当前位置:网站首页>链表的归并排序[自顶向下分治 || 自低向上合并]
链表的归并排序[自顶向下分治 || 自低向上合并]
2022-08-02 15:48:00 【REN_林森】
前言
对链表进行归并排序,不需要额外的辅助空间,可将空间复杂度降到O(1)。快慢指针寻找中点,将链拆开,递归回溯进行合并;或者从1/2/4/8进行拆链再合并&缝合链表。
一、链表排序
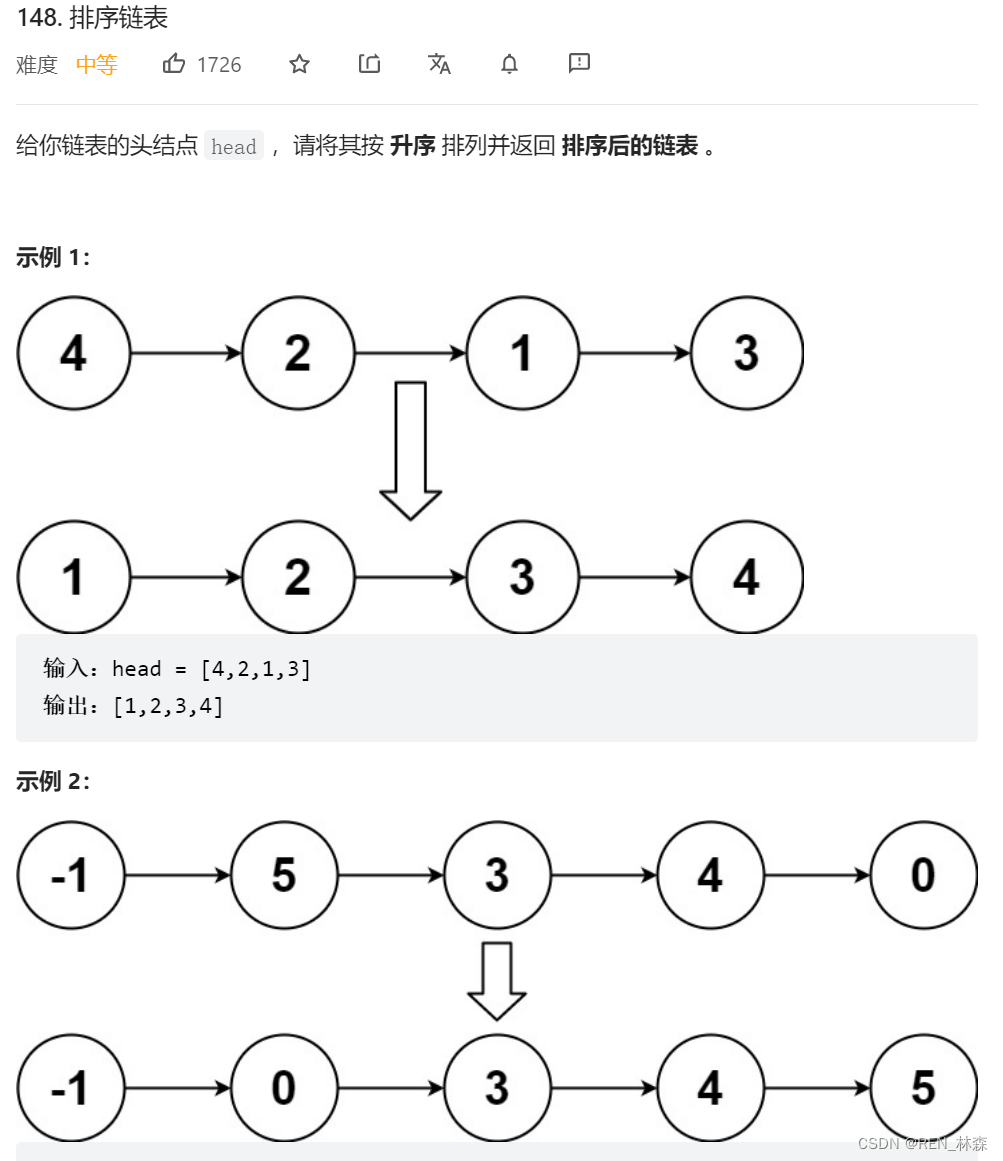
二、分治 & 合并
1、自顶向下分治
public class SortList {
// 链表归并排序。
// review: 关键点:快慢指针寻找中间节点 + 归并前的拆链(自己逻辑不清晰,merge前需要拆链,sortList时不需要拆。)
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
return sortList(head, null);
}
// 自顶向下递归将链表分解成二叉树,回溯时完成子树节点的不断合并。
private ListNode sortList(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
if (left.next != right) {
// 快慢指针找中间节点。
ListNode slow = left, fast = left;
while (fast != right) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == right) break;
fast = fast.next;
}
ListNode l1 = sortList(left, slow);
ListNode l2 = sortList(slow, right);
return mergeList(l1, l2);
}
// 分链 应该在sortList返回单个链表时进行拆链。
left.next = null;
return left;
}
private ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode p = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
p.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
p.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
p = p.next;
p.next = null;
}
p.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
// Definition for singly-linked list.
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
2、自低向上合并
// 自低向上。
class SortList2 {
// 方式二:自低向上,合并1/2/4/8个节点。
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
// 求链表长度。
int len = getListLen(head);
// 自低向上。
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int size = 1; size < len; size <<= 1) {
// 每次从头开始。
ListNode cur = dummy.next;// head在变。
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (cur != null) {
// 取第一条链。
ListNode l1 = cur;
for (int i = 1; i < size && cur.next != null; i++) cur = cur.next;
// 取第二条链。
ListNode l2 = cur.next;
// 拆第一条链。
cur.next = null;
// 取
cur = l2;
// 此刻开始,cur可能为null。
for (int i = 1; i < size && cur != null && cur.next != null; i++) cur = cur.next;
// 拆第二条链。
// 防止非正常结束循环,即链表长度不够,即cur = null。
ListNode next = null;
if (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
}
pre.next = mergeList(l1, l2);// 合并两条独立链表。
// 为后面的合并做准备。
while (pre.next != null) pre = pre.next;
cur = next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
private int getListLen(ListNode head) {
int len = 0;
while (head != null) {
head = head.next;
++len;
}
return len;
}
private ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode p = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
p.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
p.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
p = p.next;
p.next = null;
}
p.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
// Definition for singly-linked list.
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
总结
1)对链表O(nlogn)排序,可同时考察归并的分治思想,和链表的操作(链表合并/拆链等)。
2)练习掌握自顶向下思想和自低向上思想。
参考文献
[1] LeetCode 链表排序
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
第十七天笔记
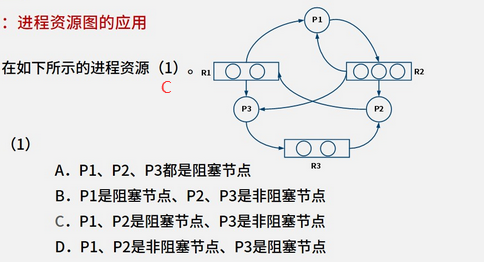
2.7 - 文件管理 2.8 - 多级目录结构 2.9 - 位示图
JZ69 跳台阶
策略路由下发
从幻核疑似裁撤看如何保证NFT的安全
代码随想录笔记_哈希_61扑克牌中的顺子
AI智能剪辑,仅需2秒一键提取精彩片段
JZ11 旋转数组的最小数字
助力疫情防控,30行代码就能搞定无服务器实时健康码识别!
Go-6-常用命令-go包管理问题-两个路径-GO111MODULE
【wpf】ListView 和 ItemsControl 的一点区别
机械臂速成小指南(十七):直线规划
跨境电商看不到另一面:商家刷单、平台封号、黑灰产牟利
05-读写锁、阻塞队列及四组API、同步队列
亲戚3.5W入职华为后,我也选择了转行……
【面经】被虐了之后,我翻烂了equals源码,总结如下
我今天终于发现demo才是一切
看我如何用多线程,帮助运营小姐姐解决数据校对系统变慢!
【Transformer专题】一、Attention is All You Need(Transformer)
[LeetCode]剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度


![【[NOI2001] 炮兵阵地】【状压DP】](/img/ae/6b01b175b0158fb804211931d57c0c.jpg)