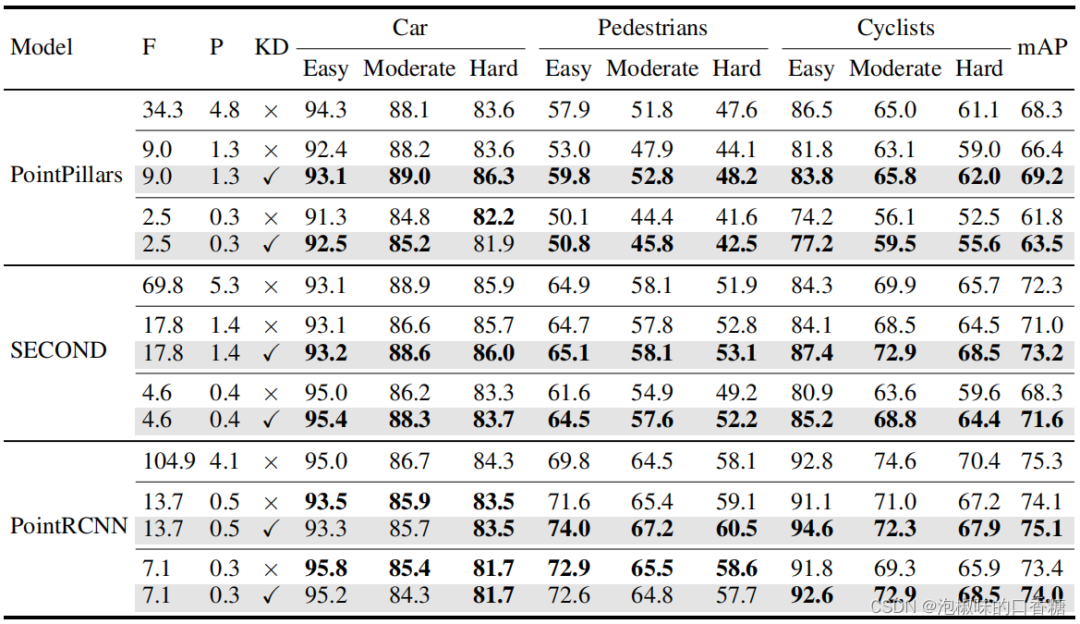
CVPR2022 | PointDistiller:面向高效紧凑3D检测的结构化知识蒸馏

企业数字化转型:信息化与数字化

lottie. JS creative switch button animal head

WiFi-IoT 鸿蒙开发套件样例开发

Cvpr2022 | pointdistiller: structured knowledge distillation for efficient and compact 3D detection
随机推荐
Constraintlayout Development Guide
Oracle/PLSQL: Lpad Function
Oracle/PLSQL: Translate Function
Oracle/PLSQL: Ltrim Function
Look! In June, 2022, the programming language ranking list was released! The first place is awesome
Press key to control LED status reversal
平均风向风速计算(单位矢量法)
h5液体动画js特效代码
消费者追捧iPhone,在于它的性价比超越国产手机
jwt的认证流程和使用案例
Memcached Foundation 12
Oracle/PLSQL: Replace Function
SQLite reader plug-in tests SQLite syntax
bluecms代码审计入门
Flink学习2:应用场景
Oracle/PLSQL: NumToYMInterval Function
C# Tcp服务器如何限制同一个IP的连接数量?
Oracle/PLSQL: Trim Function
Laravel 的 ORM 缓存包
WiFi-IoT 鸿蒙开发套件样例开发