当前位置:网站首页>Self learning neural network series - 8 feedforward neural networks
Self learning neural network series - 8 feedforward neural networks
2022-06-26 09:09:00 【ML_ python_ get√】
8 Feedforward neural networks
What you need to know before reading this article is shown in Feedforward neural network pre knowledge This article , It mainly includes perceptron algorithm 、 Activation function and other knowledge , The following mainly introduces the content of feedforward neural network , There are mainly :
- 8.1 Feedforward neural network structure
- 8.2 Learning of neural network parameters
- 8.3 Error back propagation algorithm
- 8.4 tensorflow The principle of automatic gradient calculation in
- 8.5 How to solve Nonconvex Optimization in machine learning or deep learning
1 Feedforward neural network structure
1.1 Network structure
- Feedforward neural network is a generalized structure of neural network model , All neurons are connected , Also known as fully connected neural network , The structure is as follows : By an input layer 、 Multiple hidden layers and one output layer constitute .
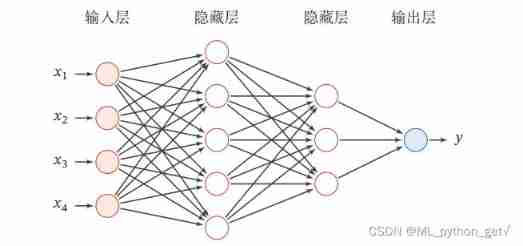
- The layers in the neural network are composed of multiple neurons
- Input layer neurons have numerical characteristics such as x = (x1,x2,x3,x4) constitute ,
- Hidden layer neurons are activation functions
- Output layer neurons are linear functions ( Return to )、sigmoid function ( Two classification ) or softmax function ( Many classification )
- Connections between neurons ( edge ) For weight , Point to the edges of the same neuron for linear combination , And then output through neurons .
1.2 A network model
The feedforward neural network model is propagated forward by the following formula :
{ z i = W i a i − 1 + b i a i = s i g m o i d ( z i ) \begin{cases} z^{i}=W^{i}a^{i-1}+b^{i} \\ a^{i}=sigmoid(z^{i} ) \end{cases} { zi=Wiai−1+biai=sigmoid(zi)Make a 0 = x Make a^{0}=x Make a0=x, By the end of i The layer is the perspective , For any two connected neurons :
- Previous hidden layer output / Input layer input : a i − 1 a^{i-1} ai−1
- Hidden layer input / Input layer output : z i = W i a i − 1 + b i z^{i}=W^{i}a^{i-1}+b^{i} zi=Wiai−1+bi
- Hidden layer output : a i = s i g m o i d ( z i ) a^{i}=sigmoid(z^{i}) ai=sigmoid(zi)
- Iterate until the model structure is satisfied
General approximation theorem : Common continuous nonlinear functions can be approximated by feedforward neural networks .
Deep learning is mainly based on neural network model , The neural network model can be regarded as a complex high-order nonlinear function .
Machine learning is based on simple models , Artificial feature engineering is very important , Play a decisive role in the model . However , Manual features require time-consuming design and verification , And it is easy to cause information loss , Therefore, neural network is introduced to automatically learn the expression of features .
2 Learning parameters of feedforward neural network
- Parameter learning method : Similar to machine learning , The learning of neural network parameters is also aimed at minimizing the loss function , The optimization method uses the common gradient descent .
2.1 Objective function
R ( W , b ) = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N L ( y n , y ^ n ) + λ ∣ ∣ W ∣ ∣ F 2 Its in ∣ ∣ W ∣ ∣ F 2 = ∑ l L ∑ i M l ∑ j M l − 1 w i j 2 R(W,b) ={1\over N}\sum_{n=1}^NL(y^n,\hat y^n)+\lambda||W||_F^2 \\ among ||W||_F^2 = \sum_l^L\sum_i^{M_l}\sum_j^{M_{l-1}}{w_{ij}^2} R(W,b)=N1n=1∑NL(yn,y^n)+λ∣∣W∣∣F2 Its in ∣∣W∣∣F2=l∑Li∑Mlj∑Ml−1wij2
2.2 gradient descent
- Final output y ^ \hat y y^ And y The loss function is constructed for l l l Layer parameters ( to update ) W l 、 b l W^l 、b^l Wl、bl Finding the gradient has :
∂ R ( W , b ) ∂ W l = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ W l + λ W l ∂ R ( W , b ) ∂ b l = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ b l {\partial R(W,b) \over \partial W^l} = {1\over N}\sum_{n=1}^N{\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial W^l} + \lambda W^l \\ {\partial R(W,b) \over \partial b^l} = {1\over N}\sum_{n=1}^N{\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial b^l} ∂Wl∂R(W,b)=N1n=1∑N∂Wl∂L(yn,y^n)+λWl∂bl∂R(W,b)=N1n=1∑N∂bl∂L(yn,y^n) - The whole training set is needed to solve the parameters of each layer , Neural networks usually use the random gradient descent method to update the parameters of a single sample or min-batch The gradient descent method is used to update the parameters of batch samples .
- It is inefficient to update parameters by calculating the gradient expression of parameters , Neural networks usually use error back propagation algorithm to achieve efficient gradient calculation .
3 Error back propagation algorithm
- The chain rule :
∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ W i j l = ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l ∂ z l ∂ W i j l ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ b l = ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l ∂ z l ∂ b l {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial W_{ij}^l } = {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^l } {\partial z^l \over \partial W_{ij}^l } \\ {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial b^l } = {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^l } {\partial z^l \over \partial b^l } ∂Wijl∂L(yn,y^n)=∂zl∂L(yn,y^n)∂Wijl∂zl∂bl∂L(yn,y^n)=∂zl∂L(yn,y^n)∂bl∂zl
- Factor analysis
∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^l } ∂zl∂L(yn,y^n) Is a duplicate , So we only need to calculate three terms :
∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^l } ∂zl∂L(yn,y^n) Is the loss function for the l l l The derivative of the linear combination of layers , Finally, it is conducted through neurons , It reflects the second stage l l l The influence of layer and its subsequent neurons on the loss function , The inclusion of a loss function is called an error term .
∂ z l ∂ W i j l 、 ∂ z l ∂ b l {\partial z^l \over \partial W_{ij}^l } 、 {\partial z^l \over \partial b^l } ∂Wijl∂zl、∂bl∂zl Similar to perceptron algorithm , The gradient method is similar to .
The main difficulty is to solve the error term : Back propagation algorithm
- Error back propagation iteration formula
δ ( l ) = ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l = ∂ L ( y n , y ^ n ) ∂ z l + 1 ∂ z l + 1 ∂ a l ∂ a l ∂ z l = δ ( l + 1 ) W l + 1 s i g m o i d ′ ( z l ) \delta(l) = {\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^l } ={\partial L(y^n,\hat y^n) \over \partial z^{l+1} } {\partial z^{l+1} \over \partial a^l} {\partial a^l \over \partial z^l} = \delta(l+1)W^{l+1}sigmoid'(z^l) δ(l)=∂zl∂L(yn,y^n)=∂zl+1∂L(yn,y^n)∂al∂zl+1∂zl∂al=δ(l+1)Wl+1sigmoid′(zl)
The error term can be solved iteratively , The other items are easy to calculate
Error back propagation algorithm
- Feedforward calculates the linear output of each layer z l z^l zl And nonlinear output a l a^l al
- For the last layer, the error term is calculated as a single-layer perceptron ( Easy to calculate )、 gradient 、 Update parameters
- Next, the error term of each layer is calculated according to the iterative formula
- Calculate the gradient of each layer of perceptron and update the parameters
4 tensorflow The principle of automatic gradient calculation in
- Calculation chart :tensorflow In this paper, the automatic calculation of gradient is realized by using the data structure such as calculation graph
- Basic concept of calculation diagram :

The calculation diagram decomposes the complex calculation process , Use intermediate nodes to represent the operation , Place the intermediate calculation result on the arrow of the node ( edge ) On , Other nodes pointing to the middle node represent constants or variables .
- The calculation chart supports local calculation , The intermediate result is calculated , So in the process of calculating the derivative, we can keep the intermediate result , Calculate the local derivative , Then pass it to the next layer
- From left to right, the calculation diagram shows the forward propagation formula of neural network , So we can see the error back propagation from the calculation diagram , That is, the calculation diagram is viewed from right to left .
- The local derivative of the addition in the calculation graph is 1; The local derivative of multiplication is another factor ;
The forward model uses the chain rule to calculate the intermediate result of the gradient W For each dimension of , The intermediate process of using chain rule to calculate gradient in reverse mode only involves Z For each dimension of . Therefore, when the output dimension is much smaller than the input dimension, the back propagation algorithm should be used .
tensorflow The calculation diagram is divided into static calculation diagram 、 Dynamic calculation diagram and Autograph
- Static calculation diagram : First use TensorFlow Definition of various operators to create a complete calculation diagram , And then open a conversation Session, Perform the calculation diagram explicitly . Once defined , It can't be changed any more .
- Dynamic calculation diagram : Every time you use an operator , This operator will be automatically added to the default calculation diagram , No need to start session, Directly execute to get the result . Convenient debugging , You can change .
- Autograph: have access to @tf.function Decorators will be defined Python Function is converted to the corresponding TensorFlow Static calculation diagram construction code .
5 Nonconvex Optimization in deep learning
- Loss functions in deep learning are generally non convex , Why is the loss function of neural network non convex ?
- Nonconvex Optimization
- The objective function is not convex
- Feasible sets are not convex sets :Lasso\ Sparse matrix factorization belongs to this class
- A large number of local optimal solutions , The local optimal solution is not necessarily the global optimal solution
- Generally, gradient descent method is used to solve
- Non convex optimization solution ideas
- Convex relaxation : Lagrange duality method to modify the objective function ( Convex function ) And constraints ( convex set )
- Gradient descent of nonconvex projection :Lasso/ Recommend matrix decomposition in the system , Project a sparse matrix onto a low rank matrix , Rank conditions form Nonconvex Sets . gradient descent 、 Projection update 、 gradient descent 、 Projection update …
- Alternate optimization : stay ALS In the algorithm, , Although the objective function is non convex , But it may be a convex function in a certain component direction
- EM Algorithm etc.
- The algorithm can be referred to :Non-convex Optimization for Machine Learning
- Neural network optimization problem
- There are many saddle points in high dimension , It is not easy to fall into local optimization
- In order to ensure generalization ability , Prevent over fitting , It is not necessary to solve the global minimum
边栏推荐
- dedecms小程序插件正式上线,一键安装无需任何php或sql基础
- Phpcms V9 adds the reading amount field in the background, and the reading amount can be modified at will
- 编程训练7-日期转换问题
- Phpcms V9 mobile phone access computer station one-to-one jump to the corresponding mobile phone station page plug-in
- phpcms v9后台增加阅读量字段,可任意修改阅读量
- 设置QCheckbox 样式的注意事项
- PD快充磁吸移動電源方案
- Yolov5 advanced camera real-time acquisition and recognition
- 外部排序和大小堆相关知识
- Phpcms applet plug-in tutorial website officially launched
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Behavior tree XML file hot load
Uniapp uses uparse to parse the content of the background rich text editor and modify the uparse style
Phpcms V9 adds the reading amount field in the background, and the reading amount can be modified at will
行为树的基本概念及进阶
cookie session 和 token
外部排序和大小堆相关知识
Yolov5 advanced camera real-time acquisition and recognition
Phpcms V9 mobile phone access computer station one-to-one jump to the corresponding mobile phone station page plug-in
Upgrade phpcms applet plug-in API interface to 4.3 (add batch acquisition interface, search interface, etc.)
phpcms v9后台增加阅读量字段,可任意修改阅读量
修复小程序富文本组件不支持video视频封面、autoplay、controls等属性问题
Unity WebGL发布无法运行问题
Talk about the development of type-C interface
深度学习论文阅读目标检测篇(七)中文版:YOLOv4《Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection》
简析ROS计算图级
什么是乐观锁,什么是悲观锁
Reverse crawling verification code identification login (OCR character recognition)
Data warehouse (3) star model and dimension modeling of data warehouse modeling
Unity webgl publishing cannot run problem
【MATLAB GUI】 键盘回调中按键识别符查找表