当前位置:网站首页>(10) Binary tree
(10) Binary tree
2022-06-23 18:38:00 【Day-3】
Theoretical content transferred from :https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51983604/article/details/116451530
Trees
Tree is a kind of nonlinear data structure , It is from n(n>=0) Finite nodes make up a set with hierarchical relations . It's called a tree because it looks like an upside down tree , In other words, it is rooted in , And the leaves below .
There is a special node , It's called the root node , The root node has no precursor node . Except for the root node , The rest of the nodes are divided into m(m > 0) Disjoint sets T1、T2、…… 、Tm, And every set of them Ti(1 <= i <= m) It is also a subtree with a structure similar to that of a tree . The root node of each subtree has and only has one precursor , But there can be 0 One or more successors .
Thus we can see that , Trees are defined recursively .
Concept and structure of binary tree
A binary tree is a finite set of nodes , The collection is empty , Or it is composed of a root node and two binary trees called left subtree and right subtree .
Characteristics of binary trees :
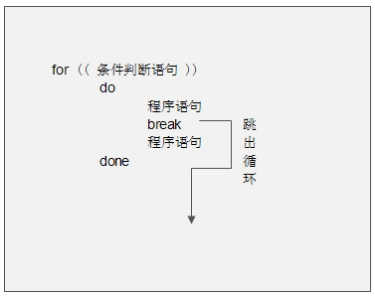
(1) Each node has at most two subtrees , In other words, the degree of nonexistence of binary tree is greater than 2 The node of .
(2) The subtree of a binary tree has left and right branches , The order of its subtrees cannot be reversed .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
char str[100];
int treeIndex = 1;
char Nil = ' ';
typedef struct BiTNode
{
char data;
struct BiTNode * lchild;
struct BiTNode * rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
bool StrAssign(char * T, char * chars)
{
if (strlen(chars)>100)
{
return false;
}
else
{
T[0] = strlen(chars);
// This is supposed to be <=, No <
for (size_t i = 1; i <= T[0]; i++)
{
T[i] = *(chars + i - 1);
}
return true;
}
}
bool InitBiTree(BiTree *T)
{
*T = NULL;
return true;
}
void DestroyBiTree(BiTree * T)
{
if (*T)
{
if ((*T)->lchild)
{
// here (*T)->lchild Modified into &(*T)->lchild
DestroyBiTree(&(*T)->lchild);
}
if ((*T)->rchild)
{
// here (*T)->lchild Modified into &(*T)->lchild
DestroyBiTree(&(*T)->rchild);
}
free(*T);
*T = NULL;
}
}
void CreateBiTree(BiTree * T)
{
char ch;
ch = str[treeIndex++];
if (ch == '#')
{
*T = NULL;
}
else
{
*T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if (!*T)
{
return;
}
(*T)->data = ch;
// here (*T)->lchild Modified into &(*T)->lchild
CreateBiTree(&(*T)->lchild);
CreateBiTree(&(*T)->rchild);
}
}
bool BiTreeEmpty(BiTree T)
{
if (T)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T)
{
int i, j;
if (!T)
{
return 0;
}
if (T->lchild)
{
i = BiTreeDepth(T->lchild);
}
else
{
i = 0;
}
if (T->rchild)
{
j = BiTreeDepth(T->rchild);
}
else
{
j = 0;
}
return i > j ? i + i : j + 1;
}
char Root(BiTree T)
{
if (BiTreeEmpty(T))
{
return Nil;
}
else
{
return T->data;
}
}
char value(BiTree T)
{
return T->data;
}
void Assign(BiTree T, char value)
{
T->data = value;
}
void PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return;
}
printf("%c", T->data);
PreOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
PreOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
}
void InOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return;
}
InOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
printf("%c", T->data);
InOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
}
void PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T)
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return;
}
PostOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
PostOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
printf("%c", T->data);
}
int main()
{
/*int i;*/
BiTree T;
char cl;
InitBiTree(&T);
StrAssign(str, "ABDH#K###E##CFI###G#J##");
CreateBiTree(&T);
printf("Empty = %d(1 = yes 0 = no) Depth of tree = %d\n", BiTreeEmpty(T), BiTreeDepth(T));
cl = Root(T);
printf(" The root of a binary tree is : %c\n", cl);
printf("\n Preorder traversal binary tree :");
PreOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n Middle order ergodic binary tree :");
InOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n Post order traversal binary tree :");
PostOrderTraverse(T);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- 【二叉树】翻转二叉树以匹配先序遍历
- Leetcode question brushing: hash table 03 (happy number)
- Why create a public OKR?
- 三一重能科创板上市:年营收102亿 市值470亿
- Stream流的使用
- 外卖江湖格局将变,美团“大哥”不好当
- 诺亚财富通过聆讯:年营收43亿 汪静波有49%投票权,红杉是股东
- 【 Huazhong University of Science and technology】 Data Sharing for retest of the initial Examination
- 测试
- STM32 (VIII) -- PWM output
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
NetSeer:可编程数据平面的流事件遥测笔记
Asynchronous or thread pool
STM32(八)------- PWM输出
Js25 topic
韬略生物冲刺科创板:年亏损过亿 实控人张大为夫妇为美国籍
halcon知识:区域(Region)上的轮廓算子(1)
QT implements a rule-based machinetranslation system course paper + assignment + project source code
又一家破产清算:那些在时代和资本裹挟下风雨飘摇的游戏公司
外卖江湖格局将变,美团“大哥”不好当
Leetcode 1218. 最长定差子序列(提供一种思路)
STM32 (VIII) -- PWM output
leetcode刷题:哈希表02 (两个数组的交集)
傑理之串口設置好以後打印亂碼,內部晶振沒有校准【篇】
吃顿饭的时间,学会simulink之BLDC基本原理
指标(复杂指标)定义和模型
Task management of embedded development foundation (thread management)
申请多域名SSL证书的要求及注意事项
用软件可编程FPGA加速网络边缘的移动应用总结
可编程数据平面(论文阅读)
MySQL -- classic interview questions




![[QT] Chapter 10: Database](/img/54/54b815b5d117a12ab7c9ce9c29eb65.png)