当前位置:网站首页>3、 Linked list exercise
3、 Linked list exercise
2022-06-26 10:55:00 【Wayne830】
Linked list exercise index
- 1、 Merge two ordered lists
- 2、 Delete the duplicate elements in the sorting linked list
- 3、 Delete the node in the linked list
- 4、 Remove linked list elements
- 5、 The middle node of a list
- 6、 Reverse a linked list
- 7、 Binary linked list to integer
- 8、 Merge two linked lists
- 9、 Palindrome list
- 10、 Rotate the list
- 11、 Exchange nodes in the linked list
- 12、 The next larger node in the linked list
- 13、 Odd and even list
- 14、 Split the list
- 15、K A set of flip list
- 16、 Reverse a linked list Ⅱ
- 17、 Addition of two numbers
1、 Merge two ordered lists
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
Title Description : Put two Ascending The linked list is merged into a new ascending linked list and returns . The new linked list is composed of all nodes of a given two linked lists .
Example 1:
input:L1=[1,2,4] L2=[1,3,4]
output:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2:
input:L1=[] L2=[]
output:[]
Example 3:
input:L1=[] L2=[0]
output:[0]
requirement :
1、 The number range of two linked list nodes [0,50]
2、-100<=Node.value<=100
analysis : This problem is to sort the linked list in general , Enter two ordered linked lists , Combine the two linked lists into a total ordered linked list , First, select the linked list type , To avoid redundant discussions , We can choose the circular linked list with the header node . In the application of linear table in the previous section , The creation of polynomials requires that each term of polynomials be arranged exponentially , Among them, the circular linked list with header node is also selected , The descending power arrangement uses the sorting method of the linked list : In the descending order of polynomials , Traverse from beginning to end , Find the first node less than the current power , Start linked list insertion , We can think of this problem as requiring that it be arranged in ascending power , So the same Traverse from beginning to end , Find the first node greater than the current power , Start linked list insertion .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
const int maxn=50;// Maximum length
const ElemType maxvalue=100;// Maximum value of node element Take negative as the minimum
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->n=0;
h->head->next=h->head;
h->head->element=maxvalue+2;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation If the input is not in ascending order Force ascending
for(;;){
// Loop input
Node *pre=h->head,*p=h->head->next;
//p The pointer is used to find the first node larger than the current input element pre The pointer thinks that p The precursor of
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<-maxvalue||q->element>maxvalue||h->n==maxn)// End input condition : The input value is small ( Big ) At minimum ( Big ) Value or exceed the maximum length required by the topic 50
break;
while(p&&p->element<q->element){
// Loop through the first node larger than the current input element
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
// Insert the current input node into pre and p Between
q->next=p;
pre->next=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=h->head;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Merge(HeaderList *h1,HeaderList *h2){
// Merge operations Save the results of the merger into h2 in
Node *p=h1->head->next,*temp;//temp Is used to p Data replication in Easy to add to h2 in
for(;p!=h1->head;p=p->next){
Node *pre=h2->head,*q=h2->head->next;
temp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->element=p->element;// Copy the data
while(q->element<=p->element){
// Loop to find the first one larger than the current one p The node of a node element
pre=q;
q=q->next;
}
// Will the current temp The node is inserted into pre and p Between
temp->next=q;
pre->next=temp;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl1,hl2;
Init(&hl1);Init(&hl2);
Input(&hl1);Input(&hl2);
//Output(&hl1);Output(&hl2);
Merge(&hl1,&hl2);
Output(&hl2);
return 0;
}

2、 Delete the duplicate elements in the sorting linked list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
Title Description : There is a list in ascending order , Given head node head, Delete all duplicate elements in the linked list , So that each element only appears once . Returns a list of results in ascending order .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,1,2]
output:[1,2]
Example 2:
input:head=[1,1,2,3,3]
output:[1,2,3]
requirement :
1、 List node number range [0,300]
2、-100<=Node.value<=100
analysis : The title has two requirements : Enter and delete duplicate elements in ascending order . The ascending input is the same as the previous question ; Deleting duplicate elements is essentially the deletion of linked lists : Define two node pointers , Traversing the linked list , If the elements indicated by two pointers are equal , Delete the second node .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
const int maxn=300;// Maximum length
const ElemType maxvalue=100;// Maximum value of node element Take negative as the minimum
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->n=0;
h->head->next=h->head;
h->head->element=maxvalue+2;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
for(;;){
// Loop input
Node *pre=h->head,*p=h->head->next,*q;
//p The pointer is used to find the first node larger than the current input element pre The pointer thinks that p The precursor of
q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<-maxvalue||q->element>maxvalue||h->n==maxn)
break;
// End input condition : The input value is small ( Big ) At minimum ( Big ) Value or exceed the maximum length required by the topic 300
while(p&&p->element<q->element){
// Loop through the first node larger than the current element
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
// Insert the current input node into pre and p Between
q->next=p;
pre->next=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=h->head;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Delete(HeaderList *h){
// Delete operation
Node *pre=h->head,*p=pre->next;
while(p!=h->head){
// Traversing the linked list
if(pre->element==p->element)// Two node elements are found to be the same
pre->next=p->next;// Delete the second node
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
//Output(&hl);
Delete(&hl);
Output(&hl);
return 0;
}


3、 Delete the node in the linked list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
Title Description : Please write a function , Make it possible to delete a given node in a linked list .
Example 1:
input:head=[4,5,1,9] node=5
output:[4,1,9]
Example 2:
input:head=[4,5,1,9] node=1
output:[4,5,9]
requirement :
1、 The linked list contains at least two nodes .
2、 The values of all nodes in the linked list are unique That is, no repeating elements .
3、 The given element to be deleted must be valid .
analysis : This problem is completed with a linked list of nodes with a header , The important function of this problem is to delete the given elements in the linked list , But there are some requirements in the title : The linked list contains two nodes , Then the user needs to input one or less than zero values again ; The values of all nodes in the linked list are unique , Then you need to traverse the linked list , If there is a duplicate element, you need to enter it again ; If the input is legal but the element to be deleted does not exist , The element to be deleted needs to be input repeatedly , Until the element to be deleted exists in the linked list . Deleting a function requires a given element to be deleted x, It is assumed that all inputs are legal , Regulations q The pointer traverses from the first element , Regulations pre The pointer traverses from the node , that pre The node pointed by the pointer is q The precursor of the node to which the pointer refers , When q The pointer found the element to be deleted ,pre The pointer field of the node pointed to by the pointer points to the current q The pointer field of the node to which the node refers .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->n=0;
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->element=-1;
h->head->next=NULL;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<0)// Enter a negative number to end the entry
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=p->next;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
bool isrepeated(HeaderList *h){
// Judge whether the value of each node in the linked list is repeated
if(h->n<2)// Meter length less than 2 illegal
return true;
else{
Node *p=h->head->next,*q=p->next;
while(p->next!=NULL){
if(p->element==q->element)// The occurrence of the same element is illegal
return true;
q=q->next;
if(q==NULL){
p=p->next;
q=p->next;
}
}
return false;
}
}
void Destory(HeaderList *h){
// Undo operation
Node *p=h->head,*q=h->head->next;
while(q!=NULL){
p->next=q->next;
free(q);
q=p->next;
}
}
bool Delete(HeaderList *h,ElemType x){
// Delete operation
Node *pre=h->head,*q=pre->next;
for(;q!=NULL;q=q->next){
if(q->element==x)
break;
pre=pre->next;
}
if(q==NULL){
// It is illegal if the element to be deleted does not exist
return true;
}
else{
pre->next=q->next;
free(q);
return false;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
Destory(&hl);
Input(&hl);// Perform input If it is illegal, re-enter
flag=isrepeated(&hl);
}
ElemType x;
bool flag2=true;
while(flag2){
cin>>x;
flag2=Delete(&hl,x);// Execution deletion If the node to be deleted is illegal, re-enter
}
Output(&hl);
Destory(&hl);
return 0;
}



4、 Remove linked list elements
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
Title Description : Given the head node of a linked list head and val, Delete all items in the linked list that meet the requirements Node.value==val The node of , And return the new header node .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,6,3,4,5,6] val=6
output:[1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2:
input:head=[] val=1
output:[]
Example 3:
input:head=[] val=7
ouutput:[]
analysis : This problem needs to delete the specified elements in the linked list , If the specified element in the linked list exists , Whether the element is repeated or not , Delete the element node equal to the specified element , Return the deleted list ; If the specified element in the linked list does not exist , Then return to the original linked list . This topic uses a single linked list with header nodes , The core of the algorithm is Delete function , Set two pointers p、q Traversing the linked list ,p The node to which the pointer refers is q The precursor of the node to which the pointer refers . if q The element of the current node pointed by the pointer is equal to the specified element , Delete the current q The node to which the pointer refers .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int INF=32767;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->n=0;
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->element=-INF;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element==-INF)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Delete(HeaderList *h,ElemType x){
// Remove element operations
Node *p=h->head;
Node *q=h->head->next;
for(;q!=NULL;q=q->next){
if(q->element==x){
p->next=q->next;
continue;
}
p=p->next;
}
}
void Destory(HeaderList *h){
// Undo operation
Node *p=h->head;
Node *q=p->next;
while(p->next!=NULL){
p->next=q->next;
free(q);
q=p->next;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
ElemType val;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
cin>>val;
Delete(&hl,val);
Output(&hl);
Destory(&hl);
return 0;
}



5、 The middle node of a list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
Title Description : Given a head node as head The non empty single chain table of , Returns the intermediate node of the linked list .
Example 1:
input:[1,2,3,4,5]
output:3
Example 2:
input:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
output:4( There are two intermediate nodes that return to the 2 individual )
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , First perform the input operation , For each valid number entered , Current table length plus 1, The linked list is formed after the input operation , Use Getvalue Function returns the intermediate value of the linked list , adopt for The loop will begin with a pointer to the first node p Point to the intermediate node , obtain element return .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;// Maximum length
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->element=-1;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<0||h->n>100)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<h->n;i++){
cout<<p->element<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
ElemType Getvalue(HeaderList *h){
// Return the intermediate node value
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<(h->n)/2;i++)
p=p->next;
return p->element;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
cout<<Getvalue(&hl)<<endl;
return 0;
}


6、 Reverse a linked list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
Title Description : Given the single chain header node head, Reverse the whole list , Return the inverted linked list .
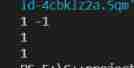
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5]
output:[5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
input:head=[1,2]
output:[2,1]
Example 3:
input:head=[]
output:[]
analysis : This topic uses a single linked list with header nodes , To simplify the linked list structure , It can traverse the data of each node of the linked list , Then it is stored in one-dimensional array in reverse order , Again, traverse the array and linked list in sequence , Use the overwrite function to overwrite the original linked list data .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e3;// Maximum length
typedef struct node{
int val;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->val=maxn+1;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->val;
if(q->val<-maxn||q->val>maxn||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Flag(HeaderList *h,int *a){
// Store the data in the linked list in reverse order into a one-dimensional array
Node *p=h->head->next;
int cnt=h->n-1;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
a[cnt]=p->val;
cnt--;
}
}
void CoverList(HeaderList *h,int *a){
// Sequentially extract elements from a one-dimensional array to cover the original linked list
Node *p=h->head->next;
int i=0;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
p->val=a[i];
i++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->val<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
int *a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*hl.n);
Flag(&hl,a);
CoverList(&hl,a);
Output(&hl);
free(a);
return 0;
}



7、 Binary linked list to integer
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-number-in-a-linked-list-to-integer/
Title Description : Give the order list reference head node , The value of each node in the list is not 0 Namely 1 That is, binary representation . Please write a function to return the decimal system of the numbers represented by the linked list .
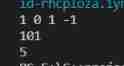
Example 1:
input:head=[1,0,1]
output:5
Example 2:
input:head=[0]
output:0
Example 3:
head=[1]
output:1
Example 4:
input:head=[0,0]
output:0
Example 5:
input:head = [1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
output:18880
requirement :
1、 Link list is not empty
2、 The total number of linked list nodes does not exceed 30
3、 Each node value is not 0 Namely 1
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , The title requires that binary numbers in the linked list be converted into decimal numbers , obviously , The value in the linked list can only be 0 or 1, Considering that the user may input incorrectly , So every time you enter a number , Check whether the input is legal , If the rule of coincidence is added to the linked list , If it is illegal, discard the current input . Secondly, the number of binary digits required to be input shall not exceed 30, Then the maximum value of the returned decimal result obtained from the sum formula of the proportional sequence is 2 0 2^0 20+ 2 1 2^1 21+…+ 2 29 2^{29} 229= 2 30 2^{30} 230-1=1073741823, Far more than int type ( Think 16 Bit computer ,int The scope is -32768~32767) The scope of the , We can choose long Type as the return value , The maximum value of its type is 2 31 2^{31} 231-1.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
typedef long l;
typedef struct node{
int i;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->i=-1;
h->n=0;
}
bool judge(int i){
// Judgment function Judge whether the input data is legal
if(i<=0||i==1)// A negative number is used to end the input
return false;
return true;
}
bool Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
if(h->n<0||h->n>30)
return false;
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
bool flag=true;
while(flag){
cin>>q->i;
flag=judge(q->i);// If the input data is illegal, the number is invalid
}
if(q->i<0||h->n>=30)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
return true;
}
l Quickpow(int a,int b){
// Fast power for each weight
l res=1;
while(b){
if(b&1)
res=res*a;
b>>=1;
a=a*a;
}
return res;
}
l Conversion(HeaderList *h){
// Conversion function
Node *p=h->head->next;
l res=0;
int len=h->n;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
res+=Quickpow(2,len-1)*p->i;// The result is the sum of each weight
len--;
}
return res;
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->i;
cout<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
cout<<Conversion(&hl)<<endl;
return 0;
}



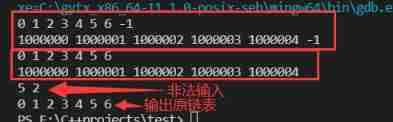
8、 Merge two linked lists
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-in-between-linked-lists/
Title Description : Given two linked lists list1 and list2, The original numbers are respectively n individual m individual . take list1 pass the civil examinations a Node to b Delete nodes , take list2 Connected to the deleted node .
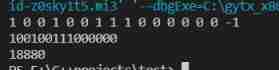
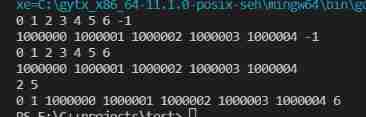
Example 1:
input:list1=[0,1,2,3,4,5] list2=[1000000,1000001,1000002] a=3 b=4
output:[0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5]
Example 2:
input:list1=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6] list2=[1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004] a=2 b=5
output:[0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6]
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list of leading nodes , The key point of this question is positioning , Find the cutting point , Use p Pointer found list1 Header deletion point of ,q Pointer found list1 The last deletion point of ,pre Pointer found list2 The end node implements the docking operation , The above node searching operations can be performed through for or while Cycle to achieve .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e4;// Maximum length
typedef long ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->element=-1;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<0||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
int Divide(HeaderList *h1,HeaderList *h2,int a,int b){
// Merge operations
if(a<=b&&a>=1&&b<h1->n-1){
Node *p=h1->head->next;
Node *q=h1->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<a-1;i++)
p=p->next;//p Pointer to h1 The first a Before the node
for(int j=0;j<b;j++)
q=q->next;//q Pointer to h1 The first b Nodes
p->next=h2->head->next;
Node *pre=h2->head->next;
for(int k=0;k<h2->n-1;k++)
pre=pre->next;//pre Pointer to h2 The end node
pre->next=q->next;
return 1;
}
else// illegal input
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl1,hl2;
Init(&hl1);Init(&hl2);
Input(&hl1);Input(&hl2);
Output(&hl1);Output(&hl2);
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
Divide(&hl1,&hl2,a,b);
Output(&hl1);
return 0;
}

9、 Palindrome list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list-lcci/
Title Description : Write a function , Check whether the input list is palindromic .
Example 1:
input:1->2
output:false
Example 2:
input:1->2->2->1
output:true
analysis : Palindromes are symmetrical , This question requires you to input a linked list , Determine whether the elements of the linked list are palindromes . We can think of Judge from the two ends of the linked list to the middle , If symmetric node elements are not equal , No reply . Because the common linked list can only move in one direction , To increase flexibility , This question uses Two way linked list with header node .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int INF=32767;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *leftlink;// Left pointer field
struct node *rightlink;// Right pointer field
}Node;
typedef struct duList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}DuList;
void Init(DuList *d){
// Initialization operation
d->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
d->head->element=-INF;
d->n=0;
d->head->rightlink=NULL;
}
void Input(DuList *d){
// Input operation
Node *p=d->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element==-INF)
break;
q->leftlink=p;
p->rightlink=q;
p=q;
d->n++;
}
}
void Output(DuList *d){
// Output operation
Node *p=d->head->rightlink;
for(int i=0;i<d->n;i++){
cout<<p->element<<" ";
p=p->rightlink;
}
cout<<endl;
}
bool Isreplies(DuList *d){
// Palindrome
Node *p=d->head->rightlink;
Node *q=d->head->rightlink;
for(int i=0;i<d->n-1;i++){
q=q->rightlink;
}
// initial p The pointer points to the first element node q Pointer to the last element node
int cnt=0;// The number of steps the pointer moves p and q Every time the pointer moves cnt Just add 1
while(cnt<d->n/2){
//cout<<p->element<<" "<<q->element<<endl;// Output the number of each round of comparison
if(p->element!=q->element)// If there are symmetric nodes with unequal elements No reply
return false;
p=p->rightlink;q=q->leftlink;//p Pointer to the right q The pointer is left to judge one by one
cnt++;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
DuList du;
Init(&du);
Input(&du);
Output(&du);
cout<<Isreplies(&du)<<endl;
return 0;
}


10、 Rotate the list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/
Title Description : Given the chain header node head, Rotate the list , Move each node of the linked list to the right k A place .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] k=2
output:[4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
input:head=[0,1,2] k=4
output:[2,0,1]
explain :
k=0 0->1->2
k=1 2->0->1
k=2 1->2->0
k=3 0->1->2
k=4 2->0->1
analysis : This problem requires that the linked list be rotated , End node moves to head k individual , First, select the circular linked list , Second, the pointer needs to move left and right , Select the bidirectional linked list , Then this question uses Double cycle linked list with header node . After initializing the linked list , Put the pointer p Move to the penultimate node , The pointer q Move to the end node (q The node pointed by the pointer is p The node referred to by the pointer is followed by )( operation Ⅰ); Secondly, because the linked list has a header node , The right pointer of the end node refers to the header node , At this point, you need to point the right pointer of the end node to the next node of the header node ( The first element node )( operation Ⅱ); And then p Pointers and q The pointer points to the position to be truncated , Truncate it ( operation Ⅲ); Finally, through the current pointer q Traverse the linked list and output the linked list .


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const long maxk=2e9;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef long l;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *rightnext;// Right pointer field
struct node *leftnext;// Left pointer field
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->rightnext=NULL;
h->head->element=101;
h->n=0;
}
bool Input(HeaderList *h,int N){
// Input operation
if(N>500)
return false;
Node *p=h->head;
Node *q;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
q->leftnext=p;
q->rightnext=p->rightnext;
p->rightnext=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
q->rightnext=h->head->rightnext;
return true;
}
bool Rotate(HeaderList *h,l k){
// Rotation operation
if(k>maxk)
return false;
Node *p=h->head,*q;
for(int i=0;i<h->n-1;i++)
p=p->rightnext;
q=p->rightnext;//Ⅰ
h->head->rightnext->leftnext=q;
q->rightnext=h->head->rightnext;//Ⅱ
for(l i=0;i<k-1;i++){
q=q->leftnext;
p=p->leftnext;
}
p->rightnext=NULL;q->leftnext=NULL;//Ⅲ
for(int i=0;i<h->n;i++){
cout<<q->element<<" ";
q=q->rightnext;
}
cout<<endl;
return true;
}
void Destory(HeaderList *h){
// Undo operation
Node *p=h->head;
Node *q=p->rightnext;
while(p->rightnext!=NULL){
p->rightnext=q->rightnext;
free(q);
q=p->rightnext;
}
free(h->head);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
l K;
int N;
Init(&hl);
cin>>N;
Input(&hl,N);
cin>>K;
Rotate(&hl,K);
Destory(&hl);
return 0;
}


11、 Exchange nodes in the linked list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swapping-nodes-in-a-linked-list/
Title Description : Given the chain header node head And integer k, The length of the list is n, Exchange the positive number in the linked list k Node and penultimate k After node values , Back to the list .(0<k≤n)
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] k=2
output:[1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
input:head=[7,9,6,6,7,8,3,0,9,5] k=5
output:[7,9,6,6,8,7,3,0,9,5]
Example 3:
input:head=[1] k=1
output:[1]
Example 4:
input:head=[1,2] k=1
output:[2,1]
Example 5:
input:head=[1,2,3] k=2
output:[1,2,3]
requirement :
1、1<=k<=n<=1e5
2、0<=Node.value<=100
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , The ontology needs to be exchanged k One and last k The value of nodes . We know how to write a program to exchange the values of two numbers , That is, the third variable is used to realize the exchange . The same goes for this question , Applying for another node space is equivalent to the third variable , Put one of the values in it , Another value is assigned to the position of this value , Then put the value in the third variable into the original position of another value , Finally, release the node space of the third variable .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const long maxn=1e5;// Maximum length
typedef int ElemType;
typedef long l;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
l n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->element=101;
h->head->next=NULL;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<0||q->element>100||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
bool SwapNode(HeaderList *h,l k){
// Commutative operation
if(k>h->n||k<=0)
return false;
Node *p=h->head,*q=p;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
p=p->next;
for(int j=0;j<h->n-k+1;j++)
q=q->next;
Node *tmp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));// The third variable stores the node value
tmp->element=p->element;
p->element=q->element;
q->element=tmp->element;
free(tmp);
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
l k;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
cin>>k;
SwapNode(&hl,k);
Output(&hl);
return 0;
}





12、 The next larger node in the linked list
Title Description : Given head node head Linked list , The node values are :node_1~node_n. Every node node_i There may be more nodes than the current node in all subsequent nodes of node_i Nodes with larger values , If there is no such thing as 0. Store the answers in a one-dimensional array (answer[i]=next_larger(node_{i+1})) And in return .
Example 1:
input:[2,1,5]
output:[5,5,0]
explain : The first bit in the output 5 Express 2 There is more than 2 The big value is 5; Second 5 Empathy ; Third 0 Express 5 There is no comparison 5 A bigger successor
Example 2:
input:[2,7,4,3,5]
output:[7,0,5,5,0]
Example 3:
input:[1,7,5,1,9,2,5,1]
output:[7,9,9,9,0,5,0,0]
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes . It's easy to think of traversing a linked list for comparison , Define two pointers p、q, The pointer p The pointed node is a pointer q The precursor of the node ,q The pointers are compared backwards one by one , To avoid out of range, it means that the target value is not found at the end of this round of search , Open up another tmp node , Its element value is -INF. If the target value is found , Put it in the array ; If the target value is not found , The pointer q Point to tmp node , The current array value is 0.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e4;// Maximum length
const long INF=1e9;
typedef long ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->element=INF+1;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
Node *q;
for(;;){
q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<1||q->element>INF||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
Node *tmp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));// To prevent cross-border
tmp->element=-INF+1;p->next=tmp;tmp->next=NULL;
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
ElemType* Solve(HeaderList *h){
Node *p=h->head->next,*q;
ElemType *ans=(ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(Node)*h->n);// A one-dimensional array holds the answers
int i=0;// The current array subscript
while(p->next!=NULL){
q=p->next;//q The node pointed by the pointer is p The node referred to by the pointer is followed by
for(;;q=q->next){
//q The pointer starts looking for the target
if(q->element>p->element){
// Find the target
ans[i]=q->element;
i++;
break;
}
if(q->element==-INF+1){
// Search to the end of the linked list, but no target is found
ans[i]=0;
i++;
break;
}
}
p=p->next;//p The pointer moves back one node
}
return ans;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
ElemType *answer;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
answer=Solve(&hl);
for(int i=0;i<hl.n;i++)
cout<<answer[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}



13、 Odd and even list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/
Title Description : Given the list , Put all odd and even nodes together .
Example 1:
input:1->2->3->4->5->NULL
output:1->3->5->2->4->NULL
Example 2:
input:2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
output:2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
explain :
Example 2 The output of the 2->3->6->7 It is the odd node of the original linked list ( The first 1、3、5、7 Nodes );1->5->4 It is the even node of the original linked list ( The first 2、4、6 Nodes )
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes . It's easy to think of defining two pointers , In steps 2 Traversing the linked list , The values of odd and even nodes are obtained respectively , Then insert the values into the new linked list . To avoid crossing the border , Add a new node at the end of the original linked list and its pointer points to itself . Store the node values accessed each time into a one-dimensional array , Defining a new linked list , Insert the elements in the one-dimensional array into the new linked list in sequence .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int INF=32767;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node{
ElemType element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->next=NULL;
h->head->element=INF;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head,*q;
for(;;){
q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<=-INF||q->element>=INF)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
Node *tmp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));// To prevent cross-border
tmp->element=-INF;tmp->next=tmp;p->next=tmp;
}
void Output1(HeaderList *h){
// Output the original linked list operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p->element!=-INF;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Output2(HeaderList *h){
// Output new linked list operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<h->n;i++){
cout<<p->element<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void Insert(HeaderList *h,int i,ElemType elm){
// Insert operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
p=p->next;
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
q->element=elm;
p->next=q;
h->n++;
}
ElemType* Getvalue(HeaderList *h){
// Get even and odd nodes
Node *p=h->head,*q=p->next;
ElemType* ans=(ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*h->n);// One dimensional array stores the results in sequence
int cnt=0;
for(;q->element!=-INF;q=q->next->next){
// Odd node
ans[cnt]=q->element;
cnt++;
}
for(;p->element!=-INF;p=p->next->next){
// Even nodes
if(p->element==INF)
continue;
ans[cnt]=p->element;
cnt++;
}
return ans;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl,res;
ElemType *ans;
Init(&hl);Init(&res);
Input(&hl);
Output1(&hl);
ans=Getvalue(&hl);
for(int i=0;i<hl.n;i++)
Insert(&res,i,ans[i]);// Insert the elements in the one-dimensional array into the new linked list in sequence
Output2(&res);
return 0;
}


14、 Split the list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list-lcci/
Title Description : Given head node head And specific values x, Please split the linked list , Make all less than x All the nodes of are greater than or equal to x Before node .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,4,3,2,5,2] x=3
output:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
Example 2:
input:head=[2,1] x=2
output:[1,2]
explain : Example 1 The specific value in is 3, Then the order in the linked list is less than 3 The node of is 1,2,2; Residual node 4,3,5 Connect in sequence 1,2,2 after
requirement :
1、 The range of the number of nodes in the linked list [0,200]
2、-100<=Node.value<=100
3、-200<=x<=200
analysis : This question requires you to input a linked list and a specific value x, Will be less than a certain value x All nodes of are placed in front of the linked list , Place the remaining nodes in sequence and then put them behind the linked list . This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , First, traverse the whole linked list , Find out the elements smaller than a specific value in sequence , Store it in a one-dimensional array ; Then the remaining node elements are sequentially stored in a one-dimensional array ; Finally, define a new linked list , Store the elements in the one-dimensional array in the new linked list through the tail insertion operation .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int INF=100;
const int maxn=200;// Maximum length
int a[maxn];// Auxiliary storage array
typedef struct node{
int element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// Head node
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->element=-INF-1;
h->head->next=NULL;
h->n=0;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<-INF||q->element>INF||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Insert(HeaderList *h,int x){
// Tail insertion operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(int i=0;i<h->n;i++)
p=p->next;//p The pointer points to the tail node
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
q->element=x;
p->next=q;q->next=NULL;
h->n++;
}
bool Findsmaller(HeaderList *h,HeaderList *h1,int x){
// Find nodes smaller than a specific value
if(x<-200||x>200)
return false;
Node *p=h->head->next;
int i=0;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
if(x>p->element){
a[i]=p->element;// Store the node elements less than a specific value into the auxiliary array in sequence
i++;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
Insert(h1,a[j]);// Insert the node elements less than a specific value into the tail of the new linked list
return true;
}
void Solve(HeaderList *h,HeaderList *h1,int x){
// The remaining nodes are inserted in sequence
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next){
if(x<=p->element)
Insert(h1,p->element);// Then insert the node elements greater than or equal to a specific value into the tail of the new linked list
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl,hl1;
Init(&hl);Init(&hl1);
Input(&hl);
Output(&hl);
int x;// Specific value
cin>>x;
Findsmaller(&hl,&hl1,x);
Solve(&hl,&hl1,x);
Output(&hl1);
return 0;
}

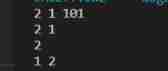
15、K A set of flip list
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
Title Description : Given a linked list , Every time k Nodes are flipped , Return to the flipped linked list . If the total number of nodes is not k Integer multiple , The remaining nodes are not flipped .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] k=2
output:[2,1,4,3,5]
explain : Will input the linked list [1,2,3,4,5] Every time 2 A flip , that 1 and 2 Flip ;3 and 4 Flip ; The remaining 1 Nodes do not flip
Example 2:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] k=3
output:[3,2,1,4,5]
Example 3:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] k=1
output:[1,2,3,4,5]
Example 4:
input:head=[1] k=1
output:[1]
analysis : This problem needs to be modified directly in the linked list , Still select the single linked list with header node . This question needs to input a positive integer less than the length of the linked list k, Every time k Elements in a flip node , We know that if all its data is put into a one-dimensional array , Implementing this functionality is not complicated . Then you can traverse the linked list and put the data into a one-dimensional array in sequence , Then implement each in the array k Turn over in groups , Finally, in order to traverse the array and linked list , Change the value of each node of the original linked list one by one .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e3;// Maximum length
const int INF=1e3;
typedef struct node{
int element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
Node *head;// The head pointer
int n;// Effective length
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->element=-1;
h->n=0;
h->head->next=NULL;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(q->element<0||q->element>INF||h->n>=maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;p->next=q;p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Swap(int *a,int *b){
// Commutative operation
int tmp=*a;*a=*b;*b=tmp;
}
bool Reverse(HeaderList *h,int *a,int k){
// Flip operation
if(k<1||k>h->n)// Illegal situation
return false;
Node *p=h->head->next;
int i=0;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
a[i++]=p->element;// The data of each node of the linked list is put into a one-dimensional array in sequence
int left,right;
for(int i=0;i+(k-1)<h->n;i+=k){
// grouping
left=i;right=left+(k-1);
while(left<right){
Swap(&a[left],&a[right]);// Flip in a group
left++;right--;
}
}
return true;
}
void Change(HeaderList *h,int *a){
// Directly put the values in the one-dimensional array into the linked list
Node *p=h->head->next;
int i=0;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
p->element=a[i++];
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int k;
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
int *a=(int*)malloc(hl.n*sizeof(int));
Output(&hl);
cin>>k;
if(!Reverse(&hl,a,k))
exit(0);
Change(&hl,a);
Output(&hl);
free(a);
return 0;
}


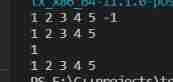

16、 Reverse a linked list Ⅱ
Title Description : Given a linked list and two integers left and right(left≤right), Move the linked list from position left To the position right The node is reversed . Return the inverted linked list .
Example 1:
input:head=[1,2,3,4,5] left=2 right=4
output:[1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
input:head=[5] left=1 right=1
output:[5]
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , Pass the previous topic , It is found that when the title requires that the linked list needs more complex operations , One dimensional array can be used for storage and operation , Then you can overwrite the original linked list with one-dimensional array values . This question can store the part that needs to be reversed into a one-dimensional array , Inversion is achieved by exchanging functions , Then overwrite the changed part of the original linked list , Return to the original linked list .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=500;// Maximum length
typedef struct node{
int element;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->n=0;
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->head->element=maxn+1;
h->head->next=NULL;
}
void Input(HeaderList *h){
// Input operation
Node *p=h->head;
for(;;){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->element;
if(h->n>=maxn||q->element<-maxn||q->element>maxn)
break;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
h->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->element<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void Swap(int *a,int *b){
// Commutative operation
int tmp;
tmp=*a;
*a=*b;
*b=tmp;
}
void Solve(HeaderList *h,int *a,int left,int right){
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<left-1;i++)
p=p->next;
Node *q=p;//Ⅰ
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<(right-left)+1){
a[cnt]=p->element;
cnt++;
p=p->next;
}//Ⅱ
int lft=0,rig=right-left;
while(lft<=rig){
Swap(&a[lft],&a[rig]);
lft++;rig--;
}//Ⅲ
for(int i=0;i<(right-left)+1;i++){
q->element=a[i];
q=q->next;
}//Ⅳ
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
HeaderList hl;
Init(&hl);
Input(&hl);
int left,right;
cin>>left>>right;
if(left>right)
exit(0);
int *a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(right-left)+1);
Solve(&hl,a,left,right);
Output(&hl);
free(a);
return 0;
}



17、 Addition of two numbers
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
Title Description : Given two non empty linked lists , Two nonnegative integers . Each of them is stored in reverse order , Each node stores one digit . Add the numbers corresponding to the two linked lists .
Example 1:
input:l1=[2,4,3] l2=[5,6,4]
output:[7,0,8]
explain :342+465=807
Example 2:
input:l1=[0] l2=[0]
output:[0]
Example 3:
input:l1=[9,9,9,9,9,9,9] l2=[9,9,9,9]
output:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
analysis : This problem uses a single linked list with header nodes , This problem needs to add the reverse numbers represented by two linked lists , There is a carry case when two numbers are added , In some cases, the added number will be more than the original knot number . Consider the limit case :① The two linked lists have the same number of nodes , Such as 999+999=1998, The limit case is one more than the length of the linked list .② The number of nodes in the two linked lists is different , Such as 99+999=1098,999+99999=100998, The limit case is that there is one more digit than the length of the two linked lists . For the sake of adding , First read the length of the two linked lists to be added , According to two limit cases , Add enough 0( Here's the picture ). Define two pointers p,q Point to the linked list respectively 1, Linked list 2 The lowest point of , Every summation ends , Both hands move backwards , Until it is empty . In addition, to save space , There is no need to declare the third linked list , Directly add each bit to cover the nodes in the second linked list . In addition , It is necessary to determine whether the current and carry are required ,IfC Function returns a Boolean value indicating whether a carry is required .
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
typedef struct node{
int val;// Data fields
struct node *next;// Pointer to the domain
}Node;
typedef struct headerList{
int n;// Effective length
Node *head;// The head pointer
}HeaderList;
void Init(HeaderList *h){
// Initialization operation
h->head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
h->n=0;
h->head->val=0;
h->head->next=NULL;
}
bool Input(HeaderList *h,int n){
// Input operation
if(h->n>maxn)
return false;
Node *p=h->head;
h->n=n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
Node *q=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
cin>>q->val;
if(q->val<0||q->val>9)
return false;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
p=q;
}
return true;
}
void AddZero(HeaderList *h1,HeaderList *h2){
// Zero operation
if(h1->n>h2->n){
//h1 Longer than h2 length
int num=abs(h1->n-h2->n);
Node *p=h2->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<h2->n-1;i++)
p=p->next;
for(int j=0;j<num;j++){
Node *x=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
x->val=0;
p->next=x;x->next=NULL;
p=x;
h2->n++;
}
}
else if(h1->n<h2->n){
//h1 The length is less than h2 length
int num=abs(h1->n-h2->n);
Node *p=h1->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<h1->n-1;i++)
p=p->next;
for(int j=0;j<num;j++){
Node *x=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
x->val=0;
p->next=x;x->next=NULL;
p=x;
h1->n++;
}
}
else{
//h1 The length is equal to h2 length
Node *p=h1->head->next,*q=h2->head->next;
for(int i=0;i<h1->n-1;i++){
p=p->next;
q=q->next;
}
Node *x=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *y=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
x->val=0;x->next=NULL;
y->val=0;y->next=NULL;
p->next=x;q->next=y;
h1->n++;h2->n++;
}
}
void Output(HeaderList *h){
// Output operation
Node *p=h->head->next;
for(;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
cout<<p->val<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
bool IfC(int a,int b){
// Determine the current digit and whether to carry
if(a+b>=10)
return true;
return false;
}
void Add(HeaderList *h1,HeaderList *h2){
// Node sum operation
Node *p=h1->head->next,*q=h2->head->next;
while(p!=NULL){
if(IfC(p->val,q->val)){
// Carry required
q->val=(p->val+q->val)%10;// Take a bit value
q->next->val+=1;// carry
p=p->next;q=q->next;
}
else{
// No carry
q->val=p->val+q->val;// Direct additive
p=p->next;q=q->next;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int n1,n2;
cin>>n1>>n2;
HeaderList hl,hl1;
Init(&hl);Init(&hl1);
Input(&hl,n1);Input(&hl1,n2);
AddZero(&hl,&hl1);
AddZero(&hl,&hl1);
//Output(&hl);Output(&hl1);
Add(&hl,&hl1);
Output(&hl1);
return 0;
}


边栏推荐
- SQL index learning notes
- ACK攻击是什么意思?ACK攻击怎么防御?
- MySQL 12th job - Application of stored procedure
- Developers, what is the microservice architecture?
- Docker中实现MySQL主从复制
- Win10 start FTP service and set login authentication
- Flutter and native communication (Part 1)
- Function run time
- Expand and collapse too high div
- Update mysql5.6 to 5.7 under Windows
猜你喜欢

哪些PHP开源作品值得关注
![Installing MySQL under Linux [details]](/img/38/77be56c3ef3923ce4c4e5df4a96f41.png)
Installing MySQL under Linux [details]
Concise course of probability theory and statistics in engineering mathematics second edition review outline

SwiftUI 开发经验之为离线优先的应用程序设计数据层

MySQL seventh job - update data
Express (I) - easy to get started

Using foreach to loop two-dimensional array
The sixth MySQL job - query data - multiple conditions
MySQL 10th job - View

ISO 26262 - 2 functional safety concept
随机推荐
Swiftui development experience: data layer of application design for offline priority
June training (the 26th day) - collective search
Redis knowledge mind map
Easyexcel - Excel read / write tool
2020.7.6 interview with fence network technology company
即构「畅直播」上线!提供全链路升级的一站式直播服务
近期工作汇报
Tape library simple record 1
Huawei secoclient reports an error "accept return code timeout" [svn adapter v1.0 exclamation point]
MySQL 8th job
Recent work report
挖财商学院证券开户安全嘛?
JWT certification agreement -- I opened a Yihong hospital
【在线仿真】Arduino UNO PWM 控制直流电机转速
The sixth MySQL job - query data - multiple conditions
CentOS安装Redis多主多从集群
Oracle11g 启动数据库时报错 ORA-27154: post/wait create failed
工程数学概率论统计简明教程第二版复习大纲
二叉树常见面试题
Linux下安装Mysql【详细】