当前位置:网站首页>Flip window join, interval join, window cogroup
Flip window join, interval join, window cogroup
2022-06-11 12:11:00 【But don't ask about your future】
List of articles
1. Window connection (Window Join)
Flink Provides a window join (window join) operator , You can define the time window , And share a common key between the two streams (key) Put the data in the window for pairing processing
1.1 Call of window connection
Implementation of window connection in code , First you need to call DataStream Of .join() Method to merge two streams , Get one JoinedStreams; Then passed .where() and .equalTo() Method to specify the join in two streams key; And then through .window() Open the window , And call .apply() Pass in the join window function for processing and calculation
stream1.join(stream2)
.where(<KeySelector>)
.equalTo(<KeySelector>)
.window(<WindowAssigner>)
.apply(<JoinFunction>)
.where() The argument for is the key selector (KeySelector), Used to specify... In the first stream key; and .equalTo() Incoming KeySelector Then... In the second stream is specified key. The same elements , If in the same window , You can match
1.2 Processing flow of window connection
First of all, according to key grouping 、 Enter the corresponding window to store ; When the window end time is reached , The operator will first count all combinations of the data of the two streams in the window , That is to do a Cartesian product of the data in the two streams ( Equivalent to cross join of tables ,cross join), And then we're going to iterate , Put each pair of matching data , As a parameter (first,second) Pass in JoinFunction Of .join() Method for calculation and processing , The results obtained are output directly . So every pair of data in the window is successfully connected and matched ,JoinFunction Of .join() Method will be called once , And output a result 
1.3 Window join instance
public class WindowJoinExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream1 = env.fromElements(Tuple2.of("a", 1000L), Tuple2.of("b", 1000L), Tuple2.of("a", 2000L), Tuple2.of("b", 2000L))
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String, Long>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple2<String, Long> stringLongTuple2, long l) {
return stringLongTuple2.f1;
}
}
)
);
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream2 = env.fromElements(Tuple2.of("a", 3000L), Tuple2.of("b", 3000L), Tuple2.of("a", 4000L), Tuple2.of("b", 4000L))
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String, Long>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple2<String, Long> stringLongTuple2, long l) {
return stringLongTuple2.f1;
}
}
)
);
stream1.join(stream2)
.where(new KeySelector<Tuple2<String, Long>, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Tuple2<String, Long> value) throws Exception {
return value.f0;
}
}).equalTo(new KeySelector<Tuple2<String, Long>, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Tuple2<String, Long> value) throws Exception {
return value.f0;
}
}
)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5)))
.apply(new FlatJoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Long>, Tuple2<String, Long>, String>() {
@Override
public void join(Tuple2<String, Long> first, Tuple2<String, Long> second, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(first + "=>" + second);
}
})
.print();
env.execute();
}
}

2. Interval connection (Interval Join)
On the e-commerce website , User behavior tends to be strongly correlated in a short time . Suppose there are two streams , One is the flow of placing orders , One is the stream of browsing data , A connection can be made for the same user , Make a join query between the user's order placing event and the user's browsing data in the last ten minutes (Interval Join)
2.1 The principle of interval connection
The interval join joins elements of two streams ( A & B ) with a common key and where elements of stream B have timestamps that lie in a relative time interval to timestamps of elements in stream A
To the yellow stream (A) Any data element in a, Divide a time interval :[a.timestamp + lowerBound, a.timestamp + upperBound], Green flow ( B) Data elements in b, key Same and timestamp here
Within a range of ,a and b Successfully paired
where a and b are elements of A and B that share a common key. Both the lower and upper bound can be either negative or positive as long as the lower bound is always smaller or equal to the upper bound. The interval join currently only performs inner joins.
When a pair of elements are passed to the ProcessJoinFunction, they will be assigned with the larger timestamp (which can be accessed via the ProcessJoinFunction.Context) of the two elements.
2.2 Call of interval connection
import org.apache.flink.api.java.functions.KeySelector;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.co.ProcessJoinFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
...
DataStream<Integer> orangeStream = ...;
DataStream<Integer> greenStream = ...;
orangeStream
.keyBy(<KeySelector>)
.intervalJoin(greenStream.keyBy(<KeySelector>))
.between(Time.milliseconds(-2), Time.milliseconds(1))
.process (new ProcessJoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String(){
@Override
public void processElement(Integer left, Integer right, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) {
out.collect(left + "," + right);
}
});
2.3 Interval connection instance
public class IntervalJoinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, String, Long>> orderStream = env.fromElements(
Tuple3.of("Mary", "order-1", 5000L),
Tuple3.of("Alice", "order-2", 5000L),
Tuple3.of("Bob", "order-3", 20000L),
Tuple3.of("Alice", "order-4", 20000L),
Tuple3.of("Cary", "order-5", 51000L)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple3<String, String, Long>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple3<String, String, Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3<String, String, Long>
element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.f2;
}
})
);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> clickStream = env.fromElements(
new Event("Bob", "./cart", 2000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=100", 3000L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=200", 3500L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=2", 2500L),
new Event("Alice", "./prod?id=300", 36000L),
new Event("Bob", "./home", 30000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=1", 23000L),
new Event("Bob", "./prod?id=3", 33000L)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Event>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
orderStream
.keyBy(new KeySelector<Tuple3<String, String, Long>, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Tuple3<String, String, Long> data) throws Exception {
return data.f0;
}
})
.intervalJoin(clickStream.keyBy(new KeySelector<Event, String>() {
@Override
public String getKey(Event data) throws Exception {
return data.user;
}
}))
.between(Time.seconds(-5), Time.seconds(10)) // Before 5 Second after 10 Second Range
.process(new ProcessJoinFunction<Tuple3<String, String, Long>, Event, String>() {
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple3<String, String, Long> left, Event right, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
out.collect(right + " => " + left);
}
})
.print();
env.execute();
}
}
result :
3. The window is connected with the group (Window CoGroup)
And window join Very similar , After merging the two streams, open a window to handle the matching elements , When calling, you only need to .join() Replace with .coGroup()
stream1.coGroup(stream2)
.where(<KeySelector>)
.equalTo(<KeySelector>)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.hours(1)))
.apply(<CoGroupFunction>)
And window join The difference is that , call .apply() Method to define a specific operation , What's coming in is a CoGroupFunction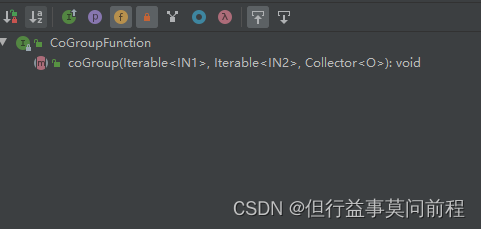
The three parameters passed in , Each represents the data in the two streams and the collector for output (Collector). The difference is , The first two parameters are no longer separate pairs of data , Instead, a traversable data set is passed in . That is, the Cartesian product of two stream data sets in the window will not be calculated , Instead, all the data collected is directly transmitted to , As for how to pair, it is completely customized . such .coGroup() Methods are called only once , And even if the data of one stream does not match the data of another stream , It can also appear in the collection
public class CoGroupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream1 = env.fromElements(
Tuple2.of("a", 1000L),
Tuple2.of("b", 1000L),
Tuple2.of("a", 2000L),
Tuple2.of("b", 2000L)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String, Long>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple2<String, Long> stringLongTuple2, long l) {
return stringLongTuple2.f1;
}
}
)
);
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream2 = env.fromElements(
Tuple2.of("a", 3000L),
Tuple2.of("b", 3000L),
Tuple2.of("a", 4000L),
Tuple2.of("b", 4000L)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String, Long>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple2<String, Long> stringLongTuple2, long l) {
return stringLongTuple2.f1;
}
}
)
);
stream1
.coGroup(stream2)
.where(r -> r.f0)
.equalTo(r -> r.f0)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5)))
.apply(new CoGroupFunction<Tuple2<String, Long>, Tuple2<String, Long>, String>() {
@Override
public void coGroup(Iterable<Tuple2<String, Long>> iter1, Iterable<Tuple2<String, Long>> iter2, Collector<String> collector) throws Exception {
collector.collect(iter1 + "=>" + iter2);
}
})
.print();
env.execute();
}
}
边栏推荐
- 采用快慢指针法来解决有关数组的问题(C语言)
- Fast build elk7.3
- 吊打面试官,涨姿势
- Adjust the array order so that odd numbers precede even numbers (C language)
- [JUC supplementary] immutable object, shared meta mode, final principle
- 反射真的很耗时吗,反射 10 万次,耗时多久。
- Elk - elastalert largest pit
- Problems encountered in installing mysql8 under centos7.x couldn't open file /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/rpm-gpg-key-mysql-2022
- Use compiler option '--downleveliteration' to allow iteration of iterations
- Addition of large numbers (C language)
猜你喜欢

解决Splunk kvstore “starting“ 问题

YARN 切换ResourceManager(Failed to connect to server:8032 retries get failed due to exceeded maximum)

flink 数据流图、并行度、算子链、JobGraph与ExecutionGraph、任务和任务槽

Notes on brushing questions (13) -- binary tree: traversal of the first, middle and last order (review)

JMeter 学习心得

C # apply many different fonts in PDF documents

Iframe value transfer

一般运维架构图

Wechat web developers, how to learn web development

flink 滚动窗口、滑动窗口、会话窗口、全局窗口
随机推荐
You call this shit MQ?
Live app development to determine whether the user is logging in to the platform for the first time
Typescript compilation options and configuration files
Addition of large numbers (C language)
进度条加载
Use cache to reduce network requests
数据如何在 Splunk 中老化?
ftp服务器:serv-u 的下载及使用
Splunk健康检查orphaned searches
How does Sister Feng change to ice?
Use of Chinese input method input event composition
合并两个有序数组(C语言)
微信授权获取手机号码
带你了解直接插入排序(C语言)
軟件項目管理 7.1.項目進度基本概念
Iframe value transfer
中文输入法输入事件composition的使用
Acwing50+acwing51 weeks +acwing3493 Maximum sum (open)
Solve the problem of swagger document interface 404
flink 时间语义、水位线(Watermark)、生成水位线、水位线的传递
