当前位置:网站首页>Matlab simulation of depth information extraction and target ranging based on binocular camera images
Matlab simulation of depth information extraction and target ranging based on binocular camera images
2022-07-23 15:04:00 【I love c programming】
Catalog
3. Preview of some simulation drawings
4. Source code acquisition method
1. Algorithm description
Binocular cameras are generally composed of two horizontally placed cameras, the left eye and the right eye . Of course, it can also be made into two items , But the mainstream binoculars we see are made of left and right . In the left and right binocular cameras , We can think of both cameras as pinhole cameras . They are placed horizontally , It means that the aperture centers of both cameras are located in x On the shaft . Their distance is called the baseline of the binocular camera (Baseline, Write it down as b), Is an important parameter of binocular . Binocular cameras are generally composed of two horizontally placed cameras, the left eye and the right eye . Of course, it can also be made into two items , But the mainstream binoculars we see are made of left and right . In the left and right binocular cameras , We can think of both cameras as pinhole cameras . They are placed horizontally , It means that the aperture centers of both cameras are located in x On the shaft . Their distance is called the baseline of the binocular camera (Baseline, Write it down as b), Is an important parameter of binocular .

Consider a space point P, It looks alike in the left eye and the right eye , Write it down as PL,PR. Due to the existence of camera baseline , The two imaging positions are different . Ideally , Because the left and right cameras are only in x There is displacement on the shaft , therefore P Your image is only in x Axis ( Corresponding to the image u Axis ) There are differences . We remember its coordinates on the left as uL, The right coordinate is uR. that , Their geometric relationship is shown in the figure 1 On the right . According to the triangle P−PL−PR and P−OL−OR Similarity relation of , Yes :
![]()
Put it in order :

here d Is the difference between the abscissa of the left and right graphs , It's called parallax (Disparity). According to parallax , We can estimate the distance between a pixel and the camera . Parallax is inversely proportional to distance : The greater the parallax , The closer you get . meanwhile , Because the parallax is at least one pixel , So there is a theoretical maximum of binocular depth , from fb determine . We see , When the baseline is longer , The maximum distance that can be measured by your eyes will become farther ; conversely , Small binocular devices can only measure very close distances .
2. Partial procedure
% Calculate the depth distance of the object
PL=imread('IMAGES\p1.jpg');
subplot(241),imshow(PL),title(' Image taken on the left ');
PL=rgb2gray(PL);
PL=255-PL;
PL1=im2bw(PL,0.8);
subplot(242),imshow(PL1),title(' Threshold segmentation image ');
se1=strel('rectangle',[5 5]);
PL2=imclose(PL1,se1); % Closed operation
se2=strel('rectangle',[5 5]);
PL3=imopen(PL2,se2); % Open operation
subplot(243),imshow(PL2),title(' Morphological processing ');
imwrite(PL3,'PL3.bmp','bmp')
k=1;sum1=0;
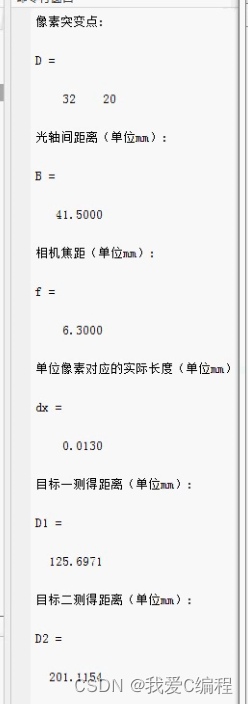
for j=1:518 % Calculate the pixel mutation point of target one
for i=1:388
sum1=sum1+PL3(i,j);
end
k=k+1;
P(k)=sum1/318;
sum1=0;
end
x=1:518;
y=P(x);
subplot(244),plot(x,y),title(' Gray scale change diagram ');
plot(x,y);
for i=2:518 % Calculate the pixel mutation point of target 2
if ((P(i-1)<0.01)&(P(i)>0.01)&(P(i)<0.16))
Z(1)=i;
continue
end
if ((P(i-1)<0.1)&(P(i)>0.16))
Z(2)=i;
continue
end
end
%===============================
% Calculate the target position of the image on the right
%===============================
PR=imread('IMAGES\p2.jpg');
subplot(245),imshow(PR);title(' Take an image on the right ');
PR=rgb2gray(PR);
PR=255-PR;
PR1=im2bw(PR,0.8);
subplot(246),imshow(PR1);title(' Threshold segmentation image ');
se1=strel('rectangle',[5 5]);
PR2=imclose(PR1,se1);
se2=strel('rectangle',[5 5]);
PR3=imopen(PR2,se2);
subplot(247),imshow(PR3),title(' Morphological processing ');
k=1;sum2=0;
for j=1:518
for i=1:388
sum2=sum2+PR3(i,j);
end
k=k+1;
Q(k)=sum2/318;
sum2=0;
end3. Preview of some simulation drawings

4. Source code acquisition method
Click the download link :
Access method 2:
Blog resource item , Search for resources with the same name as blog .
Access method 3:
If the download link fails , Blogger wechat contact .
A_059
边栏推荐
- Introduction and mechanism of Aptos
- 力扣-单调栈
- MySQL 常用命令
- [record of question brushing] 19. Delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- 爬虫中selenium实现自动给csdn博主文章点收藏
- 基於matlab的CBOC信號調制解調仿真,輸出其相關性,功率譜以及頻偏跟踪
- [software testing] how to sort out your testing business
- Common SQL of Oracle Report
- [software test] redis abnormal test encountered in disk-to-disk work
- Typora图床配置详细教程
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Head pose estimation principle and visualization_ Loveliuzz's blog - Programmer's Homestead_ Head posture estimation
Version correspondence between numpy and pytorch
Kettle implémente une connexion de base de données partagée et insère une instance de composant de mise à jour
面试官:生成订单30分钟未支付,则自动取消,该怎么实现?
Getting started with Prometheus (III)
[untitled]
Towhee weekly model
The best time to buy and sell stocks
Common JS modular specification from a code question
MySQL unique index has no duplicate value, and the error is repeated
Multiple backpacks!
Qt|模仿文字浮动字母
基于matlab的BOC调制解调的同步性能仿真,输出跟踪曲线以及不同超前滞后码距下的鉴别曲线
Jetpack系列之Room中存Map结构
Supervisor installation and use
RSA加密的使用
如何加速矩阵乘法——优化GEMM (CPU单线程篇)
The pit trodden by real people tells you to avoid the 10 mistakes often made in automated testing
数字相加的精度问题
C thread lock and single multithreading are simple to use