当前位置:网站首页>Message Oriented Middleware (message queue)
Message Oriented Middleware (message queue)
2022-06-22 08:42:00 【Ride a little snail】
List of articles
brief introduction
MQ(message queue) Message queue , Also called message oriented middleware .
Message queuing has gradually become an enterprise IT The core means of system internal communication . It has low coupling 、 Reliable delivery 、 radio broadcast 、 flow control 、 Finally, a series of functions such as consistency , Become asynchronous RPC One of the main means of .
It is an application that needs to be independently deployed on the server like a database , Provide interfaces to other system calls .
JMS standard
Message oriented middleware is compliant with JMS(java message service) A standardized software ( Most message oriented middleware follows JMS standard ).
To use Java Message service , You have to have one JMS Provider , Manage sessions and queues . There are now both open source and proprietary providers .
Open source providers include :Apache ActiveMQ、Kafka、WebMethods、 Ali's RocketMQ etc. .
Professional term
- Provider : Realization JMS Standard middleware server .
- client : Applications that send or receive messages .
- producer : A client that creates and sends messages .
- consumer : The client that receives and processes the message .
- news : What is passed between applications .
- queue : An area that holds messages sent waiting to be read , Once the news is consumed , Will be removed from the queue .
- The theme : A mechanism that supports sending messages to multiple subscribers .
- Message schema : How messages are passed between clients ,JSM Point to point mode is defined in ( sender 、 The receiver ) And publish subscribe mode ( Publisher 、 subscriber ).
Message schema
Point to point mode :Point-to-Point(P2P)
Message producers produce messages sent to queue in , Then the message consumer from queue To retrieve and consume messages .
After the news was consumed ,queue No more storage in , So it's impossible for news consumers to consume the information that has been consumed . Queue Support for multiple consumers , But for a message , Only one consumer can consume .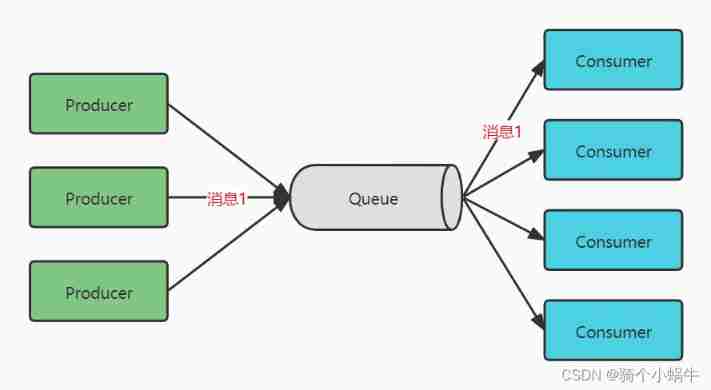
Only one consumer per message . Once consumed , The message is no longer in the message queue .
There is no time dependency between providers and consumers . When the provider sends the message , Whether the consumer is running or not , It does not affect the message being sent to the queue .
Each message will only be sent to one consumer . There may be multiple consumers listening in a queue , But messages in each queue can only be consumed by one consumer in the queue .
There is a sequence of messages . A queue will put messages in the order in which the message server put them in the queue , Send them to consumers . When it has been consumed , They will be removed from the queue header ( Unless message priority is used ).
After successfully receiving the message, the consumer needs to reply to the queue .
queue Load balancing is realized , take producer The production message is sent to the message queue , Consumption by multiple consumers . But a message can only be accepted by one consumer , When no consumers are available , This message will be saved until a consumer is available .
Publish subscribe mode :Publish/Subscribe(Pub/Sub)
Message producer ( Release ) Publish a message to topic in , There are multiple message consumers at the same time ( subscribe ) Consume the news . It's different from point-to-point , Publish to topic Will be consumed by all subscribers .
- Multiple consumers per message .
- There is a temporal dependency between publishers and subscribers . Subscribers to a topic , It must create a subscriber after , To consume a publisher's message , And for consumption news , Subscriber must remain running .
- In order to alleviate such strict time correlation ,JMS Allow subscribers to create a durable subscription . such , Even if the subscriber is not activated ( function ), It can also receive messages from publishers .
- Each message is delivered to multiple message consumers called subscribers . There are many types of subscribers , Including persistent 、 Non persistent and dynamic .
- Publishers usually don't know which subscriber is receiving the subject message .
- Messages are pushed to consumers . This means that the message is delivered to the consumer , Without asking for .
topic Implemented publishing and subscription , When you post a message , All subscriptions to this topic All of our services can get the news , So from 1 To N Every subscriber can get a copy of a message .
Message consumption mode
Sync
Subscriber or consumer invokes receive Method to receive messages ,receive Method before the message can be received ( Or before timeout ) Will be blocked all the time .
asynchronous
Subscribers or consumers can register as a message listener . When the message arrives , The system automatically calls the onMessage Method .
JMS Specification interface
ConnectionFactor Interface ( Connection factory )
Used to create a connection factory to connect to message oriented middleware .establish Connection Object's factory , Depending on the message type , The user will use the queue to connect to the factory QueueConnectionFactory Or theme connection factory TopicConnectionFactory Two kinds of . Can pass JNDI Search for ConnectionFactory object .
Connection Interface ( Connect )
Connection Indicates that in the client and JMS Links established between systems ( Yes TCP/IP socket Packaging ), Represents the communication link between the application and the message server .Connection Can produce one or more Session. Follow ConnectionFactory equally ,Connection There are also two types :QueueConnection and TopicConnection.
Destination Interface ( The goal is )
Destination Is a managed object that wraps the message destination identifier , Message destination refers to the place where messages are issued and received , Or a queue , Or the theme .It is the message sending target of the message producer or the message source of the message consumer .
- For message producers , its Destination Is a queue (Queue) Or a theme (Topic);
- For message consumers , its Destination Also a queue or topic ( I.e. source ).
therefore ,Destination It's actually two types of objects :Queue、Topic Can pass JNDI Search for Destination.
Session Interface ( conversation )
Session It's our interface for manipulating messages . Represents a single threaded context , Used to send and receive messages .Because the session is single threaded , So the message is continuous , That is, messages are received one by one in the order they are sent .
Can pass session Create producer 、 consumer 、 News, etc. .Session Provides transaction capabilities . When we need to use session send out / When receiving multiple messages , You can send these / Receive actions into a transaction . Again , Also divided QueueSession and TopicSession.MessageProducer Interface ( Message producer )
Message producer by Session establish , And used to send messages to Destination. Consumers can simultaneously ( Blocking mode ), Or asynchronous ( Non blocking ) Receive messages of queue and subject types .Again , There are two types of message producers :QueueSender and TopicPublisher. Can call message producer's methods (send or publish Method ) Send a message .
MessageConsumer Interface ( Message consumer )
Message consumer by Session establish , For receiving sent to Destination The news of . Two types of :QueueReceiver and TopicSubscriber.Can be passed separately session Of createReceiver(Queue) or createSubscriber(Topic) To create , It's fine too session Of creatDurableSubscriber Method to create a persistent subscriber .
Message Interface ( news )
It is the object transmitted between consumers and producers , That is, from one application to another . A message has three main parts .- The message header ( must ): Contains operational settings for identifying and routing messages .
- A set of message properties ( Optional ): Contains additional properties , Support compatibility with other providers and users . You can create custom fields and filters ( Message selector ).
- A message body ( Optional ): Allows users to create five types of messages ( A text message , Map message , Byte message , Stream messages and object messages ). The message interface is very flexible , And provides many ways to customize the content of the message .
The message interface is very flexible , And provides many ways to customize the content of the message .
MessageListener( Monitor )
Message listener , If a message listener is registered , Once the message arrives , The onMessage Method .EJB Medium MDB(Message-Driven Bean) It's a kind of MessageListener.
The role of message middleware
1. system decoupling
There is no direct calling relationship between systems , Just by message transmission , So the system is not very invasive , Low coupling .
2. asynchronous communication
Message queues provide an asynchronous processing mechanism , Allows the user to queue a message , But not immediately . Put as many messages as you want into the queue , Then deal with them as needed .
For some businesses that do not have to be handled in time , The system response time can be optimized through message queuing . Improve system performance .
3. Traffic peak clipping
Using message queues enables critical components to withstand sudden access pressures , It won't crash completely because of a sudden overload of requests .
4. Data collection
Massive data streams generated by distributed systems , Such as : Business log 、 Monitoring data 、 User behavior, etc , Collect and summarize these data streams in real time or in batches , Then big data analysis is the necessary technology of the Internet , It is the best choice to complete this kind of data collection through message queuing .
5. Recoverability
In some cases , The process of processing data can fail . Unless the data is persisted , Otherwise, it will cause loss . Message queues persist data until they are fully processed , In this way, the risk of data loss is avoided .
Used by many message queues " Insert - obtain - Delete " In the paradigm , Before deleting a message from the queue , Requires that your processing system explicitly indicate that the message has been processed , This ensures that your data is stored safely until you have finished using it .
6. Extensibility
Predict what needs the project will encounter in the future at the beginning of the project , It's extremely difficult . The message system inserts an implicit 、 Data based interface layer , Both processes need to implement this interface , When the application changes , You can expand or modify the processing on both sides independently , Just make sure they adhere to the same interface constraints .
7. Sequence assurance
In most usage scenarios , The order in which the data is processed is important . Most message queues are sorted anyway , And it guarantees that the data will be processed in a particular order .
Message middleware protocol
1.AMQP agreement
AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) Advanced message queue protocol , An application layer standard protocol that provides unified messaging services , Is an open standard for application layer protocols , Designed for message-oriented middleware .
The client and message middleware based on this protocol can deliver messages , Not by the client / Different middleware products , Restrictions on different development languages and other conditions .
advantage : reliable 、 Universal
Some related products :
- RabbitMQ
An independent open source implementation , Server side Erlang Language writing , Supports a variety of clients , Such as :Python、Ruby、.NET、Java、JMS、C、PHP、ActionScript、XMPP、STOMP etc. , Support AJAX.RabbitMQ Published in the Ubuntu、FreeBSD platform . - OpenAMQ
AMQP Open source implementation , use C Language writing , To run on Linux、AIX、Solaris、Windows、OpenVMS. - Apache Qpid
Apache Open source projects for , Support C++、Ruby、Java、JMS、Python and .NET. - Zyre
One Broker, Realized RestMS The protocol and AMQP agreement , Provides RESTful HTTP Access the network AMQP The ability of .
2.MQTT agreement
MQTT(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) Message queuing telemetry transmission , yes IBM Developed an instant messaging protocol , It may become an important part of the Internet of things .
The protocol supports all platforms , It can connect almost all online items with the outside world , Used as sensors and actuators ( Such as through Twitter Let the house network ) Communication protocol of .
advantage : Simple format 、 Small bandwidth 、 Mobile communication 、PUSH、 Embedded system
3.STOMP agreement
STOMP(Streaming Text Orientated Message Protocol) Streaming text oriented message protocol , It's for MOM(Message Oriented Middleware) Simple text protocol for message oriented middleware design .STOMP Provide an interoperable connection format , Allow clients with any STOMP The message broker (Broker) Interact .
advantage : Command mode ( Not topic\queue Pattern )
Some related products :
- ActiveMQ
4.XMPP agreement
XMPP(Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) Extensible message processing field protocol , It's based on extensible markup language (XML) The agreement , More for instant messaging (IM) And online live detection . For quasi instant operation between servers .
The core is based on XML streaming , This protocol may eventually allow Internet users to send instant messages to anyone else on the Internet , Even if its operating system and browser are different .
advantage : General public 、 Strong compatibility 、 Scalable 、 High safety , but XML The coding format takes up a large amount of bandwidth
5. be based on TCP/IP Custom protocol
Some special frames ( Such as :redis、kafka、zeroMq etc. ) Not strictly following according to one's own needs MQ standard , It's based on TCP\IP Self encapsulating a set of agreements , Through the network socket Interface for transmission , Realized MQ The function of .
Mainstream message oriented middleware
ActiveMQ
- Very mature , The functions are relatively complete , A large number of companies use ;
- The community is becoming less active , Less maintenance , Only once a few months ;
- Occasionally there is a low probability of losing messages ;
- Most of them are mainly used for decoupling and asynchronous communication , Less used in large-scale throughput scenarios .
RabbitMQ
- More mature , The functions are relatively complete , A large number of companies use ;
- Erlang Language development , Extremely good performance , The delay is very low ;
- Work well , The community is active , Several versions are released almost every month ;
- Throughput 10000 class , It will be slightly lower than others , This is because the implementation mechanism he has done is relatively heavy ;
- Erlang Development , Difficult language , It's hard to read the source code , It's hard to customize and control . Basically, it can only rely on the rapid maintenance and repair of the open source community bug.
- Cluster dynamic expansion can be cumbersome , This is mainly erlang The problem of language itself .
RocketMQ
- Documents are relatively simple , The interface is simple and easy to use ( The interface is not in accordance with the standard JMS standard );
- Large scale application of Alibaba , guaranteed ( Ali RI handled tens of billions of messages ), Large scale throughput can be achieved , Very good performance ;
- Distributed extension is also very convenient ;
- The community is more active , Maintenance is OK ;
- Both reliability and availability are good ;
- Support large-scale topic Number ;
- Support complex MQ Business scenario ;
- Java Language writing , We can read the source code ourselves .
Kafka
Provide only a few core functions ;
Provide ultra-high throughput ;
ms Delay of level ;
High availability and reliability ;
Distributed can be extended arbitrarily ;
Multiple copies of one data , A few machines are down , No loss of data , Does not cause unavailability ;
topic A substantial increase in throughput will result in a substantial decrease in throughput ;
So try to make sure that topic Don't overdo it , To ensure its ultra-high throughput . If you want to support a large scale topic, More machine resources need to be added
Messages may be consumed repeatedly ;
It is naturally suitable for big data real-time computing and log collection , It is widely used in the field of big data and log collection .
4 Kind of MQ contrast
| characteristic | ActiveMQ | RabbitMQ | RocketMQ | Kafka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| maturity | mature | mature | More mature | Mature logging field |
| Community activity | in | high | Higher | high |
| development language | Java | Erlang | Java | Scala |
| Cross language | Support ,Java first | Language has nothing to do | Only support Java | Support ,Java first |
| Support agreement | AMQP、MQTT、STOMP、OpenWire | AMQP、MQTT、STOMP | MQTT、TCP | Kafka |
| JMS standard | Support | Support | Not enough support | I won't support it |
| Persistence | Memory 、 file 、 database | Memory 、 file | Disk files | Disk files |
| Usability | high ( Master-slave ) | high ( Master-slave ) | Very high ( Distributed ) | Very high ( Distributed ) |
| Single machine throughput | All level | All level | All level | One hundred thousand |
| Message delay | millisecond | microsecond | millisecond | millisecond |
| reliability | There is a low probability of losing data | There is a low probability of losing data | After parameter optimization configuration , It can be done 0 The loss of | After parameter optimization configuration , News can do 0 The loss of |
| Business | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| colony | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| Load balancing | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| file | complete | complete | complete | complete |
| Open source or not | Open source | Open source | Open source | Open source |
| Community / company | Apache | Rabbit | Apache | Apache |
| Message service default port | 61616 | 5672 | 10911 | 9092 |
| Management backstage | Yes | Yes | Separate deployment | nothing |
| Manage the background default port | 8161 | 15672 | 8080 | - |
| Deployment way | Independent 、 The embedded | Independent | Independent | Independent |
| evaluation | Product maturity , The function is all ready , A large number of companies use ; There is a low probability of losing messages ; The community is not active enough , Less version maintenance , The company's product focus is not on this product | Erlang Development , Good performance , Low latency ; A large number of companies use ; The community is more active ; but erlang Difficult language , Dynamic cluster expansion is troublesome | The function is more perfect , The community is more active ; Or distributed , Good scalability | The function is relatively simple , Mainly supports simple MQ function , Real-time computing and log collection are widely used in the field of big data |
Message distribution strategy comparison :
| Message distribution strategy | ActiveMQ | RabbitMQ | RocketMQ | Kafka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publish subscribe | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| Poll distribution | Support | Support | - | Support |
| Fair distribution | - | Support | - | Support |
| retransmission | Support | Support | Support | - |
| Message pull | - | Support | Support | Support |
MQ The choice of
It was first used by everyone ActiveMQ. But people don't really use it much anymore , The large throughput scenario is not validated , The community is not very active either .
Later, we used RabbitMQ. But it is erlang Language prevents a lot of java Engineers to study and control him , For the company , Almost out of control , But it's true that people are open source , More stable support , It's also very active .
Now more and more companies will use RocketMQ.
- For small and medium-sized companies , The technical strength is relatively average , The technical challenges are not particularly high , use RabbitMQ It's a good choice ;
- For large companies , Infrastructure research and development strength is strong , use RocketMQ It's a good choice ;
- Real time computing in the field of big data 、 Log collection and other scenarios , use Kafka It's industry standard , Absolutely no problem . The community is very active , Moreover, Kafka Almost the world's norm setters in this field .
边栏推荐
- Multi tenancy and Implementation
- 377. combined total Ⅳ
- MySQL sub database and sub table
- FastCorrect:语音识别快速纠错模型丨RTC Dev Meetup
- Interpreting the technology group in maker Education
- 深入理解MySQL索引凭什么能让查询效率提高这么多?
- Flask blog practice - realize the classified management of blogs
- Flask blog practice - display the navigation menu and home page data of the whole site
- 复杂科学在创客教学研究中的应用
- 12 yuan sharing mode
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
电机学感应电动机重点知识总结(现有题目中反映的)
Email giant exposes serious vulnerability, user data is stolen
The role of subject integration in steam Education
面试突击59:一个表中可以有多个自增列吗?
Flask blog practice - create background management application
Detailed sorting of Oracle and MySQL pages
Several methods to prevent repeated form submission + actual measurement
Luogu p4292 [wc2010] reconstruction plan
Flask blog practice - form validation using wtforms
深入理解MySQL索引凭什么能让查询效率提高这么多?
解读创客教育中的技术一族
I spring and autumn web Penetration Test Engineer (elementary) learning notes (Chapter 2)
What actions might cause thread context switching?
【路径规划】辅助点与多段贝塞尔平滑RRT
矩阵分解
Yolov5 reports an error: attributeerror: 'upsample' object has no attribute 'recommend_ scale_ Solution of 'factor'
Remove the restriction of video memory occupied by tensorflow GPU
377. combined total Ⅳ
Powerful database design tool PowerDesigner
我的第一个Go程序








