当前位置:网站首页>Detailed understanding and learning of transactions in MySQL (transaction management, transaction isolation level, transaction propagation mechanism)
Detailed understanding and learning of transactions in MySQL (transaction management, transaction isolation level, transaction propagation mechanism)
2022-06-09 05:45:00 【Daxiong who loves learning】
This article mainly aims at MySQL To explain in detail , It includes Business management 、 Transaction isolation level 、 Transaction propagation mechanism .
Among them Case explanation of transaction isolation level and Parameter interpretation of transaction propagation mechanism Two explanation schemes are given respectively in , It is suggested that you can combine their two interpretation schemes .
One 、 What is the business
Transactions are a series of tight operations in an application , All operations must be completed successfully , Otherwise, all changes made in each operation will be undone . That is, affairs are atomic , A series of operations in a transaction are all successful , Or none of them . There are two ways to end a transaction , When all the steps in the transaction are executed successfully , Transaction submission . If one of the steps fails , A rollback operation will occur , Undo all actions from the beginning of the transaction before undo .
Two 、 Business management (ACID)
- Atomicity (Atomicity)
Atomicity It means that a transaction is an inseparable work unit , Either the operations in the transaction occur , Or none at all . - Uniformity (Consistency)
The integrity of the data before and after the transaction must be consistent . - Isolation, (Isolation)
The isolation of transactions is multiple users Concurrent When accessing the database , A transaction opened by a database for each user , Can't be disturbed by the operation data of other transactions , Multiple concurrent transactions should be isolated from each other . - persistence (Durability)
Persistence means that once a transaction is committed , It changes the data in the database permanently , Next, even if the database fails, it should not have any impact
Take a simple example to understand the above four points
2.1 Atomicity (Atomicity)
For the same transaction

This process consists of two steps
A: 800 - 200 = 600
B: 200 + 200 = 400
Atomic representation , These two steps work together , Or failing together , You can't just take one of these actions
2.2 Uniformity (Consistency)
For a transaction, the state before and after the operation is consistent

Before operation A:800,B:200
After the operation A:600,B:400
Consistency means that after a transaction is completed , Logical operation
2.3 persistence (Durability)
Indicates that the data after the end of the transaction will not be lost due to external reasons
Before operation A:800,B:200
After the operation A:600,B:400
If before operation ( The transaction has not yet been committed ) Server down or power down , After restarting the database , The data status should be
A:800,B:200
If after the operation ( The transaction has been committed ) Server down or power down , After restarting the database , The data status should be
A:600,B:400
2.4 Isolation, (Isolation)
For multiple users at the same time , It is mainly to exclude the influence of other transactions on this transaction

Business one )A towards B Transfer accounts 200
Business two )C towards B Transfer accounts 100
3、 ... and 、 Transaction isolation level
The isolation level is getting higher and higher from top to bottom , The performance is getting worse , The isolation levels are :
- Read uncommitted : When a transaction has not yet been committed , The changes it makes can be seen by other things .
- Read submitted : After a transaction is committed , The changes it makes will be seen by other things .
- Repeatable ( Default ): Data seen during the execution of a transaction , It is always consistent with the data seen when the transaction is started . Of course, at the level of repeatable read isolation , Uncommitted changes are also invisible to other transactions .
- Serialization :“ Write ” Will add “ Write lock ”,“ read ” Will add “ Read the lock ”. When there is a read/write lock conflict , Subsequent transactions must wait for the previous transaction to complete , In order to proceed .
| Transaction isolation level | Dirty reading | It can't be read repeatedly | Fantasy reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read uncommitted (read-uncommitted) | yes | yes | yes |
| It can't be read repeatedly (read-committed) | no | yes | yes |
| Repeatable (repeatable-read) | no | no | yes |
| Serialization (serializable) | no | no | no |
3.1 Raised questions
| abnormal | explain |
|---|---|
| Dirty reading | Dirty read means that one transaction reads uncommitted data from another |
| It can't be read repeatedly | Non repeatable reading refers to the inconsistency of the reading results of the same data by a transaction . The difference between dirty reading and non repeatable reading is : The former reads the uncommitted dirty data of the transaction , The latter reads the data that the transaction has committed , Just because the data has been modified by other transactions, the results of the two previous reads are different |
| Fantasy reading | Unreal reading is when a transaction reads a range of data , Because of the operation of other transactions, the results of the previous two reads are inconsistent . The difference between unreal reading and unrepeatable reading is , Non repeatable reading is for a certain line of data , And unreal reading is for uncertain multi line data . Therefore, unreal reading usually occurs in range queries with query conditions |
3.2 Case explanation
Case a
Dirty reading
Dirty reading is when a transaction is accessing data , And the data has been modified , This modification has not yet been committed to the database , At this time , Another transaction also accesses this data , And then I used this data .
for example :
Zhang San's salary is 5000, Business A Change his salary to 8000, But the business A Not yet submitted .
meanwhile ,
Business B Reading Zhang San's salary , I read that Zhang San's salary is 8000.
And then ,
Business A Something goes wrong , and Roll back It's a matter of . Zhang San's salary is rolled back to 5000.
Last ,
Business B The read salary of Zhang San is 8000 The data is dirty , Business B Did a dirty reading .
It can't be read repeatedly
Within a transaction , Read the same data multiple times . Before the end of the business , Another transaction also accesses the same data . that , Between two reads in the first transaction , Due to the modification of the second transaction , So the data read by the first transaction twice may be different . This happens that the data read twice in a transaction is different , So it's called unrepeatable reading .
for example :
In the transaction A in , I read that Zhang San's salary is 5000, Operation not completed , The transaction has not been submitted .
meanwhile ,
Business B Change Zhang San's salary to 8000, And commit the transaction .
And then ,
In the transaction A in , Read Zhang San's salary again , At this time, the salary becomes 8000. The result of reading two times in a transaction does not result in , It leads to non repeatable reading .
Fantasy reading
A phenomenon that occurs when a transaction is not executed independently , For example, the first transaction modifies the data in a table , This modification involves all data rows in the table . meanwhile , The second transaction also modifies the data in this table , This modification is to insert a new row of data into the table . that , In the future, the user who operates on the first transaction will find out whether there are any modified data rows in the table , It's like an illusion .
for example :
The present salary is 5000 Of the employees 10 people , Business A Read all salaries as 5000 The number of people is 10 people .
here ,
Business B Insert a salary for 5000 The record of .
At this time , Business A Read the salary again as 5000 The employees' , Record as 11 people . At this time, unreal reading .
remind
The point of unrepeatable reading is to modify :
The same conditions , The data you read , Read it again and find that the value is different
The point of unreal reading is to add or delete :
The same conditions , The first 1 Time and number 2 The number of records read is not the same
Case 2
Dirty reading
Dirty read refers to a transaction accessing uncommitted data of another transaction , The following process :
- hypothesis a The value of is 1, Business 2 hold a Change it to 2, The transaction has not yet been committed
- At this time , Business 1 Read a, Good reading a The value of is 2, Business 1 Read complete
- Result Affairs 2 Rolled back the right a Modification of ( Or not commit), therefore a The value of changes back to 1
- This leads to the fact that a The value of is 1, But the business 1 The results obtained are 2, So the business 1 Read dirty data , Dirty reading happens

It can't be read repeatedly
Non repeatable read refers to the process that a transaction reads the same data multiple times , The content of the data value has changed , As a result, it is impossible to read the same value , It describes the same data update/delete The phenomenon of , The following process :
- Business 1 Read a, here a = 1
- At this point, the transaction 2 take a It is amended as follows 2, And successfully submitted , The change takes effect
- Business 1 Read again a, here a = 2
- Business 1 Read the same value twice in the same transaction , The content of the data value has changed , An unrepeatable read occurs
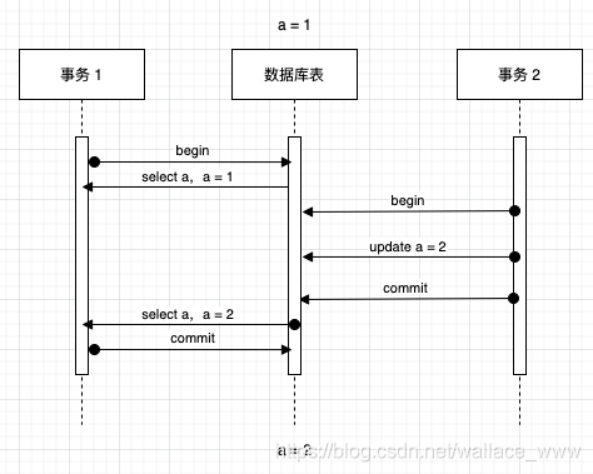
Fantasy reading
Phantom read refers to the process of a transaction reading the same data multiple times , Global data ( Such as the number of data rows ) It has changed , It seems that I have hallucinated , The description is for the whole table insert/delete The phenomenon of , The following process :
- Business 1 Number of first reads , obtain 10 Data
- At this point, the transaction 2 A piece of data was inserted and successfully submitted , The change takes effect , Data becomes 11 strip
- Business 1 Read the quantity again , obtain 11 Data , On business 1 There is one more one for me , It seems that I have hallucinated , Unreal reading occurs

Or another scenario , For example, for fields with uniqueness constraints ( Such as id), The following process occurs :
- Business 1 To insert id = 5 The record of , Query database first , Discover that there is no id = 5 The data of , It can be inserted normally .
- It's time for business 2 Insert a piece of data id = 5.
- Business 1 Insert id = 5 when , An error reporting uniqueness conflict is found , On business 1 It's like seeing a ghost , I just checked it out , Why is there another .

Four 、 Transaction propagation mechanism
- REQUIRED: Support current transaction , If there is no current transaction , Just create a new transaction . This is the most common choice . required
- SUPPORTS: Support current transaction , If there is no current transaction , Just in a non transactional way . supports
- MANDATORY: Support current transaction , If there is no current transaction , Throw an exception . mandatory
- REQUIRES_NEW: New transaction , If there are currently transactions , Suspend current transaction . requires_new
- NOT_SUPPORTED: Perform operations in a non transactional way , If there are currently transactions , Suspend the current transaction . not_supported
- NEVER: To execute in a non transactional manner , If there are currently transactions , Throw an exception . never
- NESTED: Support current transaction , If the current transaction exists , A nested transaction is executed , If there is no current transaction , Just create a new transaction . nested
4.1 Parameter interpretation
Explain a
REQUIRED
This is the default value of the transaction , When ServiceA.methodA The transaction level of is REQUIRED,ServiceB.methodB It's also REQUIRED when ,ServiceA.methodA Started a business ,ServiceB.methodB By ServiceA.methodA call , Find yourself in a business , No more business , If ServiceA.methodA No transactions , be ServiceB.methodB Start your own business .
If the current transaction exists, add the current transaction , If it is not in the transaction, start a new transaction .
REQUIRES_NEW
When ServiceA.methodA The transaction level of is REQUIRED,ServiceB.methodB It's also REQUIRES_NEW when ,ServiceA.methodA Started a business ,ServiceB.methodB By ServiceA.methodA call , Then suspend ServiceA.methodA The business of , Start your own business again , The two transactions are isolated , When ServiceB.methodB After submission , Just go on ServiceA.methodA The business of . It is associated with REQUIRED The difference between transactions is the degree of rollback of transactions , because ServiceB.methodB It's a new business , So there are two different transactions . If ServiceB.methodB Submitted , that ServiceA.methodA Failure rollback ,ServiceB.methodB It won't roll back . If ServiceB.methodB Failure rollback , The exception it throws is ServiceA.methodA Capture ,ServiceA.methodA Transactions can still be committed .
Restart the transaction , Whether or not a transaction currently exists , Suspend the current transaction if it exists , Restart transaction , Continue to complete the suspended transaction after committing . Transaction isolation , Whether rollback fails or not does not affect each other , But the exception thrown by the outer transaction can be caught .
SUPPORTS
When the annotated method is in a transaction , It is executed as a transaction , This is similar to the annotation REQUIRED, Rollback with outer rollback , It does not itself initiate a transaction , When the outer layer has no transactions , Then execute as if there were no transactions .
If you are currently in a transaction , That is to run in the form of a transaction , If you are not currently in a transaction , Then run it in a non transactional form
NOT_SUPPORTED
When the annotated method is in a transaction , Then execute as if there were no transactions , The outer transaction is suspended , Continue to complete the suspended transaction after execution , Similar to REQUIRES_NEW, It's all segregated , But labels NOT_SUPPORTED Is not in a transaction , If the operation fails, it will not be rolled back , But exceptions can be caught by outer transactions .
Isolate outer transactions , And cannot afford to deal with affairs , When there is a transaction in the outer layer, the outer layer transaction is suspended , After executing your own method, continue to complete the suspended transaction , Outer rollback does not affect its own operation , But the exception thrown by the outer transaction can be caught .
MANDATORY
Must run in a transaction . in other words , Can only be called by one parent transaction . otherwise , You have to throw an exception .
NEVER
When ServiceA.methodA The transaction level of is REQUIRED,ServiceB.methodB It's also NEVER when ,ServiceA.methodA Started a business ,ServiceB.methodB By ServiceA.methodA call ,ServiceB.methodB Will throw an exception
Cannot run in a transaction . otherwise , Itself will throw an exception .
NESTED
This level and REQUIRES_NEW Understanding is basically the same , Difference is that NESTED Not to start a new business , But to build a savepoint, The submission time should be submitted together with the outer affairs , Roll back together , But one advantage is that it has a savepoint. For example, self rollback fails , The outer layer can choose a new branch to execute and try to complete its own transaction .
Start a “ nesting Of ” Business , It is a real sub transaction of an existing transaction . When the nested transaction begins execution , It will get a savepoint. If this nested transaction fails , We'll roll back to savepoint. Nested transactions are part of external transactions , It will be committed only after the external transaction has ended .
Explain two
Here we will use the following classes to demonstrate ( Omit the interface layer )
UserService
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UsersMapper usersMapper;
@Override
public void saveParent() {
Users user = new Users();
user.setId("1");
user.setUsername("parent");
usersMapper.insert(user);
}
@Override
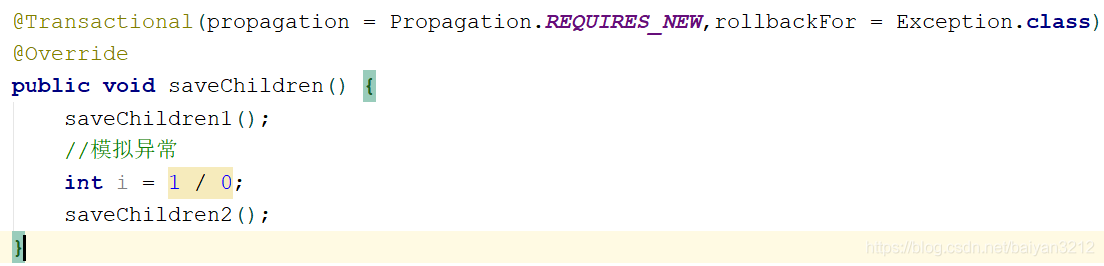
public void saveChildren() {
saveChildren1();
// Simulate anomalies
int i = 1 / 0;
saveChildren2();
}
public void saveChildren1(){
Users user = new Users();
user.setId("2");
user.setUsername("children1");
usersMapper.insert(user);
}
public void saveChildren2(){
Users user = new Users();
user.setId("3");
user.setUsername("children2");
usersMapper.insert(user);
}
}
TestTransService
@Service
public class TestTransServiceImpl implements TestTransService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
public void testTrans() {
userService.saveParent();
userService.saveChildren();
}
}
Unit test class
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class UserTest {
@Autowired
private TestTransService transService;
@Test
public void test(){
transService.testTrans();
}
}
The test scenario is in class TestTransService Method of another class
Methods are executed in the order of saving first parent, Save again children1, Save again children2
The case where the transaction is not opened
First of all, we do not add @Transaction annotation ,saveChildren Simulate abnormal conditions in

Error report in execution

In the database

No rollback was found when an exception occurred ,children1 Still saved successfully
Next, we will focus on the different propagation levels of transactions ( Be careful : The database will be emptied after each demonstration )
1.REQUIRED( need , Default level , It is mainly used for adding, deleting and modifying )
scene 1:
First, we add transaction annotations to the upper methods

The lower level called method does not add

Run the test Report errors java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
At this time, there is no new data in the database to prove that the transaction rollback is effective

Explain that the upper level method starts the transaction , The transaction isolation level is required Under the circumstances , The underlying method will also join the transaction
scene 2:
Shield upper level transactions

Open the lower layer savechildren Method Affairs

Run the test , I found that this time parent Saved successfully

Note the transaction isolation level is required Under the circumstances , If there is no current transaction , Create a new transaction by yourself .
scene 3:
Upper layer method and lower layer savechildren Methods are annotated with transaction annotations
After operation and conditions 1 There is no data stored in the database

The service isolation level is required Under the circumstances , If there are currently transactions , Will join the upper layer to call this transaction . Become a whole affair
To put it more generally :
required Under the circumstances , Parents have food , Will feed the children , Parents have no food , Children have their own meals , Both parents and children have meals , Children will eat with their parents ( The food here is business )
2.SUPPORTS( Support )
scene 1:
Add transactions to the underlying methods , The transaction propagation behavior is set to supports

The upper layer method masks transactions

The data in the database after running is as follows

It indicates that the underlying called method transaction is supports Under the circumstances , Follow the upper method , If there is no current transaction , Then the underlying method does not execute transactions
Note that if the upper level method transaction is supports, It is equivalent to that there is no transaction at present , So the bottom layer does not execute transactions
situation 2
The underlying method remains unchanged , The upper level method starts the transaction , And set to required

After execution

It indicates that the underlying called method transaction is supports Under the circumstances , If there are currently transactions , Then the underlying method joins the transaction .
To put it more generally :
supports Under the circumstances , Parents have food , Children have food to eat , Parents have no food , The children have no food
3.MANDATORY( mandatory )
Be similar to supports, But if the upper layer calling method has no transaction at present , An exception will be thrown
as follows , The upper layer shields transactions

The underlying method starts the transaction and sets it to mandatory

An error is reported on the console after execution

It indicates that the underlying called method transaction is mandatory Under the circumstances , If there is no current transaction , May be an error .
To put it more generally :
mandatory Under the circumstances , Parents have food , Children have food to eat , Parents have no food , Children will cry loudly when they quit
4.REQUIRES_NEW
scene 1:
The upper layer calls the method to start the transaction Set the propagation level to required

The lower level opens the transaction , Set to requires_new
After operation There is no data in the database Like and requried equally , Are current transactions executed , But it's not true. Let's go on to the scene 2

scene 2:
We add exception simulation in the upper layer method

The exception simulation is masked in the lower layer method

As before requried Experience , In this case, if you are in the same transaction , There should be no data in the database
In fact, the database after execution is as follows

We found that saveParent Method rolled back , But at the bottom saveChildren Method has no rollback
explain , The transaction level is requires_new Under the circumstances , If the current transaction , Then suspend the transaction , Create a new transaction for your own use , If there is no current transaction , And required Agreement .
To put it more generally :
requires_new Under the circumstances , Parents have food , Children don't eat their parents' meals , Just eat your own food
5.NOT_SUPPORTED
situation 1:
The upper level method does not open the transaction

The lower level method starts the transaction and sets it to NOT_SUPPORTED

The results are as follows

It is the same as not opening the transaction
situation 2:
The underlying method remains unchanged , The upper level method starts the transaction

It was found after execution that saveParent Method rollback , however saveChildren Method has no rollback

explain , The transaction level is not_supported Under the circumstances , Whether there is a transaction or not , Will suspend the transaction , No transactions .
To put it more generally :
not_supported Under the circumstances , Parents whether they have food or not , Children don't eat
6.NEVER
The above code does not change , Change the propagation level of the underlying method to never

The execution console will report an error

explain , The transaction level is never Under the circumstances , To execute in a non transactional manner , If there are currently transactions , Throw an exception
To put it more generally :
never Under the circumstances , Parents have food , Feed the children , The child will cry if he doesn't eat
7.NESTED( nesting )
scene 1:
The upper layer method simulates the exception and starts the transaction

The lower level method sets the transaction to NESTED

Execution results

It feels and required Is it very similar Let's move on
scene 2:
This time, the mock exception is placed on the underlying method


perform

The result is still no data , The results are consistent , Is it true and required equally , Are all involved in one transaction . Let's take a look at
scene 3:
We use it on the upper floor tay catch Catch exceptions of the underlying methods

perform

Found that the underlying method rolled back , But the upper layer method does not rollback .
Let's take another look at the scenario where we set the underlying method transaction to required

After execution

The upper and lower methods are rolled back ,
So explain Nested Actually and required Dissimilarity ,required Is to add the lower level called method to the current transaction , and nested It is equivalent to that the current transaction is not a transaction , But and required_new Dissimilarity , If the current transaction of the upper layer is rolled back , The underlying layer will be rolled back , If an abnormal rollback occurs in the lower layer , Upper level transactions can be handled through catch The exception control of the underlying method does not rollback itself , This is their biggest difference
To put it more generally :
nested amount to , The leader made a mistake , Subordinates will be punished along with them , But the subordinates made mistakes , Leaders can choose whether to be punished with their subordinates or not .
边栏推荐
- Leetcode 929.独特的电子邮件地址
- Tricks | [trick6] learning rate adjustment strategy of yolov5 (one cycle policy, cosine annealing, etc.)
- IP address division and subnet
- @Differences between jsonformat and @datetimeformat
- Record TCP time once_ Blood cases caused by wait
- Add failed when BigDecimal is 0.00
- MySQL add field or create table SQL statement
- Data inconsistency between the reids cache and the database, cache expiration and deletion
- BigDecimal当为0.00时add失败
- Embedded audio and video solutions webrtc vs metartc
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
redis 分布式锁的几种实现方式
Practical guide to GStreamer application development (III)
Data inconsistency between the reids cache and the database, cache expiration and deletion
Mysql5.7 one master multi slave configuration
Lucene构建索引与执行搜索小记
Yoyov5's tricks | [trick7] exponential moving average (EMA)
Record rsyslog lost logs
After the SSL certificate is installed, the website still shows insecurity
Tricks | [trick6] learning rate adjustment strategy of yolov5 (one cycle policy, cosine annealing, etc.)
Alibaba cloud AI training camp - machine learning 2:xgboost
Alibaba cloud AI training camp - SQL basics 3: complex query methods - views, subqueries, functions, etc
BigDecimal当为0.00时add失败
Ffmpeg pulls webrtc streams, and the first all open source solution in the metartc industry is coming
Analysis of the most complete webrtc server technology selection in history
[it] Fuxin PDF Keeping Tool Selection
Practical guide to GStreamer application development (I)
latex中\cdots后面接上句子,后面的句子格式会乱怎么回事。
Alibaba cloud AI training camp MySQL foundation 1:
Gstreamer应用开发实战指南(四)
pytorch with Automatic Mixed Precision(AMP)

![Tricks | [trick6] learning rate adjustment strategy of yolov5 (one cycle policy, cosine annealing, etc.)](/img/e8/d11adffb784b0875c69f6fe5a32b63.png)







