当前位置:网站首页>Curiosity mechanism in reinforcement learning
Curiosity mechanism in reinforcement learning
2022-06-27 09:27:00 【Drunk heart】
Reference link :
https://www.leiphone.com/category/ai/TmJCRLNVeuXoh2mv.html
https://tianjuewudi.gitee.io/2021/12/02/qiang-hua-xue-xi-zhong-de-hao-qi-xin-jiang-li-ji-zhi/#!
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/339809
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1367441
https://blog.csdn.net/triplemeng/article/details/84912694
https://blog.csdn.net/wzduang/article/details/112533271
Reference paper :
Curiosity-driven Exploration by Self-supervised Prediction
Large-Scale Study of Curiosity-Driven Learning
Curiosity-driven Exploration for Mapless Navigation with Deep Reinforcement Learning
1. background
In recent years , We see a lot of innovation in the area of deep reinforcement learning . from 2014 Year of DeepMind The depth of the Q Learning framework to 2018 year OpenAI Released play Dota2 Of OpenAI Five Game robots , We live in an exciting and hopeful Era .
Today we will learn about deep reinforcement learning The most exciting 、 One of the most promising strategies —— Curiosity drives learning .
Reinforcement learning is based on reward mechanisms , That is, each goal can be described as maximizing rewards . However , The problem now is external rewards ( That is, the reward given by the environment ) By Artificially hard coded functions , It's not scalable .
The idea of curiosity driven learning is to build a Agents with intrinsic reward functions ( The reward function is generated by the agent itself ). This means that agents will become self learners , Because he is a student , They are also feedbacks .
2. Several practical cases
If you are trying to learn how to find what you want to buy in a maze of supermarkets . You look around , But I just can't find . If you don't get every step “ Carrot ”, even “ Big stick ” either , No feedback , You may doubt whether you are going in the right direction at every step . under these circumstances , How to avoid spinning in place ? Then you can use your curiosity . While shopping in the supermarket , You will try to predict “ I'm in the meat section now , So I think the area around the corner is the aquatic area ”. If the prediction is wrong , You will be surprised “ yo , little does one think ”, And get the satisfaction reward of curiosity . This makes you more willing to explore new places in the future , Just to see if expectations are consistent with reality .
Looking for something in a maze , Only when you find this thing can you get a reward , The rest of the time is a long-term exploration . In order to avoid the agent always exploring aimlessly in the maze , We can make the rewards denser by defining additional reward functions .
On a sunny weekend afternoon , When a three-year-old child's motivation in life is out of reach ( Like college , Work , house , Family and so on ), Can still play heartlessly in the playground . As a human subject (human agent), Her behavior is what psychologists call intrinsic motivation (intrinsic motivation) The drive of curiosity .
3. The reason why the curiosity mechanism was born
At present, there are two main problems in reinforcement learning :
- The problem of sparse rewards , Action and feedback ( Reward ) The time difference between . If every action has a reward , Then you will learn quickly , For quick feedback . contrary , If you reward washing , It is difficult for agents to learn from it .
- Design intensive 、 Well defined external rewards are difficult , And it's usually not scalable .
4. Curiosity mechanism
Curiosity mechanism is to encourage agents to take action , To reduce the uncertainty of the learners' ability to predict the consequences of their own behavior . Curiosity is essentially an internal reward , That is, the error of the agent in predicting the consequences of its own behavior in the current state . Measuring curiosity error requires establishing an environmental dynamic model , Predict the next state given the current state and action . Through the curiosity module (Intrinsic Curiosity Module, ICM) To generate the agent's curiosity reward .
Good feature space enables the agent to predict the next state according to the current state and action . Define curiosity as a given current state s t s_t st And action a t a_t at New state of prediction s t + 1 s_{t+1} st+1 And the new state of reality s t + 1 ∗ s_{t+1}^* st+1∗ Error between . Considering the influence of random noise of external environment , An agent may take uncontrollable environmental noise as part of curiosity , Thus affecting the agent's exploration behavior . therefore , We need to construct a good feature space according to the following three rules :
- Modeling objects that can be controlled by agents ;
- Modeling things that an agent can't control but may affect ;
- Modeling things that agents cannot control and have no influence on .
Compact the space 、 A stable feature space that retains sufficient information about observations is used for ICM Module construction , Make sure you have ICM The agent of the module can eliminate uncontrollable things and control all things that can affect it .ICM The module consists of two neural networks , The reverse model for learning the feature representation of the state and the next state and the forward dynamic model for generating the predictive feature representation of the next state .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-iBJ91RgJ-1654093917645)(https://gitee.com/zuiyixin/blog-graph/raw/master/202206011124497.png)]
According to the rules of the feature space we set , We only want to predict the changes in the environment that may be caused by the behavior of agents , At the same time, it ignores the changes that affect the agent . It means , What we need is not to predict from the original sensory space , Instead, it converts sensory input into feature vectors , Only the information related to the actions performed by the agent is represented .
To learn this feature space : We use self-monitoring , Training neural network on agent reverse dynamic task , Given its current state s t s_t st And the next state s t + 1 s_{t+1} st+1 Predict learning body behavior a t ^ \hat {a_t} at^ .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-LZZOx5El-1654093917646)(https://gitee.com/zuiyixin/blog-graph/raw/master/202206012103026.png)]
We use this feature space to train the forward model , Given current state ϕ ( s t ) \phi(s_t) ϕ(st) Feature representation and action of , Use this model to predict the next state ϕ ( s t + 1 ) \phi(s_{t+1}) ϕ(st+1) The future of means .
And we provide the agent with the prediction error of the forward dynamic model ( The difference between the predicted next state and the real next state ), As an internal reward to encourage their curiosity .
C u r i o s i t y = ϕ p r e d i c t ( s t + 1 ) − ϕ ( s t + 1 ) Curiosity = \phi_{predict}(s_{t + 1}) - \phi(s_{t + 1}) Curiosity=ϕpredict(st+1)−ϕ(st+1)
that , We are ICM There are two models in :
1. Reverse model ( Blue ): State s t s_t st and s t + 1 s_{t + 1} st+1 Encode to the eigenvector trained to predict the motion ϕ ( s t ) \phi(s_{t}) ϕ(st) and ϕ ( s t + 1 ) \phi(s_{t+1}) ϕ(st+1) in .
a t ^ = g ( s t , s t + 1 ; θ I ) \hat{a_t} = g(s_t,s_{t+1};\theta_I) at^=g(st,st+1;θI)
among , a t ^ \hat{a_t} at^ It's a predicted action ,g Is the learning function of the inverse model , θ I \theta_I θI Is a parameter of the inverse model . The corresponding inverse loss function is :
m i n θ I L I ( a t ^ , a t ) \underset{\theta_I}{min} L_I(\hat{a_t},a_t) θIminLI(at^,at)
2. Forward model ( Red ): take ϕ ( s t ) \phi(s_t) ϕ(st) and a t a_t at As input , And predict the characteristic representation of the next state ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) \hat{\phi}(s_{t + 1}) ϕ^(st+1).
ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) = f ( ϕ ( s t ) , a t ; θ F ) \hat{\phi}(s_{t + 1}) = f(\phi(s_t),a_t;\theta_F) ϕ^(st+1)=f(ϕ(st),at;θF)
among , ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) \hat{\phi}(s_{t + 1}) ϕ^(st+1) Is the characteristic representation of the next state ,f Is the learning function of the forward model , θ F \theta_F θF Is a parameter of the forward model . The corresponding inverse loss function is :
L F ( ϕ ( s t ) , ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) ) = 1 2 ∣ ∣ ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) − ϕ ( s t ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 L_F(\phi(s_t),\hat{\phi}(s_{t+1})) = \frac{1}{2} ||\hat{\phi}(s_{t+1})-\phi(s_t)||^2_2 LF(ϕ(st),ϕ^(st+1))=21∣∣ϕ^(st+1)−ϕ(st)∣∣22
Then mathematically speaking , Curiosity will be the difference between the eigenvector of the next state we predict and the real eigenvector of the next state .
r t i = η 2 ∣ ∣ ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) − ϕ ( s t + 1 ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 r^i_t = \frac{\eta}{2}||\hat{\phi}(s_{t + 1}) - \phi(s_{t + 1})||^2_2 rti=2η∣∣ϕ^(st+1)−ϕ(st+1)∣∣22
among , r t i r^i_t rti It's No t The intrinsic reward value of the moment , η \eta η It's the gauge factor , ϕ ^ ( s t + 1 ) − ϕ ( s t + 1 ) \hat{\phi}(s_{t + 1}) - \phi(s_{t + 1}) ϕ^(st+1)−ϕ(st+1) Is the difference between the predicted next state and the actual next state . Last , The overall optimization problem of the module is the reverse loss , A combination of positive losses .
m i n θ P , θ I , θ F [ − λ E π ( s t ; θ P ) [ ∑ t r t ] + ( 1 − β ) L I + β L F ] \underset{\theta_P,\theta_I,\theta_F}{min} \left[-\lambda E_{\pi(s_t;\theta_P)}[\sum_t r_t]+(1-\beta)L_I+\beta L_F \right] θP,θI,θFmin[−λEπ(st;θP)[t∑rt]+(1−β)LI+βLF]
among , θ P , θ I , θ F \theta_P,\theta_I,\theta_F θP,θI,θF Represent strategy separately , Reverse model , Parameters of the forward model , λ \lambda λ Represents the importance of loss to learning intrinsic rewards , β \beta β It is a scalar that weighs the loss of the reverse model and the loss of the forward model ( Be situated between 0 and 1 Between ), L I L_I LI Is the loss of the reverse model , L F L_F LF Is the loss of the forward model .
Take a look back. :
- Due to the problems of external reward realization and sparse reward , We want to create the intrinsic rewards of agents .
- So , We create curiosity , This is the error of the agent in predicting the action result in its current state .
- Using curiosity will promote our learning body Support conversion with high prediction error ( It will be higher in the area where the agent spends less time or in the area with dynamic complexity ), So as to better explore our environment .
- But because we can't predict the next frame ( Too complicated ) To predict the next state , So we use ** Better features represent , Only the elements that can be controlled or influenced by the agent .** Add , It is recommended to design the feature space reasonably in the task .
- To generate curiosity , We use an intrinsic curiosity module consisting of two models : Used to represent the characteristics of the learning state and the next state Reverse model And a prediction feature representation for generating the next state Forward model .
- Curiosity will equal The difference between the forward dynamic model and the reverse dynamic model .
5. Related knowledge
5.1 Random Network Distillaiton
Random Network Distillaiton, Random network distillation , abbreviation RND. and Curiosity The goal is the same , It also solves the problem of sparse reward by adding internal exploration reward to agents . The core of both is to give high rewards to states that have not been explored , But there are different ways to judge whether the state has been explored .
And Curiosity Different ,RND Have two networks , The structures of the two networks are consistent , Input as status s t s_t st , Generate a set of vectors , In fact, feature extraction . A network is called target The Internet , At first, after random parameters , Its parameters are no longer updated . Another network is called Predictor The Internet , Its parameters can be continuously learned and adjusted , The goal of learning is to give the same state s t s_t st , Its output and Target The closer the network is, the better .
Therefore, when the output difference between the two networks is greater , The more it shows that this state has not been explored before , We should give greater rewards , On the contrary, when the two tend to be consistent , This indicates that this state has been encountered many times , After full study , Smaller rewards should be given . The reward function formula is :
r t i = ∣ ∣ f ^ ( s t + 1 ) − f ( s t + 1 ) ∣ ∣ 2 2 r^i_t = ||\hat{f}(s_{t + 1}) - f(s_{t + 1})||^2_2 rti=∣∣f^(st+1)−f(st+1)∣∣22
f Namely target The output of the network , f ^ \hat{f} f^ Is the predicted value .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-nqvhxgck-1654093917646)(https://gitee.com/zuiyixin/blog-graph/raw/master/202206012215841.png)]
5.2 be based on “ accident ” Curiosity
What is mentioned in the text is based on “ accident ” Curiosity ,ICM The method also establishes a prediction model of world dynamics , And reward the agent when the model fails to make a good prediction , This reward marks “ accident ” or “ Something new ”. Be careful , Explore places you've never been before , Not at all ICM A direct component of the curiosity mechanism .
about ICM In terms of method , It's just getting more “ accident ” One way , The goal is to maximize the overall rewards obtained . The fact proved that , In some environments, there may be other ways to cause “ Self accident ”, This leads to unpredictable results .
stay 《Large-Scale Study of Curiosity-Driven Learning》 In the article ,ICM The author of the method and OpenAI Of researchers have shown that , be based on “ Unexpected maximization ” There may be potential risks in the reinforcement learning approach : Agents can learn to indulge and procrastinate , Don't do anything useful to complete the current task .
To understand why , Look at a common thought experiment , The experiment is called “ Noisy TV problems ”, In the experiment , The agent is placed in a maze , The task is to find a very valuable project ( And the supermarket example before this article “ cheese ” similar ).
There is also a TV in the test environment , The agent has a TV remote control . The number of TV channels is limited ( Each channel shows different programs ), Each key will switch to random channel . How the agent will behave in such an environment ?
For an approach based on accidental curiosity , Changing the channel will bring huge rewards , Because every channel change is unpredictable and unexpected . It is important to , Even after all available channels have been cycled once , Because the content of the channel is random , So every new change is still an accident , Because the agent always predicts what program will be played after changing the channel , This prediction is likely to go wrong , Cause an accident .
Even if the agent has seen every program on every channel , This random change is still unpredictable . therefore , Constantly reap unexpected curiosity agents , Will eventually stay in front of the TV forever , Will not look for that very valuable item , This is similar to a kind of “ delay ” Behavior . that , How to define “ Curiosity ” To avoid such procrastination ?
5.3 be based on “ situation ” Curiosity
stay 《Episodic Curiositythrough Reachability》 In the article , We explored a memory based “ Situational curiosity ” Model , it turns out to be the case that , This model is not easy to produce “ Self indulgence ” Immediate satisfaction . Why? ?
The above experiment is still taken as an example , After the agent continuously changes the TV channel for a period of time , All the programs will eventually appear in memory . therefore , Television will no longer be attractive : Even if the sequence of programs appearing on the screen is random and unpredictable , But all these programs are already in memory .
** This is the same as the method mentioned above “ Based on accidents ” The main difference between the methods of : Our method doesn't even predict the future .** On the contrary , Intelligent experience checks past information , Find out if you have seen and observed the current results . therefore , Our agents will not be provided by noisy TV “ Instant satisfaction ” Attracted by the . It must explore the world beyond television , To get more rewards .
How to judge whether the agent sees the same thing as the existing memory ? It may be pointless to check whether the two match exactly : Because in the real world , There are very few identical scenes . such as , Even if the agent returns to the same room , The observation angle will also be different from the previous memory scene .
We will not check whether there is an exact match in the memory of the agent , Instead, the trained deep neural network is used to measure the similarity between the two experiences . To train the network , We will guess whether the two observations are very close in time . If the two are very close in time , It is likely that it should be regarded as different parts of the same experience of the agent .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-6z8BUN9f-1654093917647)(https://gitee.com/zuiyixin/blog-graph/raw/master/202206012229034.jpeg)]
Is it new or old “ Accessibility ” Figure decision . in application , This graph cannot be obtained , We train the neural network estimator , Estimate a series of steps between observations .
边栏推荐
- 文件名设置导致writelines写入报错:OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument
- C# 解决使用SQLite 的相对路径问题
- Design of multiple classes
- prometheus告警流程及相关时间参数说明
- Video file too large? Use ffmpeg to compress it losslessly
- openpyxl表格读取实例
- Freemarker
- Conception de plusieurs classes
- Oracle uses an SQL to find out which data is not in a table
- Fake constructor???
猜你喜欢

Privacy computing fat offline prediction

支付宝微信支付业务流程图
Nosql 数据库 -Redis 安装

有关二叉树的一些练习题
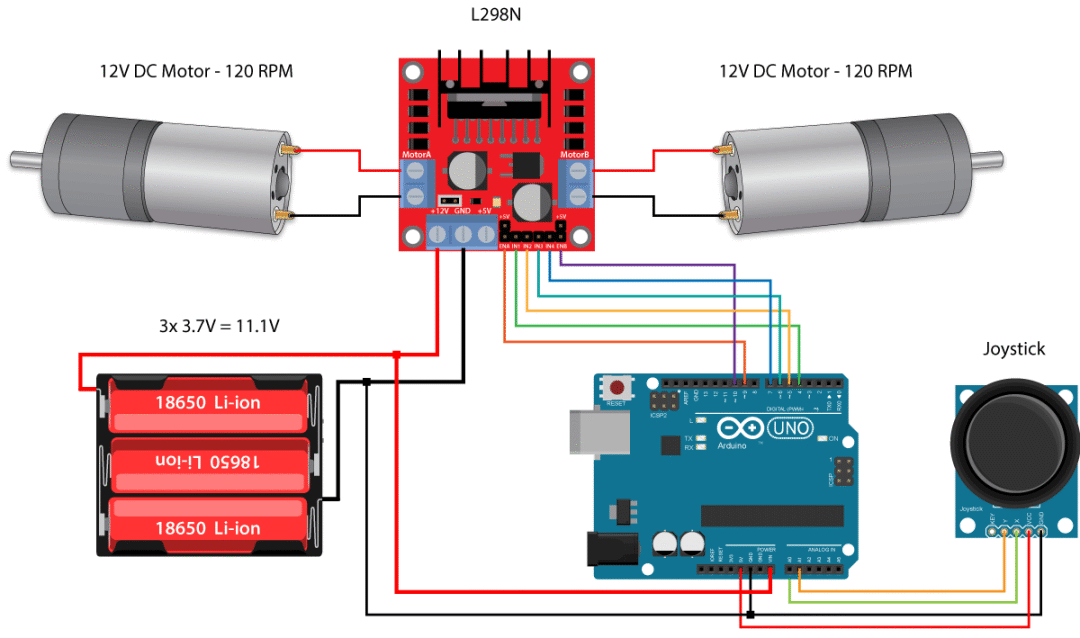
Principle and application of the most complete H-bridge motor drive module L298N

Enumeration? Constructor? Interview demo

提高效率 Or 增加成本,开发人员应如何理解结对编程?
Scientists develop two new methods to provide stronger security protection for intelligent devices
There is no doubt that this is an absolutely elaborate project

Markem imaje马肯依玛士喷码机维修9450E打码机维修
随机推荐
SVN版本控制器的安装及使用方法
Preliminary understanding of pytorch
ThreadLocal digs its knowledge points again
Quelques exercices sur les arbres binaires
VIM from dislike to dependence (19) -- substitution
Summary of three basic interview questions
ucore lab5
One week's experience of using Obsidian (configuration, theme and plug-in)
力扣84柱状图中最大的矩形
视频文件太大?使用FFmpeg来无损压缩它
I'm almost addicted to it. I can't sleep! Let a bug fuck me twice!
借助原子变量,使用CAS完成并发操作
The most direct manifestation of memory leak
E+h secondary meter repair pH transmitter secondary display repair cpm253-mr0005
[MySQL basic] general syntax 1
CLassLoader
Semi supervised learning—— Π- Introduction to model, temporary assembling and mean teacher
支付宝微信支付业务流程图
更改pip镜像源
Prometheus alarm process and related time parameter description
