当前位置:网站首页>2019年海淀区青少年程序设计挑战活动小学组复赛试题详细答案
2019年海淀区青少年程序设计挑战活动小学组复赛试题详细答案
2022-08-04 17:56:00 【51CTO】
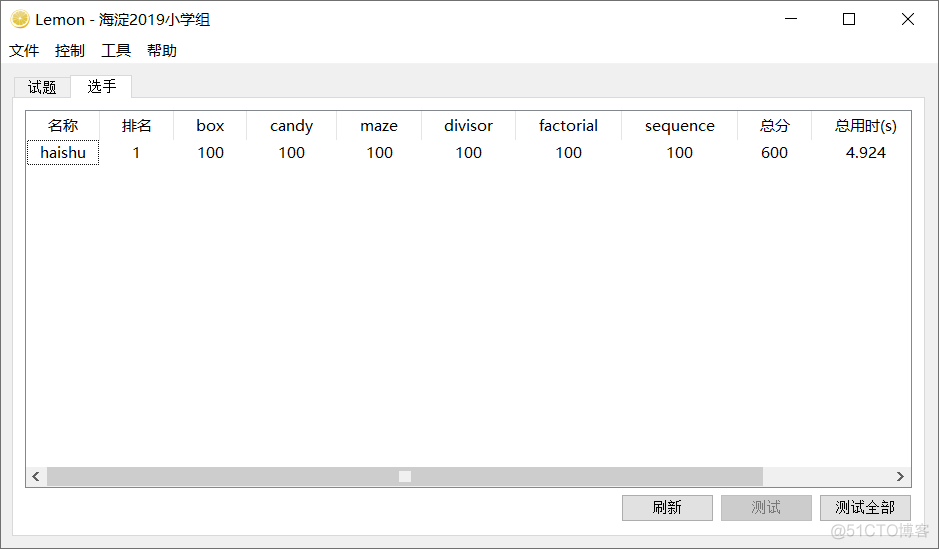
六个程序的评测结果:
1 约数
2 阶乘
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// zero count from tail of n!
int zeroCnt1(int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(n)
{
n /= 5;
cnt += n;
}
return cnt;
}
// zero count from tail of n!! when n is even
int zeroCnt2(int n)
{
n /= 10;
int cnt = n;
while(n)
{
n /= 5;
cnt += n;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << zeroCnt1(n) << ' ';
if(n % 2)
{
cout << 0;
}
else
{
cout << zeroCnt2(n) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
3 序列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[200005];
int main()
{
int n, i;
cin >> n;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
for(i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -= 2)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
if(n % 2)
{
i = 1;
}
else
{
i = 0;
}
for(; i < n; i += 2)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
4 糖果
#include <iostream>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
char a[10000000 + 5];
inline string read()//inline继续加快速度
{
// getchar()在数据量较大时比scanf和cin快
char ch = getchar();
string res = "";
while(ch>='A' && ch<='Z')
{
res += ch;
ch = getchar();
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
freopen("candy.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("candy.out", "w", stdout);
int cnt[128];
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));
int start = 0;
int maxLen = 26;
int len;
bool same = false;
//string a = read();
scanf("%s", a);
int Size = strlen(a);
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
cnt[a[i] - 65]++;
if(2 == cnt[a[i] - 65])
{
same = true;
for(int j = start; j < i; j++)
{
if(a[j] == a[i])
{
len = i - j;
if(len < maxLen)
{
maxLen = len;
}
start = j + 1;
break;
}
}
cnt[a[i] - 65] = 1;
}
}
if(!same)
{
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << maxLen << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
5 迷宫
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 205;
// 4 directions: right, left, down, up
const int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
const int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int n, m, ans;
char a[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
void dfs(int x, int y)
{
for(int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++)
{
int nextX = x + dx[dir];
int nextY = y + dy[dir];
if(!vis[nextX][nextY] && nextX >= 1 && nextX <= n && nextY >= 1 && nextY <= m && (a[nextX][nextY] == '.' || a[nextX][nextY] == '*'))
{
vis[nextX][nextY] = true;
if(a[nextX][nextY] == '*')
{
ans++;
}
dfs(nextX, nextY);
}
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("maze.in", "r", stdin);
freopen(“maze.out”, “w”, stdout);
int startX, startY;
cin >> n >> m; // n rows m columns
int row, col;
for(row = 1; row <= n; row++)
{
for(col = 1; col <= m; col++)
{
cin >> a[row][col];
if('S' == a[row][col])
{
startX = row;
startY = col;
}
}
}
vis[startX][startY] = true;
dfs(startX, startY);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
6 盒子
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int N = 500000 + 5;
int n, a[N];
int main()
{
freopen("box.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("box.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
multiset<int, greater<int> > s; // 每个元素代表每个堆有几个元素
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// 对于降序集合,lower_bound得到的是第一个小于a[i]的元素的位置
// 只有堆的个数小于等于a[i],a[i]才能加入该堆的最底部
// 如果最小堆的个数大于a[i],说明要为a[i]新建一堆
multiset<int>::iterator it = s.lower_bound(a[i]);
if(it == s.end()) // s里没有这个元素
{
// 新加一个堆,堆的大小为1(就是包含了这个元素)
s.insert(1);
}
else
{
// 把元素放到这个堆里,堆的元素个数加1
int cnt = *it + 1;
s.erase(it);
s.insert(cnt);
}
}
printf("%d", s.size());
return 0;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
EasyCVR本地接入国标设备映射公网后,本地设备出现无法播放与级联的解决方法
R语言缺失时间序列的填充及合并:补齐时间序列数据中所有缺失的时间索引、使用merge函数合并日期补齐之后的时间序列数据和另外一个时间序列数据(补齐左侧数据)
荣耀互联对外开放,赋能智能硬件合作伙伴,促进全场景生态产品融合
数仓相关,总结
R语言dplyr包group_by函数和summarise_at函数计算dataframe计算不同分组的计数个数和均值、使用%>%符号将多个函数串起来
情绪的波动起伏
2022 May 1 Mathematical Modeling Question C Explanation
Web端即时通讯技术:WebSocket、socket.io、SSE
企业调查相关性分析案例
Introduction of three temperature measurement methods for PT100 platinum thermal resistance
DMPE-PEG-Mal,二肉豆蔻酰磷脂酰乙醇胺-聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺简述
flink-cdc支持并行读取一张mysql表的binlog不?
Boosting之GBDT原理
"No title"
dotnet core 使用 CoreRT 将程序编译为 Native 程序
离散化求前缀和
Cholesterol-PEG-Maleimide,CLS-PEG-MAL,胆固醇-聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺一种修饰性PEG
【日记】UPNP功能会允许自动给光猫追加端口映射
npm配置国内镜像(淘宝镜像)
localstorage本地存储的方法