当前位置:网站首页>Vins fusion GPS fusion part
Vins fusion GPS fusion part
2022-06-11 05:00:00 【Immediately】
summary
VINS Fusion stay VINS Mono On the basis of , Added GPS And other sensors that can obtain global observation information , bring VINS The global information can be used to eliminate the cumulative error , Thus, the closed-loop dependency is reduced .
Local sensor ( Like a camera ,IMU, Lidar, etc ) It is widely used in mapping and location algorithms . Although these sensors can be used without GPS The area of information , Achieve good local positioning and local mapping effect , But these sensors can only provide local observations , Limited its application scenarios :
The first problem is the lack of global constraints on local observations , When we run the algorithm at different locations each time , Will get the positioning and mapping results under different coordinate systems , It is difficult to combine these measurements , Create a global effect .
The second problem is that the estimation algorithm based on local observations must have cumulative drift , Although loop back detection can eliminate drift to some extent , But for large-scale scenarios with a large amount of data , The algorithm is still difficult to handle .
Compared to local sensors , Global sensor ( Such as GPS, Barometer, magnetometer, etc ) Can provide global Observations . These sensors use a globally uniform coordinate system , And the variance of the output observation data does not increase with time accumulation . But there are also some problems with these sensors , As a result, it can not be directly used for accurate positioning and mapping . With GPS For example ,GPS Data is usually not smooth , There is noise , And the output rate is low .
therefore , A simple and intuitive idea is to combine local sensors with global sensors , To achieve the effect of local accurate global zero drift . This is the same. VINS Fusion The core content of this paper .
Fusion principle
VINS Fusion The algorithm architecture of is shown in the figure :
The following figure shows the constraint between observation and state in the form of factor graph :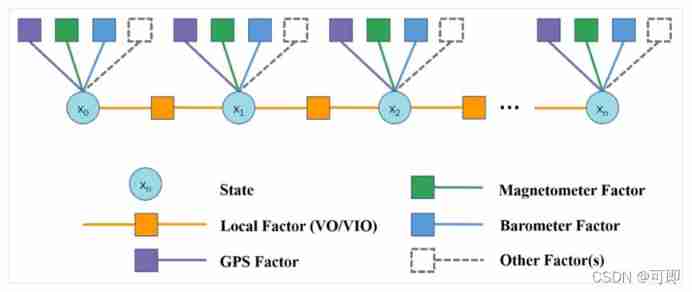
The circle is the state quantity ( Such as posture , Speed , Bias, etc ), The yellow square is the constraint of local observation , From VO/VIO Relative pose transformation of ; The square of other colors is the constraint of global observation , For example, the purple square is from GPS Constraints .
Local constraints ( residual ) Build reference for vins mono The paper , It calculates the pose residuals between two adjacent frames . This is only about GPS Global constraints . The first, of course, is to GPS coordinate , That is, longitude and latitude are converted into geodetic coordinate system . It is customary to choose the right-hand coordinate system ,x,y,z The positive direction of the axis is the northeast earth or the northeast sky . Then we can calculate the residual of the global constraint :
among z by GPS Measured value ,X For state prediction ,h The equation is the observation equation .X It can be calculated by the state of the previous time and the pose transformation between the current time and the previous time . Specific to the method of this article , Is the use VIO Get the relative pose of the current time and the previous time dX, Add to the position of the previous moment X(i-1), Get the position and posture at the current time Xi. It should be noted that , there X Take the first frame as the origin . By observing the equation h, Convert the coordinates of the current state to GPS In coordinate system . This builds a global constraint .
The subsequent optimization is left to BA The optimizer performs iterative optimization ,vins fusion Continue to use ceres As an optimizer .
Code implementation
1. GPS and VIO data input
One thing that needs to be clear is ,VIO The output of is the cumulative pose transformation relative to the first frame , That is, take the first frame as the origin .VINS Fusion receive vio Output local pose transformation ( Relative to the first frame ), as well as gps Output longitude and latitude coordinates , To merge . The interface that accepts data input is in global_fusion/src/globaOptNode.cpp In file , The key code of the interface definition is as follows :
void GPS_callback(const sensor_msgs::NavSatFixConstPtr &GPS_msg)
{
m_buf.lock();
gpsQueue.push(GPS_msg); // Every time you receive gps Message added to gpsQueue In line
m_buf.unlock();
}
void vio_callback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &pose_msg)
{
double t = pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
last_vio_t = t;
Eigen::Vector3d vio_t; // Translation matrix , The converted code is omitted
Eigen::Quaterniond vio_q; // Rotating quaternion , The converted code is omitted
globalEstimator.inputOdom(t, vio_t, vio_q); // Time , translation , Quaternions are added as predictions globalEstimator
m_buf.lock();
while(!gpsQueue.empty())
{
sensor_msgs::NavSatFixConstPtr GPS_msg = gpsQueue.front();
double gps_t = GPS_msg->header.stamp.toSec();
// Find and vio The odometer data differ by 10ms Inside gps data , As matching data
if(gps_t >= t - 0.01 && gps_t <= t + 0.01)
{
double latitude = GPS_msg->latitude;
double longitude = GPS_msg->longitude;
double altitude = GPS_msg->altitude;
double pos_accuracy = GPS_msg->position_covariance[0];
globalEstimator.inputGPS(t, latitude, longitude, altitude, pos_accuracy); // The key , take gps Data input as observations to globalEstimator in
gpsQueue.pop(); // Satisfied gps The message pops up
break;
}
else if(gps_t < t - 0.01)
gpsQueue.pop(); // Will be obsolete gps The message pops up
else if(gps_t > t + 0.01)
break; // explain gps Information is later , Just don't change gps There's a queue , sign out
}
m_buf.unlock();
// ... Other omissions
}
2. GPS and VIO The fusion
VINS Fusion The fusion GPS and VIO The code of the data is global_fusion/src/globalOpt.cpp In file , Here is a detailed introduction .
a. receive GPS data , receive VIO Data and go to GPS Coordinate system
// Receive the input above vio data
void GlobalOptimization::inputOdom(double t, Eigen::Vector3d OdomP, Eigen::Quaterniond OdomQ)
{
vector<double> localPose{
OdomP.x(), OdomP.y(), OdomP.z(),
OdomQ.w(), OdomQ.x(), OdomQ.y(), OdomQ.z()};
localPoseMap[t] = localPose;
// utilize vio Coordinate transformation of local coordinates of , Get the global pose of the current frame
Eigen::Quaterniond globalQ;
globalQ = WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 3>(0, 0) * OdomQ;
Eigen::Vector3d globalP = WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 3>(0, 0) * OdomP + WGPS_T_WVIO.block<3, 1>(0, 3);
vector<double> globalPose{
globalP.x(), globalP.y(), globalP.z(),
globalQ.w(), globalQ.x(), globalQ.y(), globalQ.z()};
globalPoseMap[t] = globalPose;
}
// Receive the input above gps data
void GlobalOptimization::inputGPS(double t, double latitude, double longitude, double altitude, double posAccuracy)
{
double xyz[3];
GPS2XYZ(latitude, longitude, altitude, xyz); // take GPS To the ground Cartesian coordinate system
vector<double> tmp{
xyz[0], xyz[1], xyz[2], posAccuracy};
GPSPositionMap[t] = tmp;
newGPS = true;
}
It's up there VIO The local coordinates of the data go to GPS Coordinate calculation process , The formula is as follows :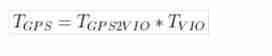
In this formula GPS2VIO In the later optimization process , The calculation method is as follows :
b. Fusion optimization
Here is the key code for fusion , It can be seen that the process is as follows :
1. structure t_array and q_array, Used to store translation and rotation variables , It is convenient to input the optimization equation , And take out after optimization .
2. utilize RelativeRTError::Create() structure VIO Constraints between two frames , Enter the optimization equation
3. utilize TError::Create() structure GPS Global constraints that make up , Enter the optimization equation
4. Take out the optimized data
void GlobalOptimization::optimize()
{
while(true)
{
if(newGPS)
{
newGPS = false;
// ceres The definition section is omitted
// add param
mPoseMap.lock();
int length = localPoseMap.size();
// ********************************************************
// *** 1. structure t_array, q_array Used to store optimization variables , Take it out after optimization ***
// ********************************************************
double t_array[length][3];
double q_array[length][4];
map<double, vector<double>>::iterator iter;
iter = globalPoseMap.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++, iter++)
{
// Take out the data part and omit
// Added parameterblock
problem.AddParameterBlock(q_array[i], 4, local_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(t_array[i], 3);
}
map<double, vector<double>>::iterator iterVIO, iterVIONext, iterGPS;
int i = 0;
for (iterVIO = localPoseMap.begin(); iterVIO != localPoseMap.end(); iterVIO++, i++)
{
// ********************************************************
// ********************* 2. VIO constraint *******************
// ********************************************************
iterVIONext = iterVIO;
iterVIONext++;
if(iterVIONext != localPoseMap.end())
{
Eigen::Matrix4d wTi = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity(); // The first i The transformation matrix of the frame
Eigen::Matrix4d wTj = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity(); // The first j The transformation matrix of the frame
// Take out the data part and omit
Eigen::Matrix4d iTj = wTi.inverse() * wTj; // The first j Frame to i The transformation matrix of the frame
Eigen::Quaterniond iQj; // The first j Frame to i Rotation of frames
iQj = iTj.block<3, 3>(0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d iPj = iTj.block<3, 1>(0, 3); // The first j Frame to i Translation of frames
ceres::CostFunction* vio_function = RelativeRTError::Create(iPj.x(), iPj.y(), iPj.z(),
iQj.w(), iQj.x(), iQj.y(), iQj.z(),
0.1, 0.01);
problem.AddResidualBlock(vio_function, NULL, q_array[i], t_array[i], q_array[i+1], t_array[i+1]);
}
// ********************************************************
// ********************* 3. GPS constraint *******************
// ********************************************************
double t = iterVIO->first;
iterGPS = GPSPositionMap.find(t);
if (iterGPS != GPSPositionMap.end())
{
ceres::CostFunction* gps_function = TError::Create(iterGPS->second[0], iterGPS->second[1],
iterGPS->second[2], iterGPS->second[3]);
problem.AddResidualBlock(gps_function, loss_function, t_array[i]);
}
}
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
// ********************************************************
// ******************* 4. Take out the optimization results *****************
// ********************************************************
iter = globalPoseMap.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++, iter++)
{
// Take out the optimization results
vector<double> globalPose{
t_array[i][0], t_array[i][1], t_array[i][2],
q_array[i][0], q_array[i][1], q_array[i][2], q_array[i][3]};
iter->second = globalPose;
if(i == length - 1)
{
Eigen::Matrix4d WVIO_T_body = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix4d WGPS_T_body = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity();
// The remaining deposited portion is omitted , obtain WGPS_T_WVIO
WGPS_T_WVIO = WGPS_T_body * WVIO_T_body.inverse();
}
}
updateGlobalPath();
mPoseMap.unlock();
}
std::chrono::milliseconds dura(2000);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(dura);
}
return;
}
A key part of the above code appears , namely WGPS_T_WVIO The calculation of . You know from the previous code , This 4*4 The matrix is used to do VIO To GPS Coordinate system transformation .
summary
Optimize the process :
First of all , To determine if there is gps data , The whole algorithm is in ceres Optimization algorithm under the framework .
So the overall steps are ceres Optimization steps , First, add the optimization parameter block (AddParameterBlock function ), Parameter is globalPoseMap Medium 6 Dimensional pose ( Rotation in the code is represented by quaternions , So we have 7 dimension ).
Then add CostFunction, By building factor heavy load operator Method realization ( The specific implementation needs to learn ceres library ). This section has two factor, One is pose graph optimization , The other is to use gps Make position constraints .
take factor After adding , Conduct ceres solve , Update at this point gps and vio Coordinate system conversion parameters between , Use it later updateGlobalPath Function to update the pose .
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41843971/article/details/86748719
Residuals :
Then start adding the residual term , There are two residual terms in total :vio factor as well as gps factor
– vio factor:
Of the residual term costfunction Create by relativeRTError To provide . The observed values are determined by vio The results provide . At this time, the calculation is based on i Always for reference , from i To j The displacement values of these two moments and the rotation values of quaternions are transferred into the cost function as observations . here iPj On behalf of i To j The displacement of ,iQj On behalf of i To j Quaternion transformation of . When adding the residual term , You need to add the current i The posture of the moment and j The posture of the moment . That is to say, we use the observed value to estimate i The posture of the moment and j The posture of the moment .
– gps factor:
Of the residual term costfunction Create by TError To provide . The observed values are determined by Gps The results of the data provide . When adding the residual term , Just add the current i The posture of the moment .
TError And RelativeRTError
Intuitively understand :
{0, 1,2,3,4, 5,6…}
To estimate these moments , The position and posture at each moment .
I have two observations , On the one hand is GPS Get the position of each moment (x,y,z)( also GPS The signal can provide the accuracy of getting this position at this time posAccuracy), No cumulative error , Low accuracy . On the other hand VIO Get the position of each moment (x,y,z) And the corresponding attitude quaternion (w,x,y,z), There is a cumulative error , High accuracy in a short time . In order to get a better fusion result , So we use this strategy : Of the observed values , The initial position is determined by GPS Provide , also vio Observations trust i To j Time displacement and attitude change . Do not trust vio An absolute displacement and an absolute rotation attitude are obtained . Trust only short-term i To j Amount of change , Take this variation as the observed value of the whole cost function , To solve the .
So the two residual terms TError And RelativeRTError The difference corresponds to GPS Position signals and vio Estimated in a short time i To j The influence of the amount of pose change at the moment on the final result . In the process of iterative solution AutoDiffCostFunction Automatically solve the differential to iterate .
(1)TError
TError(x,y,z,accuracy), The last item is positioning accuracy , Can be GPS The system provides . Except that the direct observed value is subtracted from the true value , Besides this accuracy As denominator . It means that the higher the accuracy ,accuracy The smaller it is , The greater the impact on the results .
(2)RelativeRTError
RelativeRTError(dx,dy,dz,dqw,dqx,dqy,dqz,t_var,q_var), The last two items are the weight distribution ratio between displacement and rotation , And in order to make TError Corresponding . In the program , The last two items should be set to a constant value according to experience , They correspond to each other 0.1 as well as 0.01. The residual error is obtained directly according to the deviation between the actual value and the observed value .
Link to the original text :https://blog.csdn.net/huanghaihui_123/article/details/87183055
Local Factor: Local observation constraints ,VIO Relative pose transformation , The residual of pose between two adjacent frames is calculated
边栏推荐
- Sorting out relevant programming contents of renderfeature of unity's URP
- Emlog new navigation source code / with user center
- [Transformer]AutoFormerV2:Searching the Search Space of Vision Transformer
- Following the wave of lack of core, Lianrui launched a number of gigabit network card solutions
- C语言试题三(程序选择题进阶_含知识点详解)
- Legend has it that setting shader attributes with shader ID can improve efficiency:)
- Sealem Finance打造Web3去中心化金融平台基础设施
- Pytoch machine learning GPU usage (conversion from CPU to GPU)
- jvm调优六:GC日志分析和常量池详解
- [Transformer]CoAtNet:Marrying Convolution and Attention for All Data Sizes
猜你喜欢

四大MQ的区别

KD-Tree and LSH

oh my zsh正确安装姿势

Paper reproduction: expressive body capture

Redis persistence (young people always set sail with a fast horse, with obstacles and long turns)

Apply the intelligent OCR identification technology of Shenzhen Yanchang technology to break through the bottleneck of medical bill identification at one stroke. Efficient claim settlement is not a dr

Emlog new navigation source code / with user center

AAAI2022-ShiftVIT: When Shift Operation Meets Vision Transformer

Yolact paper reading and analysis

华为设备配置BGP/MPLS IP 虚拟专用网地址空间重叠
随机推荐
Possible errors during alphapose installation test
The solution "no hardware is configured for this address and cannot be modified" appears during botu simulation
C language test question 3 (grammar multiple choice question - including detailed explanation of knowledge points)
Powerful new UI installation force artifact wechat applet source code + multiple templates support multiple traffic main modes
华为设备配置MCE
Redis persistence (young people always set sail with a fast horse, with obstacles and long turns)
Leetcode classic guide
BP neural network derivation + Example
Learning summary 01- machine learning
CoDeSys get system time
Yolov5 training personal data set summary
Paper reproduction: pare
Lianrui: how to rationally see the independent R & D of domestic CPU and the development of domestic hardware
Leetcode question brushing series - mode 2 (datastructure linked list) - 83:remove duplicates from sorted list
Comparison of gigabit network card chips: who is better, a rising star or a Jianghu elder?
Chia Tai International; What does a master account need to know
Batch naming picture names
Yolact paper reading and analysis
Unzip Imagenet after downloading
华为设备配置通过GRE接入虚拟专用网