当前位置:网站首页>Fundamentals of scala (3): operators and process control
Fundamentals of scala (3): operators and process control
2022-06-29 01:38:00 【Think hard of Xiao Zhao】
Hello everyone , I can't think of Xiao Zhao .
Creation time :2022 year 6 month 27 Japan
Blog home page : Click here to enter the blog home page
—— Migrant workers in the new era
—— Look at the world with another kind of thinking logic
Today is to join CSDN Of the 1212 God . I think it's helpful and troublesome. I like it 、 Comment on 、️ Collection
List of articles
One 、 Operator
Scala Operators in and Java The operators in are basically the same .
Arithmetic operations
+ - * / %,+and-Show positive and negative signs in the unary operation table , To express addition and subtraction in a binary operation ./To divide or divide , Keep only integer parts and discard decimal partsbesides ,
+It also means adding two strings
Relationship between operation
== != < > <= >=- stay Java in ,
==Compare the values of the two variables themselves , The first address of two objects in memory ,equalsCompare whether the contents contained in the string are the same . - Scala Medium
==More similar to Java Mediumequals, andeq()The comparison is the address
Logical operations
&& || !, The result of the operation is Boolean value- Scala Short circuit is also supported
&& ||
The assignment operation
= += -= *= /= %=- stay Scala There is no
++and--This grammar , adopt+=、-=To achieve the same effect
An operation
& | ^ ~<< >> >>>, among<< >>Is a signed shift left and right ,>>>unsigned right shift
stay Scala In fact, there is no operator in , All operators are method calls .
- When an object's method is called , spot . It can be omitted
- If there is only one function parameter , Or no parameters ,() It can be omitted
- Operator priority :
(characters not shown below)
* / %
+ -
:
= !
< >
&
^
|
(all letters, $, _)
Take a chestnut :
object Test {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Standard addition operation
val i: Int = 1.+(1)
// When an object's method is called ,. It can be omitted
val n: Int = 1 + (1)
// If there is only one function parameter , Or no parameters ,() It can be omitted
val m: Int = 1 + 1
println(i + " , " + n + " , " + m)
}
}
Two 、 Process control
Scala Process control in is the same as other programming languages , It also contains branch statements 、 Loop statement, etc .
if - else
Basic grammar :
if ( Conditional expression ) {
Code segment
}else if ( Conditional expression ) {
Code segment
}else {
Code segment
}
Take a chestnut :
object Test01_ifelse {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
println(" Please enter your age :")
val age: Int = StdIn.readInt();
if (age >= 18 && age < 30) {
println(" middle-aged ")
} else if (age < 18) {
println(" juvenile ")
} else {
println(" The elderly ")
}
}
}
What's special :
- Different from other languages ,Scala Medium
if elseAn expression actually has a return value , It can also be used as an expression , Defined as the return value of the last statement executed - Scala Inconsistent return value types in , Take their common ancestor type .
- The return value can be
Unittype , At this point, the value of the last expression is ignored , obtain() - scala There is no ternary conditional operator in , It can be used
if (a) b else creplacea ? b : c - Nested branches have the same characteristics .
Take a chestnut :
object Test01_ifelse {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
println(" Please enter your age :")
// The return value of the branch statement
val result: Unit = if (age >= 18) {
println(" congratulations , Grown up ")
} else if (age < 18) {
println(" sorry , You're underage ")
} else {
println(" You're a man ")
}
println("result:" + result)
val result2: String = if (age >= 18) {
println(" congratulations , Grown up ")
" congratulations , Grown up "
} else if (age < 18) {
println(" sorry , You're underage ")
" sorry , You're underage "
} else {
println(" You're a man ")
" You're a man "
}
println("result:" + result2)
// Return values of different types take the public parent class
val result3: Any = if (age >= 18) {
println(" congratulations , Grown up ")
" congratulations , Grown up "
} else if (age < 18) {
println(" sorry , You're underage ")
age
} else {
println(" You're a man ")
age
}
println("result:" + result3)
// java The ternary operation in a?b:c scala Use in if (a) b else c
val res: String = if(age>=18){
" adult "
}else{
" A minor "
}
val res1 = if (age>= 18) " adult " else " A minor "
}
}
for
Scala Medium for The loop is called for Derivation
Range traversal :
for (i <- 1 to 10) {
println(i + ":hello world")
}
iRepresents a cyclic variable<-It is equivalent to assigning traversal value to variable1 to 10RichIntA method call in , Return to oneRange- Close back and forth
for (i <- 1 until 10) {
println(i + ":hello world")
}
untilIt's alsoRichIntOne of the methods in , returnRangeclass- Before closed after opening
A range is also a collection , You can also traverse ordinary collections .
for (i <- Array(10, 28, 9, 3, 2)) {
println(i)
}
for (i <- List(10, 28, 9, 3, 2)) {
println(i)
}
for (i <- Set(10, 28, 9, 3, 2)) {
println(i)
}
Cycle step :by + step
for (i <- 1 to 10 by 2) {
println(i)
}
for (i <- 30 to 10 by -2) {
println(i)
}
Cycle guard :
Cycle guard , That is, circulation protection ( Also known as conditional judgment , The guards ). The protection type is true Then go inside the circulatory body , by false Then skip , Be similar to continue.
grammar :
for(i <- collection if condition) {
}
Equivalent to :
if (i <- collection) {
if (condition) {
}
}
Take a chestnut :
for (i <- 1 to 10) {
if (i != 5) {
println(i)
}
}
for (i <- 1 to 10 if i != 5) {
println(i)
}
A nested loop :
Nested loops can combine conditions into one for in .
grammar :
for (i <- 1 to 3) {
for (j <- 1 to 3) {
println("i = " + i + ",j = " + j)
}
}
Equivalent to :
for (i <- 1 to 3; j <- 1 to 5) {
println("i = " + i + ",j = " + j)
}
Take a chestnut : Print multiplication tables
object Test03_PracticeMulTable {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
for (i <- 1 to 9; j <- 1 to i) {
print(s"$j * $i = ${
i * j} \t")
if (j == i) println()
}
}
}
Loop introduces variables :
The introduced variable in the loop , But not a cyclic variable .
for (i <- 1 to 10; j = 10 - i) {
println("i = " + i + ", j = " + j)
}
Equivalent to :
for {
i <- 1 to 10;
j = 10 - i
} {
println("i = " + i + " , j = " + j)
}
Loop return value :
- Scala in for The default return value of the loop is
Unit, example().
val a: Unit = for (i <- 1 to 10) {
println(i)
}
- yield:Java One method of threading in is yield Indicates a thread concession
- scala Is a keyword in Express : At present for The loop generates a collection type as the return value , Then return .
- Return the results processed during traversal to a new Vector Collection , Use yield keyword .
val b: immutable.IndexedSeq[Int] = for (i <- 1 to 10) yield i * i
// default implementation is Vector, Vector(1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100)
while and do…while
While and do…While The use of and Java The usage is the same in language , It is not recommended to use , The result type is Unit.
grammar :
while ( The loop condition ) {
The loop body ( sentence )
Loop variable iteration
}
do{
The loop body ( sentence )
Loop variable iteration
} while( The loop condition )
Cycle break
Scala The built-in control structure specifically removes break and continue, In order to better adapt to functional programming , It is recommended to use the functional style to solve break and continue The function of , Not a keyword .Scala Use in breakable Control structure to achieve break and continue function .
Break the loop by throwing an exception
try {
for (i <- 0 until 5) {
if (i == 3)
throw new RuntimeException
println(i)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception => // Exit loop
}
Use scala Medium Breaks Medium break Method ( It is equivalent to encapsulating exception capture ), Throw and catch exceptions .
import scala.util.control.Breaks
Breaks.breakable(
for (i <- 0 until 5) {
if (i == 3)
Breaks.break()
println(i)
}
)
This is the end of the sharing , I hope to learn from you Scala Language helps !!!
边栏推荐
- [temperature detection] thermal infrared image temperature detection system based on Matlab GUI [including Matlab source code 1920]
- IPFs Brief
- Typescript (5) class, inheritance, polymorphism
- 4276. good at C
- Fibonacci sequence
- QT is based on RFID Management System (applicable to most RFID Management Systems)
- Design and development of VB mine sweeping game
- Linux7 (centos7) setting oracle11 boot auto start
- Redis data migration (III)
- Installing Oracle database in docker
猜你喜欢

Day 7 scripts and special effects
Scala Foundation (3): Operators and Process Control
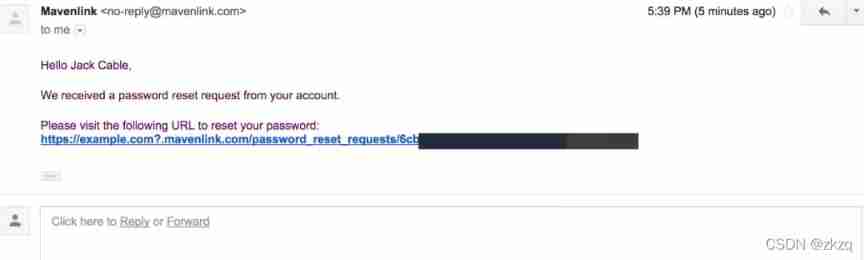
Vulnerability mining | routine in password retrieval
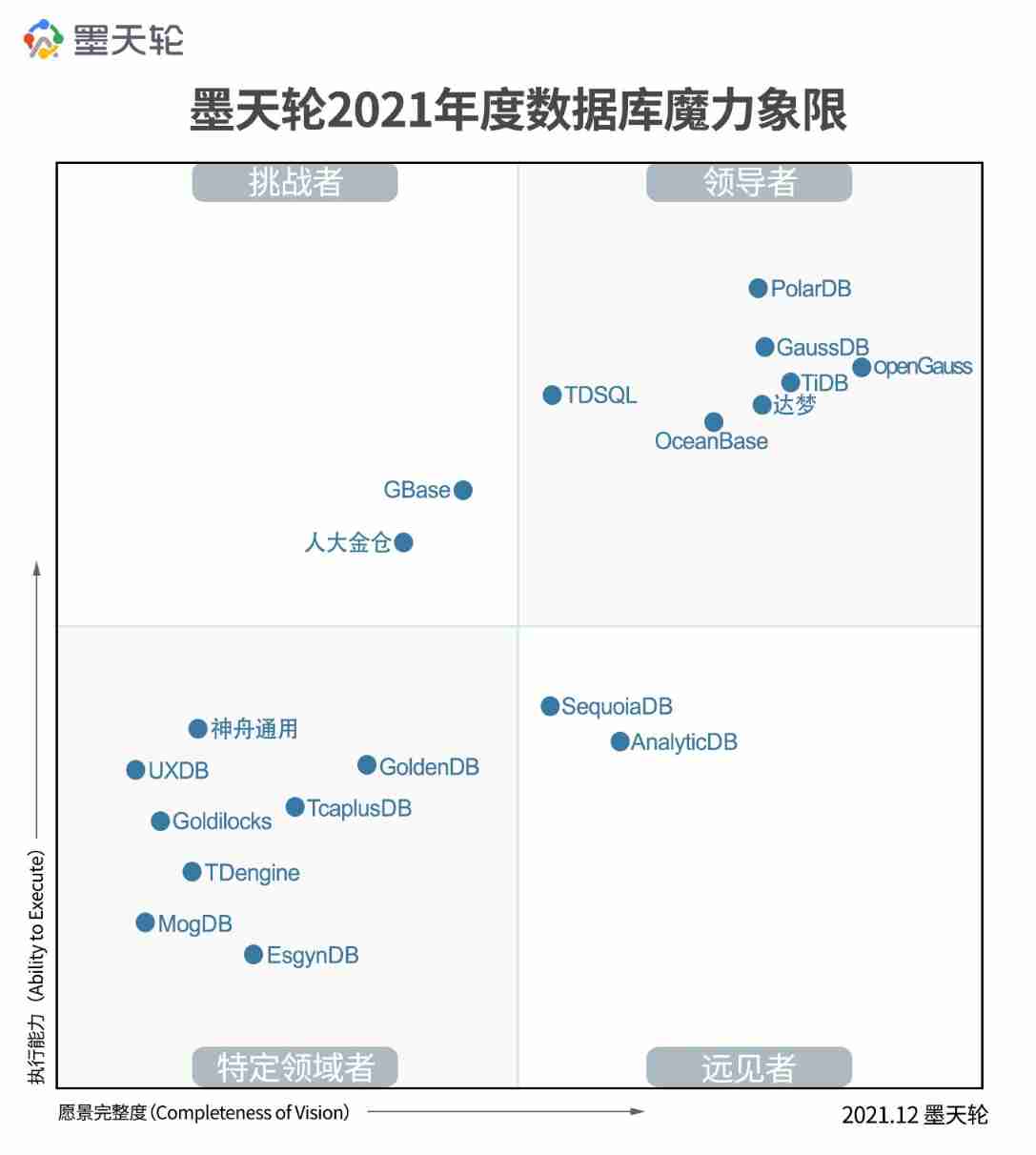
Magic Quadrant of motianlun's 2021 China Database

Edrawmax mind map, edrawmax organization chart

ASP. Net based on LAN
Introduction to UE gameplay 44 (animation import FBX and production standard)

Rasa对话机器人之HelpDesk (五)

Rasa dialogue robot helpdesk (V)

我把整个研发中台拆分过程的一些心得总结
随机推荐
Introduction to super dongle scheme
[RRT 3D path planning] rapid expansion of random tree UAV 3D path planning based on MATLAB [including Matlab source code phase 1914]
测试只能干到35岁?35岁+的测试就会失业?
Analysis of parsing principle of OData metadata request response in SAP ui5 application
Scala Foundation (3): Operators and Process Control
Using autogluon to forecast house price
[js practice every m days] JS export object analysis based on libcef application (steam)
IPFS简述
Near consensus mechanism
致我们曾经遇到过的接口问题
Magic Quadrant of motianlun's 2021 China Database
Rasa dialogue robot helpdesk (V)
What is the difference between immunohistochemistry and immunohistochemistry?
4276. 擅长C
Sword finger offer 14- I. cut rope
Kuboardv3 and monitoring kit installation
Typescript (5) class, inheritance, polymorphism
Is Huatai Securities safe
AHA C language, C language programming introductory books and PPT (PDF version) download website
[TS] as type assertion
