当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 15 string localization and message Dictionary (1)
Chapter 15 string localization and message Dictionary (1)
2022-07-02 17:40:00 【yaoxin521123】
List of articles
Chapter 15 String localization and message dictionary ( One )
This article outlines string localization , And describes how to export 、 Import and manage message dictionaries .
String localization
When localizing the text of an application , Will create a list of text strings for a language , Then when the application locale is different , Establish a convention to replace the translated versions of these messages in another language .
Support the following process of localizing strings :
- Developers include localizable strings in their code ( stay
RESTApplications or business intelligence models ).
This mechanism varies , But the most common mechanism is $$$Text macro . Instead of hard coded text strings , Developers include $$$Text Instances of macros , Provide the following values for macro parameters :
- Default string
- The domain to which this string belongs ( When grouping strings into fields , Localization is easier to manage )
- The language code of the default string
write "Hello world"
Replace with
write $$$TEXT("Hello world","sampledomain","en-us")
- When compiling code , The compiler will be in the message dictionary as
$$$TextEach unique instance of the macro generates entries .
The message dictionary is global , Therefore, you can easily view it in the management portal ( for example ). There are some class methods that can help with common tasks .
- After development , The publishing engineer exports the message Dictionary of this domain or all domains .
The result is one or more XML Message file , It contains the text string of the original language .
The release engineer sends these documents to the translator , Request translation version .
Translators use whatever they like
XMLCreate tools to deal withXMLMessage file . essentially , They translate text from the original language into a new language , Without changing the surroundingXML.The converter returns a new
XMLMessage file , The file has the same structure and :
- identification
<MsgFile>New language attribute of elementRFC1766value . - Contains translated text in the recognized language .
- The release engineer will translate
XMLThe message file is imported into the same namespace as the exported original file .
The translation and the original coexist in the news dictionary .
- At run time , The application selects the text to be displayed according to the browser's default language .
Message Dictionary
The message dictionary is a global, Include by domain name 、 Language name and message ID Organized text string :
- The text of each message is at most
32KCharacter string . If the database enables long strings , Then the string may be longer , But the default maximum value is32K. Messages may contain only text , It may also contain one or more elements%1、%2And other specified parameters . When the application page needs , You can replace these parameters with text ( For example, the file name in the error message ) display messages . - The domain name is an arbitrary string . It identifies a set of related text items , For example, all messages of a specific application or page . If you assign a domain to a group of messages , You can later perform specific actions on all messages with the same domain .
The domain name is case sensitive , It can contain upper and lower case characters . If the domain name uses % start , Think that all messages in this domain are system messages visible in all namespaces . otherwise , When creating messages , It is only visible in the namespace that defines it .
- The language name is consistent with
RFC1766All lowercase language marks . It consists of one or more parts : Main language labels ( for example enorja) Optionally followed by a hyphen (-) And secondary language tags (en-gborja-jp`). - news
IDIs an arbitrary string ; It uniquely identifies a message . newsIDIt only needs to be unique in the domain . You can assign a messageIDOr allow the compiler to assign a , It depends on the convention used to create the message . newsIDCase sensitive , It can contain upper and lower case characters .
Message dictionary storage
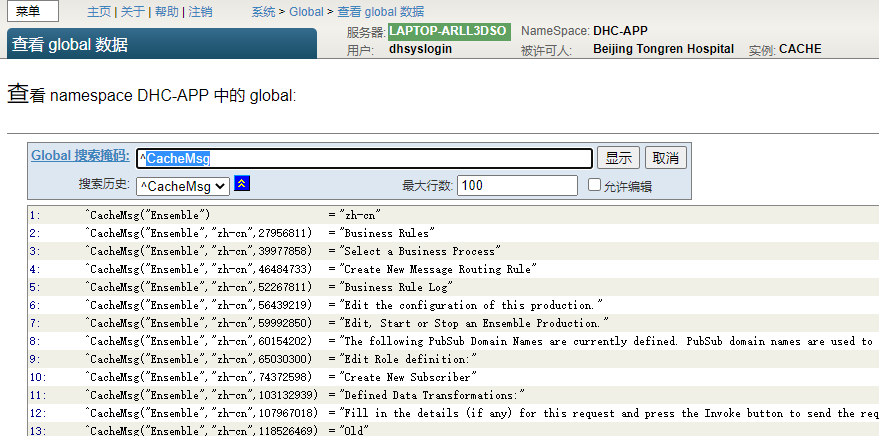
Each user-defined namespace stores its message dictionary under the name ^IRIS.Msg Subscript global . ^IRIS.Msg The subscript order in is domain 、 Language and messages ID.
To view the namespace ^IRIS.Msg
- Start the management portal .
- Switch to the namespace of interest .
- single click System Explorer > Globals.
- stay
IRIS.MsgIn line , Click view .
for example
DHC-APP>zw ^IRIS.Msg
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble")="zh-cn"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",27956811)="Business Rules"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",46484733)="Create New Message Routing Rule"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",52267811)="Business Rule Log"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",56439219)="Edit the configuration of this production."
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",59992850)="Edit, Start or Stop an Ensemble Production."
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",60154202)="The following PubSub Domain Names are currently defined. PubSub domain names are used to group PubSub subscribers and their associated subscriptions."
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",65030300)="Edit Role definition:"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",74372598)="Create New Subscriber"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",103132939)="Defined Data Transformations:"
^IRIS.Msg("Ensemble","zh-cn",140775628)="Suspended"
...
DHC-APP>zw ^CacheMsg
^CacheMsg("Ensemble")="zh-cn"
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",27956811)="Business Rules"
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",39977858)="Select a Business Process"
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",46484733)="Create New Message Routing Rule"
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",52267811)="Business Rule Log"
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",56439219)="Edit the configuration of this production."
^CacheMsg("Ensemble","zh-cn",59992850)="Edit, Start or Stop an Ensemble Production."
边栏推荐
- TCP拥塞控制详解 | 2. 背景
- 选择 SAP Spartacus 作为 SAP Commerce Cloud Storefront 实现框架的五个理由
- Leetcode question brushing record | 933_ Recent requests
- 每日一题——倒置字符串
- Introduce the scrollintoview() method attribute in detail
- Timing / counter of 32 and 51 single chip microcomputer
- 微信小程序 —— 上下浮动的箭头
- About me
- TCP congestion control details | 2 background
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 237 VP补题
猜你喜欢

Goodbye, shucang. Alibaba's data Lake construction strategy is really awesome!

Map集合详细讲解
The bottom simulation implementation of vector

Easyswoole3.2 restart failed
LeetCode:1380. Lucky number in matrix -- simple

Are you holding back on the publicity of the salary system for it posts such as testing, development, operation and maintenance?

Solution to the problem that the easycvr kernel of intelligent video analysis platform cannot be started as a service

每日一题——小乐乐改数字

从收集到输出:盘点那些强大的知识管理工具——优秀笔记软件盘点(四)

Simple linear programming problem
随机推荐
微信小程序 —— 上下浮动的箭头
The construction of scalable distributed database cluster and the partition design of oneproxy sub database
Chrome browser quick access stackoverflow
executescalar mysql_ ExecuteScalar()
[web technology] 1233 seconds understand web component
将您的基于 Accelerator 的 SAP Commerce Cloud Storefront 迁移到 Spartacus
What are the green field and brown field models in software development - green field development and brown field development
The difference of message mechanism between MFC and QT
LeetCode:1380. Lucky number in matrix -- simple
Idea2021.1 installation tutorial
AtCoder Beginner Contest 237 VP补题
JS20 array flattening
泡椒凤爪制作教程
Sword finger offer 24 Reverse linked list
简单介绍BASE64Encoder的使用
Visibilitychange – refresh the page data when the specified tab is visible
什么是软件开发中的 green field 和 brown field 模式 - 绿地开发和棕地开发
[fluent] dart data type map type (create map set | initialize map set | traverse map set)
Solving simple differential equations
About me