当前位置:网站首页>Demand and business model innovation - demand 11 - overview of demand analysis
Demand and business model innovation - demand 11 - overview of demand analysis
2022-06-12 02:46:00 【SpriCoder】
Book11- Overview of requirements analysis
1. The fundamental task of requirements analysis

1.1. Basic task content
- Build an analytical model , Reach a common understanding between developers and users of demand information
- According to common understanding , Be creative , Create software system solutions
1.1.1. Build an analytical model , Reach a common understanding between developers and users of demand information
- Decomposing complex systems into simple parts and the connections between them , determine Essential characteristics
- Reach a common understanding of the information content with users
- The analysis activities mainly include distinguish 、 Define and structure , Its purpose is Get information about something that can be transformed into knowledge , This analytical activity is called modeling —— Build a demand analysis model
1.1.2. According to common understanding , Be creative , Create software system solutions
- Decompose a problem into independent 、 Simpler and easier to manage Of Son Problems to help find solutions
- The process of creating a solution is creativity Of
- Help developers to define problems , And determine the logical relationship between the defined things , These logical relations can form information reasoning , Then it can be used to validate the solution correctness .
1.2. Build an analytical model
1.2.1. Model
- A model is an abstraction of things , Help people have a better understanding before creating a thing
- Focus on the computational nature of the problem ( data 、 function 、 Rules and so on )
- It is a way of thinking and reasoning about the system . The goal of modeling is to establish a representation of the system , This representation describes the system in a precise and consistent manner , Make the system easier to use
- The process of modeling is modeling .
- Modeling benefits :
- Reduce application complexity through modeling abstraction .
- Understand information more deeply in the process of modeling .
- It can help people remember details better .
- Better communication with other developers .
- Better communication with users and other stakeholders .
- Provide documentation for future maintenance and upgrades .
- Modeling methods
- abstract
- decompose
- Projection
1.2.1.1. abstract (Abstraction)
- On the one hand, it requires people to focus only on important information , Ignore secondary content : By emphasizing the essential characteristics , It reduces the complexity of the problem
- On the other hand, it also requires people to keep cognition at an appropriate level , Mask deeper details : Infer a broader and more general relationship between the elements of the problem , Help people find solutions
1.2.1.2. decompose (Decomposition / Partitioning)
- “ Divide and rule ”: Decompose a single complex and difficult problem into several relatively easier subproblems , And master the relationship between the sub problems
- Decomposed solutions can often provide solutions to problems
1.2.1.3. Projection (Projection)
- Multi view method
1.3. Two worlds and three models
- Model is the simplification and abstraction of complex system , Focus on specific components and relationships between components , At the same time, ignore the secondary information irrelevant to the component .
1.3.1. Computing world and computing model
- Use The constituent unit of software As a component of the model
- Software Build relationships between units As the relationship between model components
- Calculation model : The components used and the relationships between components are elements of software , From the software ( Computing world ) Model of .
- The computing world is based on computing science , Characterized by formalization , The description of information is clear 、 The characteristics of accuracy and certainty
- The demand analysis stage is not appropriate Establish a formal calculation model
- The point is the problem , Lack of technical details related to software implementation
- The user cannot understand
- The model based on the computing model is the understanding model of the developer , But it is not the common understanding model of users and developers .

1.3.2. Problem world and business model
- Use Important concepts in the problem domain As a component of the model
- Use Business linkages between concepts As the relationship between components
- Used Business description The way , have Informal features
- Business model elements ( Business concept and business connection ) Is inaccurate in the selection and definition of 、 Uncertainty and fuzziness
- You can extract the most important and essential content from the requirement information
- It can reach the common understanding of users and developers
- Non formal features make it unsuitable for requirement modeling , Not enough to describe an effective software solution
- The problem world is complex , The elements of the business model are inaccurate in selection and definition 、 Non formal features of uncertainty and fuzziness .
1.3.3. Software analysis model ( Analysis of the view )
- Be situated between Computing model and business model The model form between the two
- The analytical model uses the of the computational model Component form , When describing the solution, it has a more rigorous and applicable description than the business model .
- The analytical model is The performance of components Using the business model on The way of expression
- The analytical model is semi formal
- Not as rigorous as the computational model , No formal features
- More stringent than the business model , It has semi formal characteristics .
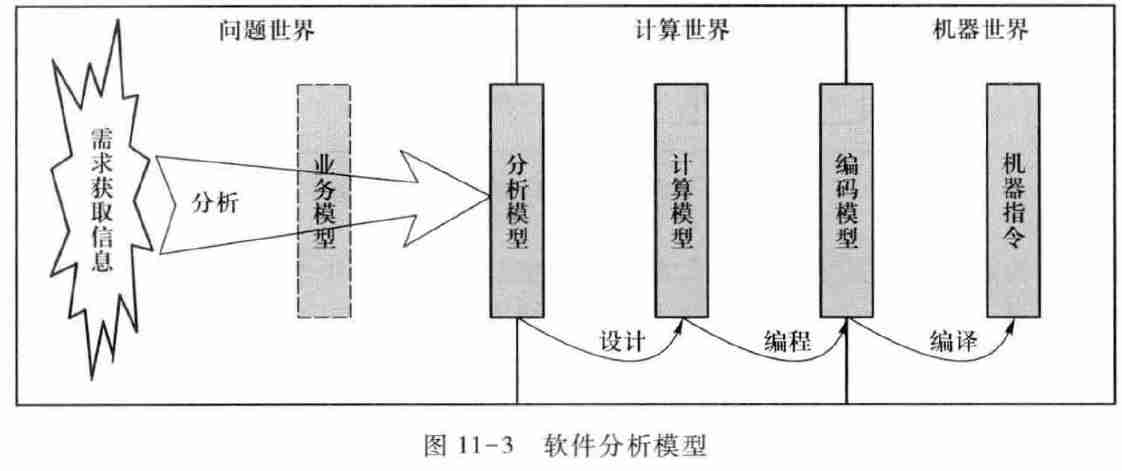
1.3.4. The difference between the three models

- There is no business model in the actual production
- The demanders directly acquire information according to the demand to establish an analysis model
- The computing model can be seen as a pre implementation build draft , Is the design model of software .
1.4. Description of the model
- The three elements are interdependent , Each element All for The next element Provides a necessary environment
- grammar : Usage rule —— How to use model elements , And in what way organization 、 Connect or associate These elements
- semantics : What a particular model element has meaning
- pragmatics : Of model elements Context , And the factors that affect the meaning of the model elements Constraints and assumptions
- The analysis model : It has high requirements for language and pragmatics , Because the content described by the model is complex
- Analyze model characteristics :
- Pragmatic complexity
- Semantic richness
- The grammar is strict but not too complicated
- Many researchers have tried to build a formal or semi formal model language that can describe various scenarios in software development , But they all failed in the end
1.4.1. Description of the model : Multi view method
- Viewpoint analysis requires people to model a complex system , From different perspectives , In a static system, different contents, which are interwoven, coexisted and relatively independent, are disassembled into different parts , Then model each disassembled sub part separately .
- viewpoint (Viewpoints)
- The different contents in the system, which are interwoven, coexisted and relatively independent, are disassembled into different parts
- Each viewpoint is an independent model , Describe with independent model language and representation
- Multi view
- Model descriptions of all viewpoints are integrated , It is the model description of the original complex system
- According to the relationship between different parts of the system , Establish relationships between elements in different models , Thus, multiple independent model descriptions are semantically connected

1.4.2. Model 、 Model language and representation
- Software analysis model is the integration of multiple viewpoint models .

1.5. Requirements modeling
- The key to requirements analysis is to model real-world problems , Problem domain modeling .
- Common influencing factors
- Problem domain model : Real time applications ( flow )/ Information system application
- Skills of demand analysts
- Customer's process requirements
- Availability of methods and tools
- The usual way is :
- First, a preliminary model is established according to the obtained problem domain information .
- Then analyze user needs , Adjust the model , Get an intermediate model form .
- Last , The adjusted model is logically reasoned and verified , If it meets the expected expectations , Then it is the final solution model .

2. Build solutions

- Building a solution system is difficult , Creative process .
- The inspiration of the needs analyst is also important .
- In creative activities , Scientific factors also play an important role .
- Scientific factors
- External cause
- Problem domain characteristics
- demand
- technology 、 Method
- Internal cause
- Technical background
- Knowledge background
- Experience / habit
- External cause

3. Requirements analysis technology
3.1. Model 、 notation 、 technology 、 Methods and tools
- The model is represented in context as one of the following three
- Abstract information body : Focus on the minimum completeness of knowledge
- View
- Model language
3.2. Common requirements analysis techniques
3.2.1. Structured Technology
- Data modeling
- Entity relation diagram Entity Relationship Diagram
- Process modeling
- Data flow diagram Data Flow Diagram
- Context map Context Diagram
- Microspecification Mini-Specification
- The data dictionary Data Dictionary
- Behavior modeling
- state ( transformation ) chart / matrix State (Transition) Diagram/Matrix
- The process / Data relationship modeling
- Functional entity matrix Function/Entity Matrix
- Information engineering methods
- Functional breakdown diagram Function Decomposition Diagram
- Process dependency diagram Process Dependency Diagram
3.2.2. Object oriented technology
- UML
- Use case diagram Use-Case Diagram
- Class diagram Class Diagram
- Interaction diagram ( Sequence diagram / Communication diagrams ) Interaction(Sequence / Communication)Diagram
- Activity diagrams Activity Diagram
- Object constraint language Object Constraint Language
- State diagram State Chart Diagram
3.2.3. Simple summary
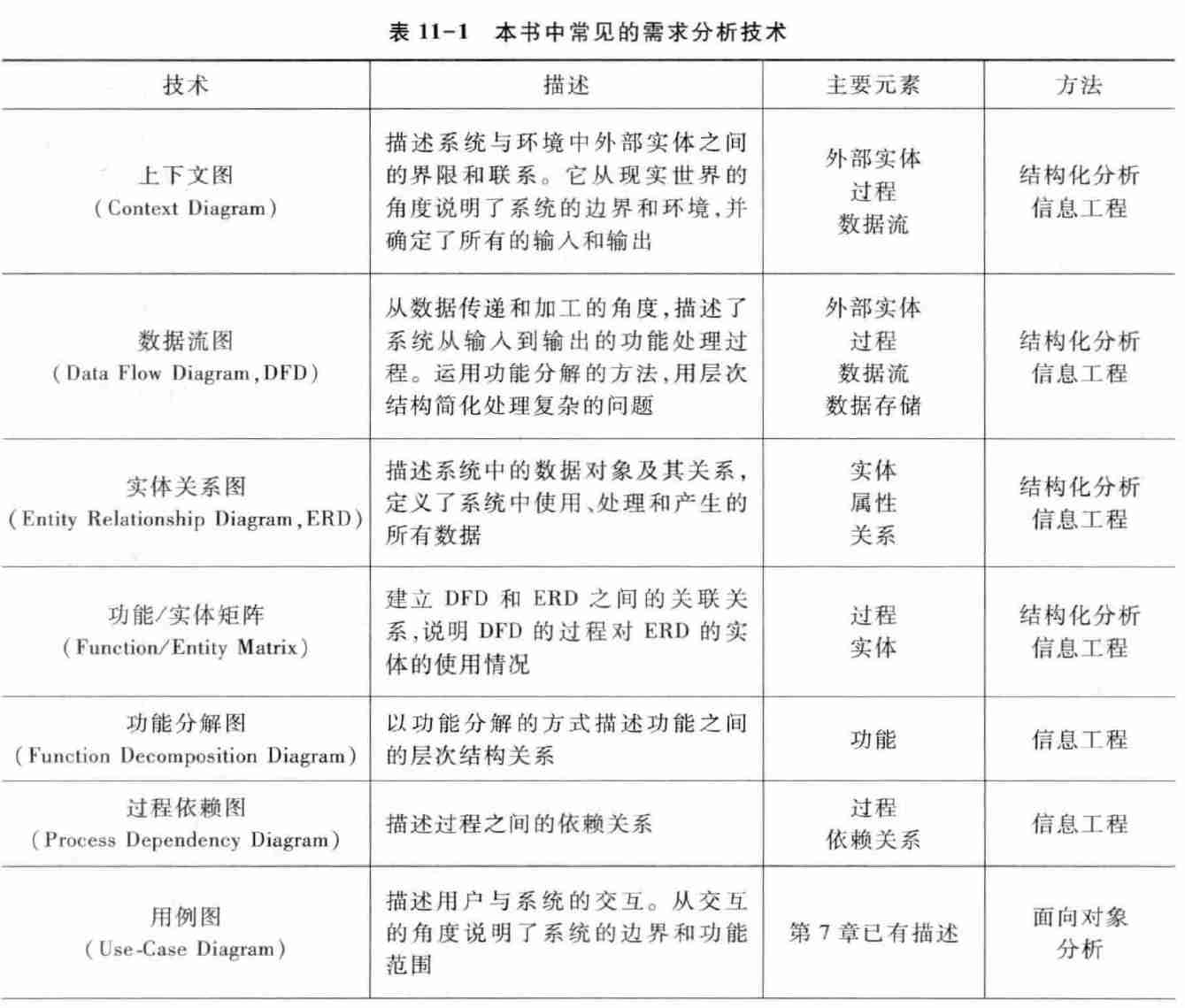

3.3. Comprehensive application of technology
3.3.1. The need for comprehensive application
- How to select requirements analysis technology for each perspective ?
- Each requirement analysis technology has its own characteristics , It is unique in application
- Complex applications require modeling from multiple perspectives
- How to realize the cooperation between them ? Only through the organic combination and integration of a variety of requirements analysis technologies can we fully describe complex applications
3.3.2. The development process of demand analysis technology

- See textbooks for more P263
- 20 century 50 years : code 、 Machine centered
- 20 century 60 years : Hardware and software are different 、 Personal heroism
- 20 century 70 years : Formal method : λ \lambda λ Calculus and Turing machines 、DFD、ERD、 Functional entity matrix 、 Entity life history and fact matrix .
- 20 century 80 years : Focus on software efficiency 、 State diagram 、 Functional breakdown diagram 、 Process dependency diagram
- 20 century 90 years : object-oriented
- 20 century 90 s : Workflow challenges 、 Business process reengineering
3.4. Application characteristics of technology
Overview and classification of requirements analysis technology
3.4.1. Wieringa frame
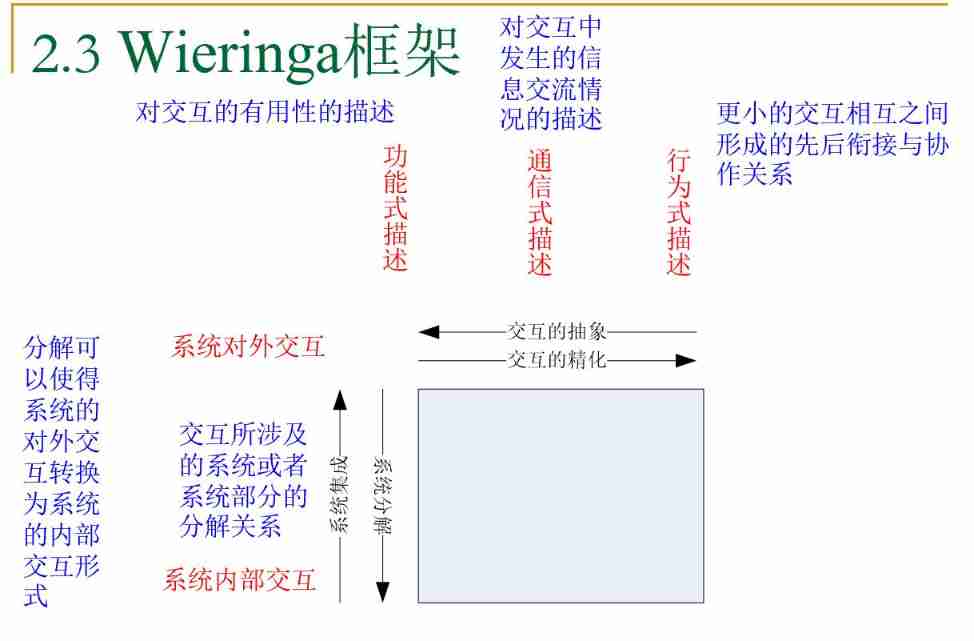 |  |
|---|
- Functional description : Interaction is purposeful ,“ Users can use ATM Withdraw money ”
- Communication description : The system communicates information with surrounding entities ,“ The user enters the card number 、 password 、 amount of money ,ATM Withdraw the corresponding cash ”
- Behavioral description : Function split , More detailed , Every step of the interaction
- function - signal communication - Behavior is gradually refined , Gradually expand the system functions .
- Another route is system decomposition
- External interaction of the system :
- Component functions : Functional description of the interaction of components within the system after decomposition , Such as " Depositors can use ATM Withdraw money " → \rightarrow →“ The card reader can read the bank card data ; The touch screen can display … And allow depositors … The keyboard allows the depositor to enter the password and amount ; The remote connection can connect to the bank database for verification … The cash outlet can spit out the corresponding amount of cash ”.
- Component communication :“ After decomposition, the internal components of the system are described interactively , Such as “ The depositor enters the bank card number 、 Password and withdrawal amount ,ATM The system gives the corresponding amount of cash ” → \rightarrow →“ The card reader reads the bank card data and provides it to the remote connection ; The keyboard receives the password entered by the depositor and provides it to the remote connection , Get the amount of cash input by the depositor and provide the banknote outlet ; The touch screen displays... To the depositor … The remote connection sends the bank card number to the bank database 、 password , Get the validation result data ; The cash outlet spits out the corresponding amount of cash ”.
- Component behavior : After decomposition, the interaction behavior of components in the system is described , Sequence diagram
- System internal interaction
- External interaction of the system :
- Requirements analysis technology
- external function
- External communication
- External behavior
- Conceptual components
- Component functions
- Component communication
- Component behavior
- The external interaction refinement and system decomposition of the system are carried out simultaneously , Sequential cohesion : External behavior → \rightarrow → External communication → \rightarrow → External behavior .
- Based on the analysis of 、 When modeling a simple system , After the external interaction refinement and system decomposition of the system are completed , End requirements analysis , Software design .
- If the system is complex , Further decompose the internal interaction : Component functions → \rightarrow → Component communication → \rightarrow → Component behavior
3.4.2. Zachman frame
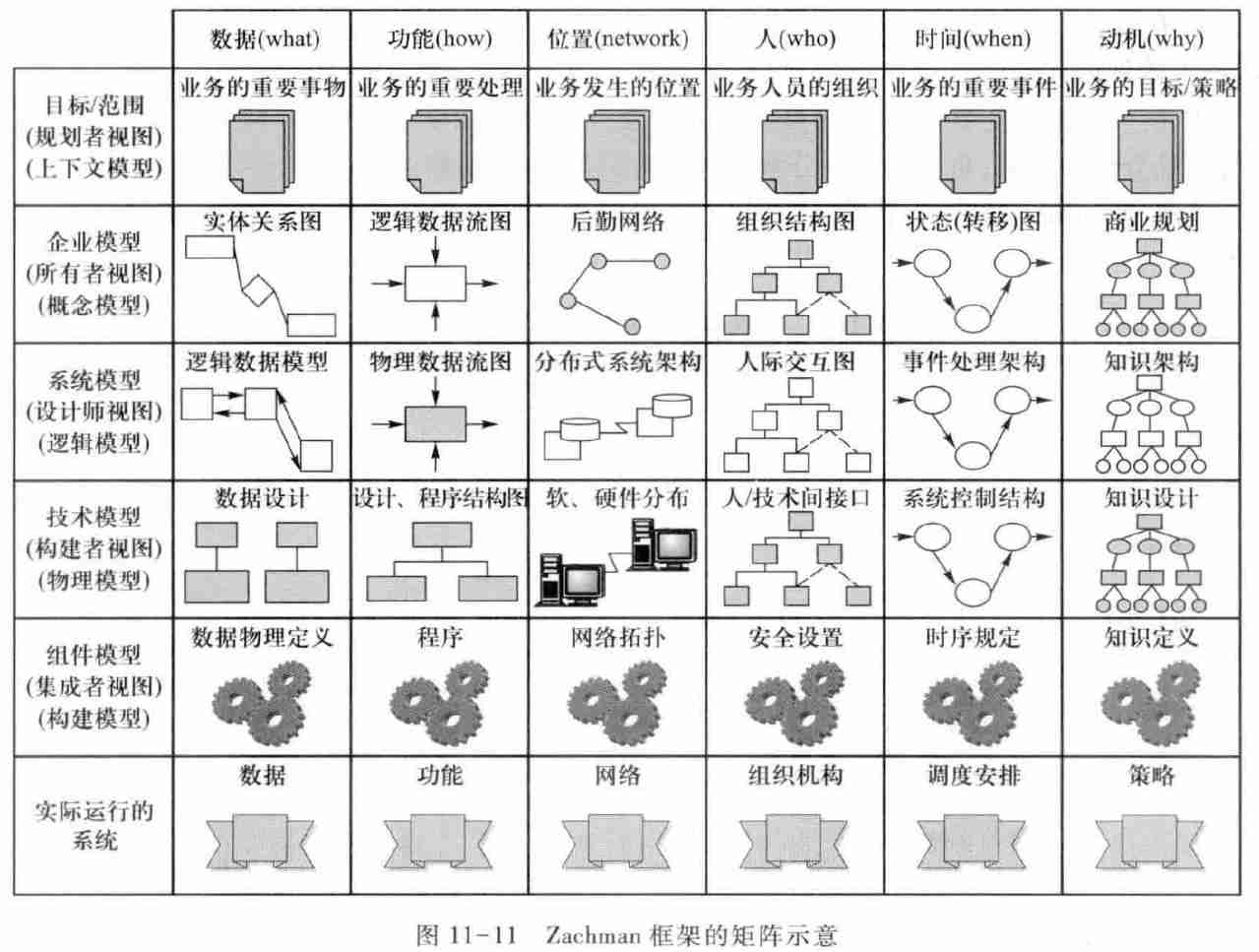
- Focus on all modeling techniques in software production
- Describe the distributed network of the software system , People draw topologies of locations
- Describe the organizational structure of the enterprise , Use a hierarchical model 、 Matrix model and mesh model
3.4.2.1. Zachman The rows of the matrix
- The goal is / Range ( Planner view )
- Care about the cost and benefit of software systems
- The scale of the final system 、 form 、 A rough description of the location space and basic objectives
- The planner's view defines the prospects and scope of the project .
- Enterprise model ( Owner view )
- Care about how the software system will participate in and help the actual work
- For business entities 、 A description of business processes and their interactions with systems
- Use business concepts to define the solution of the system —— The analysis model .
- System model ( Designer view )
- Pay attention to the needs of the software system and the selection limitations of the design method
- Description of the basic functions and design space of the software system —— Architecture .
- Technology model ( Builder view )
- Focus on the program
- Control logic in software system 、 Algorithm 、I/O Description of control and various other specific technical details —— A design model that describes the detailed design
- Component model ( Integrator view )
- Focus on assembly
- For the components of the software system 、 Description of interface and coding program
- Actual operating system :
- Describe the actual status and performance of the system after it is put into use .
3.4.2.2. Zachman The columns of the matrix
- data : Things of great significance to the enterprise and the enterprise's understanding of these things
- function : The tasks performed by the enterprise in the business and the understanding of the task by the enterprise .
- Location : Geographical distribution of organizational activities and software systems , And how they relate to other aspects of the organization .
- people : Personnel and organizations involved after the software system is introduced
- Time : Events within the system - The time factor between events , It is expressed as business planning and scheduling 、 Event response and control structure of the system .
- motivation : This column is for the motivation of the enterprise to establish the target system , It reveals the goal of the enterprise 、 Purpose 、 Business planning 、 Knowledge structure 、 Ideological line and decision-making basis .

4. Demand analysis method
- Traditional analysis : There is no way (1950’s)
- Rely on individual intelligence , According to personal habits
- Lack of structure 、 Do not repeat 、 It's not measurable , Lengthy 、 confusion 、 Biased 、 No structure, etc
- Structural analysis
- Traditional structured analysis (late 1960’s), Modern structured analysis (late 1970’s), Focus on data flow , With DFD As the core technology , auxiliary ERD,STD…
- Information engineering (late 1980’s), Based on data knowledge structure ,ERD As the core technology , auxiliary DFD,STD, FDD, PD…
- Object oriented analysis (1990’s)
- Focus on the object , With UML( Class diagram ) As the core technology
- Take comprehensive ideological innovation as the ideal , Take the inheritance of structured technology as the reality
4.1. Structural analysis

- The structural analysis method describes the display world as the flow of data in the information system , And the transformation from data to information in the process of data flow .
- Data flow diagram : System input 、 Handle 、 Storage and output
- Entity relation diagram : Store data information
- State transition diagram : Identify all events that the system needs to respond to .
- Analysis inhibition : Pay too much attention to the original system
4.2. Information engineering
- Improvements to the structured approach
- Develop systems from an information perspective
- Including functional decomposition diagram and process dependency diagram technology
4.3. Object oriented analysis
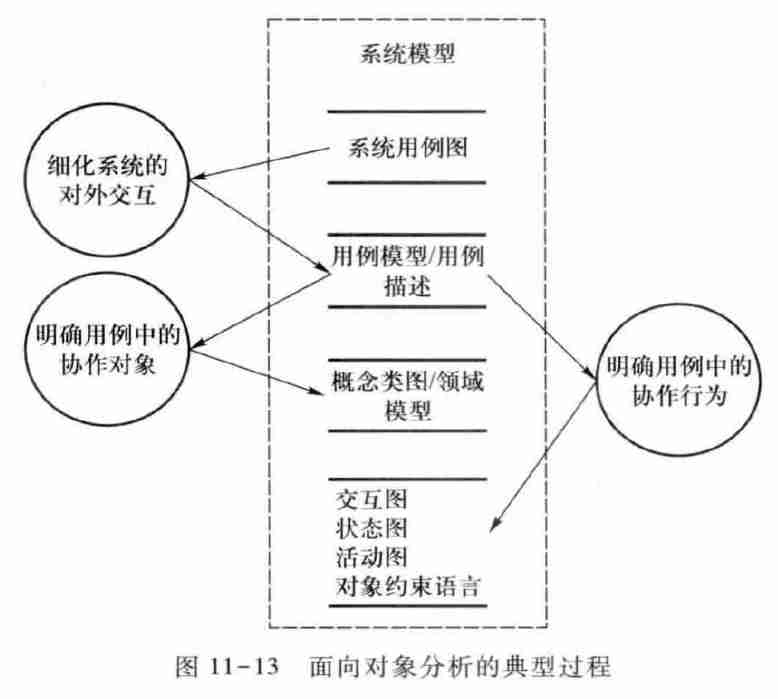
5. Modeling and analysis of early demand stage
5.1. Early demand stage and late demand stage

- Goal oriented analysis (Goal Oriented Analysis)
- Problem domain oriented analysis (Problem Domain Oriented Analysis): Early demand stage analysis
- Demand oriented analysis : Analysis of later demand stage .
- Domain analysis (Domain Analysis)
- Enterprise modeling (Enterprise Modeling)
5.2. Problem domain oriented analysis
- Problem framework
- characteristic
- solve
- Frame decomposition and combination
- The basic idea
- Study all possible problem domains , Find some simple problem types that recur , Such as workpiece system 、 Connect the system .
- Analyze the characteristics of each problem framework , Determine the understanding and solution of the problem
- Systematize the establishment and classification of the problem framework , Take the simple problem framework as the basic unit , Decompose complex problems
5.3. Domain analysis
- field : scope of business 、 A collection of problems 、 A collection of applications 、 A range of knowledge with common terms .
- Product family : There are a lot of commonalities 、 Products with a few differences .
- To discover 、 Analyze and define reusable requirements .
5.4. Sample analysis
- Not aware of the difficulties of different people in understanding the model at the same time .
- Object models are used extensively in projects , But there are many problems , Mainly in the following aspects :
- It ignores that objects should have both state and behavior ;
- The object has too many responsibilities ;
- The relation division of objects is not clear ;
- Others such as use case models 、 Behavioral models 、 State machine models are commonly used . The improper use of the use case model is mainly the relationship between subsystems , Sometimes I feel that the boundary of each subsystem is not well established . Behavioral models , The main problem of the state machine model is that the demand personnel face a demand , I don't know how to use sequence diagram , Communication diagrams , Activity diagram or state diagram .
6. Requirements analysis activities
6.1. Important activities in the requirements analysis stage

6.2. Demand refinement
- Define the requirements of users Implication factors
- Be careful :
- Refinement of user requirements : Transform the user requirements expressed from the perspective of problem domain and business into the system requirements expressed from the perspective of software and technology
- Need to add hidden factors : Add problem domain information to system level requirements , Like the price 、 Quantity and other details .
- Non functional requirements also need to be transformed from high-level expression to a series of more detailed and specific requirements
- Requirements refinement will also find new detailed requirements
- The requirements are well understood , And the developer can start to stop the refinement process when designing the scheme
- The detailed requirements should be identified and recorded one by one

- Record of requirements
- identifier (ID), Every requirement should be able to pass ID The only way to identify yourself .
- The source of the (Source), Be able to trace back to the source of demand , For example, specific stakeholders .
- reason (Rational), The purpose for which the requirement is proposed .
- priority (Priority), See the next section for details .
- cost (Cost), Estimated realization cost .
- risk (Risk), Possible risks in the process of realizing this requirement .
- variability (Volatility), The possibility of future changes .
 |  |
|---|
6.3. Prioritize requirements
6.3.1. Situations where requirements need to be prioritized
- Project resources are limited
- The project is developed in stages
- At the beginning of the project , Not all the user requirements can be defined .
6.3.2. The method of prioritizing
6.3.2.1. Cumulative votes
Normal voting , Empowerment
6.3.2.2. Zoning
- Importance : The indispensability of demand .
- Urgency : The degree of time urgency required .
- punitive : The degree of punishment that can result from neglecting requirements .
- cost : The cost of achieving the requirements .
- risk : The degree of risk that may arise in the implementation of requirements .
- Not important but urgent : Does the stored voice of wechat use .

6.3.2.3. Top-N
- N The value of is not explicitly limited , What is really limited is Top-N The total implementation cost of the requirements
- Choose the highest priority N A need
6.3.2.4. Data quantification
 |  |
|---|
- Priority judgment based on time delay cost
- Same delay cost , Short task first
- The workload is the same , High delay costs are preferred
- Weighted shortest task first ( important + The degree of emergency )
- All priorities are local and temporary
6.4. Demand negotiation
- Identify the factors of conflict , Avoid emotional conflict
- Clarify the conflict resolution space
- Determine the best solution

7. Summary of this chapter
- Requirements analysis is the most important and core activity in requirements engineering , Its modeling of information is the key to understanding problems , It is also the key to creating the right solution
- Requirements analysis involves many technologies and methods , The effective implementation of requirements analysis activities requires analysts to master and determine the selection and use of these methods
- Many important sub activities will be performed in the requirements analysis process , Their effective integration ensures the success of the whole requirements analysis
边栏推荐
- Audio and video technology under the trend of full true Internet | Q recommendation
- 余压监控系统在高层民用建筑的应用
- Force deduction solution summary 875- coco who likes bananas
- Abaqus中批量对节点施加集中力荷载
- No writing, please forgive me
- Force deduction solution summary interview question 17.11- word distance
- Force deduction solution summary 396 rotation function
- Force deduction solution summary 398 random number index
- Summary of force deduction solution 436- finding the right interval
- 一起教育科技单季营收2.3亿:同比降51% 净亏大幅收窄
猜你喜欢

The program actively carries out telephone short message alarm, and customizes telephone, short message and nail alarm notifications

Apache simple honeypot

Acl2022 | DCSR: a sentence aware contrastive learning method for open domain paragraph retrieval
![[high code file format API] downing provides you with the file format API set Aspose, which can create, convert and operate more than 100 file formats in just a few lines of code](/img/df/f4d311308e9e76c5ae9fdc11c926b8.jpg)
[high code file format API] downing provides you with the file format API set Aspose, which can create, convert and operate more than 100 file formats in just a few lines of code

SSH public key login failed with error: Sign_ and_ send_ pubkey: no mutual signature supported
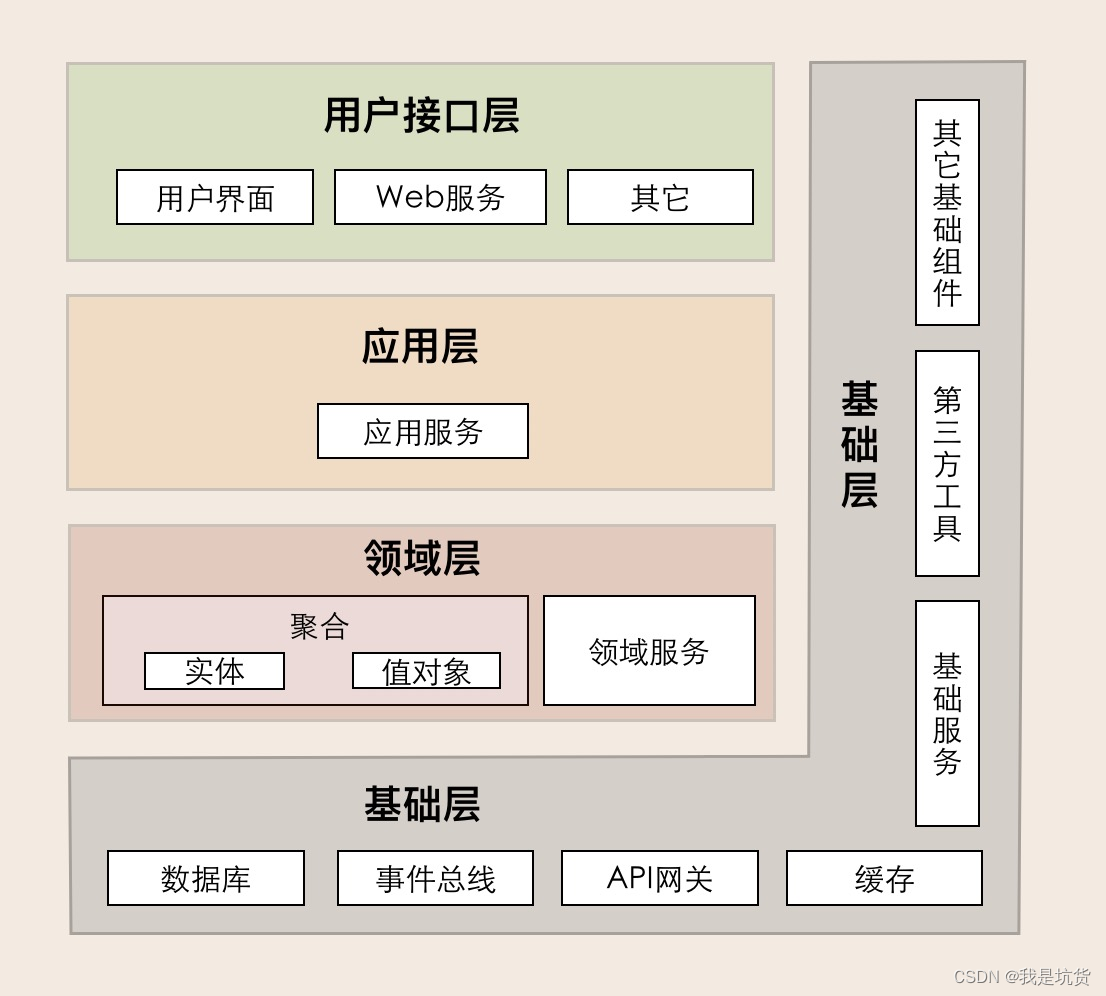
Layered architecture of DDD

RPC 入门

Maya Front Office Rendering plug - in Mel script Tool

Requirements and business model innovation - Requirements 7- user requirements acquisition based on use case / scenario model

Hypergraph tilted data is merged into root node and transferred to 3dfiles
随机推荐
Don't rush to work after the college entrance examination. There are plenty of opportunities after working. It's not bad for these three months
Layered architecture of DDD
如何防止商場電氣火灾的發生?
Force deduction solution summary 450- delete nodes in the binary search tree
No writing, please forgive me
ssh公钥登录失败报错:sign_and_send_pubkey: no mutual signature supported
I2C协议概述
Calculus review 2
Research Report on Chinese psoriasis drug market evaluation and investment direction (2022 Edition)
高考完不要急着去打工了,打工以后有的是机会,不差这三个月
Common errors when mysql8 connects through JDBC
Restful interface design specification [for reference only]
Hypergraph tilted data is merged into root node and transferred to 3dfiles
oracle之模式对象
The force deduction solution summarizes the shortest distance of 821 characters
Penetration test - file upload
Application of residual pressure monitoring system in high-rise civil buildings
2022西式面点师(技师)复训题库及在线模拟考试
Using SSH public key to transfer files
[digital signal processing] correlation function (periodic signal | autocorrelation function of periodic signal)