当前位置:网站首页>Set set you don't know
Set set you don't know
2022-07-02 15:13:00 【Xiao afai_】
This issue is wonderful :
Set Implementation class of interface
HashSet The implementation of the
Set Interface
Basic introduction
characteristic :
- Set: disorder ( The sequence of deposit and withdrawal is different, so the subscript cannot be used to traverse ), No repetition
- List: Orderly , Element is not repeatable
Traverse :foreach, iterator
Capacity expansion : Initial capacity 16, Load factor 0.75, Expansion increment 1 times
Set、Queue、List implement Collection, and Map Will not be achieved Collection Interface
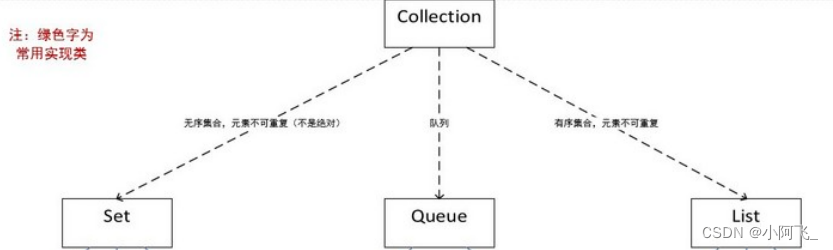
ThreeSet And Collection etc. Relational UML chart

Those who can't understand the relationship arrow in this figure can go to this blog , It's introduced in detail UML chart
List aggregate &UML chart _ Little Alfie _ The blog of -CSDN Blog UML The secret that you can understand at a glance and List How much do you know about the set in the interface ?https://blog.csdn.net/yifei_345678/article/details/125483171?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
Set Implementation class of interface
Set and List Collections also belong to interfaces , Cannot directly create an instantiated object , You need to implement classes to create ,HashSet、ThreeSet Are commonly used implementation classes
1、HashSet
characteristic
- Non-thread safety
- from HashMap Support
- There is no guarantee of insertion order
- Exist in java.util package Class in , It is also called a set , In this container Only non repeating objects can be stored
- It stores The only element And allow null values ( According to the hashcode To determine whether the element exists )
- performance parameter : Initial capacity , Load factor ( The default value is : Initial capacity 16, Load factor 0.75)
HashSet The implementation of the
about HashSet for , It is based on HashMap Realized ,HashSet Bottom use HashMap To save all elements , therefore HashSet The implementation of is relatively simple , relevant HashSet The operation of , Basically, they call the underlying layer directly HashMap To complete , We should be Save to for HashSet Object overlay in hashCode() and equals()
Known implementation interfaces are :
Serializable, Cloneable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, Set<E>
Known subclasses :
JobStateReasons, LinkedHashSet
Code knowledge
Once there was a problem , Ask how to ArrayList Remove the repeated elements in ( duplicate removal ), There are many ways , Little apes can try to write a few by themselves , Here is a simple and fast method : Use HashSet duplicate removal
public class SetDemo {
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
@BeforeAll
public void setup() {
set.add(1);
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(3);
}
@Test
public void test01() {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>(new HashSet<Integer>(list));
System.out.println(tmp);
}
}The output is 123(ArrayList It can store repeated elements , But here we use HashSet duplicate removal )
1、 Create a new one Set Set and put elements
public class SetDemo {
private Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
@BeforeAll
public void setup() {
set.add(1);
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(4);
set.add(5);
set.add(3);
}
}2、 You can use the following two methods to traverse the elements , because HashSet Only non duplicate objects can be stored in , Therefore, the repeated elements will be automatically de duplicated when outputting
@Test
public void test02() {
for(Integer e: set) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
// Using Iterators
@Test
public void test03() {
Iterator<Integer> it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
} 3、set.remove(i) What is passed in is the element , This is because HashSet There is no guarantee of insertion order , No subscript concept , So you can only pass in elements
@Test
public void test05() {
set.remove(3);
System.out.println(set);
}Delete the first step Set The elements in the collection 3, The output is 1245
2、TreeSet
characteristic
- Is a containing Orderly And There are no repeating elements Set
- Role is Provide orderly Set aggregate , Natural ordering ( such as 123456...) Or according to the information provided Comparator( The comparator ) Sort
- TreeSet Is based on TreeMap Realized , and ThreeMap The bottom is Map( Key value pair )
Code knowledge
Create a student class and implement the comparator interface
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private Integer sid;
private String sname;
private int age;
public Student(Integer sid, String sname, int age) {
super();
this.sid = sid;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(Integer sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}It also needs to be implemented in this student class hashCode and equals Method :
/*
*hashCode You can try to turn the student name into a unique number , Compared with ID card
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((sid == null) ? 0 : sid.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((sname == null) ? 0 : sname.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (sid == null) {
if (other.sid != null)
return false;
} else if (!sid.equals(other.sid))
return false;
if (sname == null) {
if (other.sname != null)
return false;
} else if (!sname.equals(other.sname))
return false;
return true;// Students with the same student number, name and age are the same students
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [sid=" + sid + ", sname=" + sname + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
/**
* Realization Comparable<Student> Methods that need to be rewritten after the interface
* Sort by age , The same age is compared with the student number , The default is ascending
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if(this.getAge()-o.getAge()==0) {
return this.getSid()-o.getSid();
}
return this.getAge() - o.getAge();
}And then use ThreeSet
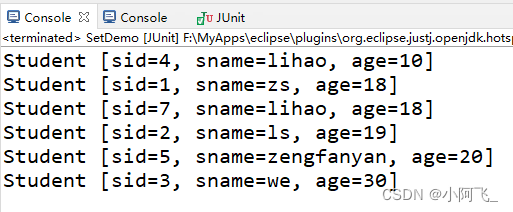
@Test
public void test04() {
TreeSet<Student> stu = new TreeSet<>();
stu.add(new Student(1,"zs", 18));
stu.add(new Student(1,"zs", 18));
stu.add(new Student(2,"ls", 19));
stu.add(new Student(4,"lihao", 10));
stu.add(new Student(7,"lihao", 18));
stu.add(new Student(5,"zengfanyan", 20));
stu.add(new Student(3,"we", 30));
for(Student s: stu) {
System.out.println(s);
}
} Run output :
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Leetcode - Search 2D matrix

LeetCode 2310. 个位数字为 K 的整数之和
List集合&UML图

C language exercises - (array)
Kityformula editor configure font size and spacing
Mavn builds nexus private server
02_线性表_顺序表

Li Chuang EDA learning notes 15: draw border or import border (DXF file)

Practice of compiling principle course -- implementing an interpreter or compiler of elementary function operation language

解决el-radio-group 回显后不能编辑问题
随机推荐
Principles, language, compilation, interpretation
The past and present lives of visual page building tools
How does CTO help the business?
Add vector formula in rich text editor (MathType for TinyMCE, visual addition)
使用mathtype编辑公式,复制粘贴时设置成仅包含mathjax语法的公式
【C语音】详解指针进阶和注意点(2)
[noi Simulation Competition] scraping (dynamic planning)
[untitled] leetcode 2321 Maximum score of concatenated array
LeetCode_滑动窗口_中等_395.至少有 K 个重复字符的最长子串
原则、语言、编译、解释
TiDB混合部署拓扑
AtCoder Beginner Contest 254
Points clés de l'examen de principe de compilation pour l'année scolaire 2021 - 2022 [Université chinoise d'outre - mer]
08_ 串
C # delay, start the timer in the thread, and obtain the system time
C# 线程传参
MFC A对话框调用B对话框函数并传参
MFC console printing, pop-up dialog box
数据库内容输出有问题怎么解决
Mavn builds nexus private server