当前位置:网站首页>Opencv_ 100 questions_ Chapter IV (16-20)
Opencv_ 100 questions_ Chapter IV (16-20)
2022-06-10 22:38:00 【Fioman_ Hammer】
List of articles
16. Prewitt filter
Previtt The filter is a first-order differential filter , It and Sobel The difference between filters is ,Sobel The coefficient in the direction of the filter spindle is 2 and -2, and Prewitt All the coefficients of the filter are -1 and 1, Whether it's vertical (Y Axis direction ) Or horizontal (X Axis direction )
The longitudinal (Y Axis direction ): 
Another difference is Sobel The operator is the preceding pixel value minus the following , and Prewitt The filter is the following pixel value minus the previous one
The transverse (X Axis direction ):

Code implementation :
# @Time : 2022/6/10 15:40
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def BGR_to_GRAY(image):
b = image[..., 0].copy()
g = image[..., 1].copy()
r = image[..., 2].copy()
out = 0.2126 * r + 0.7152 * g + 0.0722 * b
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
return out
def prewitt_filter(image):
kSize = 3
if len(image.shape) == 3:
image = BGR_to_GRAY(image)
# zero Padding
H, W = image.shape
pad = kSize // 2
out = np.zeros((H + pad * 2, W + pad * 2), dtype=np.float32)
out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
temp = out.copy()
outX = out.copy()
outY = out.copy()
kernelX = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [-1, 0, 1]])
kernelY = np.array([[-1, -1, -1], [0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1]])
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
outY[pad + y, pad + x] = np.sum(kernelY * (temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize]))
outX[pad + y, pad + x] = np.sum(kernelX * (temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize]))
outX = np.clip(outX, 0, 255)
outY = np.clip(outY, 0, 255)
outX = outX[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
outY = outY[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return outX, outY
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH,"gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath,cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
prewittX,prewittY = prewitt_filter(imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("Origial",imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("PrewittX",prewittX)
cv.imshow("PrevittY",prewittY)
cv.waitKey(0)
17. Laplacian filter
Laplace filter is also called harmonic filter , It is a filter that detects edges by quadratic differentiation of image brightness , Because the digital image is discrete ,x Direction and y The first derivative of the direction is calculated according to the following formula :
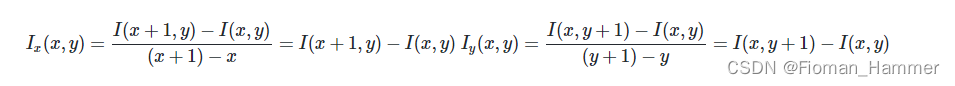
Therefore, the quadratic differential is calculated according to the following formula :

We inform you ,Laplician The expression is as follows :
To express this expression as a convolution kernel is like this :

It seems that Laplacian operator can be understood in this way , Use its four neighborhood pixels and center point pixels to make the difference , The final result is the result of Laplace filtering . differ Sobel operator , They are divided into vertical and horizontal , Laplacian does not know direction , Direct result .
Code implementation :
# @Time : 2022/6/10 16:02
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def BGR_to_GRAY(image):
b = image[..., 0].copy()
g = image[..., 1].copy()
r = image[..., 2].copy()
out = r * 0.2126 + g * 0.7152 + b * 0.0722
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
return out
def laplacian_filter(image):
kSize = 3
if len(image.shape) == 3:
image = BGR_to_GRAY(image)
H, W = image.shape
# zero padding
pad = int(kSize / 2)
out = np.zeros((H + pad * 2, W + pad * 2), dtype=np.float32)
out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
laplacianKernel = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, -4, 1], [0, 1, 0]])
temp = out.copy()
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
out[pad + y, pad + x] = np.sum(laplacianKernel * temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize])
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH, "gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
laplacianFilter = laplacian_filter(imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("Original", imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("LaplacianFilter", laplacianFilter)
cv.waitKey(0)
18. Emboss filter
Use Emboss The filter can make the outline of the object clearer ;
Emboss Filter core is :

How to understand this filter ? In fact, it is the difference between the lower right corner and the upper left corner , Then add it to the original pixel value .
The coefficient of the farthest angle is 2, Others are 1.
What is the significance of this filtering ? If the position of this center is the edge , Then the difference must exist , You can enhance the whole edge .
# @Time : 2022/6/10 16:17
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def BGR_to_GRAY(image):
b = image[..., 0]
g = image[..., 1]
r = image[..., 2]
out = 0.2126 * r + 0.7152 * g + 0.0722 * b
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
return out
def emboss_filter(image):
if len(image.shape) == 3:
image = BGR_to_GRAY(image)
H, W = image.shape[:2]
embossKernel = np.array([[-2, -1, 0], [-1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 2]])
# zero padding
kSize = 3
pad = int(kSize / 2)
out = np.zeros((H + 2 * pad, W + 2 * pad), dtype=np.float32)
out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
temp = out.copy()
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
out[y + pad, x + pad] = np.sum(temp[y:(y + kSize), x:(x + kSize)] * embossKernel)
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH, "gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath, cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
embossFilter = emboss_filter(imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("Original", imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("EmbossFilter", embossFilter)
cv.waitKey(0)
19. LoG filter
LoGGauss - Laplace (Laplacian of Gaussian) Abbreviation , Gaussian filter is used to smooth the image, and then Laplacian filter is used to make the image outline clearer . In order to prevent the Laplace filter from calculating the quadratic differential, the image noise will be more obvious , So we first use Gaussian filter to suppress noise .
The formula is defined as follows : 
Implementation code :
# @Time : 2022/6/10 17:01
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
def BGR_to_GRAY(image):
b = image[..., 0]
g = image[..., 1]
r = image[..., 2]
out = r * 0.2126 + g * 0.7152 + b * 0.0722
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
def LoG_filter(image, kSize=5, sigma=3.0):
if len(image.shape) == 3:
image = BGR_to_GRAY(image)
H, W = image.shape
# zero padding
pad = int(kSize / 2)
out = np.zeros((H + 2 * pad, W + 2 * pad), dtype=np.float32)
out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W] = image.copy().astype(np.float32)
# LoG Kernel
K = np.zeros((kSize, kSize), dtype=np.float32)
for x in range(-pad, -pad + kSize):
for y in range(-pad, -pad + kSize):
K[y + pad, x + pad] = (x ** 2 + y ** 2 - sigma ** 2) * np.exp(-(x ** 2 + y ** 2) / (2 * (sigma ** 2)))
K /= (2 * np.pi * (sigma * 6))
K /= K.sum()
temp = out.copy()
# filtering
for y in range(H):
for x in range(W):
out[pad + y, pad + x] = np.sum(K * temp[y:y + kSize, x:x + kSize])
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out[pad:pad + H, pad:pad + W].astype(np.uint8)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH,"gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath,cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
LoGFilter = LoG_filter(imageOriginal,5,1.5)
cv.imshow("Original",imageOriginal)
cv.imshow("LoGFilter",LoGFilter)
cv.waitKey(0)
20. Histogram
Generally speaking, histogram should express , The horizontal direction should represent a certain state , The vertical direction shows the number of times this state occurs .
The histogram will cut the data to be displayed into groups according to the range of values / interval , These groups / Intervals are called... In English bin, Then the number of data in each data segment will be counted and displayed in strips of different lengths . So the histogram itself is also a kind of bar graph
plt.hist() Function to draw histogram
hist(x, bins=None, range=None, density=None, weights=None,
cumulative=False, bottom=None, histtype='bar', align='mid',
orientation='vertical', rwidth=None, log=False,
color=None, label=None, stacked=False, normed=None,
**kwargs):
Parameter interpretation :
x:(n,) array or sequence of (n,) arrays. This parameter specifies each bin( The box ) Distributed data , Corresponding x Axis .bins:This parameter executes bin( The box ) The number of , That is to say, there are several bar graphs in totalnormed:This parameter has been discarded , UsedensityParameter instead of .range:Yuanzu or None. bin The upper and lower . If not provided , By default (x.min(),x.max())density:Whether to display in density , The default is None, The density form is actually normalization .align:Alignment mode “left”: Left ,“mid”: middle ,"right:" Rightbottom:y The starting position of the axis , value typeorientation:Direction , horizontal: level , vertical: vertical
# @Time : 2022/6/10 17:27
# @Author : Fioman
# @Phone : 13149920693
# @Tips : Talk is Cheap,Show me the code! ^_^^_^
from settings import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__ == '__main__':
imagePath = os.path.join(OPENCV_100_Q_PATH,"gray_01.bmp")
imageOriginal = cv.imread(imagePath,cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
plt.hist(imageOriginal.ravel(),bins=256,rwidth=0.8,range = (0,255))
plt.show()
边栏推荐
- [MySQL] Table constraints
- Advanced advanced programmers must know and master Or else, stupid
- 鯨會務智慧景區管理解决方案
- Ability to deliver packages within D days [abstract class dichotomy -- Abstract judgment method]
- Mmcv Config class introduction
- TcaplusDB君 · 行业新闻汇编(四)
- SQL Server查询区分大小写
- Sealem Finance打造Web3去中心化金融平台基础设施
- 数字孪生:第三人称鼠标操作
- Modify frontsortinglayer variable of spritemask
猜你喜欢

Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (VI)

中小型会议如何进行数字化升级?

Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (V)

罗永浩:我要是负责人 能让苹果产品上去三个台阶不止

What are MySQL clustered indexes and nonclustered indexes?
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB查看进程状态介绍

Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (I)

Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure

Differences between disk serial number, disk ID and volume serial number

Opencv_100问_第三章 (11-15)
随机推荐
Whale conference sharing: what should we do if the conference is difficult?
Array intersection of two arrays II
鲸会务智慧景区管理解决方案
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB日常巡检介绍
Tcapulusdb Jun · industry news collection (III)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb viewing process status introduction
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB机器初始化和上架介绍
Notes (II)
进阶高级程序员必知必会. 要不然,蠢材吗
笔记(五)- JVM
【问题】解决Websocket字符串长度限制问题单包过大
Capacity expansion mechanism of ArrayList
Web3生态去中心化金融平台——Sealem Finance
Array rotates the array from bits of the specified length
leetcode 130. Surrounded Regions 被围绕的区域(中等)
CCF CSP 202109-3 脉冲神经网络
datagrip 报错 “The specified database user/password combination is rejected...”的解决方法
Shell basic concepts
Basic use of mathtype7.x
A number that appears only once in an array