当前位置:网站首页>Go language core 36 lectures (go language practice and application 23) -- learning notes
Go language core 36 lectures (go language practice and application 23) -- learning notes
2022-06-23 23:16:00 【Zhengziming】
45 | Use os In bag API ( Next )
In our last article . from “os.File What types implement io Interfaces in packages ” This question starts with , This paper introduces a series of related contents . Today we continue to expand around this knowledge point .
Knowledge expansion
problem 1: It can be applied to File What are the operation modes of values ?
in the light of File The operation modes of values mainly include read-only mode 、 Write only mode and read-write mode .
These patterns are represented by constants os.O_RDONLY、os.O_WRONLY and os.O_RDWR representative . When we create or open a file , One of these three modes must be set as the operation mode of the file .
besides , We can also set additional operating modes for the files here , The options are as follows .
- os.O_APPEND: When writing to a file , Append new content to existing content .
- os.O_CREATE: When the file on the given path does not exist , Create a new file .
- os.O_EXCL: Need and os.O_CREATE Use together , Indicates that there cannot be an existing file on the given path .
- os.O_SYNC: Synchronize on open files I/O. It ensures that the contents read and written are always synchronized with the data on the hard disk .
- os.O_TRUNC: If the file already exists , And it's a regular file , Then empty anything that already exists .
For the use of the above operating modes ,os.Create Functions and os.Open Functions are ready-made examples .
func Create(name string) (*File, error) {
return OpenFile(name, O_RDWR|O_CREATE|O_TRUNC, 0666)
}os.Create Function is calling os.OpenFile Function , The operation mode given is os.O_RDWR、os.O_CREATE and os.O_TRUNC The combination of .
This basically determines the behavior of the former , namely : If parameters name Represents that the file above the path does not exist , Then create a new , otherwise , First empty all the contents of the existing file .
also , It returns File Both read and write methods of values are available . Here we need to pay attention to , Multiple modes of operation are through bitwise OR operator | Combined .
func Open(name string) (*File, error) {
return OpenFile(name, O_RDONLY, 0)
}I said earlier ,os.Open The function : Open an existing file in read-only mode . The root cause is that it calls os.OpenFile Function , Only a single mode of operation is provided os.O_RDONLY.
above , Is my understanding of what can be applied to File A simple explanation of the operation mode of the value . stay demo88.go There are also a few examples in the file , For your reference .
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
type flagDesc struct {
flag int
desc string
}
func main() {
fileName1 := "something2.txt"
filePath1 := filepath.Join(os.TempDir(), fileName1)
fmt.Printf("The file path: %s\n", filePath1)
fmt.Println()
// Example 1.
contents0 := "OpenFile is the generalized open call."
flagDescList := []flagDesc{
{
os.O_WRONLY | os.O_CREATE | os.O_TRUNC,
"os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC",
},
{
os.O_WRONLY,
"os.O_WRONLY",
},
{
os.O_WRONLY | os.O_APPEND,
"os.O_WRONLY|os.O_APPEND",
},
}
for i, v := range flagDescList {
fmt.Printf("Open the file with flag %s ...\n", v.desc)
file1a, err := os.OpenFile(filePath1, v.flag, 0666)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("The file descriptor: %d\n", file1a.Fd())
contents1 := fmt.Sprintf("[%d]: %s ", i+1, contents0)
fmt.Printf("Write %q to the file ...\n", contents1)
n, err := file1a.WriteString(contents1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("The number of bytes written is %d.\n", n)
file1b, err := os.Open(filePath1)
fmt.Println("Read bytes from the file ...")
bytes, err := ioutil.ReadAll(file1b)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("Read(%d): %q\n", len(bytes), bytes)
fmt.Println()
}
// Example 2.
fmt.Println("Try to create an existing file with flag os.O_TRUNC ...")
file2, err := os.OpenFile(filePath1, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0666)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("The file descriptor: %d\n", file2.Fd())
fmt.Println("Try to create an existing file with flag os.O_EXCL ...")
_, err = os.OpenFile(filePath1, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_EXCL, 0666)
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
}problem 2: How to set access permissions for regular files ?
We already know ,os.OpenFile The third argument to the function perm It represents the permission mode , The type is os.FileMode. But actually ,os.FileMode Type can represent , But it's far more than permission mode , It can also represent file patterns ( It can also be called file type ).
because os.FileMode Is based on uint32 Redefinition of type , So each of its values contains 32 A bit . Here 32 Of the bits , Each bit has its own meaning .
such as , If the binary number in its highest bit is 1, Then the file pattern represented by this value is equivalent to os.ModeDir, in other words , The corresponding file represents a directory .
And such as , If one of them 26 On the first bit is 1, Then the file pattern represented by the corresponding value is equivalent to os.ModeNamedPipe, in other words , That file represents a named pipe .
actually , In a os.FileMode Type value ( hereinafter referred to as FileMode value ) in , Only the lowest 9 Only bits are used to indicate the permission of the file . When we get a value of this type , You can combine it with os.ModePerm The value of a constant is bitwise and manipulated .
The value of this constant is 0777, Is an octal unsigned integer , Its lowest 9 Every bit is 1, And higher 23 Every bit is 0.
therefore , After such biting and operation , We can get this FileMode All bits in the value used to represent the file permission , That is, the permission mode represented by this value . This will be the same as we call FileMode It's worth it Perm The results obtained by the method are consistent .
Here 9 In bits used to represent file permissions , Every time 3 A group of bits , It can be divided into 3 Group .
From high to low , this 3 Groups represent the file owners ( That is, the user who created the file )、 The user group to which the file owner belongs , And the access rights of other users to the file . And for each group , Among them 3 Bits from high to low indicate the read permission 、 Write and execute permissions .
If on one of these bits is 1, Then it means that the corresponding permission is enabled , otherwise , It means that the corresponding permission is closed .
therefore , Octal integer 0777 It means : All users in the operating system have read access to the current file 、 Write and execute permissions , And octal integers 0666 said : All users have read and write permissions to the current file , But they have no permission to execute .
We're calling os.OpenFile Function , You can set its third parameter according to the above instructions . But should pay attention to , Only when creating a new file , The third parameter value here is valid . In other cases , Even if we set this parameter , It will not have any impact on the target file .
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
type argDesc struct {
action string
flag int
perm os.FileMode
}
func main() {
// Example 1.
fmt.Printf("The mode for dir:\n%32b\n", os.ModeDir)
fmt.Printf("The mode for named pipe:\n%32b\n", os.ModeNamedPipe)
fmt.Printf("The mode for all of the irregular files:\n%32b\n", os.ModeType)
fmt.Printf("The mode for permissions:\n%32b\n", os.ModePerm)
fmt.Println()
// Example 2.
fileName1 := "something3.txt"
filePath1 := filepath.Join(os.TempDir(), fileName1)
fmt.Printf("The file path: %s\n", filePath1)
argDescList := []argDesc{
{
"Create",
os.O_RDWR | os.O_CREATE,
0644,
},
{
"Reuse",
os.O_RDWR | os.O_TRUNC,
0666,
},
{
"Open",
os.O_RDWR | os.O_APPEND,
0777,
},
}
defer os.Remove(filePath1)
for _, v := range argDescList {
fmt.Printf("%s the file with perm %o ...\n", v.action, v.perm)
file1, err := os.OpenFile(filePath1, v.flag, v.perm)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
continue
}
info1, err := file1.Stat()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error: %v\n", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("The file permissions: %o\n", info1.Mode().Perm())
}
}summary
In order to focus on os.File Type itself , In these two articles, I mainly talked about how to os.File Type applies to regular files . The pointer type of this type implements many io Interfaces in packages , Therefore, its specific function can be self-evident .
Through the value of this type , We can not only read all kinds of files 、 write in 、 Shut down etc , You can also set the starting index position for the next read or write .
Before using values of this type , We have to create it first . therefore , I've highlighted a few that you can create , And get a function of this type .
Include :os.Create、os.NewFile、os.Open and os.OpenFile. How do we create File value , It determines what we can do with it .
utilize os.Create function , We can create a new file in the operating system , Or empty all the contents of an existing file and reuse it .
Corresponding File Value above , We can read and write the file in any way . although os.NewFile Function is not used to create a new file , But it can wrap an available file based on a valid file descriptor File value .
os.Open The function is to open an existing file . however , We can only return through it File Value to read the corresponding file .
os.OpenFile Is the most flexible of these functions , Through it , We can set the operation mode and permission mode of the opened file . actually ,os.Create Functions and os.Open Functions are just a simple encapsulation of it .
In the use of os.OpenFile Function , We must understand the true meaning of operation mode and permission mode , And the right way to set them .
I have explained them in detail in the extension of this paper . meanwhile , I also wrote some code in the corresponding sample file .
You need to read and understand the code carefully , And realize the true meaning of these two modes in the process of running them .
What I'm talking about in this article is for os Come on , It's just that part of the iceberg on the sea . This code contains a lot of knowledge , And it's very malleable .
If you want to fully understand them , You may also need to refer to the documentation and tutorials on the operating system and so on . For reasons of length , I'm just doing a guide here , Help you get to know some important program entities in the package , And give you an entry point to go deeper , I hope you're already on your way .
Thinking questions
Today's question is : How to pass os In bag API Create and manipulate a system process ?
Note source code
边栏推荐
- 运维故障经历分享
- WebService client request failed can not create a secure xmlinputfactory
- 2022 cloud consulting technology series storage & CDN special sharing meeting
- Go language learning
- AndroidKotlin全面详细类使用语法学习指南
- How to set up a website construction map
- Industry 4.0 era: the rise of low code may bring about changes in the pattern of manufacturing industry
- Ambire Guide: the arbitrum odyssey begins! Week 1 - Cross Chain Bridge
- What are the processes, levels, stages and key points of requirements analysis in software development
- Phpmailer sends mail PHP
猜你喜欢

Talking about the knowledge of digital transformation

The technical design and practice of decrypting the red envelopes of Tiktok Spring Festival

Summary of some indicators for evaluating and selecting the best learning model

Face and lining of fresh food pre storage
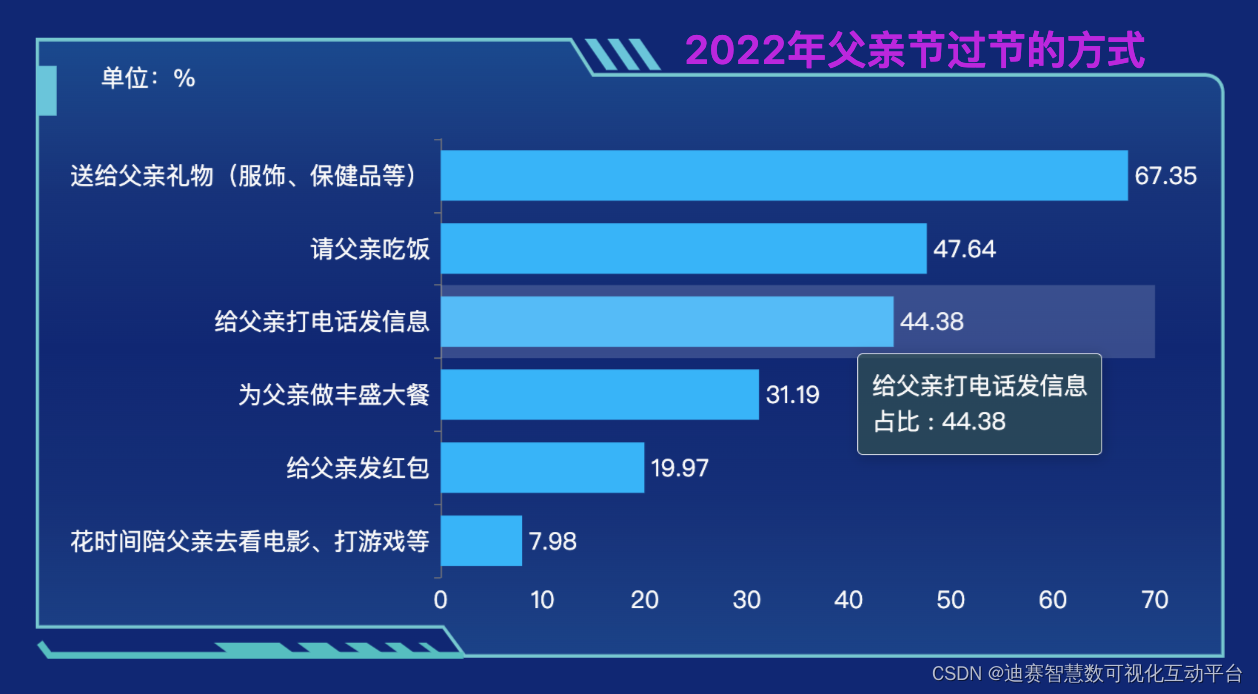
迪赛智慧数——柱状图(基本柱状图):2022年父亲节过节的方式

Ambire Guide: the arbitrum odyssey begins! Week 1 - Cross Chain Bridge
Phpmailer sends mail PHP
How to write and read ASM file system data

《阿里云天池大赛赛题解析》——O2O优惠卷预测
详解四元数
随机推荐
解密抖音春节红包背后的技术设计与实践
Fabric.js 手动加粗文本iText
MySQL事務隔離
Notes to nodejs (III)
Recommended | January activity 2-core 4G lightweight application server, enterprise nationwide purchase 6.7 yuan / month!!!
Website construction column setting form which website construction company is better
混沌工程,了解一下
Urgent! Tencent cloud container security supports the detection of Apache log4j2 vulnerabilities for the first time. It is in free trial
AAAI 2022 | Tencent Youtu 14 papers were selected, including image coloring, face security, scene text recognition and other frontier fields
The Sandbox 归属周来啦!
Ambire 指南:Arbitrum 奥德赛活动开始!第一周——跨链桥
How to set ulimit value for SYSTEMd service in easycvr?
Website construction is not set to inherit the superior column. How to find a website construction company
Apache log4j 2 reported high-risk vulnerability, coding teamed up with Tencent to protect software security
《阿里云天池大赛赛题解析》——O2O优惠卷预测
Payment industry tuyere project: smart digital operation 3.0
什么是免疫组织化学实验? 免疫组织化学实验
Detailed process of deploying redis cluster and micro service project in docker
Common core resource objects of kubernetes
WebService client request failed can not create a secure xmlinputfactory