当前位置:网站首页>Checkout design in SAP Spartacus
Checkout design in SAP Spartacus
2022-06-11 13:17:00 【Hua Weiyun】
https://sap.github.io/spartacus-docs/extending-checkout
The checkout feature in Spartacus is CMS-driven, which means every page in the checkout flow is based on CMS pages, slots and components.
Spartacus Medium checkout The function is also CMS-driven. checkout flow Each page in is based on CMS page,slots and Components.
Routing and Configuration
In the checkout, you often have links from one step to another, which is the reason for registering each checkout page as a semantic page in the storefront configuration.
stay checkout In the process , We usually jump from one link to another , therefore Spartacus Take in Storefront In the configuration , Each one checkout page Registered as semantic page.
default checkout To configure :
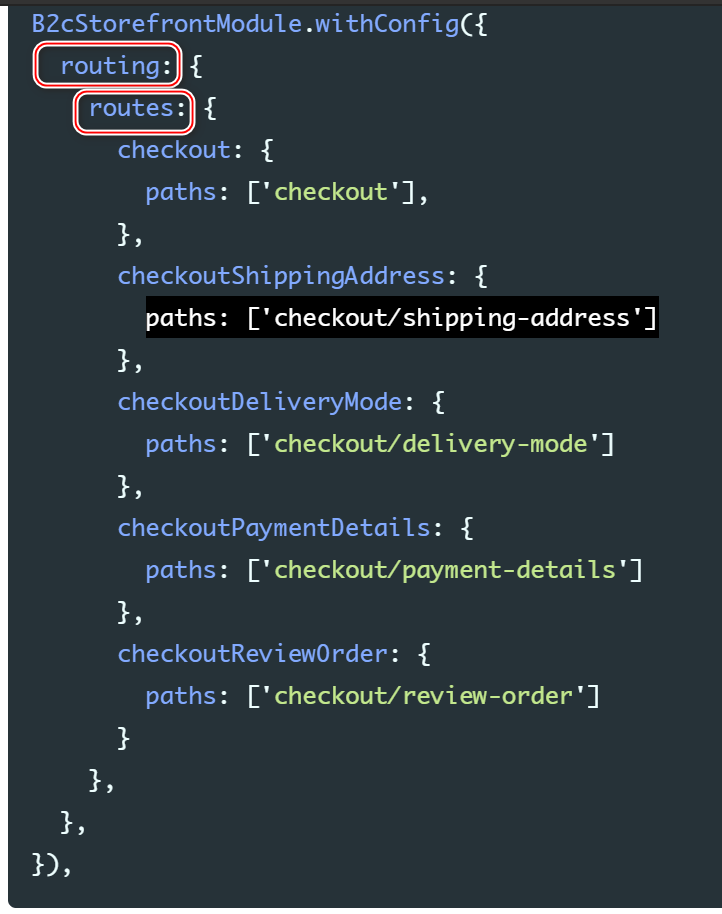
Although the default checkout has four steps, the default configuration defines five semantic pages.
This additional page has a general checkout route that is linked to from every component that should redirect to the checkout. From this general checkout page, Spartacus redirects to the correct checkout step.
Although the default checkout Only 4 A step , But the configuration contains 5 individual semantic page , Have a general routing , Path is route.

4 The page corresponding to each step :

If you want to link to the checkout, always point to this general checkout page, regardless of how your checkout is set up. For example, with a multi-step checkout, you can use your CheckoutGuard to take care of redirecting to the correct checkout step.
Use your own implementation of CheckoutGuard Jump to the right checkout step Up .
With a single-step checkout, you can set all components on this checkout route and remove the CheckoutGuard from the component configuration.
If you want to achieve single step checkout step , from Component configuration Remove CheckoutGuard.
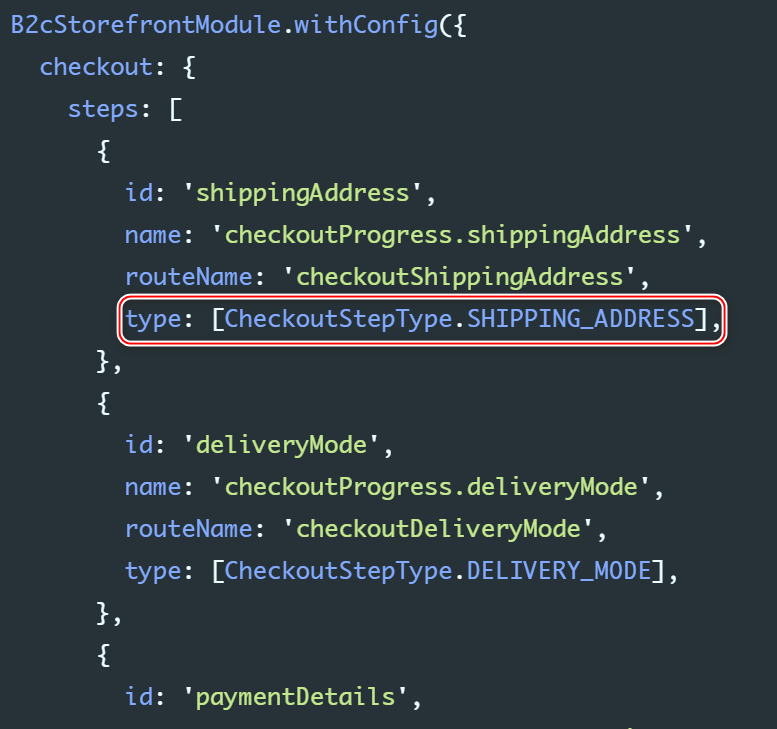
Aside from the route configuration, you can also configure the checkout by defining the responsibility of each step, the route to the page, and the order of the steps. The following is the default configuration:
B2cStorefrontModule.withConfig({ checkout: { steps: [ { id: 'shippingAddress', name: 'checkoutProgress.shippingAddress', routeName: 'checkoutShippingAddress', type: [CheckoutStepType.SHIPPING_ADDRESS], }, { id: 'deliveryMode', name: 'checkoutProgress.deliveryMode', routeName: 'checkoutDeliveryMode', type: [CheckoutStepType.DELIVERY_MODE], }, { id: 'paymentDetails', name: 'checkoutProgress.paymentDetails', routeName: 'checkoutPaymentDetails', type: [CheckoutStepType.PAYMENT_DETAILS], }, { id: 'reviewOrder', name: 'checkoutProgress.reviewOrder', routeName: 'checkoutReviewOrder', type: [CheckoutStepType.REVIEW_ORDER], }, ], },})- id:checkout step Unique identification of
- name:used in the CheckoutProgress component to indicate which checkout steps have been completed.
be used for CheckoutProgress in , Identify which one has been completed checkout step .
- routeName:specifies the semantic page for each step - Every checkout The steps of the semantic Page name
- type: be used for checkout guards
steps The steps in the array determine checkout order .
Every checkout component is a CMS component.
Every checkout Component All are CMS Component.
Furthermore, in the default checkout, all components are CMSFlexComponents.
Go further , every last Component All are CMSFlexComponents.
For Angular or web components that do not need any data from CMS (for example, login), you can use the CMS component of type CMSFlexComponent as a placeholder.
For those who don't need to come from CMS Data Angular perhaps Web Component, We can use The type is CMSFlexComponent Of CMS Component, As placeholder. This type of Component, Have special flexType attribute , stay Spartacus CMS mapping in ,flexType Properties are used .
these components have more guards defined in the configuration, but are otherwise identical to regular CMS components.
CMSFlexComponent There are more... In the configuration guards, besides , Same as ordinary CMS Component There's no difference .
The checkout uses component guards instead of page guards. You protect routes by applying guards in the CMS component mapping.
- checkout Step use Component guard, instead of page guard.
- stay CMS Component mapping It defines guard.
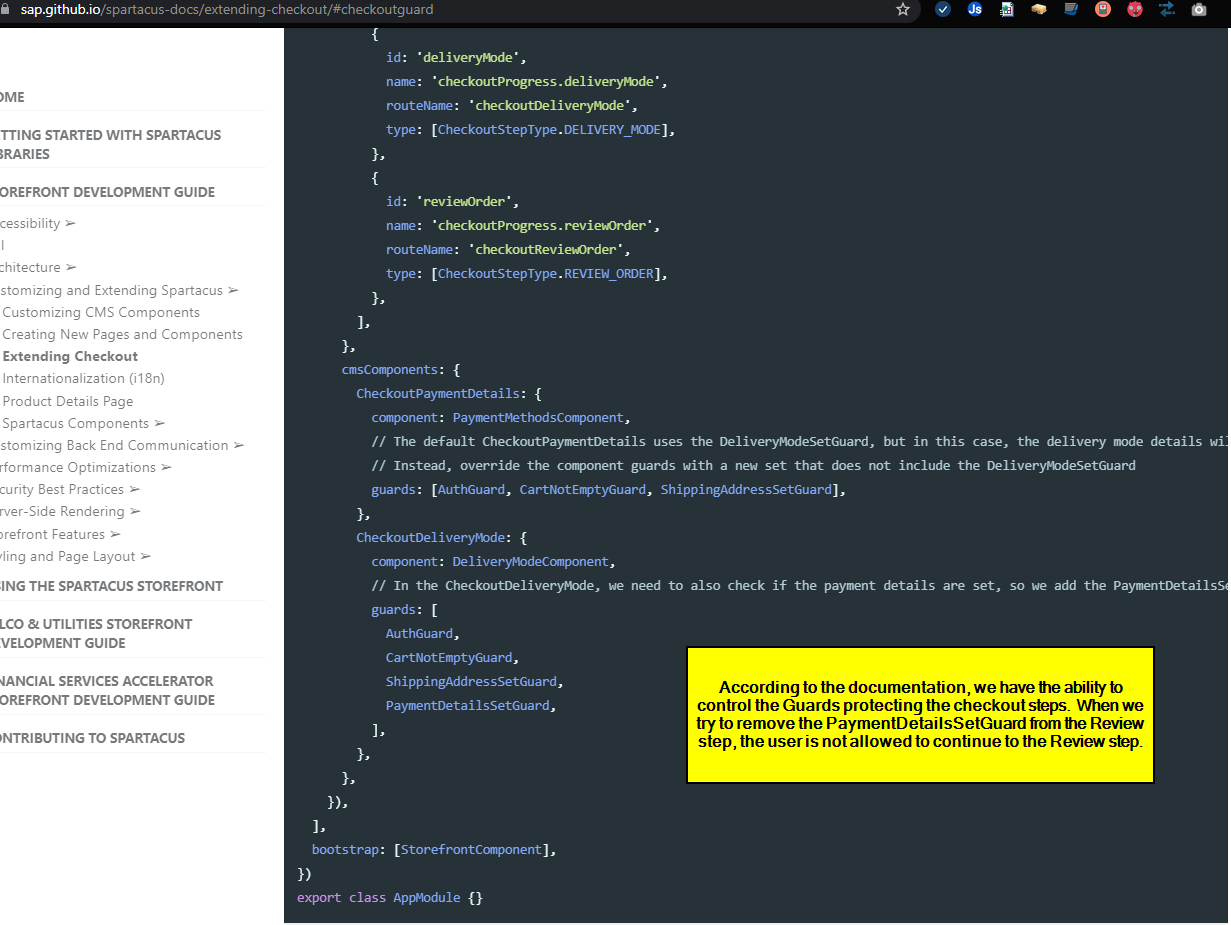
Spartacus Provides the following Component guard:
(1) ShippingAddressSetGuard
(2) DeliveryModeSetGuard
(3) PaymentDetailsSetGuard
(4) CheckoutGuard
As an example, if you wanted to restrict access to the Review Order page, so that it displays only when the shipping address, delivery mode and payment details were correctly set, you would set guards for the review order component to guards: [ShippingAddressSetGuard, DeliveryModeSetGuard, PaymentDetailsSetGuard].
for example , Suppose the demand is Review Order Page It can only be opened when the first three steps have passed , Is to Review order Component Set the following guard:
[ShippingAddressSetGuard, DeliveryModeSetGuard, PaymentDetailsSetGuard]when you try to access the Review Order page, Spartacus first checks the guards for every component on that page, and only displays the page if every guard returns true. If one of the guard returns false, or returns a redirect URL, Spartacus redirects to the provided URL.
therefore , When trying to visit Review Order When the page is ,Spartacus First, go through all the Component guards, Only these guard All return true after , To open Review order page .
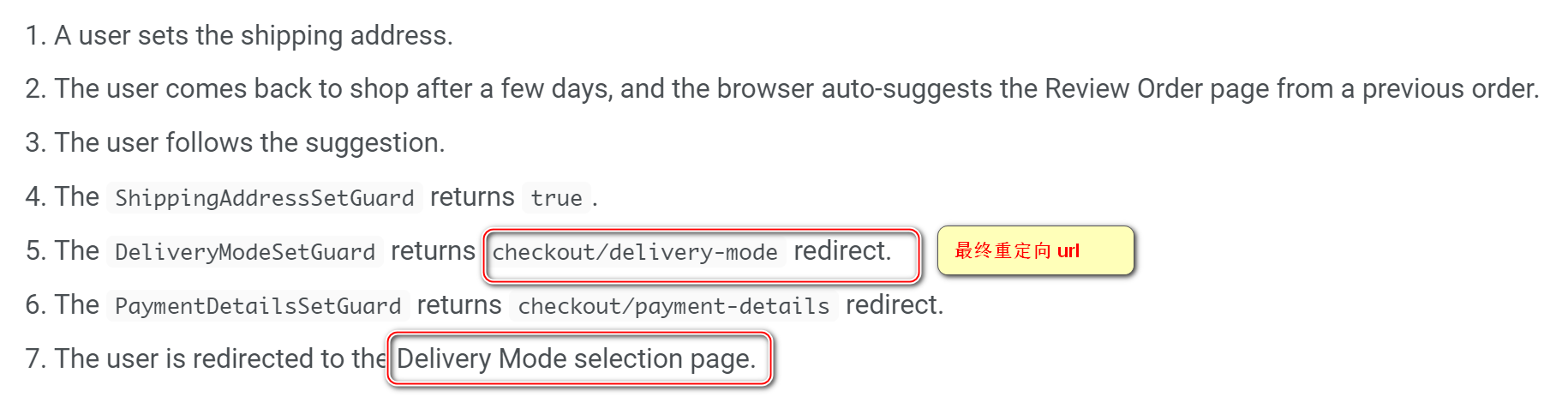
The order of the guards is important because the first redirect is used. In general, you should define guards in the same order as the checkout flow.
Component guard Which one to return first redirect url, The user is redirected to which url Go to . therefore Component guard The order is important .
How to define redirection url
In the checkout configuration, for each step, you specify a type attribute and the type of data that should be set. A guard looks for the first step that contains the specific type and then redirects to this step.
For example, ShippingAddressSetGuard searches the checkout configuration for the first step with a type containing CheckoutStepType.shippingAddress, then reads the step route and redirects to that page.

CMS Catalog Content and Default Template
After clicking the shopping cart button , Jump to checkout route:

When from cart Jump to checkout when , There is one cancel operation ,cancel Yes. checkout default step: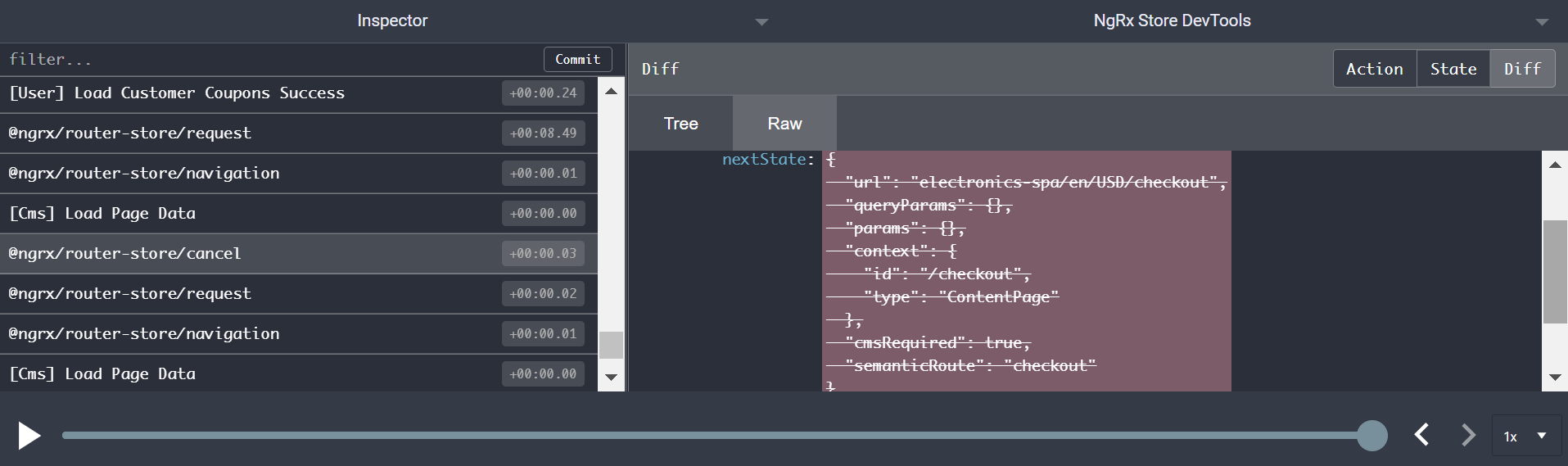
And then launch a campaign to checkout/shipping-address Request :

Finally jump to shipping address url:
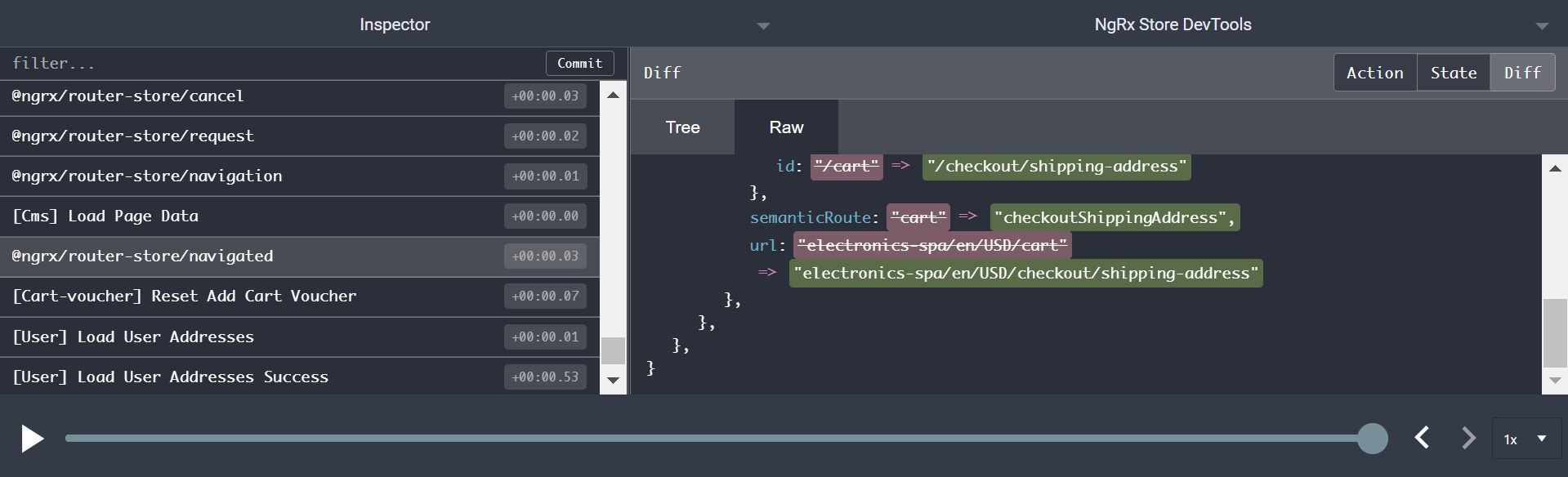
http://localhost:4200/electronics-spa/en/USD/checkout
In the default checkout, Spartacus uses a modified MultiStepCheckoutOrderSummaryPageTemplate.
As shown in the figure below :
contain 16 individual content slot: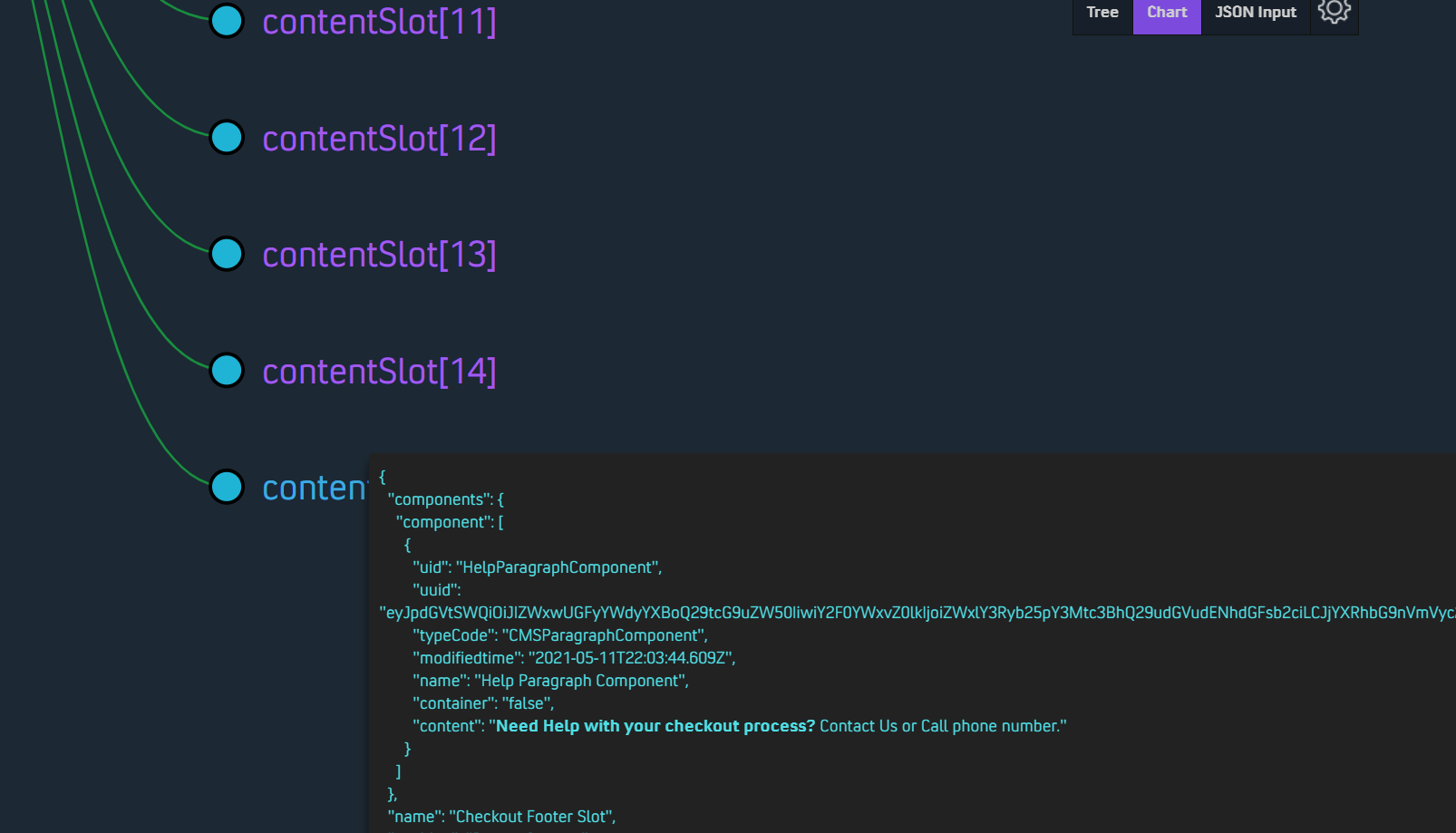
Exchange checkout The sequence of steps
An example :
The following scenario describes how to change the order of two steps. In the default configuration, the checkout flow starts with setting a shipping address, followed by setting the delivery mode, and finally by filling in the payment details. In this scenario, the configuration is modified so that the payment details step occurs before the delivery mode step.
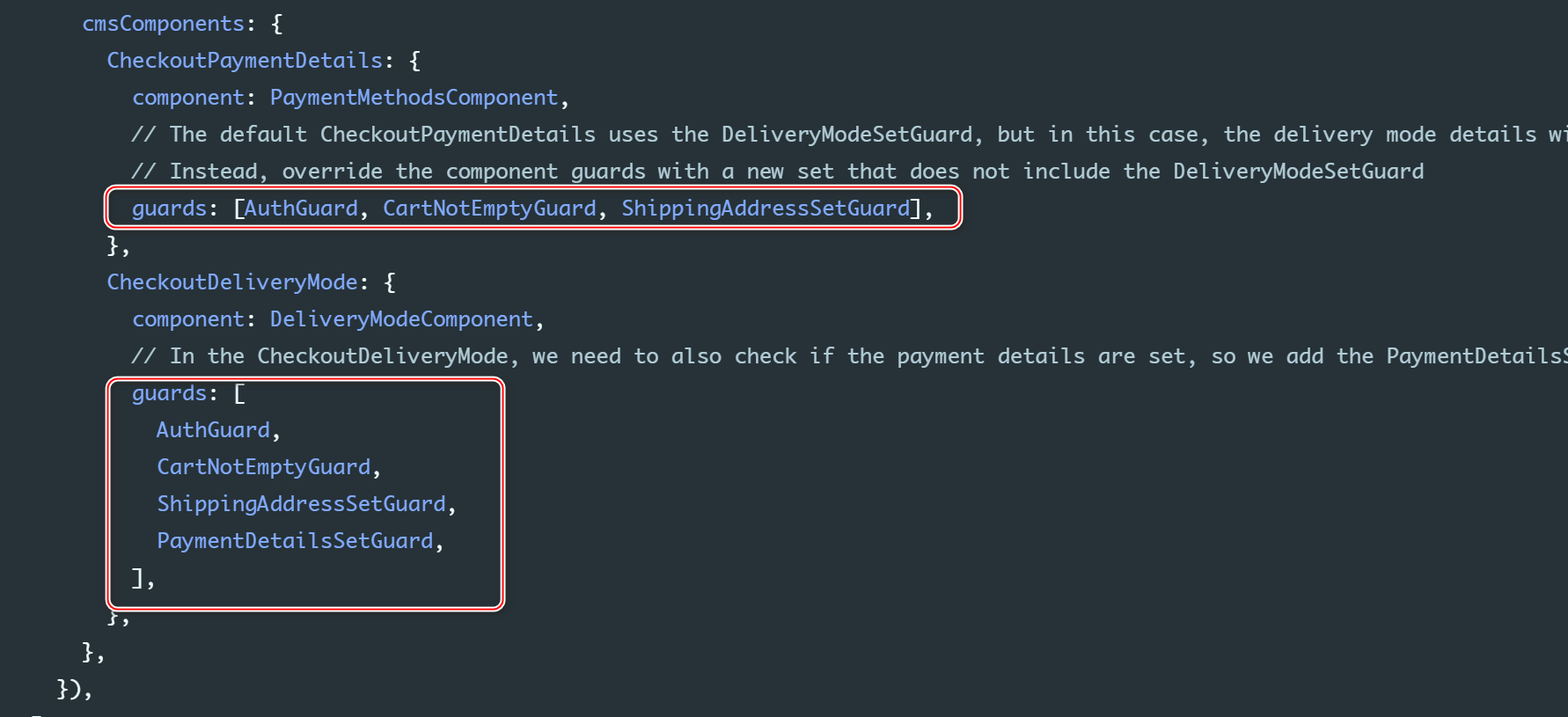
@NgModule({ imports: [ B2cStorefrontModule.withConfig({ ...restOfConfig, checkout: { // You must specify all of the steps (this configuration is not merged with the default one) steps: [ { id: 'shippingAddress', name: 'checkoutProgress.shippingAddress', routeName: 'checkoutShippingAddress', type: [CheckoutStepType.SHIPPING_ADDRESS], }, // Change the payment details step to be before the delivery mode { id: 'paymentDetails', name: 'checkoutProgress.paymentDetails', routeName: 'checkoutPaymentDetails', type: [CheckoutStepType.PAYMENT_DETAILS], }, { id: 'deliveryMode', name: 'checkoutProgress.deliveryMode', routeName: 'checkoutDeliveryMode', type: [CheckoutStepType.DELIVERY_MODE], }, { id: 'reviewOrder', name: 'checkoutProgress.reviewOrder', routeName: 'checkoutReviewOrder', type: [CheckoutStepType.REVIEW_ORDER], }, ], }, cmsComponents: { CheckoutPaymentDetails: { component: PaymentMethodsComponent, // The default CheckoutPaymentDetails uses the DeliveryModeSetGuard, but in this case, the delivery mode details will not be set yet. // Instead, override the component guards with a new set that does not include the DeliveryModeSetGuard guards: [AuthGuard, CartNotEmptyGuard, ShippingAddressSetGuard], }, CheckoutDeliveryMode: { component: DeliveryModeComponent, // In the CheckoutDeliveryMode, we need to also check if the payment details are set, so we add the PaymentDetailsSetGuard guards: [ AuthGuard, CartNotEmptyGuard, ShippingAddressSetGuard, PaymentDetailsSetGuard, ], }, }, }), ], bootstrap: [StorefrontComponent],})export class AppModule {}CheckoutPaymentDetails Component, Only in entering payment step Load when :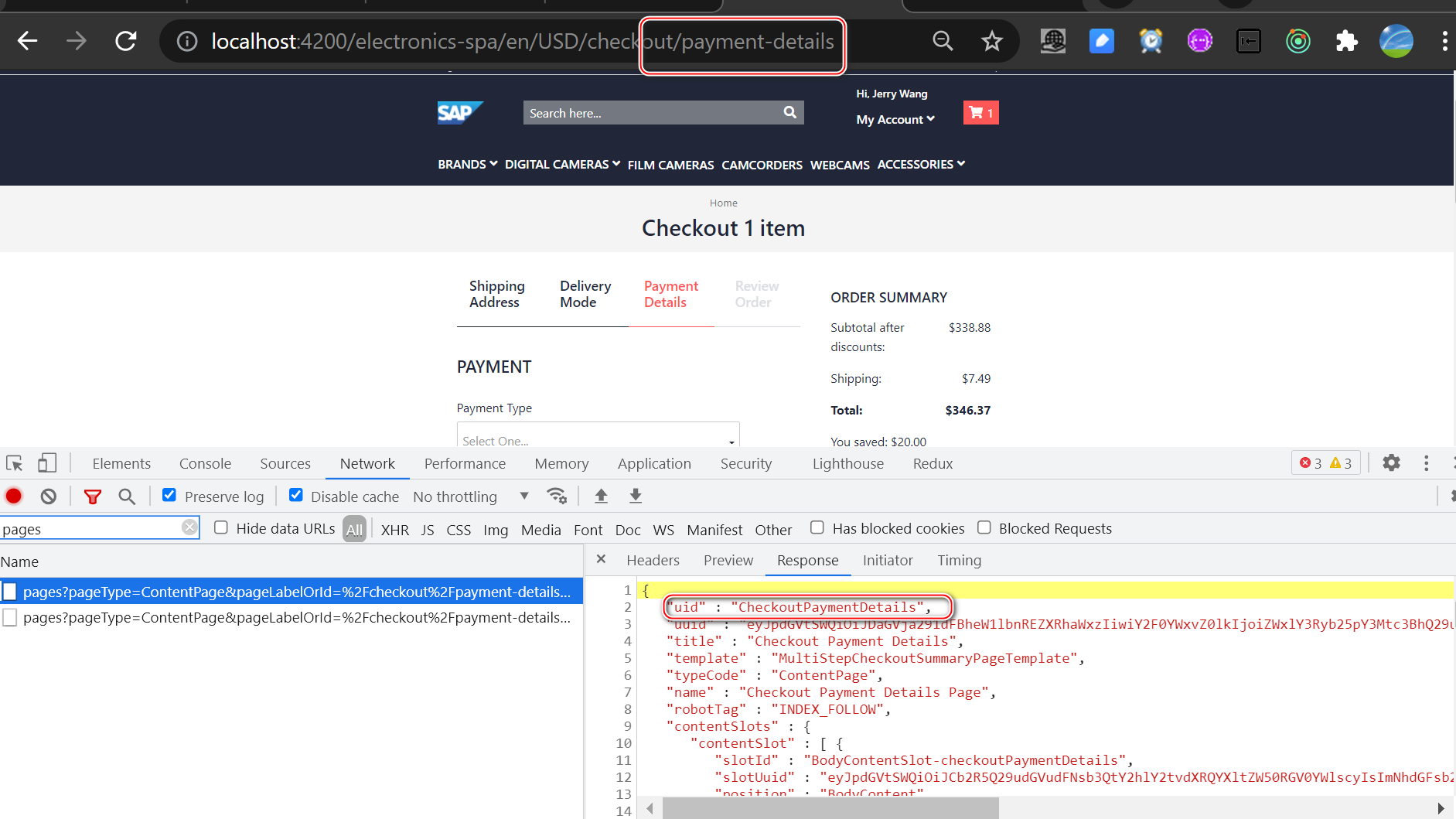
CheckoutPaymentDetails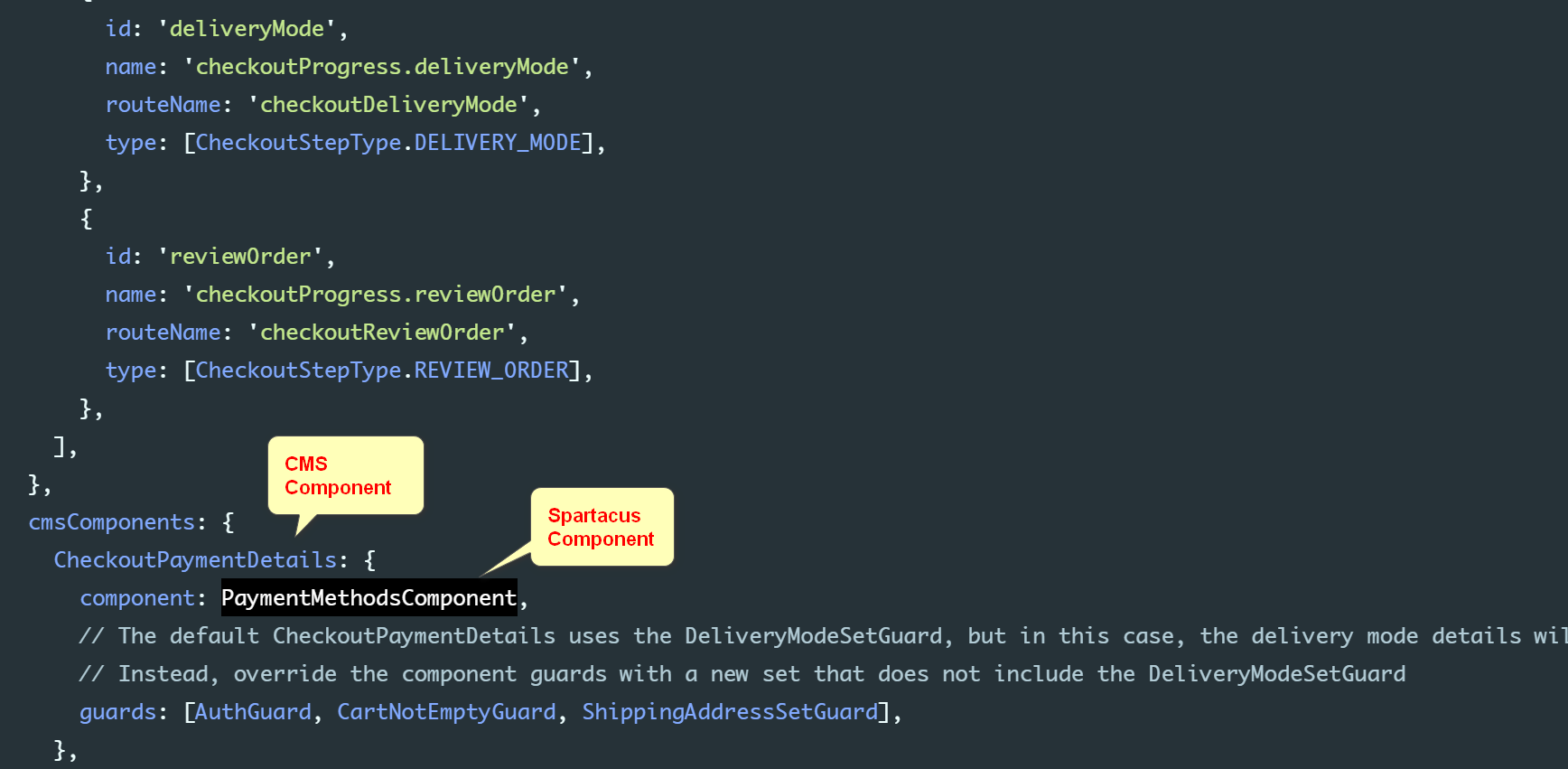

stay CMS Component mapping Specified in Component guard:
边栏推荐
- 如何同步openstack RDO源至本地进行离线安装
- [bug resolution] after uploading the image, cancel the upload and upload again. The last image still exists
- On the continuing Life of Distributed Locks - - Distributed Locks Based on redis
- C language - data storage
- 使用华为HECS云服务器打造Telegraf+Influxdb+Grafana 监控系统【华为云至简致远】
- 刚高考完有些迷茫不知道做些什么?谈一谈我的看法
- What do you need to do to "surpass" the general database in the time sequence scenario?
- 逆向学习入门-优秀的汇编调试工具OllyDbg
- Jdbctemplate data background management. I don't know why roleid is empty when adding users
- 火山引擎云数据库 veDB 在字节内部的业务实践
猜你喜欢
![[arcgis] City relevance analysis](/img/f4/454266e1ed586240bce9a7f36aa52e.png)
[arcgis] City relevance analysis

Some transformation thoughts of programmers after they are 35 years old

历史上的今天:Apple II 问世;微软收购 GECAD;发明“软件工程”一词的科技先驱出生...
![[filter] design of time-varying Wiener filter based on MATLAB [including Matlab source code 1870]](/img/1a/7b80f3d81c1f4773194cffa77fdfae.png)
[filter] design of time-varying Wiener filter based on MATLAB [including Matlab source code 1870]

The Tree (AVL, 2-3-, 红黑,Huffman)
![[bug resolution] the form is paged to display the total data res.data total](/img/92/1ddde16d35465f8dd53ebf90e249b8.png)
[bug resolution] the form is paged to display the total data res.data total

Log management system, summary in multiple ways

程序员到了35岁之后的一些转型思考

逆向学习入门-优秀的汇编调试工具OllyDbg

live share使用体验
随机推荐
How to write high-performance code (IV) optimize data access
Hashicopy之nomad应用编排方案07(提交Job)
【信号去噪】基于稀疏性 (BEADS) 实现色谱基线估计和去噪附matlab代码和论文
添加环境路径
详解C语言实参与形参的区别
About uni app configuration, app does not display the top title bar setting
【滤波器】基于matlab时变维纳滤波器设计【含Matlab源码 1870期】
UI inspiration analysis Notes 6: feature
不谈赛道,不聊风口,开源数据库巨头Cassandra如何在国内讲好“新故事” | C位面对面
使用华为HECS云服务器打造Telegraf+Influxdb+Grafana 监控系统【华为云至简致远】
PKI/TLS瑞士军刀之cfssl
Shader shader
After five years of losing the lawsuit, the trillion reptile army is ready to move
火山引擎云数据库 veDB 在字节内部的业务实践
Is byte really the end of the universe?
【bug解决】上传图片后,取消这次上传 再次执行上传,上次的图片还存在
[backtrader source code analysis 46] cerebro Py code comments (boring, one of the core backtrader codes, recommended for reading, comments for reference only)
The tree (AVL, 2-3-, red black, Huffman)
Condition debug of pycharm
31w赛题奖金!当 AI for Science 撞上“先导杯”,会擦出什么样的火花?