当前位置:网站首页>Log management system, summary in multiple ways
Log management system, summary in multiple ways
2022-06-11 12:42:00 【A cicada smiles】
One 、 Background
Log management in the project is one of the basic functions , Different users and scenarios have specific requirements for logs , Therefore, different strategies need to be used for log collection and management , If it's in a distributed project , The system design of log is more complex .
- Log type : Business operations 、 Information printing 、 Request link ;
- Role requirements : R & D end 、 User side 、 Service level 、 The system level ;

Users and needs
- User side : Addition, deletion and modification of core data , Business operations log ;
- R & D end : Log collection and management strategy , Exception log monitoring ;
- Service level : Key log printing , Problem discovery and troubleshooting ;
- The system level : Link generation in distributed projects , Monitoring system ;
In different scenes , Different technical means need to be selected to realize log collection and management , For example, log printing 、 Operation record 、ELK System, etc , Be careful to avoid abnormal interruption of the program caused by log management .
The more complex the system design and business scenario , The more you rely on the output of the log , In a large-scale architecture , Usually, an independent log platform will be built , Provide the collection of log data 、 Storage 、 Analysis and other complete solutions .
Two 、Slf4j Components
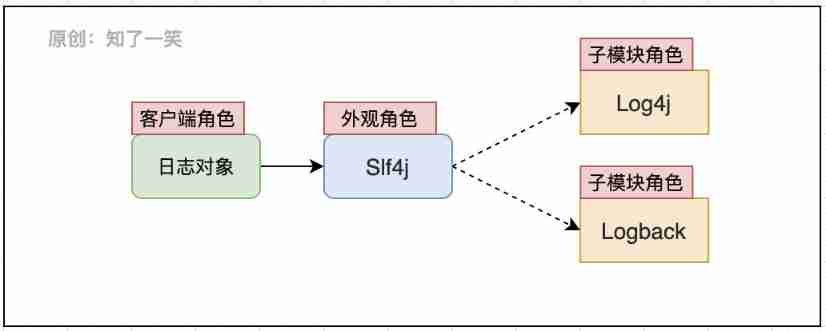
1、 Appearance mode
The components of the log follow the design pattern ,Slf4j As the appearance object of the log system , Define the criteria for the specification log , The specific implementation of logging capability is entrusted to each sub module ;Slf4j Specify the loading method and function interface of log object , Interact with the client to provide log management function ;
private static final org.slf4j.Logger logger = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(Impl.class) ;
Direct use of... Is generally prohibited Logback、Log4j And other specific implementation components API, Avoid unnecessary trouble caused by component replacement , Unified maintenance of logs can be achieved .
2、SPI Interface
from Slf4j and Logback Component interaction , During the use of logs , The basic entry point is to use Slf4j The interface of , Identify and load Logback The specific implementation of ;SPI Defined interface specification , Usually as a third party ( external ) Implementation of components .

Above SPI As the connection point between the two sets of components , Look at the process of loading the source code , trace LoggerFactory The source code of :
public final class org.slf4j.LoggerFactory {
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
}
private final static void bind() {
try {
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\".");
}
}
}
}
Only a few lines of schematic source code are posted here , stay LoggerFactory When initializing binding associations in , If no specific log implementation component is found , Yes, the corresponding exception information will be reported , And it USES the System.err Output error prompt .
3、 ... and 、 Custom components
1、 Functional encapsulation
For logs ( Or others ) Common functions , Usually, independent code packages are encapsulated in Code Engineering , As a public dependency , Unified management and maintenance , For the custom encapsulation of logs, refer to the previous documents , There are usually several core points involved here :
- starter load : Package configuration starter Components , Can be scanned and loaded by the frame ;
- aop Faceted programming : Usually add log comments on relevant methods , You can automatically record the action ;
- annotation annotation : Define the core parameters and processing logic that need to be marked for logging ;
As for how to assemble the log content , Adapt business semantics , And the subsequent management process , Then design corresponding strategies according to specific scenarios , For example, how to store logs 、 Whether to analyze in real time 、 Whether to execute asynchronously, etc .
2、 Object parsing
In custom annotations , It will involve the problem of object parsing , That is, put the attribute to be resolved from the object in the annotation , And concatenate the values into the log content , It can enhance the semantic readability of business logs .
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map aggregate
HashMap<String,Object> infoMap = new HashMap<>() ;
infoMap.put("info","Map Description of ") ;
// List aggregate
ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>() ;
arrayList.add("List-00");
arrayList.add("List-01");
// User object
People oldUser = new People("Wang",infoMap,arrayList) ;
People newUser = new People("LiSi",infoMap,arrayList) ;
// Packaging object
WrapObj wrapObj = new WrapObj("WrapObject",oldUser,newUser) ;
// Object property resolution
SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// objName
Expression objNameExp = parser.parseExpression("#root.objName");
System.out.println(objNameExp.getValue(wrapObj));
// oldUser
Expression oldUserExp = parser.parseExpression("#root.oldUser");
System.out.println(oldUserExp.getValue(wrapObj));
// newUser.userName
Expression userNameExp = parser.parseExpression("#root.newUser.userName");
System.out.println(userNameExp.getValue(wrapObj));
// newUser.hashMap[info]
Expression ageMapExp = parser.parseExpression("#root.newUser.hashMap[info]");
System.out.println(ageMapExp.getValue(wrapObj));
// oldUser.arrayList[1]
Expression arr02Exp = parser.parseExpression("#root.oldUser.arrayList[1]");
System.out.println(arr02Exp.getValue(wrapObj));
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class WrapObj {
private String objName ;
private People oldUser ;
private People newUser ;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class People {
private String userName ;
private HashMap<String,Object> hashMap ;
private ArrayList<Object> arrayList ;
}
Pay attention to the... Used above SpelExpressionParser Parser , namely Spring The native of the framework API; Many problems encountered in business , Suggestions are given priority from the core dependence (Spring+JDK) Find a solution in , Spend more time getting familiar with the whole picture of the core components in the system , It will be of great help to develop vision and ideas .
3、 Pattern design
Here's a more complex solution to user-defined logs , adopt AOP Pattern recognition log annotation , And parse the object attributes to be recorded in the annotation , Build the corresponding log body , Finally, adapt different business strategies according to the scenario marked by the annotation :

The higher the versatility of the function , The more abstract the built-in adaptation strategy is when encapsulating , When dealing with complex logical processes , Be good at using different components together , Can share the pressure of business support , Form a stable and reliable solution .
Four 、 Distributed Links
1、 Link identification
Distributed system based on microservice implementation , Processing a request will go through multiple sub Services , If an exception occurs to a service in the process , You need to locate the request action of this exception , So as to better judge the cause of the abnormality and solve it again .
The action of positioning depends on a core identification :TraceId- The trajectory ID, That is, when each service flows , Will carry the binding of the request TraceId, This can identify which actions of different services are generated by the same request .
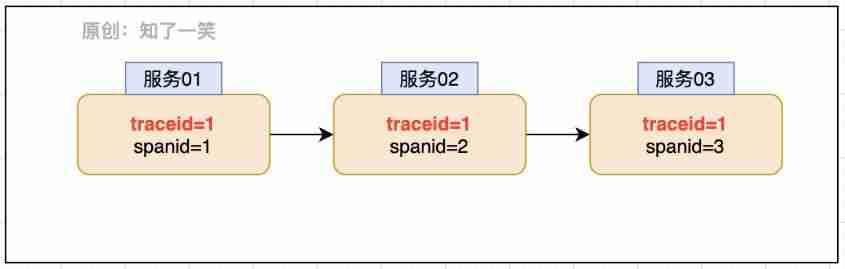
adopt TraceId and SpanId The requested link view can be restored , Combined with relevant log printing records and other actions , You can quickly solve the abnormal problem . In the micro service system Sleuth Components provide support for this capability .
The core parameters of the link view can be integrated Slf4j In the component , Here you can refer to org.slf4j.MDC grammar ,MDC Provide parameter transfer mapping capability before and after the log , Inner packaging Map Container management parameters ; stay Logback In the component ,StaticMDCBinder Provide the binding of this capability , In this way, the log print can also carry the identification of the link view , Complete integration of this capability .
2、ELK system
The logs generated by the link view are very large , How to manage the logs of these documents and how to use them quickly is also a key problem , A common solution is ELK system , It has been updated to ElasticStack product .

- Kibana: Can be in Elasticsearch Use graphics and charts to visualize data ;
- Elasticsearch: Provide data storage , The ability of search and analysis engines ;
- Logstash: Data processing pipeline , Able to collect from multiple sources at the same time 、 transformation 、 Push data ;
Logstash Provide log collection and transmission capabilities ,Elasticsearch Store a lot of JSON Format of logging ,Kibana Then you can display the data in a visual way .
3、 Service and configuration
Configuration dependency : You need to configure... In the service Logstash Address and port , Log transmission address , And the name of the service ;
spring:
application:
name: app_serve
logstash:
destination:
uri: Logstash- Address
port: Logstash- port
Configure read :Logback Load the above core parameters in the component configuration , In this way, in the configuration context, you can use name Use this parameter for the value of ;
<springProperty scope="context" name="APP_NAME" source="spring.application.name" defaultValue="butte_app" />
<springProperty scope="context" name="DES_URI" source="logstash.destination.uri" />
<springProperty scope="context" name="DES_PORT" source="logstash.destination.port" />
Log transfer : Configure the transmission content accordingly , Appoint LogStash Service configuration , code , Core parameters, etc ;
<appender name="LogStash" class="net.logstash.logback.appender.LogstashTcpSocketAppender">
<!-- Log transfer address -->
<destination>${DES_URI:- }:${DES_PORT:- }</destination>
<!-- Log transfer code -->
<encoder class="net.logstash.logback.encoder.LoggingEventCompositeJsonEncoder">
<providers>
<timestamp>
<timeZone>UTC</timeZone>
</timestamp>
<!-- Log transfer parameters -->
<pattern>
<pattern>
{
"severity": "%level",
"service": "${APP_NAME:-}",
"trace": "%X{X-B3-TraceId:-}",
"span": "%X{X-B3-SpanId:-}",
"exportable": "%X{X-Span-Export:-}",
"pid": "${PID:-}",
"thread": "%thread",
"class": "%logger{40}",
"rest": "%message"
}
</pattern>
</pattern>
</providers>
</encoder>
</appender>
Output format : You can also set the format of the log , Manage log files or console output ;
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %contextName [%thread] %-5level %logger{100} - %msg %n</pattern>
About Logback Other configuration of component log , For example, output location , Level , Data transmission mode, etc , You can refer to the official documents , Continuous optimization .
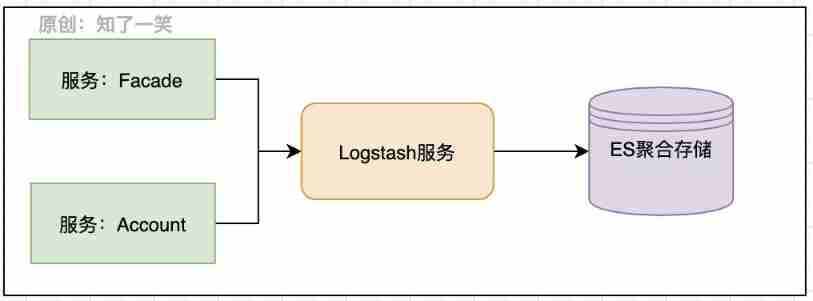
4、 Data channel
Let's look at the data transmission to Logstash After service , How to retransmit to ES Of , The corresponding transmission configuration is also required here , Be careful logstash and ES The same version is recommended , In this case, it is 6.8.6 edition .
The configuration file :logstash-butte.conf
input {
tcp {
host => "192.168.37.139"
port => "5044"
codec => "json"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"]
index => "log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
- Input configuration : Appoint logstash Connected host And port , And specify the data format as json type ;
- Output configuration : Specifies the output of log data ES Address , And designate index The index is created on a daily basis ;
start-up logstash service
/opt/logstash-6.8.6/bin/logstash -f /opt/logstash-6.8.6/config/logstash-butte.conf
So complete ELK The log management link is realized , By using Kibana The tool can view the log records , according to TraceId You can find the view link .
5、 ... and 、 Reference source code
Application warehouse :
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-flyer-parent
Component encapsulation :
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-frame-parent
边栏推荐
- 4、LockSupport与线程中断
- Oracle 将数据导出到CSV(Excel)文件的方法
- Troubleshoot Splunk kvstore "starting"
- Seckill multi-level cache ----- product details page
- 2、CompletableFuture
- Record a CODIS memory cleanup
- 2、CompletableFuture
- 8. 18 arhat enhancements for atomic operations
- 1、线程基础知识
- What are the advantages of comprehensive venues?
猜你喜欢

How about Lenovo Xiaoxin 520? Which is more worth buying than dangbei D3x?

Technical difficulties of secsha

知物由学 | 行为时序建模在社交引流黑产识别中的应用

母婴店的利润来源有哪些?

Redis data type Daily use Scenarios
![Harmonyos application development -- General app interface framework appgeneralframework[app general framework][api v6]](/img/b6/d1d7d0e670af9505a4fabee76211c6.jpg)
Harmonyos application development -- General app interface framework appgeneralframework[app general framework][api v6]

联想小新520怎么样?对比当贝D3X哪款更值得买?
How does Wireshark modify the display format of packet capturing time and date?

Redis數據類型日常使用場景

netstat 命令详解
随机推荐
Technical difficulties of secsha
Oracle 将数据导出到CSV(Excel)文件的方法
Luo Jing: connection Efficiency Optimization Practice
Some common websites
Record a troubleshooting of MySQL master-slave asynchrony
Security mechanism of verification code in seckill
App manual signature of openharmony standard system
场馆坪效这么低?关键在这两方面
4、LockSupport与线程中断
STM32 development of practical series 7-data Porter DMA
How to optimize SEO on the mobile terminal? Do you need to optimize GoogleSEO on the mobile terminal for a separate m domain name?
Stone technology: R & D strength and excellent quality help upgrade the sweeping robot industry
8. 18 arhat enhancements for atomic operations
Redis RDB and AOF
游泳馆暑期业绩翻倍的方法
机械设备制造企业,如何借助ERP系统做好委外加工管理?
Flip window join, interval join, window cogroup
Ettercap sniffing of man in the middle attack
Harmonyos application development -- mycalculator based on self-made grid layout [my calculator][api v6]
What is QoS? (quality of service)