当前位置:网站首页>Requirements and business model innovation - Requirements 7- user requirements acquisition based on use case / scenario model
Requirements and business model innovation - Requirements 7- user requirements acquisition based on use case / scenario model
2022-06-12 02:44:00 【SpriCoder】
Book7- Based on use cases / Expand the scenario model to obtain user requirements
1. Related news
- list
- Bubble mart with a market value of 100 billion yuan (12.11)
- Investors' comments on Wang Ning : Educational background is average , No serious work experience , Speaking with a calm expression , Not contagious , There is no elite in the team .
- After listing : Wang Ning is calm and steady , Not much , Don't show your face , Have " Consumer Entrepreneurs " Many excellent characters of .
- Airbnb list (12.10)
- 12 year ,30-68-144(164) dollar / stocks
- At home : Way home 、 Piglet short rent 、 Meituan B & B
- Bubble mart with a market value of 100 billion yuan (12.11)
- Community group purchase
- JD shares in Xingsheng , Meituan prefers to investigate corruption
- Yonghui supermarket has fresh colorful food 10 Billion Tencent investment : Hippopotamus like
- B The new year's party
- Energetic Forest , TVB, Wuhan cultural tourism , Hubei radio and television
- CCTV video ( Future TV ) Learning and thinking A clap of the title
- The poster is as follows , It contains many elements of the business model

2. Deployment of user requirements acquisition activities
- The first half of demand acquisition : determine Project prospect and scope
- The second half of demand acquisition : With scene / Use case model Expand to get
- Three elements : Determine scope , Models and processes , Access method
2.1. matters needing attention
- Always check Project boundaries , There must be no requirements left out : Reference system properties , Design and obtain activity plan around system boundary , There is no omission in the scope , Excluded from the scope
- structured : With the input of the system and the outside world / The output stream is a clue, and attention is paid to expanding the acquisition process .
- object-oriented : Based on business needs 、 System features 、 Target model 、 Work results of prospect and scope stage such as activity diagram .
- More rounds " obtain → \rightarrow → analysis " Finally, the user requirements are obtained .
- Arrange the acquisition method according to the content .
- Timely organization of acquired requirements , Provide guidance for subsequent acquisition
- Adequate background reading
- 1+ Round foreground and scope ,2+ Round get : to open up -> closed
2.1.1. Get the key points in multiple rounds
- Prospect and scope stage
- Get ready : Background data acquisition and analysis
- The first round : Problem analysis ( thorough )
- The second round : High level solution development ( confirm )
- User requirements acquisition stage
- Get ready : Clarify the theme and content , Prepare the material
- The first round : Clarify the task and the main problems in the task ( thorough )
- The second round : Clarify the details of the task , Clarify difficult content ( skill 、 difficult )
- The third round : Identify solutions ( confirm )
2.1.2. Get method arrangement
- Interview : Conventional methods
- Group interview : Fast way
- questionnaire : Users are scattered
- Brainstorming :" The invention " demand
- uncertainty : Prototype
- Situational : Observe
2.1.3. Organization of user requirements
- scene / Use case model driven
- Sort and classify the information obtained from the demand acquisition behavior ( frame )
- Guide and organize the development of demand acquisition behavior
- Provide background and contextual knowledge for the analysis of detailed information
- The essential
- Expand the previous layer ( Business needs )
- Prepare the deployment of the next layer ( System level requirements )
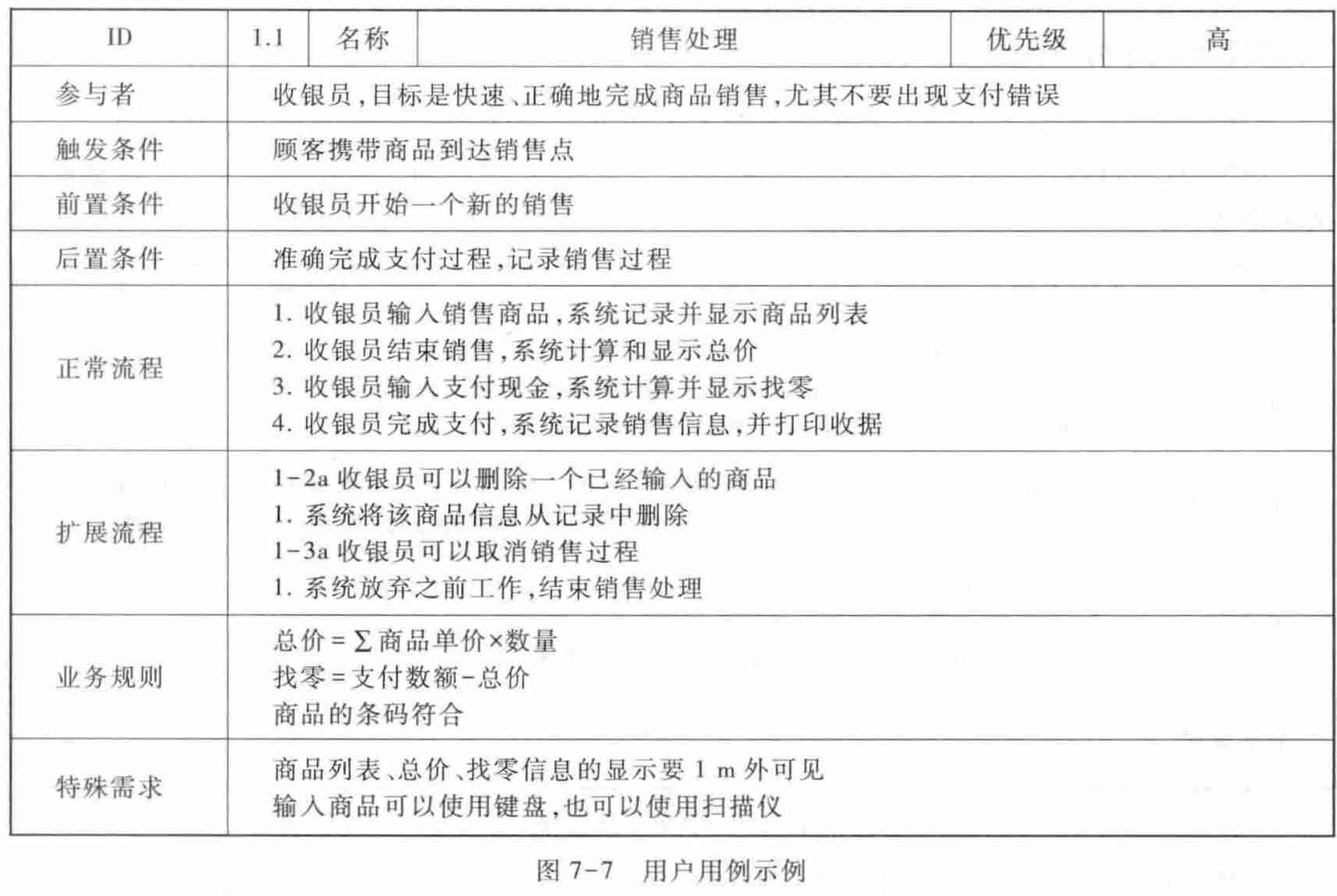
2.2. The main line of user demand acquisition activities —— Use cases / Scene models

- The goal model is used to organize the design of the system The goal is 、 characteristic 、 Mission And other contents related to business needs , The process of target analysis is to establish the target model and verify its accuracy correctness 、 completeness 、 Uniformity The process of .
- Use cases / The scenario model is used to organize the relevant contents of user requirements , Use cases / Scenario analysis is to build use cases / The process of scene modeling , But use cases / Scenario analysis cannot complete the content related to user needs correctness 、 completeness 、 Uniformity Validation of the .
- Object oriented analysis model or structured analysis model is used for Describe the details of the software solution , Organize and guide the establishment of system level requirements . Object oriented analysis or structured analysis is the process of establishing object-oriented analysis model or structured analysis model , At the same time, it can also verify the correctness of relevant contents of user requirements 、 Completeness and consistency .
- Use cases / The scenario model does not guarantee the correctness of the content related to user requirements 、 completeness 、 The main means of consistency .
- Use cases / The scenario model can organize the progress of each requirement acquisition activity in time , show 、 Provide for analysis activities , And further guide the follow-up acquisition activities after obtaining the analysis results , So it is the user The main clue in the requirement acquisition activity .
3. scene / Use cases
3.1. Why " Use cases and scenarios "
- Scenes are more basic elements , A use case is a special scenario , It is the type of scenario that requirements engineers prefer to use in organizing requirements .
- Get notes : a matter of expediency
- The user needs + Problem domain characteristics
- Hybrid 、 Unclear, etc
- Use cases and scenarios
- Scene unit
- Problem domain features or user requirements + Problem domain characteristics
- Well organized
3.1.1. scene
- [Zorman1995] Define a scenario as a response to the behavior of the system and the environment Partial description
- [Plihon1998] Define the scene as a pair of A sequence of actions or events Description of , The behaviors and events in the sequence are a special example of a task that the system needs to complete .
- [Jarke1996] It is considered that the scene contains the sequence of behaviors and the environment in which behaviors occur , The environment describes the subject of the behavior 、 Object and context settings
- The above description is not enough as an accurate definition of the scene , It is also difficult for people to give a very accurate definition of the scene [Rolland1998a]
- The scenario emphasizes the interaction between the system and the external environment to complete the expected task , have Focus on the real world ( Business model design : Tell a story -> scene ) Characteristics of , It USES scene 、 Interaction between actors 、 The evolution of events over time And other ways to describe the use of the system

3.1.2. Use case definitions
- Use cases
- relevant Scene collection The narrative of Text description
- The concept of use cases is [Jacobson1992] First of all Objectory Method
- UML Define use cases as " stay System ( Or subsystems or classes ) Interaction with external objects In which The sequence of actions Description of , Includes a variety of Different sequences and wrong sequences , They can jointly provide a Valuable service "[Rumbaugh2004].
- Each sequence of actions becomes a scene . A use case is a collection of multiple scenarios , The use case that carries the goal of success and failure .

3.1.3. Use cases and scenarios
- Use cases / Organize user requirements by scenario ( And problem domain properties )
- It is very popular with practitioners
- Easy to accept
- Easy to use
- use-case driven !
- Various methods , There's a lot of difference
- It can also be used to handle business requirements and system level requirements
- It can also be used to deal with design problems 、 Test questions ……

3.2. scene / Organizational characteristics of use cases
 |  |
|---|
- On the left is the use case / How the scene is organized , Organize multiple independent requirements into a story , Let the user 、 Stakeholders in areas such as customers seem more receptive , Popular with stakeholders .
- On the right side of the left figure are all requirements organized in their own independent ways , Each requirement is independent of the others , More in line with the developer's perspective , Popular with developers .

- weaknesses
- Only consider Other contents and functional requirements The connection between , But it can't describe the relationship between other contents , For example, the interdependence of quality requirements ( Target model )、 Jump of interface requirements ( Human computer interaction document in external interface )、 The relationship between external interface requirements and quality requirements (IF As the main body, carry the goal to achieve )…
- Only consider the existence of contact Fact , But can't analyze the connection rationality , For example, whether there are missing functional requirements 、 Whether the data requirements and business rules are sufficient 、 Whether the quality requirements are feasible ( Demand analysis )
- therefore , Although use cases / Of the scene advantage clear as daylight , But it is only a form of organization after all , You can't rely on use cases alone / The scenario model solves all the problems [Gottesdiener2002], Target model 、 Other model forms such as object-oriented analysis model or structured model are still necessary .
3.3. user / The hierarchy of the scene
- user / The scene is hierarchical , Used to organize the content of business requirements , Here's the picture .

- It can be used to organize the contents of user use cases .
- It can be used to organize system level requirements
 |  |
|---|
3.4. Based on use cases / Scenario for software development
- Use case driven software development is, to some extent, demand driven software development .

4. Use cases / Scene models
- Use cases / The scenario model is more the organizational content of the demand content , Has not formed a rigorous 、 Accurate grammar .
- The difference model of scenarios is as follows :

4.1. Scene positioning
4.1.1. The form of the scene : The expression mode of the scene
- describe (Description)
- Normality of representation
- Informal language : Complete freedom 、 There are no rules
- Semi formal language : There are certain rules but not strict
- Formal language : There is a formal system , Complete grammar 、 Semantics and semantics
- Media form (Medium): Narrative free text 、 Structured text 、 Strongly restricted text ( Semi formalization )、 It is recommended to use forms 、 Chart 、 Images and other non formal languages .
- Normality of representation
- appearance : The effect when the scene is expressed
- Static appearance ( Lord ): Present as one or more descriptive texts or pictures .
- Dynamic appearance : In a dynamic way , Users can view according to the sequence .
- Interactive appearance : Users can control and change the change sequence and effect of the scene to a certain extent .

4.1.2. Content of the scene
- Main focus : About the present , About the future , About solutions
- Environmental scope :
- Details of behavior within the system
- Interaction between system and application environment
- The system interacts with the external environment
- Promote the integration of organizational background 、 The description of environmental context information such as cultural background and objectives is included in the content of the scene .
- The level of abstraction
- Concrete ( Example scenario ): For individual actors 、 event 、 A detailed description of the plot , Little or no abstract content , Zhang San goes to some ATM take 1000 Yuan
- In the abstract ( Type scene ): Describe facts in terms of categories and abstract concepts in experience , The depositor is in ATM Take the money .
- Mixed : Part concrete, part abstract , Depositors should start from ATM To take 1000 Yuan .
- Coverage : functional requirement , Non functional requirements
- Particle size
- The whole business process ( In the early )
- The process of completing a task ( Mid - )
- Detailed processing steps of an interactive behavior ( later stage )
- Example type
- Normal process
- Abnormal flow
4.1.3. The purpose of the scene
- describe (descriptive): Record the requirements that have been obtained , That is to sort out the information obtained in each demand acquisition behavior .
- Documentation of requirements
- Basis of demand negotiation
- Explore (exploratory): The main use of
- Demand acquisition : Explore with needs as a focus
- Requirements modeling and analysis : Focus on solutions
- explain (explanatory): Use examples to illustrate the reason or feasibility
- Reduce model complexity
- Verification of requirements

4.1.4. Life cycle

- The scenario application and processing found in practice can be summarized as 5 In this case
- ( More complex systems ) Capture and build information about from the current system Now? Scene , They describe the state of the problem domain and the problem . Do... For the present scene Further analysis , Transformation produces about Future scenarios , Describe the expected system Solution . Will be about the future scene Documentation , Generate requirements specifications for the system , Pictured 7-13(a) Shown .
- ( A relatively simple system ) Analyze problems and expectations in the current system , Capture 、 Analyze and build scenarios about the future . And then I will talk about Future scenarios are documented , Generate requirements specifications for the system , Pictured 7-13(b) Shown .
- ( The main ) Analyze problems and expectations in the current system , Capture 、 Analyze and build scenarios about the future , And establish the requirement model according to the scenario description . under these circumstances , Requirements engineering will not generate special requirements specifications except for scenarios , It is Use scenarios as an alternative to requirements specifications , Pictured 7-13 Shown .
- ( There are existing parts and reverse parts ) According to the established requirements specification , Explain and build scenarios about the future , Then build the requirements model for the solution described in the scenario , Pictured 7-13(d) Shown .
- ( Requirements validation ) Build the requirements model according to the solution described in the requirements specification . At the same time, establish scenarios that can verify the solution , Finally, a scenario is used to verify the correctness of the requirements model , Pictured 7-13(e) Shown .
- The scene information is through the interview 、 Prototype 、 Observation and other basic requirements acquisition methods .
4.2. Use case positioning
- Use cases are one of the scenario methods
4.2.1. Use case positioning
- The use case is Static structured text describe .
- The content of a use case can be a description of the current world , It can also be a description of the internal behavior of the solution system to be determined in the future , It can also be a kind of Description of the expected solution .
- Use cases may be used to describe interactions within the system ( System level requirements ), It may also be used for Describe the interaction between the system and the environment ( The user needs ), It may also be used to describe the context and context of the behavior ( Business needs ), Tend to the second .
- Use cases are type level event descriptions , Mainly used to describe functional requirements , Other types of requirements can be included
- Use cases can be more abstract , You can also be more specific , It can also be very specific .
- The content of use cases includes both normal processes , It also contains abnormal process .
- Use cases can be used for various purposes ( Same scene ), Include a description of 、 Explore and explain . Requirements acquisition and verification are the main application stages in requirements engineering , It can also be used for requirements modeling 、 Communication and consultation .
- Various lifecycle feature roots of scenarios 、 Both the application and the process apply to the use case .
- It is not allowed to use the function decomposition method before the high-level functional requirements are obtained .
4.2.2. The meaning and usage of use cases
- Main participants : The requesting user
- Auxiliary participants : External objects requested by the system in the process of realizing the objectives of the main participant .

4.3. Use case model
4.3.1. Use cases

4.3.2. participants
- Participants are roles that interact with the system .
- Participants can be an organization 、 Another system 、 External device or event concept .

4.3.3. Relationship
4.3.3.1. relation
- relation : The relationship between use cases and actors , Describes the interaction between use cases and actors .

4.3.3.2. contain
- Multiple use cases have the same behavior , We can abstract them into abstract use cases .

4.3.3.3. Expand
- Do not modify the original use case , Create additional use cases for new requirements , Extend existing use cases with additional use cases .
- Prior to the execution of additional use cases, the process of the original use cases shall be executed first .
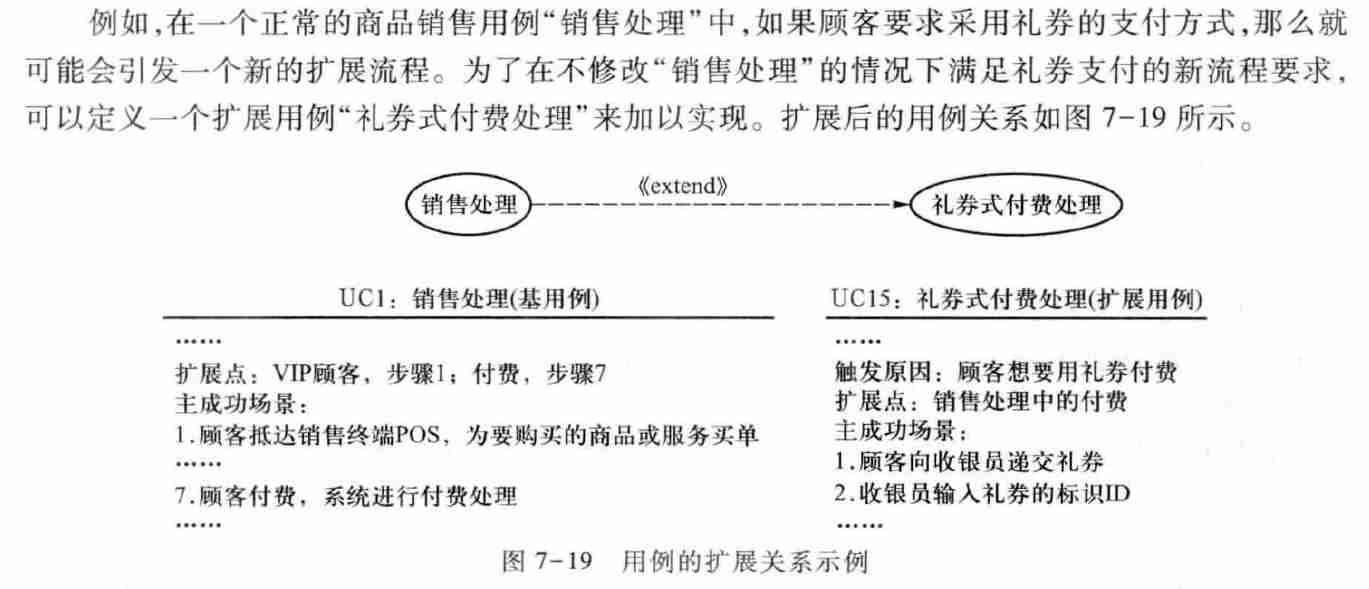
- Reduce complexity , Represents the complex processing behavior extension of the use case
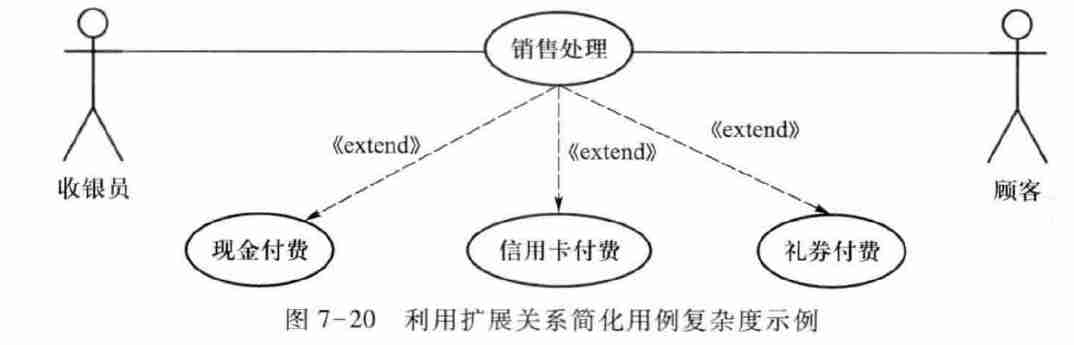
4.3.3.4. Use case generalization
The child use case inherits the features of the parent use case and adds new features .

4.3.3.5. Participant generalization
The child participant inherits the characteristics of the parent participant and adds new characteristics .

4.3.4. System boundary

5. Based on the scene / Use case model deployment requirements acquisition

- Build the initial use case model based on the prospect and scope : According to the system use case diagram 、 The target model establishes the initial use case / Scene models
- ( iteration ) Expand use cases
- According to the use case / Scene model guidance acquisition , Perfect the hierarchy : Select the appropriate requirements acquisition method to obtain the detailed description of the use case , For example, interview 、 Prototype 、 Brainstorming 、 Observe …
- Use cases / Scene organization obtains content
- Analyze use cases / The scenario finds the requirements that still need to be obtained
- Select the appropriate model to analyze the use case description
- Class diagram 、 Sequence diagram 、 Entity relation diagram 、 Business rule model ……
- Verification scenario / Use case model : Review use case descriptions
- Maintain use cases / Scene models
- Use cases that are newly organized or modified / Scenarios perfect use cases / Scene models
- According to the use case / Scenario model organization requirements analysis model
5.1. Establish the initial scenario according to the system use case diagram and the target model / Use case model
The layer by layer expansion of scenarios is not equal to use cases !

5.2. According to the use case / Scenario models guide requirements acquisition , Perfect the hierarchy
- The initial system use case involves The theme Need to get .
- Summary of the findings in the use case description New theme Need to get .

- Found in specific use cases Fuzzy 、 Incorrect 、 Incomplete The details need to be obtained
5.3. Use cases that are newly organized or modified / Scenarios perfect use cases / Scene models

5.4. According to the use case / Scenario model organization requirements analysis model
- The system complexity is relatively high , We start with local demand analysis , Avoid missing requirements , Ensure the consistency of all parts .

5.5. Analyze use cases / Scenario discovery still needs to obtain the requirements
- Use cases / The scenario does not verify the correctness of the content 、 Completeness and consistency , We need to use analytical techniques to verify .
 |  |
|---|
- The interaction of the leftmost graph is insufficient , Revised to improve one : Unable to draw system sequence diagram .
- Improve the inadequate description of data , Revised as improvement 2 : Cannot create concept class diagram .
5.6. Example
- Normal process ( The trigger condition , Every night )
- Fleet Attendance report , Include personnel Attendance report and vehicle Attendance report
- If there's a new mission , Create a new vehicle plan .
- According to the car plan , Issue a waybill
- Issue exit permit for waybill .
- Expansion process
3aThere is no car plan , It is also possible to open the circuit .3bThe vehicle selection of the open circuit sheet may not be counted as the attendance reporting vehicle4There is no waybill , It is also possible to issue a separate exit permit .
| Expand use cases | Organize access to content |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Use case expansion | Organize access to content |
 |  |
- Interview report : Interviewee : Dispatcher - Vehicle attendance report

5.7. Use analytical models ( Behavior + structure ) Analyze use case descriptions
- The cashier enters the member number ;
- The cashier enters the goods ;
- The system displays the purchase information ;
The cashier repeated 2-3 Step , Until all inputs are completed - The system displays the total price and complimentary information ;
- Customer payment ;
- System change ;
- System update data ;
- The system prints the receipt ;
- The customer leaves
5.7.1. Process refinement and improvement

5.7.2. Interactive clarity ( Information transmission ) improvement
 |  |
|---|
5.8. Use case documentation
 |  |
|---|
6. Summary of this chapter
- The deployment process of requirements acquisition is progressive 、 Iterative , scene / Use case model plays an important role in it
- scene / Use cases are the means of organizing requirements , It is a more acceptable way for users to express demand clues
- In practice , scene / Use case models are very different , It is necessary to correctly master and use the scenarios of requirements / Use case features
- Around the scene / The use case model is the core , You can expand the acquisition activities of user requirements
边栏推荐
- Force deduction solution summary 398 random number index
- WPS table learning notes - highlight duplicate values
- Force deduction solution summary 388- longest absolute path of file
- 函数模板 Function Templates
- errno: -4091, syscall: ‘listen‘, address: ‘::‘, port: 8000
- Unity3D中DrawCall、Batches、SetPassCall
- Ue4\ue5 touch screen touch event: single finger and double finger
- Layered architecture of DDD
- Application of ard3m motor protector in coal industry
- maya前台渲染插件mel脚本工具
猜你喜欢

Solutions to errors in ROM opening by MAME

AcrelCloud-6000安全用电云平台在某商业广场的应用

【高代码文件格式API】道宁为您提供文件格式API集——Aspose,只需几行代码即可创建转换和操作100多种文件格式

RPC 入门

ssh公钥登录失败报错:sign_and_send_pubkey: no mutual signature supported

ARD3M电动机保护器在煤炭行业中的应用

Comment prévenir les incendies électriques dans les centres commerciaux?

How to make div 100% page (not screen) height- How to make a div 100% of page (not screen) height?
el-upload上传文件

Hypergraph tilted data is merged into root node and transferred to 3dfiles
随机推荐
DbNull if statement - DbNull if statement
The market value has exceeded $3trillion. Why should apple, which has been criticized as a loser, rise again and again?
I2C协议概述
Force deduction solution summary 398 random number index
【无标题】2022煤矿安全检查考题及在线模拟考试
Application of ankery anti shake electric products in a chemical project in Hebei
Using SSH public key to transfer files
Swiftyjson analyse les fichiers json locaux
力扣解法汇总386-字典序排数
How to make div 100% page (not screen) height- How to make a div 100% of page (not screen) height?
Several common instructions for virsh to create / shut down / stop virtual machines
Wave view audio information
Introduction to program environment and preprocessing C language (advanced level)
Force deduction solution summary 699- dropped blocks
如何防止商場電氣火灾的發生?
Force deduction solution summary 467- unique substring in surrounding string
函数模板 Function Templates
Force deduction programming problem - solution summary
Force deduction solution summary 905- array sorted by parity
[digital signal processing] correlation function (periodic signal | autocorrelation function of periodic signal)